Feb 5 & 11 - Axial Muscles
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Bilateral action
Contract together.
Unilateral action
Only one side contracts.
Axial Muscle Categories
Includes head and neck, vertebral column, respiration, abdominal wall, pelvis and perineum.
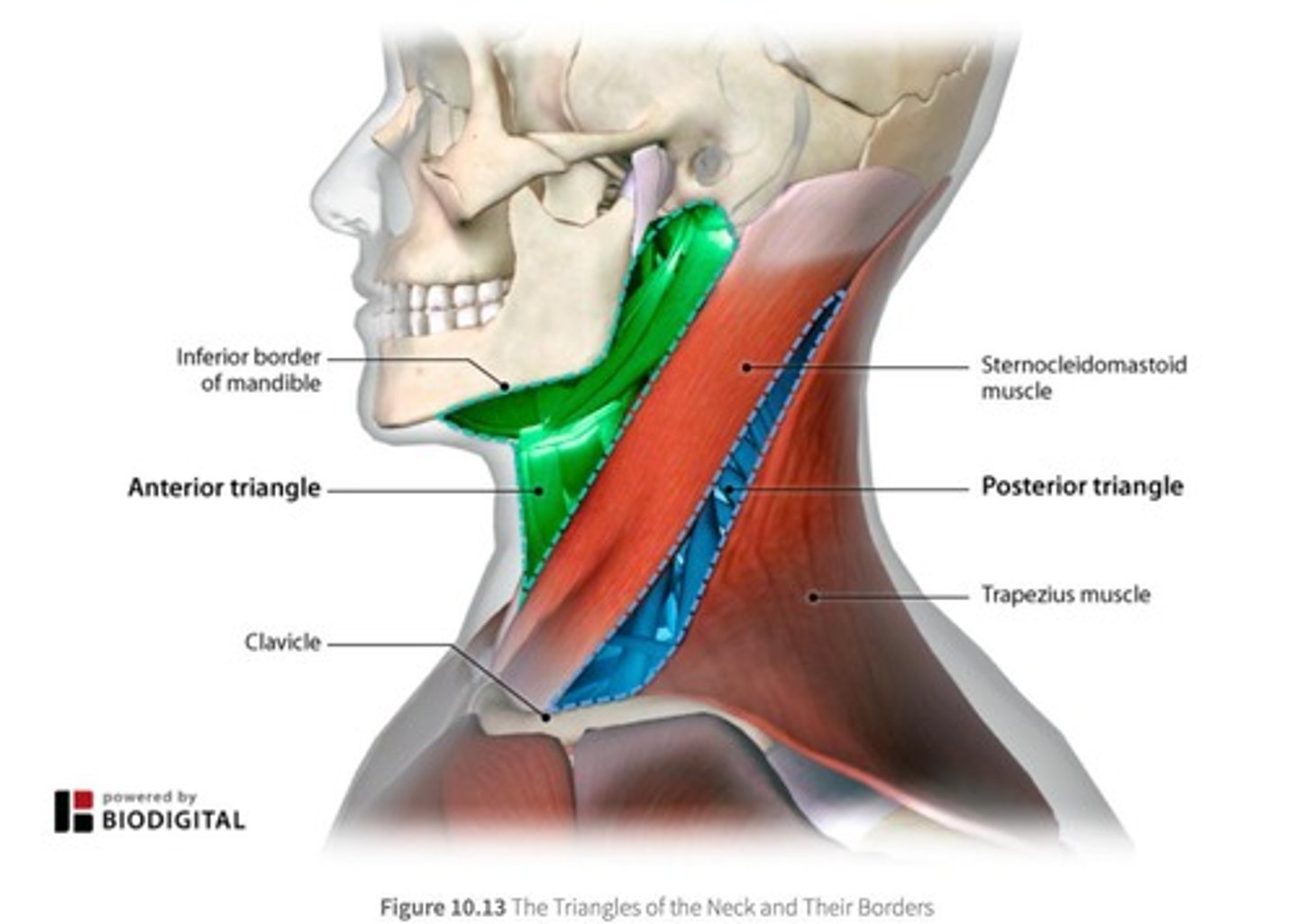
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
Bilaterally: flexion of head at the neck; Unilaterally: lateral flexion and contralateral rotation of the head.
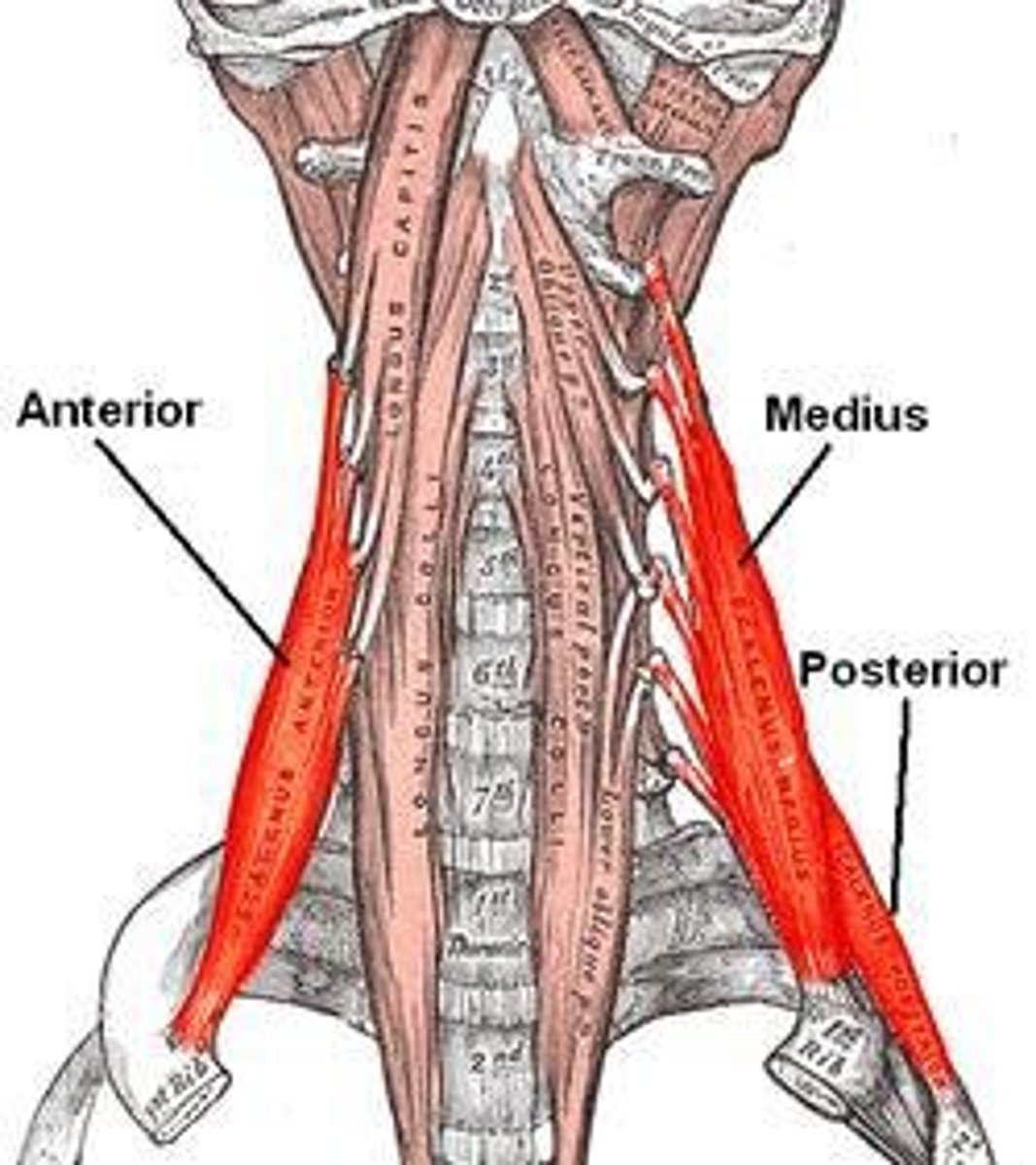
Scalene group
Origins on C-spine TPs and insert into rib 1 & 2; Accessory breathing muscles.
Extrinsic muscles of the back
Produce and control limb & respiratory movements.
Intrinsic muscles of the back
Act specifically on vertebral column to move the vertebrae & maintain posture.
Spinotransversales muscles
Thick & flat 'bandage' muscles that wrap vertical muscles and hold them in position.
Splenius cervicis
Part of the spinotransversales muscles; bilaterally extends head/neck, unilaterally causes lateral flexion and ipsilateral rotation.
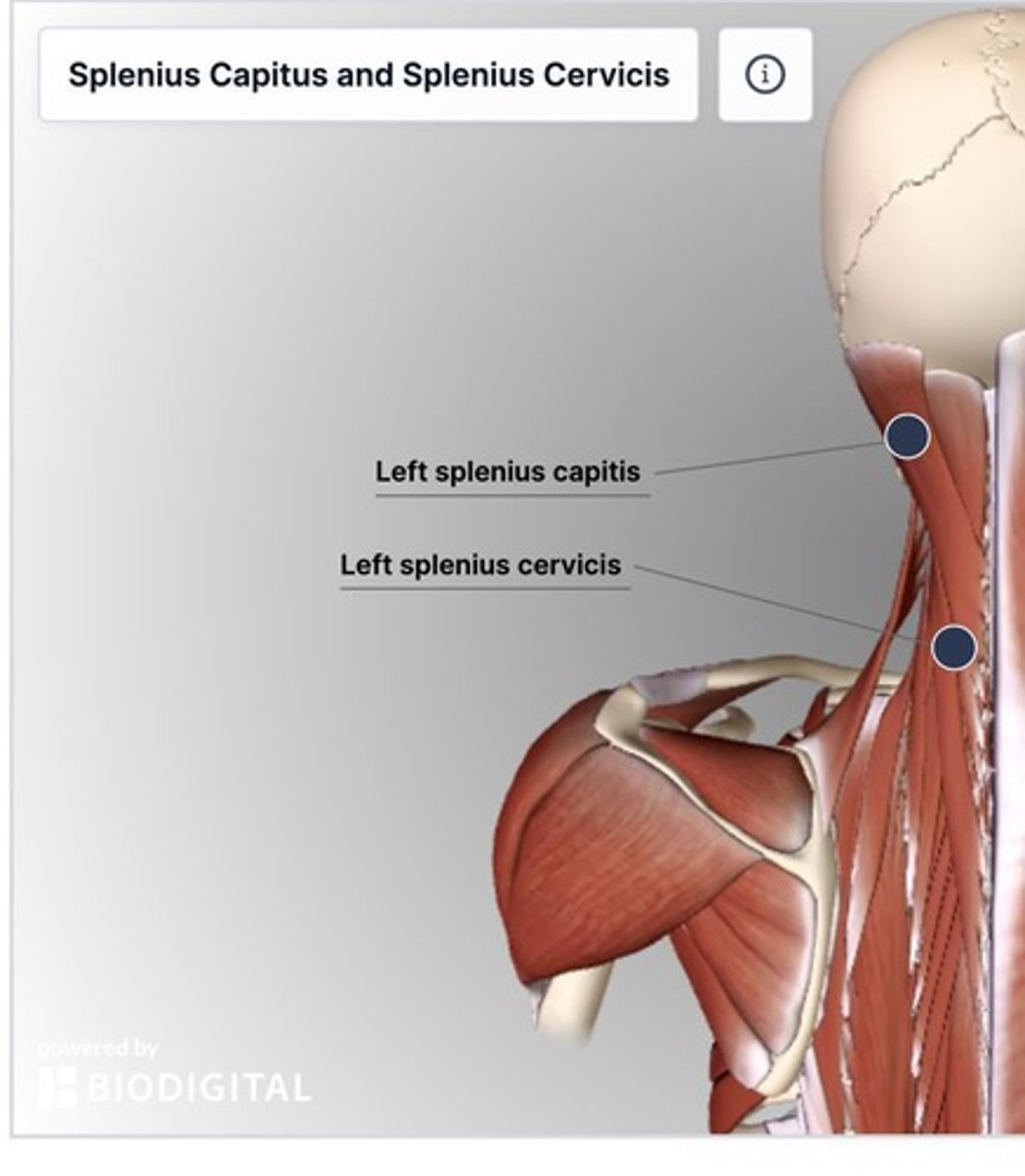
Splenius capitus
Part of the spinotransversales muscles; bilaterally extends head/neck, unilaterally causes lateral flexion and ipsilateral rotation.
Erector spinae muscles
Important postural muscles with fibres that extend from sacrum to skull.
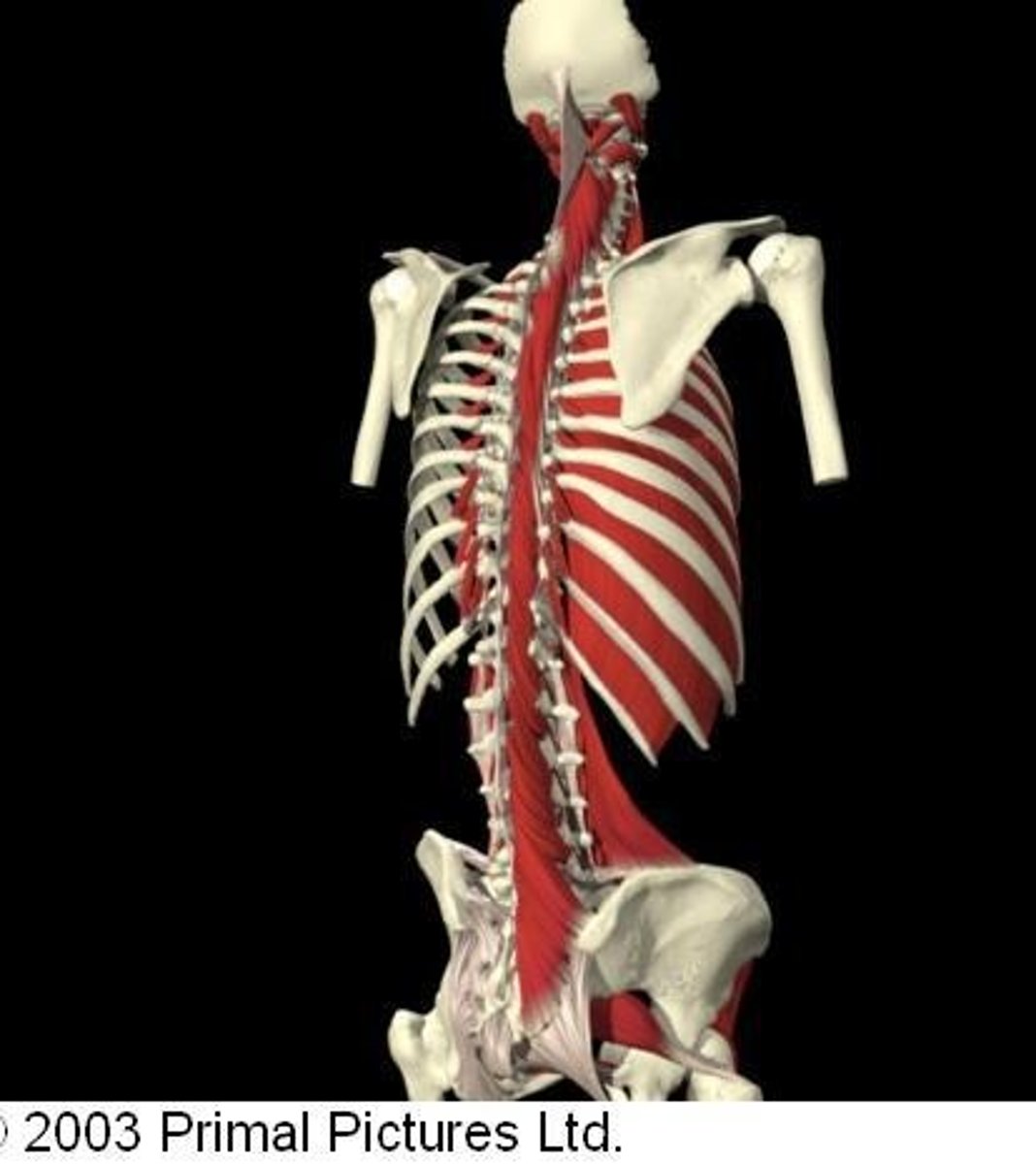
Iliocostalis
1st column of the erector spinae muscles.
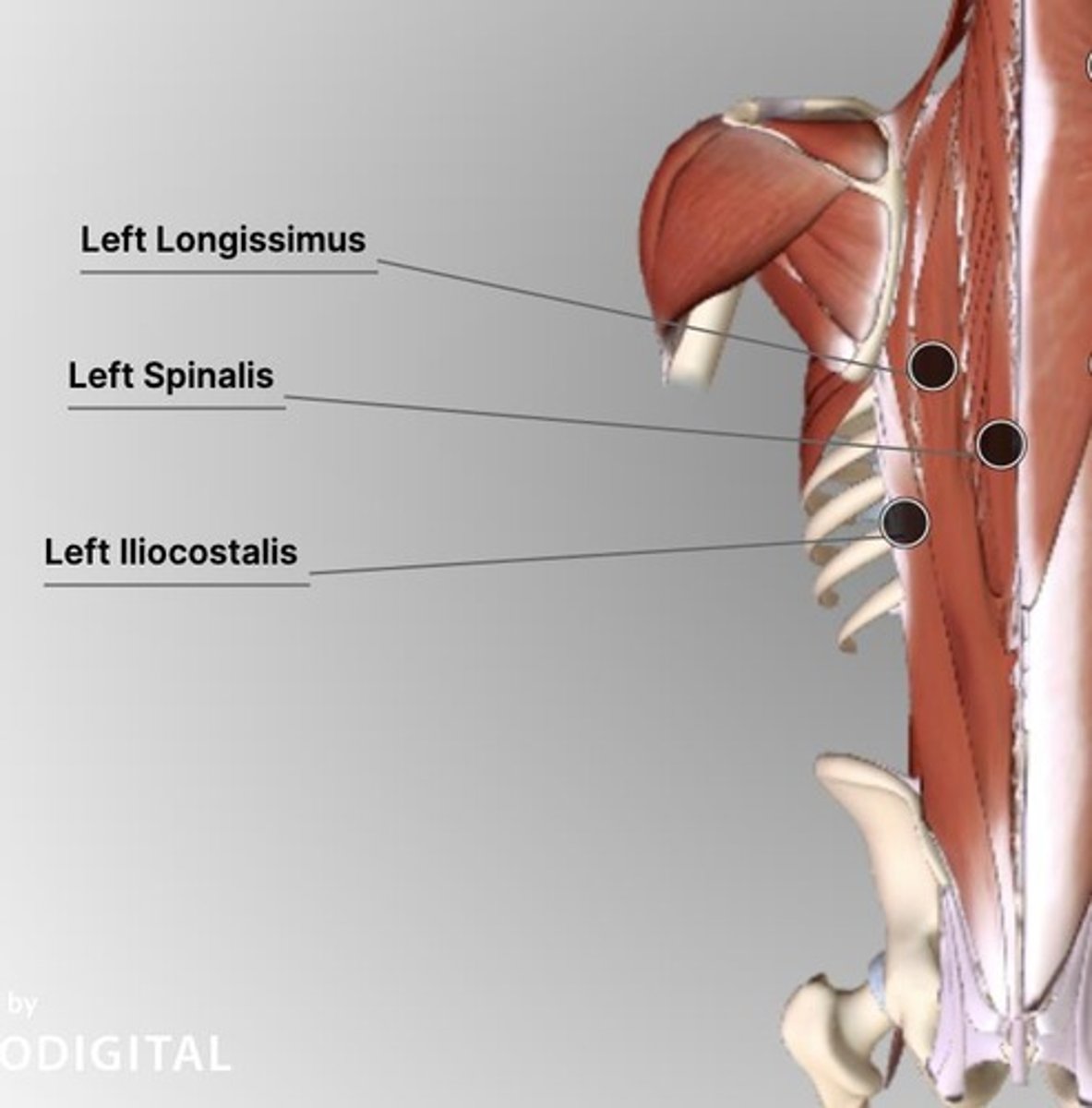
Longissimus
2nd column of the erector spinae muscles.
Spinalis
3rd column of the erector spinae muscles.
Thoracolumbar fascia
Part of the intrinsic muscles of the back; binds muscles from pelvis to cranium.
Superficial layer of back muscles
Includes spinotransversales muscles.
Intermediate layer of back muscles
Massive muscle group laid in three columns between SPs centrally and rib angles laterally.
Accessory breathing muscles
Muscles that assist in breathing, such as the scalene group.
Muscles of respiration
Muscles involved in the process of breathing.
Anterior neck muscles
Muscles involved in facial expression, extrinsic eye movement, mastication, tongue movement, pharynx, and larynx.
Supra & Infrahyoid muscles
Muscles located in the anterior neck region.
Bilaterally
Extend vertebral column and maintain upright posture.
Unilaterally
Lateral flexion.
Erector Spinae
A muscle group that extends the vertebral column.
Transversospinalis Muscle Group
A group of muscles with shorter fibers than the erector spinae that extend the vertebral column and head bilaterally and cause contralateral rotation unilaterally.
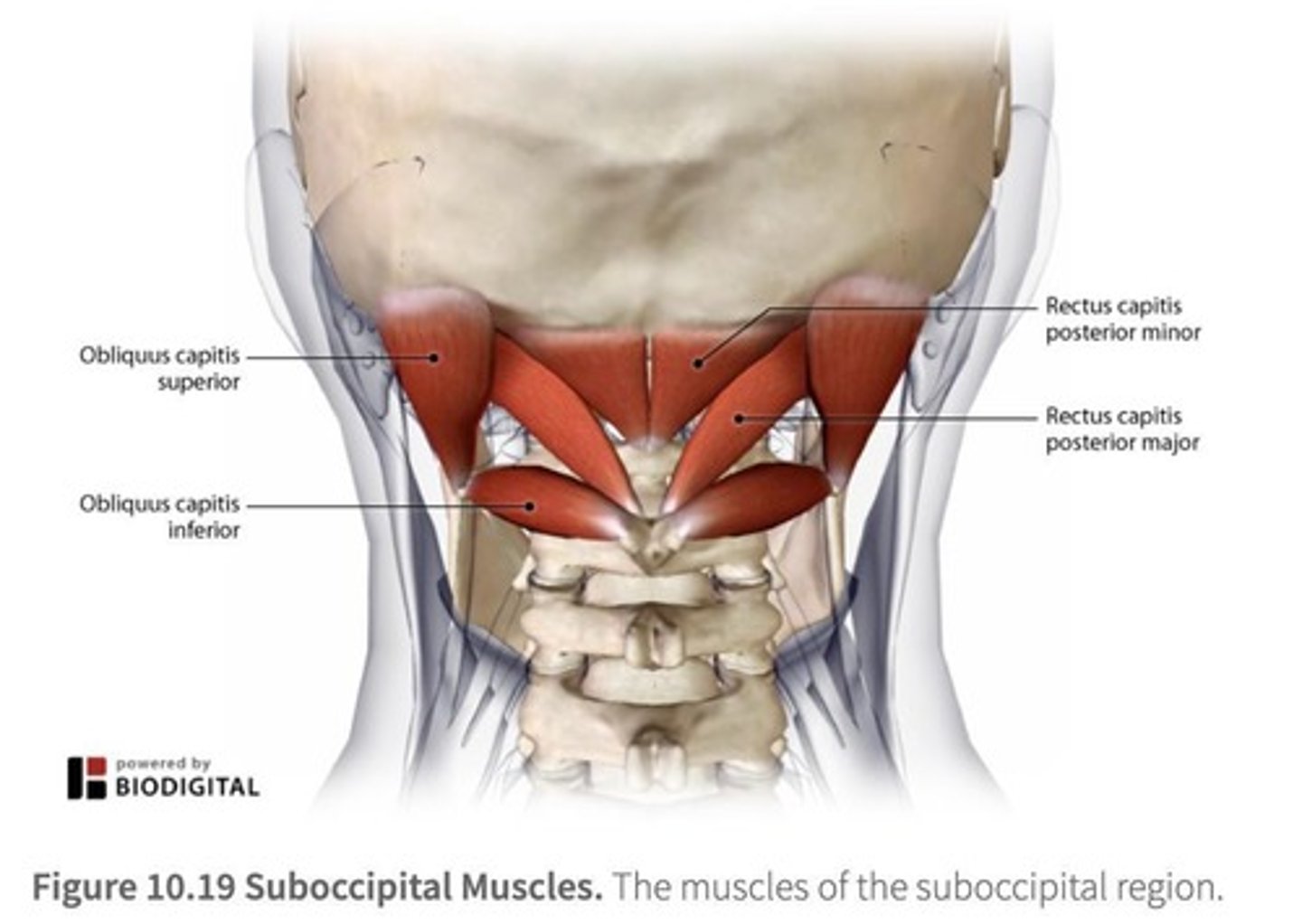
Suboccipital Triangle
An anatomical region where the suboccipital nerve and vertebral artery are found, formed by muscles that attach C1 & C2 to the base of the skull.
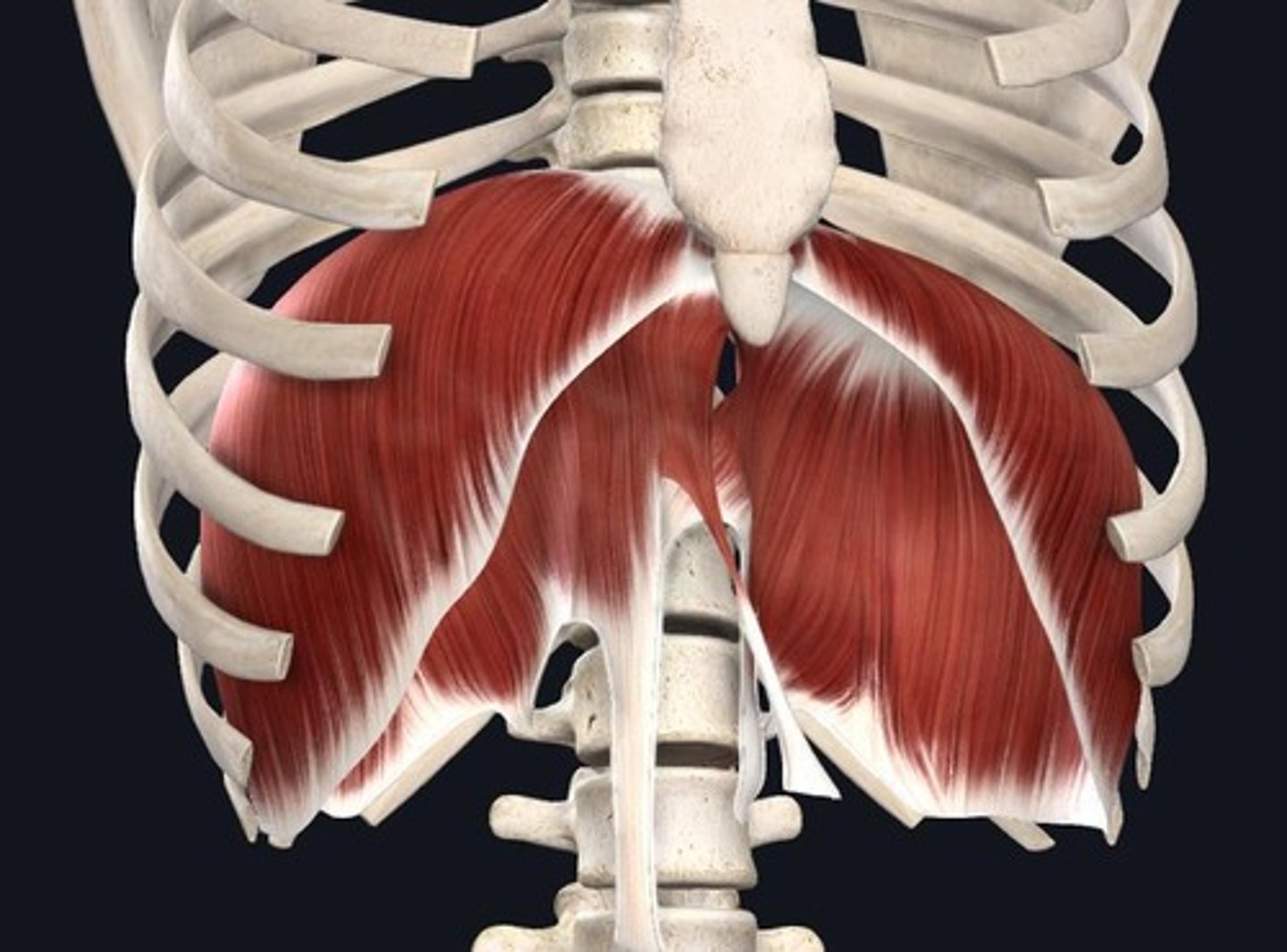
Diaphragm Muscle
Muscle contraction during inspiration causes it to flatten, increasing the size of the thoracic cavity and drawing breath in.
External Intercostal Muscle
Muscle that elevates the ribs during respiration.
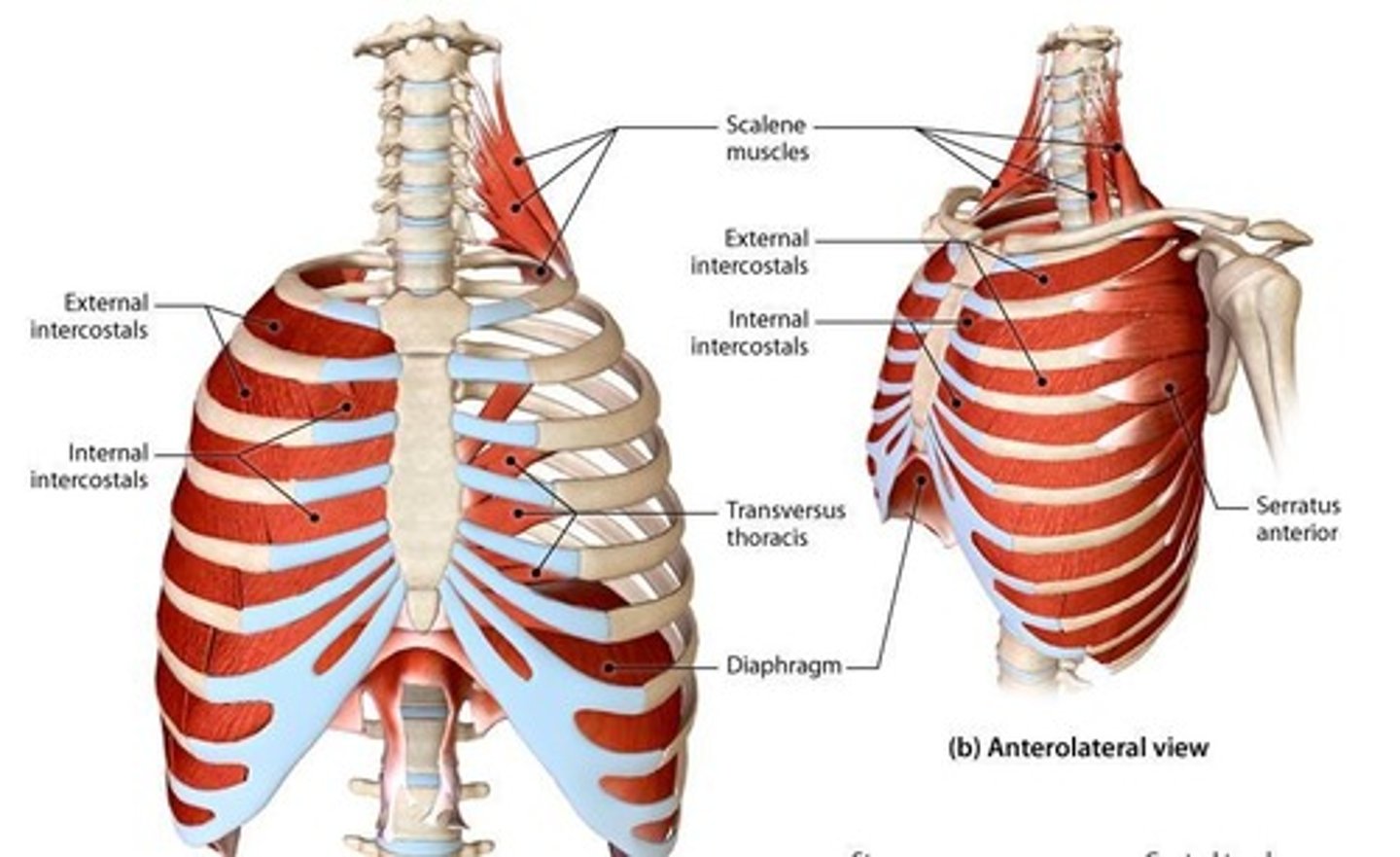
Scalene Muscle Group
Muscles that assist in elevating the ribs.
Serratus Posterior Superior
Muscle that elevates the ribs.
Levator Costarum
Muscle that elevates the ribs.
Internal Intercostal Muscle
Muscle that depresses the ribs.
Transversus Thoracic Muscle
Muscle that depresses the ribs.
Serratus Posterior Inferior
Muscle that depresses the ribs.
Rectus Abdominis
Muscle that compresses the abdominal wall and flexes the vertebral column bilaterally.

External Oblique
Muscle that compresses the abdominal wall, depresses ribs, and causes lateral flexion and contralateral rotation unilaterally.
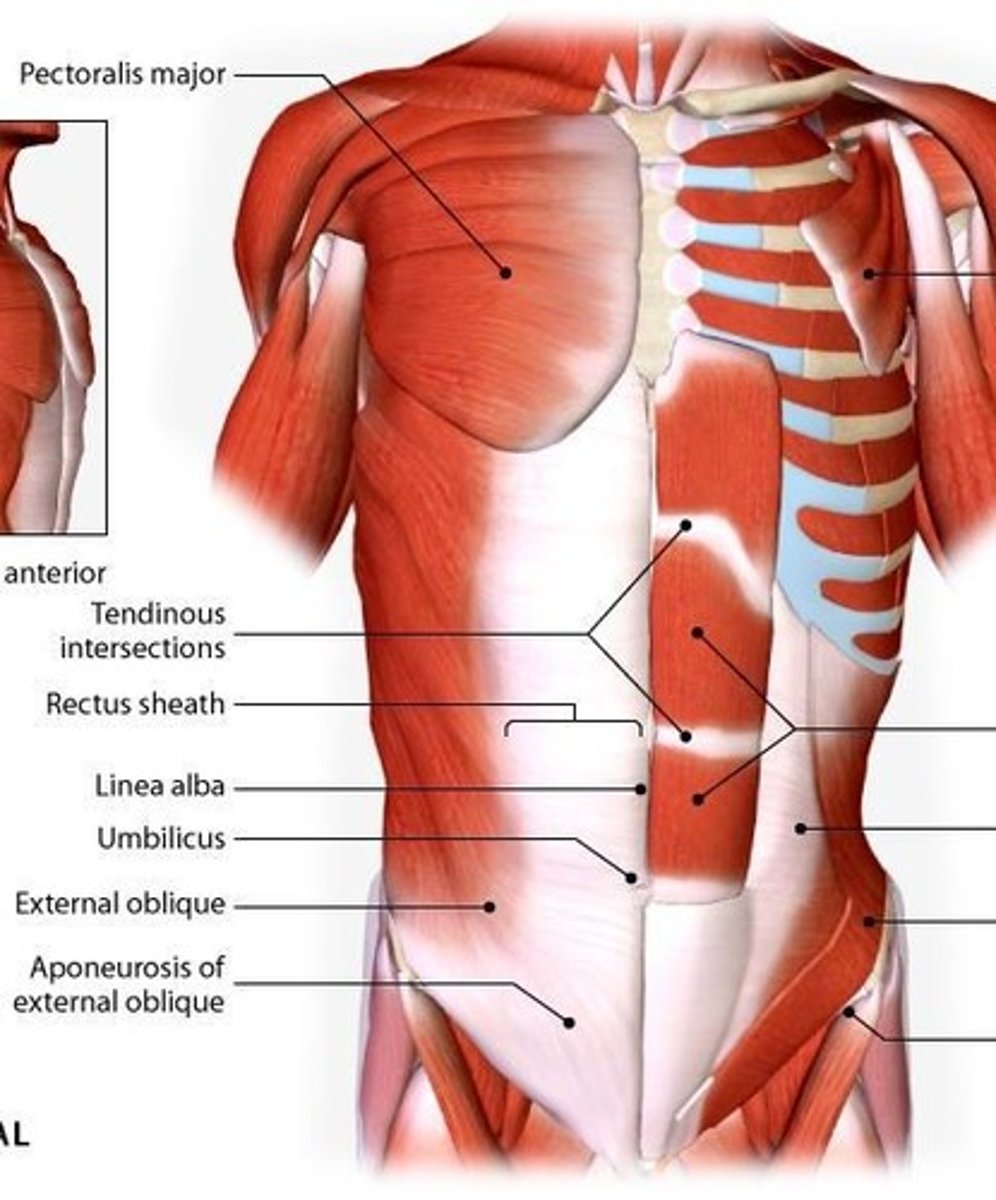
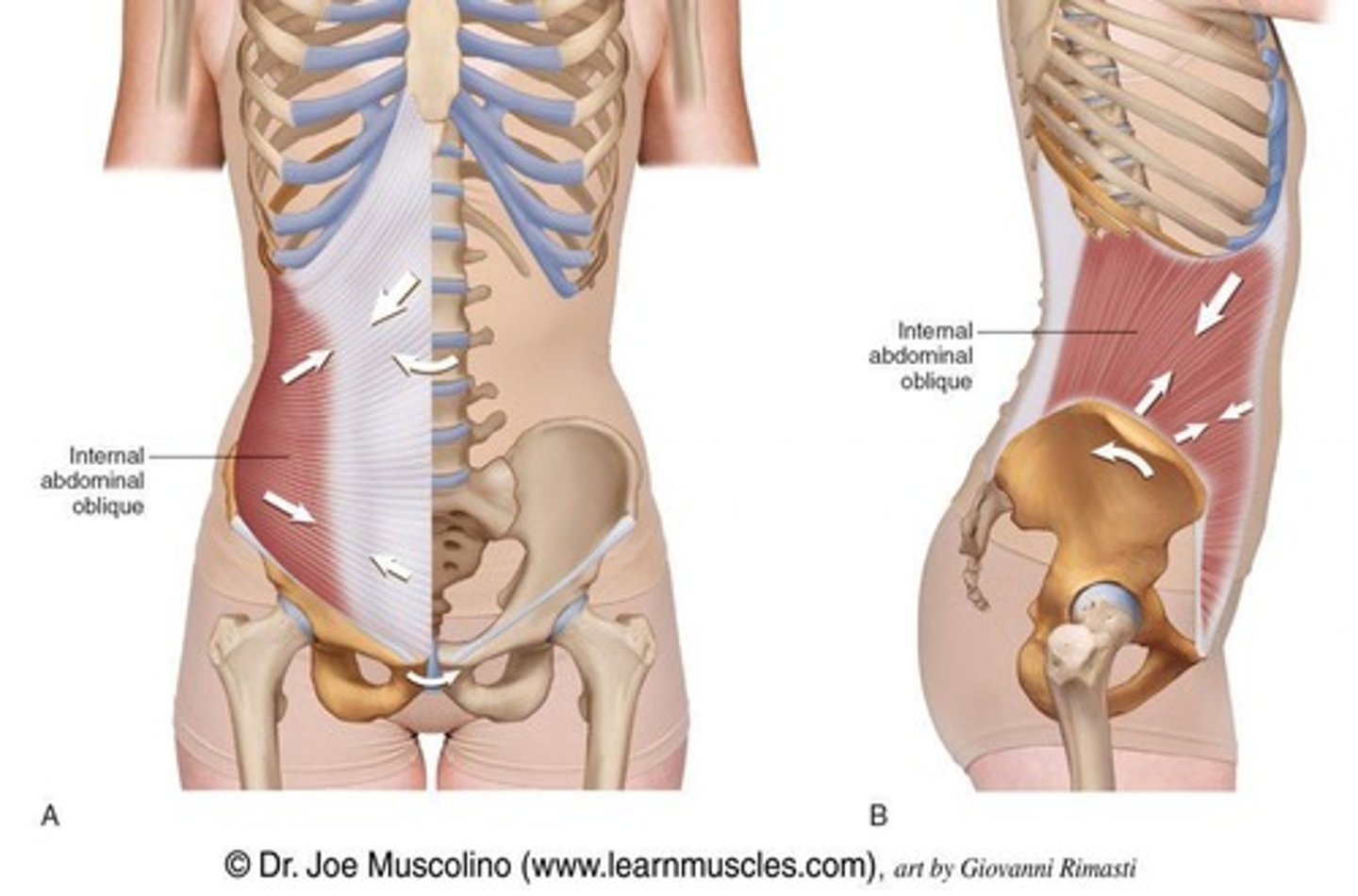
Internal Oblique
Muscle that compresses the abdominal wall, depresses ribs, and causes lateral flexion and ipsilateral rotation unilaterally.
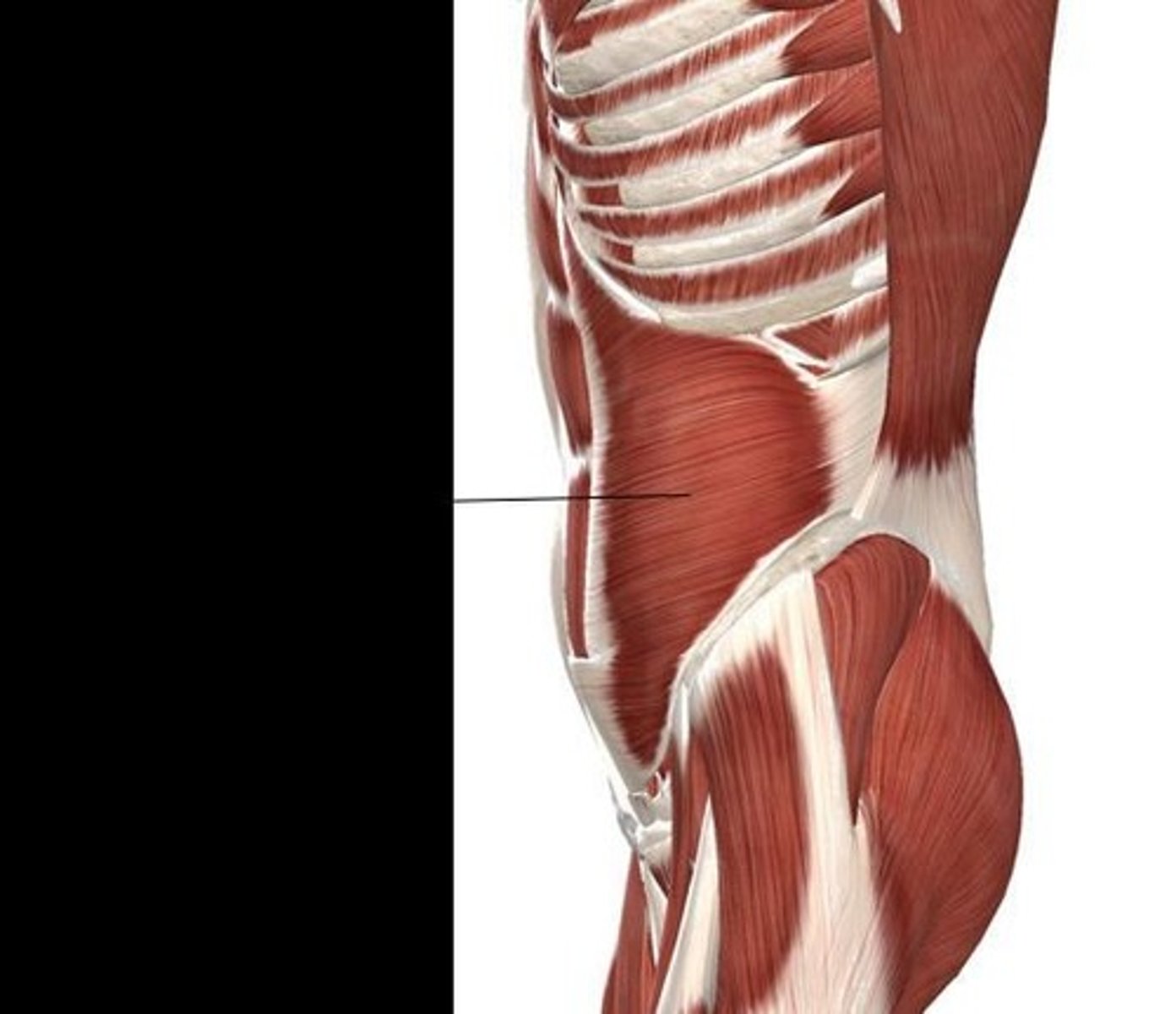
Transversus Abdominis
Deepest of the anterior abdominal muscles that compresses the abdominal wall and supports abdominal organs.
Psoas Major
Muscle primarily responsible for hip flexion and contributes to flexion of the vertebral column when femurs are fixed.
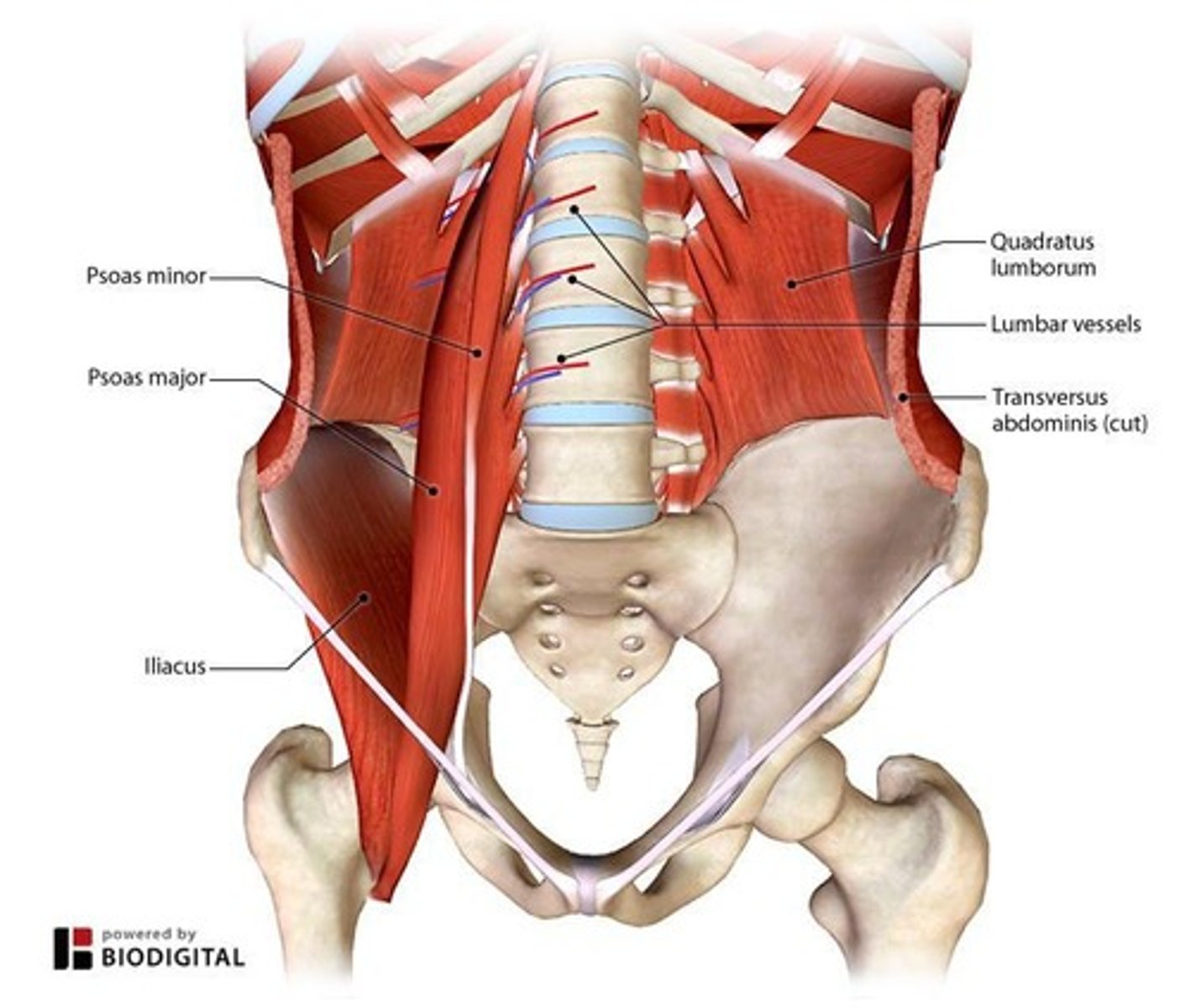
Iliacus
Muscle that works with the psoas major for hip flexion.
Quadratus Lumborum
Muscle that causes lateral flexion of the vertebral column (weak!).
Aponeurosis
Dense regular connective tissue that forms from abdominal muscles.
Rectus Sheath
Formed by the aponeuroses and encloses the rectus abdominis muscle.
Linea Alba
Vertical landmark where the aponeuroses meet.
Tendinous Inscriptions
Fibrous horizontal lines of connective tissue in the rectus abdominis muscle.