PSYC 1F90: Textbook
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
uncritical acceptance
the tendency to believe claims because they seem true or because it would be nice if they were true
desirable terms
terms that are outlined are biased towards the person that the concept is being described to
confirmation bias
tendency to remember or notice things that confirm our expectations
pseudoscience
unfounded belief system that seems to be based on science
clinical
treatment pf psychological and behaviour disturbences
counselling
treatment of milder emotional and behaviour disturbances
psychiatrist
a medical doctor with training in the diagnosis and treatment of mental and emotional disorders
psychoanalyst
a mental health professional (usually a MD) trained to practice psychoanalysis
counsellor
a mental health professional who specializes in helping people with problems that do not invoice serious mental disorders
scientific observation
investigation in a systematic way
casual obersvation
gathers empirical evidence
introspection
personal observation of your own thoughts, feelings, and behaviours
structuralism
the study of sensations and personal experience analyzed as basic elements
imageless thought
a term describing the inability of introspections to become subjectively aware of some mental processes
cognitive unconscious
the part if the mind of which we are subjectively unaware and that is not open to introspection
wertheimer
gestalt psychology— study of thinking, learning, and perception in whole units but not analysis into parts
james
functionalism— school of psychology that considers behaviour in terms of active adaptations
watson
behaviourism— school of thoughts in psychology that emphasized study of observable actions over study of the mind
skinner
radical behaviourism— approach that reject both introspection and any study of mental events (like thinking)
freud
psychoanalytic psychology— out behaviour is influenced by unconscious thoughts, impulses, and desires
cognitive
cognitive psychology— the study of information processing, thinking, reasoning, and problem solving
maslow
humanistic psychology— study of people as inherently good and motivated to learn and self improve
dynamic unconscious
the parts of the mind that are beyond awareness, especially in conflicts impulses and desires not directly known to a person
psychoanalysis
approach to psychotherapy emphasizing the exploration of the unconscious
psychodynamic theory
any theory of behaviour that emphasizes internal conflicts, motives, and unconscious forces
operational definition
defining a scientific concept by stating the specific actions or procedures used to measure it
determinism
the idea that all behaviour has prior causes that would completely explain ones choices and actions
free will
the ability to freely make choices that are not controlled by genetics, learning, or unconscious forces; humans are able to make their own choices
self- actualization
the process of fully developing personal potentials
the biological perspective
seeks to explain behaviours in terms of biological principles like genetics, brain processes, and evolution
the psychological perspective
views behaviour as the result of psychological processes with another
the social perspective
stresses the impact that social contexts— like crowds, groups, and cultures have on human behaviour
self- report
asking a question and participants write their own response, sample may be taken
observational
data that comes from watching participants and recording their behaviour
observational: structured
observing situations made up by the researcher
observational: observer effect
changes in organisms when they realized their being observed
observational: observer bias
tendency of an observer distorting observations to match their perception
physiological
data that comes from participants processes (brain, heart, muscles, hormone)
secure attachment
a stable and positive emotional bond
insecure avoidant attachment
an anxious emotion marked by a tendency to avoid reunion
insecure- ambivalent attachment
an anxious emotional bond marked by both a desire to with parent and some resistance to be reunited
when can babies read expression
36-48 months
dominant
a gene whose influence will be expressed each time the gene is present
recessive
a gene whose influence will be expressed only when paired with a second recessive gene of the same type
neutral stimulus
conditoned stimulus
neutral stimulus that through pairing with unconditioned stimulus, comes to elicit a learned response
conditioned response
learned reaction elicited by pairing an originally neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus
extinction
weakening of a learned response after its apparent extinction
spontaneous recovery
reappearance of a learned response after its apparent extinction
stimulus generalization
tendency to respond to stimuli similar to a conditioned response
stimulus descrimination
the learned ability to respond differently to similar stimulus
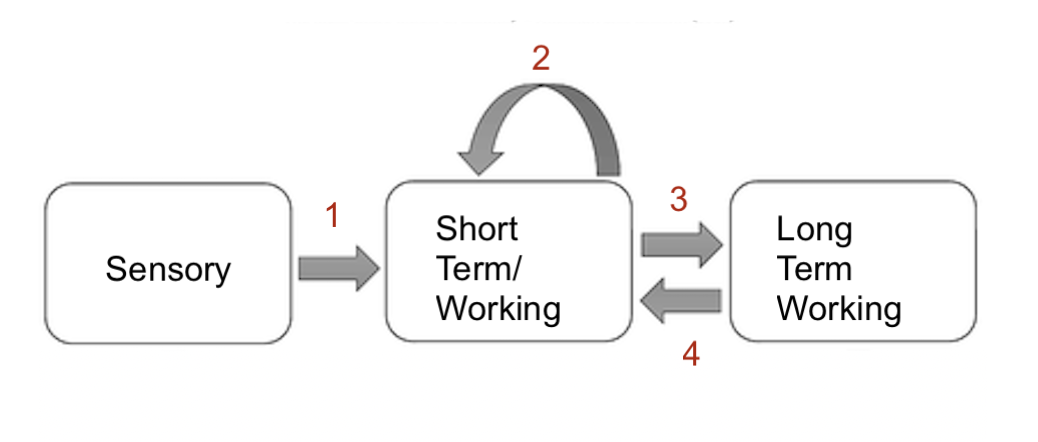
what system is 1
attention
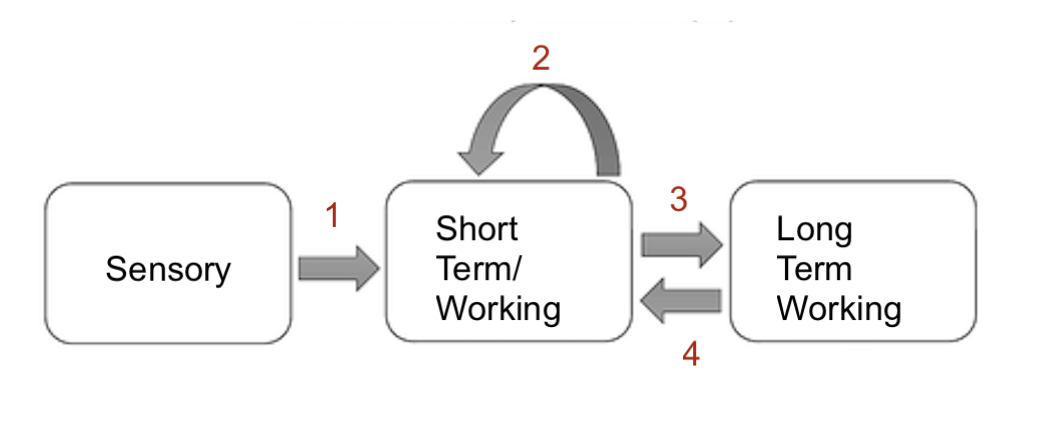
what system is 2
maintenance rehearsal
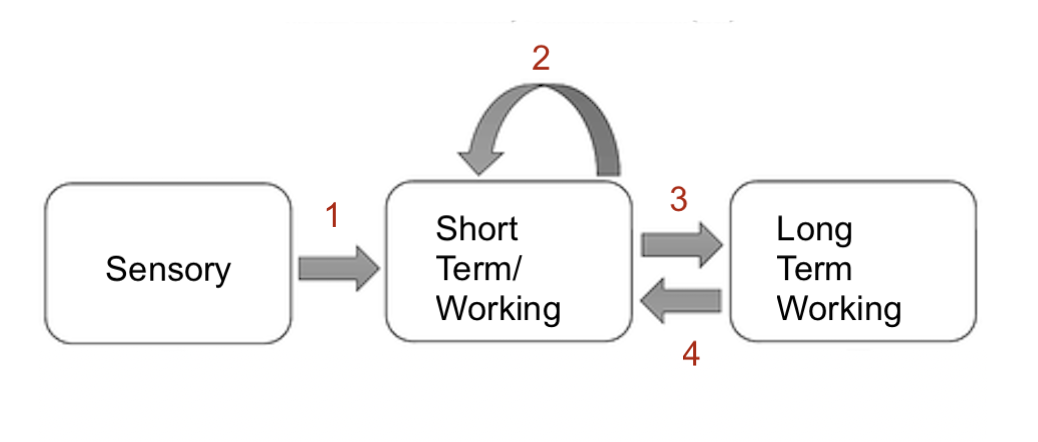
what system is 3
encoding
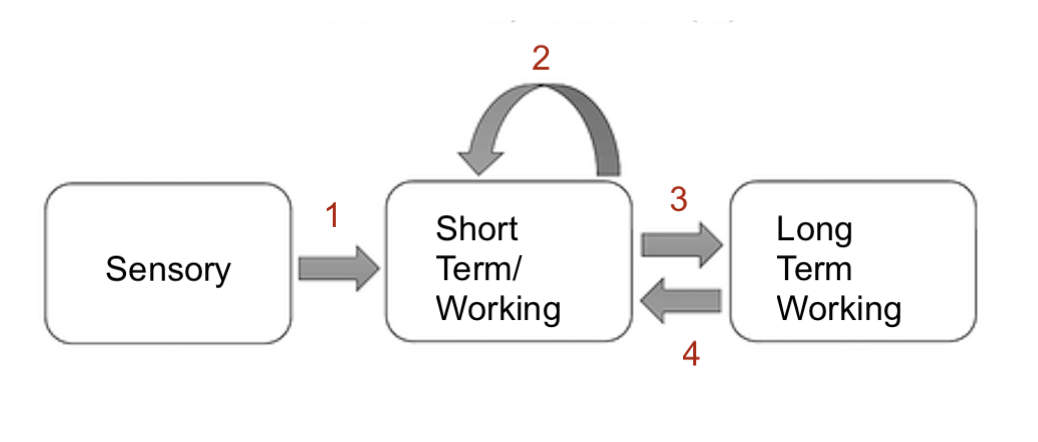
what system is 4
retrieval
chunking
process of grouping similar or meaningful information together
maintenance rehearsal
repeating information over and over to keep it active in short term memory
encoding: rote rehearsal
learning by simple repetition
encoding: elaborative rehearsal
making memories that are meaningful through processing that encodes links between new information and existing memories and knowledge
storing information in LTM according to meaning
meaning of individual words
the idea that information is being stored as a set of abstract concepts and properties based on what the information means to you
retrieval cue
any information that can prompt or trigger the retrieval of particular memories— enhance memory
reintegration
process by which memories are reconstructed or expanded by starting with one memory and then following chains of association to other
spreading activation
when ideas are further apart in the network and it takes a longer chain of associations to connect them during the process of spreading activation
muscle memory
how to do things that require motor or performance skills
classical and instrumental conditioning
stored in LTM and we draw on those memories automatically with no conscious awareness
priming
would have activated memories that you have stored and are ‘sleeping’ in your LTM
flashbulb memory
especially vivid and detailed recollection of an emotional event
state dependent learning
memory influenced by ones physical state at the time of learning and at the time of retrieval
interference
the tendency for more information/ memories to impair retrieval of older memories and reverse
motivated forgetting
repression— forgetting specific memories
unconscious forgetting due to emotion