Organic Chemistry 2 Reagents
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
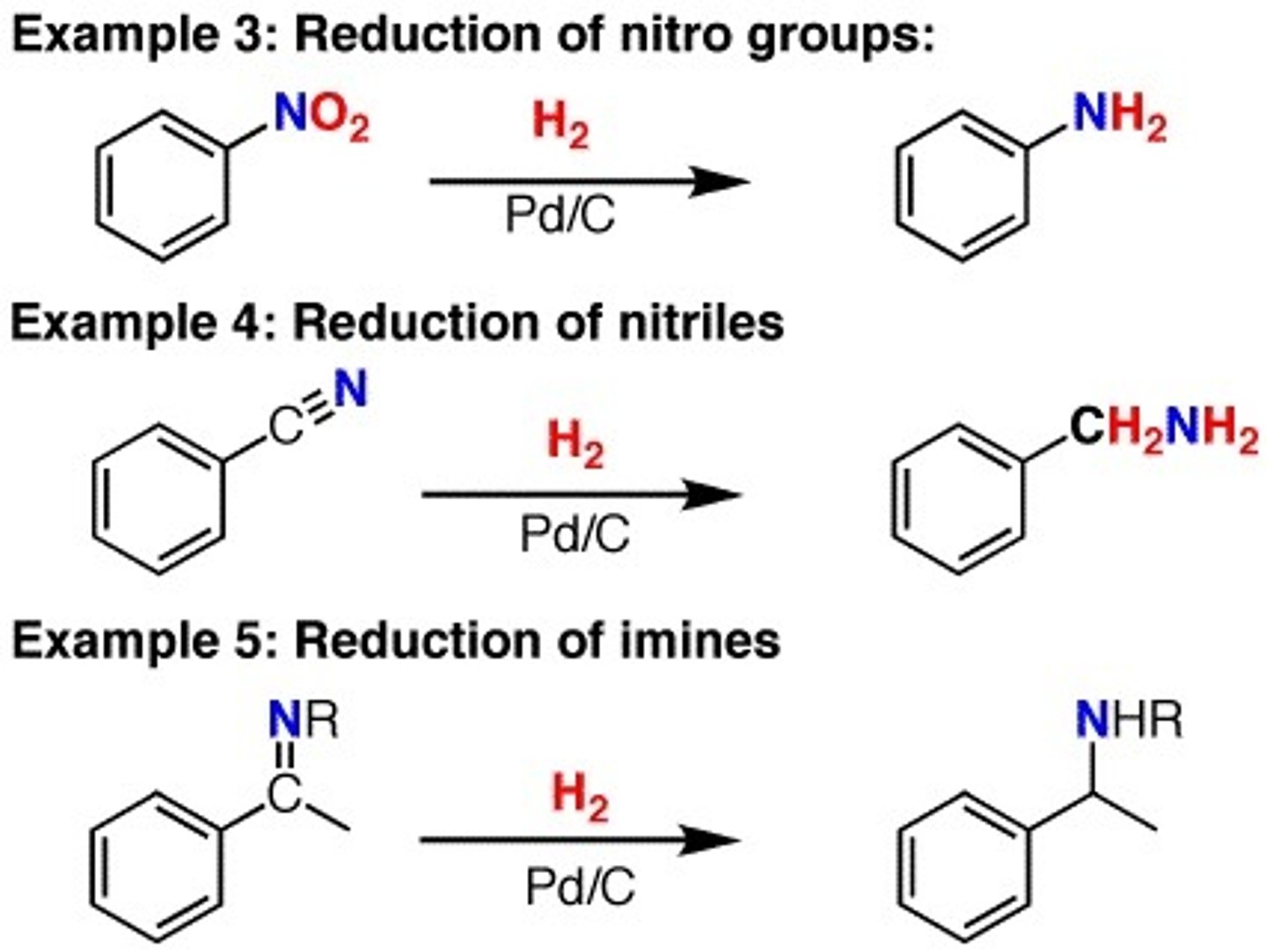
Hydrogenation: H2,Ni high pressure/ H2,Pd
Reducing agent... Reduces Alkynes and Alkenes - Alkanes
Aldehydes- primary alcohols
Ketones- secondary alcohols
Esters- two alcohols
Imine- amine
Amide- amine
Nitrile- primary amine
Nitro- amine
10% NaOH
Aldol Condensation
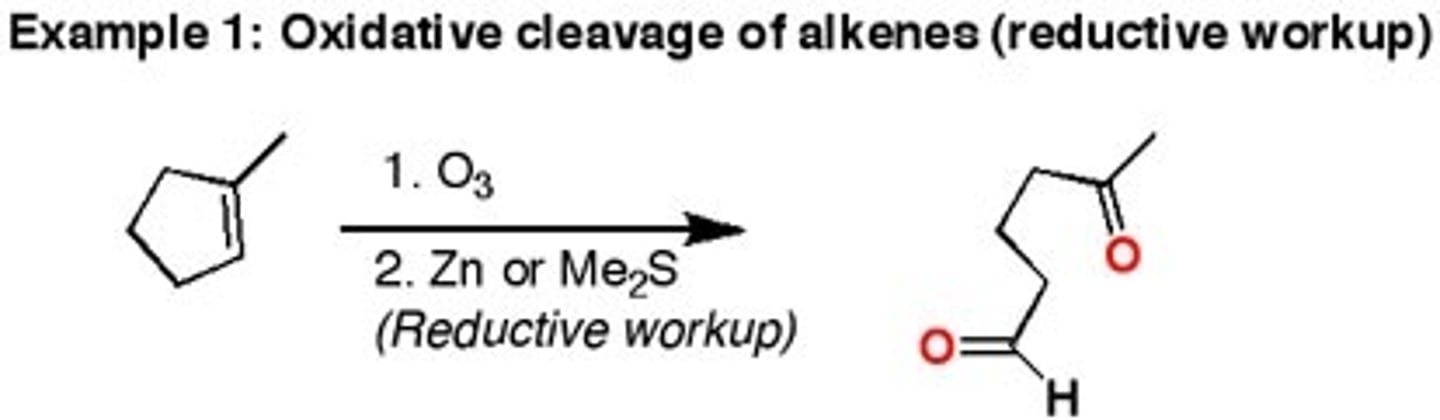
1.O3
2.Zn or Me2S
Or
1.03
2.H2O2
1.Ozonolysis (oxidation of an alkene)
2.Hydrogen peroxide does further oxidation. Product = carboxylic acid
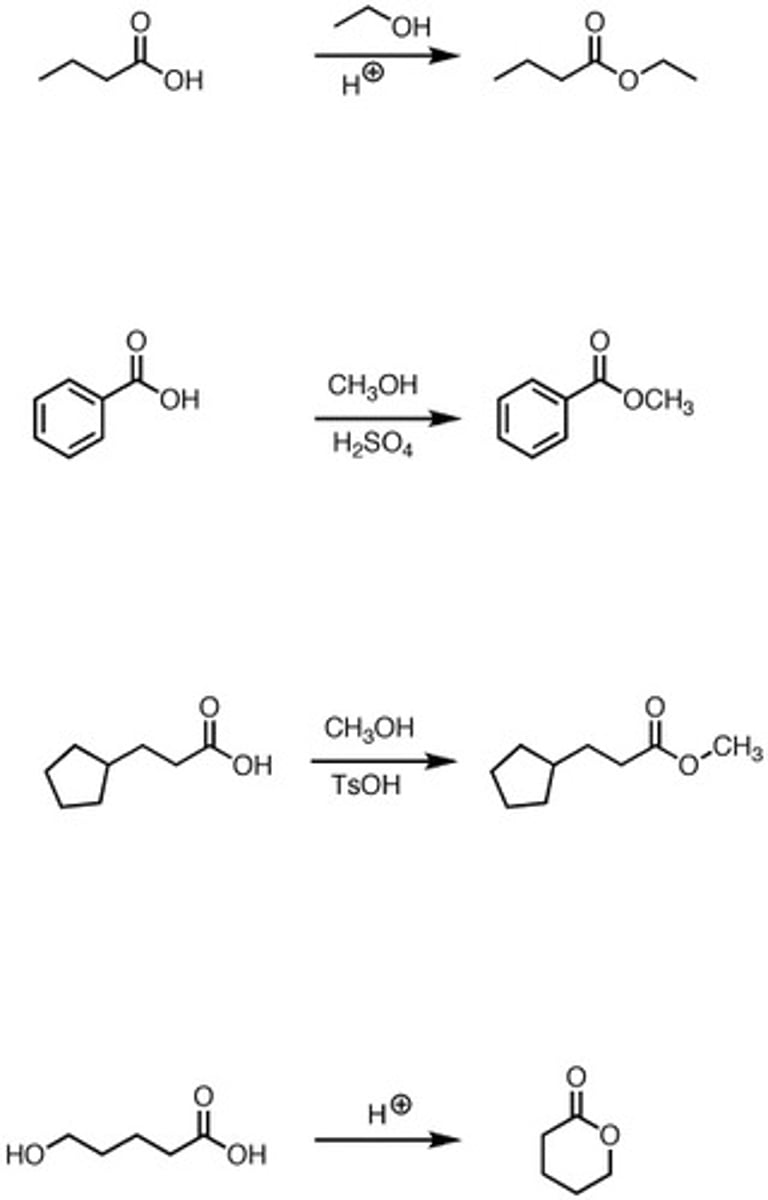
Carboxylic acid + 1. Alcohol 2. H3O+ (Work-up step)
Fischer esterification.
Carboxylic acid turns into an ester.
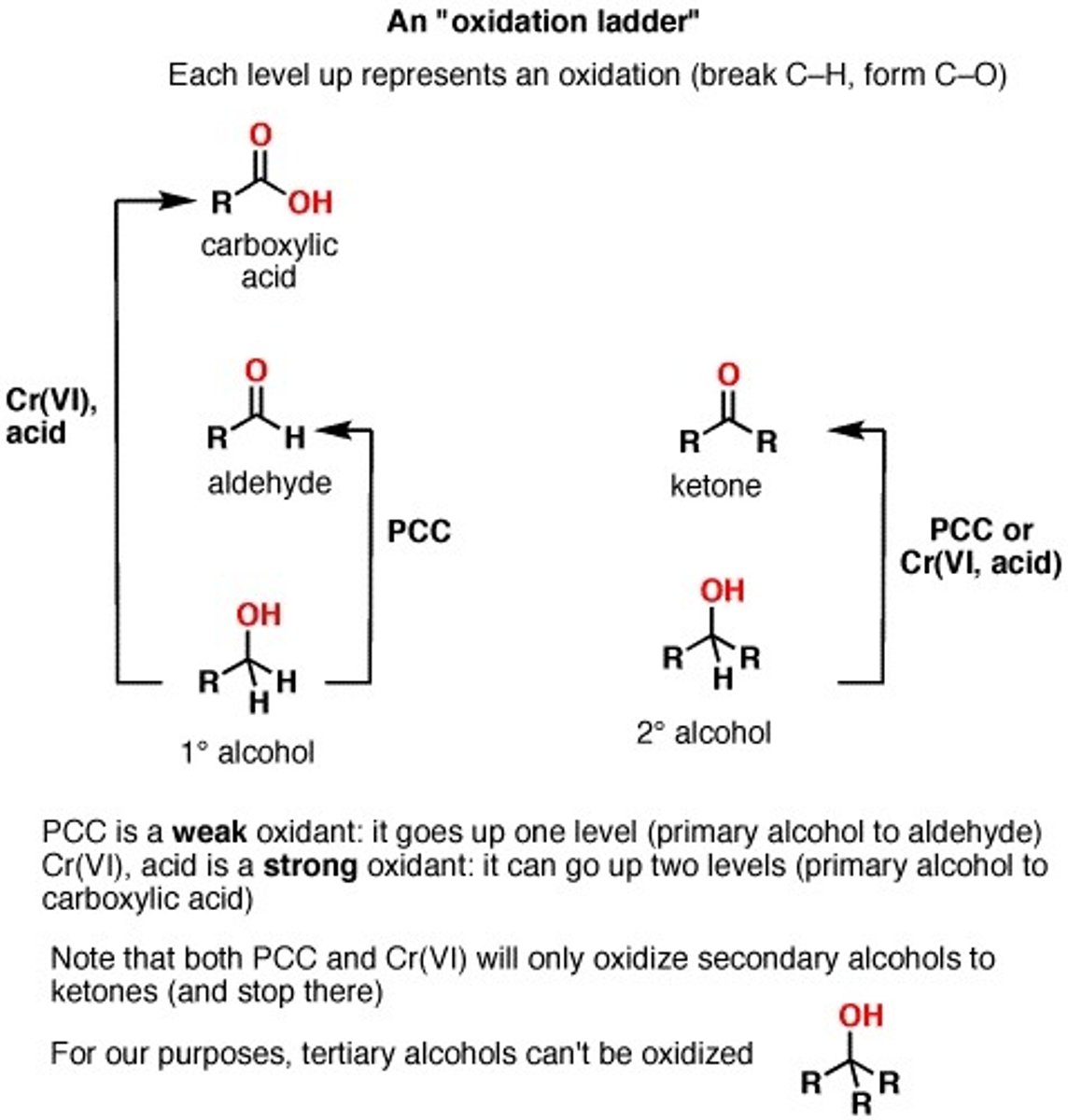
Alcohol + PCC
Primary alcohol + PCC = Aldehyde
Secondary alcohol + PCC = Ketone
"Please stop oxidation at aldehyde & ketone"
Aldehyde or ketone + ethylene glycol and acid
Cyclic acetal
This serves as a protecting group for aldehydes or ketones. You can then react another part of the molecule without touching the aldehyde or ketone part.
You deprotect the cyclic acetal and get your ketone or aldehyde back by acid and water.
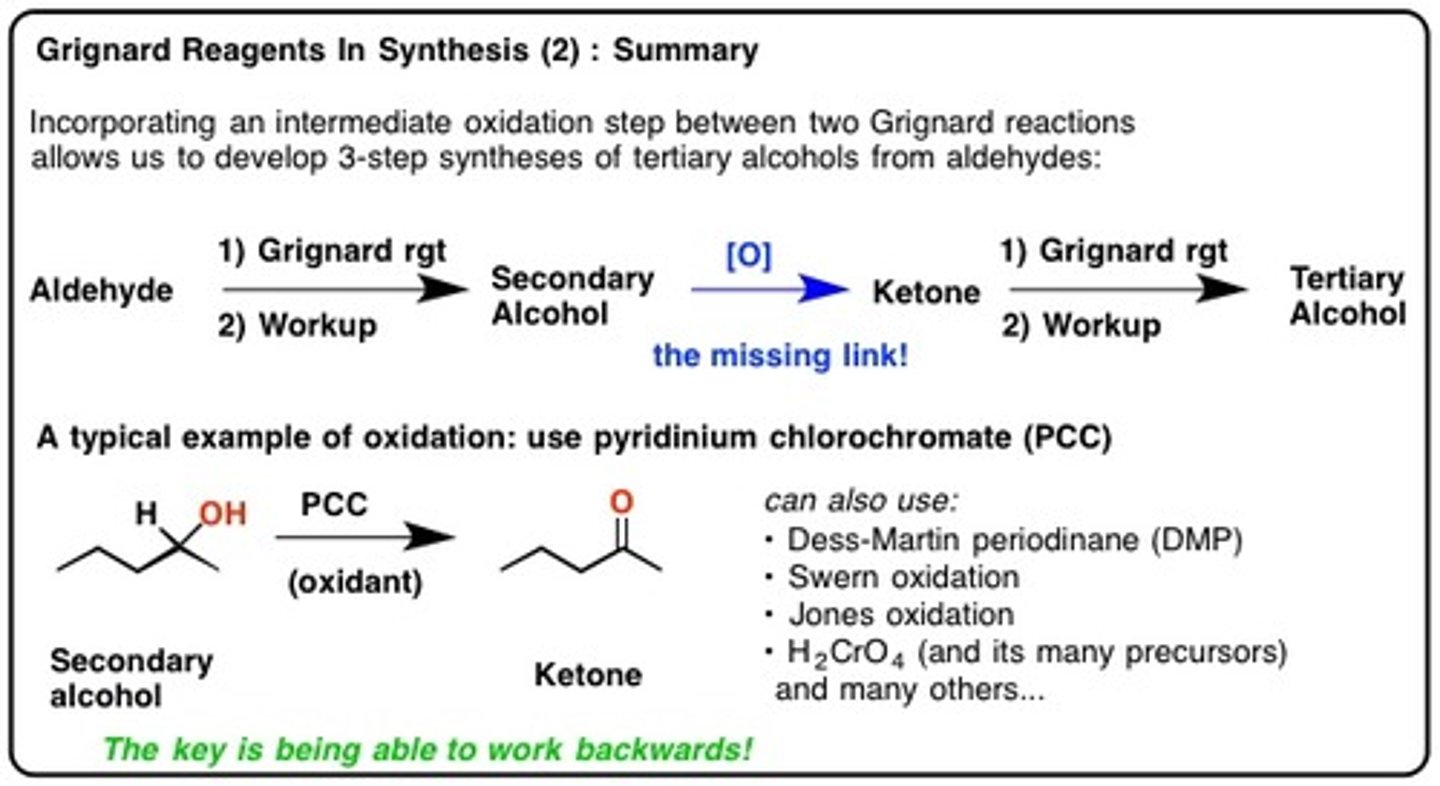
R-MgBr
Grignards reagent
The purpose is to add carbons to a molecule.
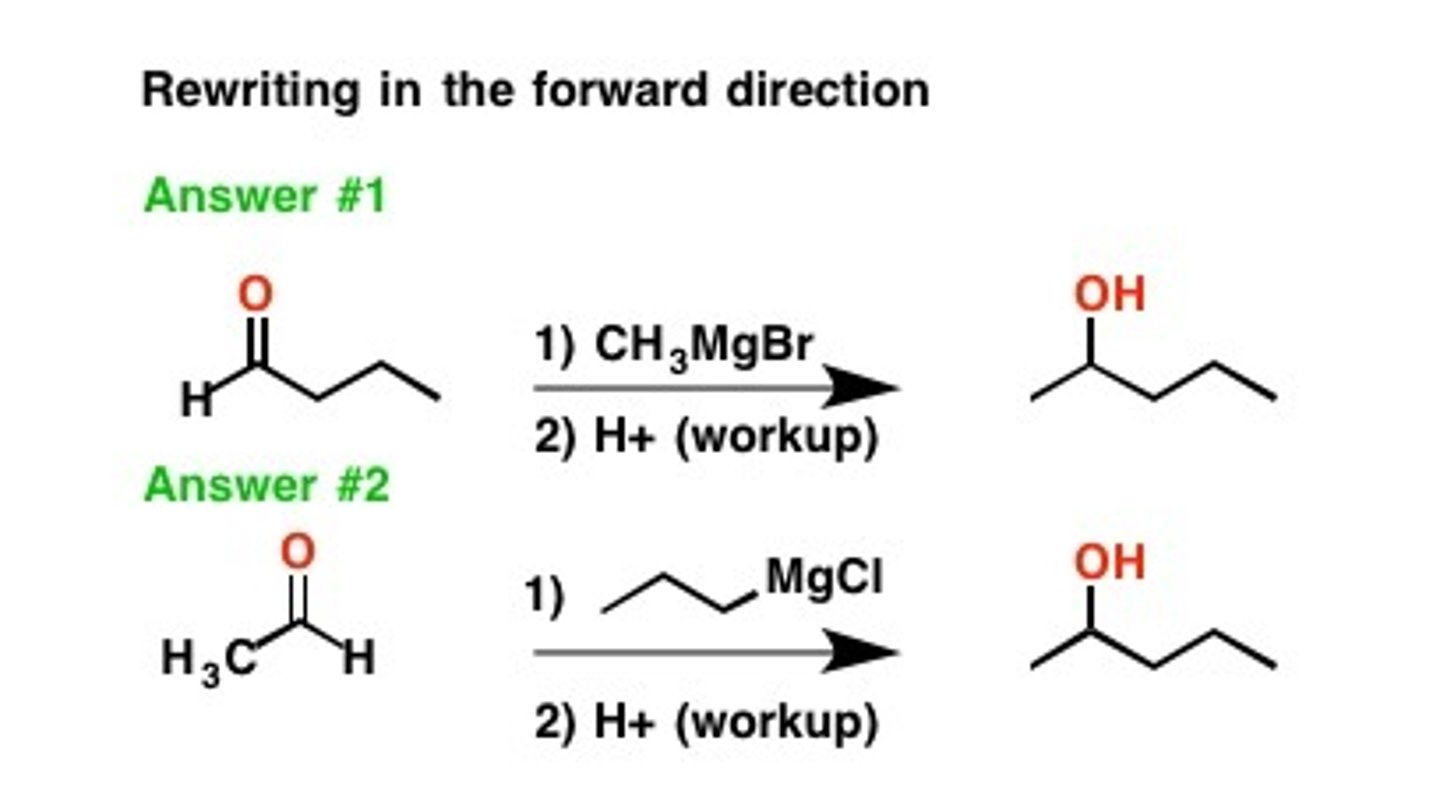
Grignard workup
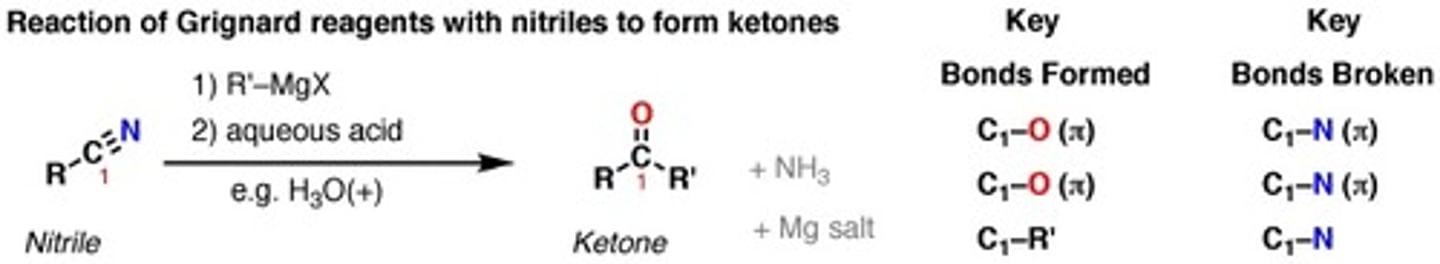
Nitrile + 1. R-MgBr 2. H3O+
Ketone
H3O+ (Acidic work-up step)
Purposes: a)acidic work-up step
b) acidic hydrolysis
c) Cleaves =N+ to =O
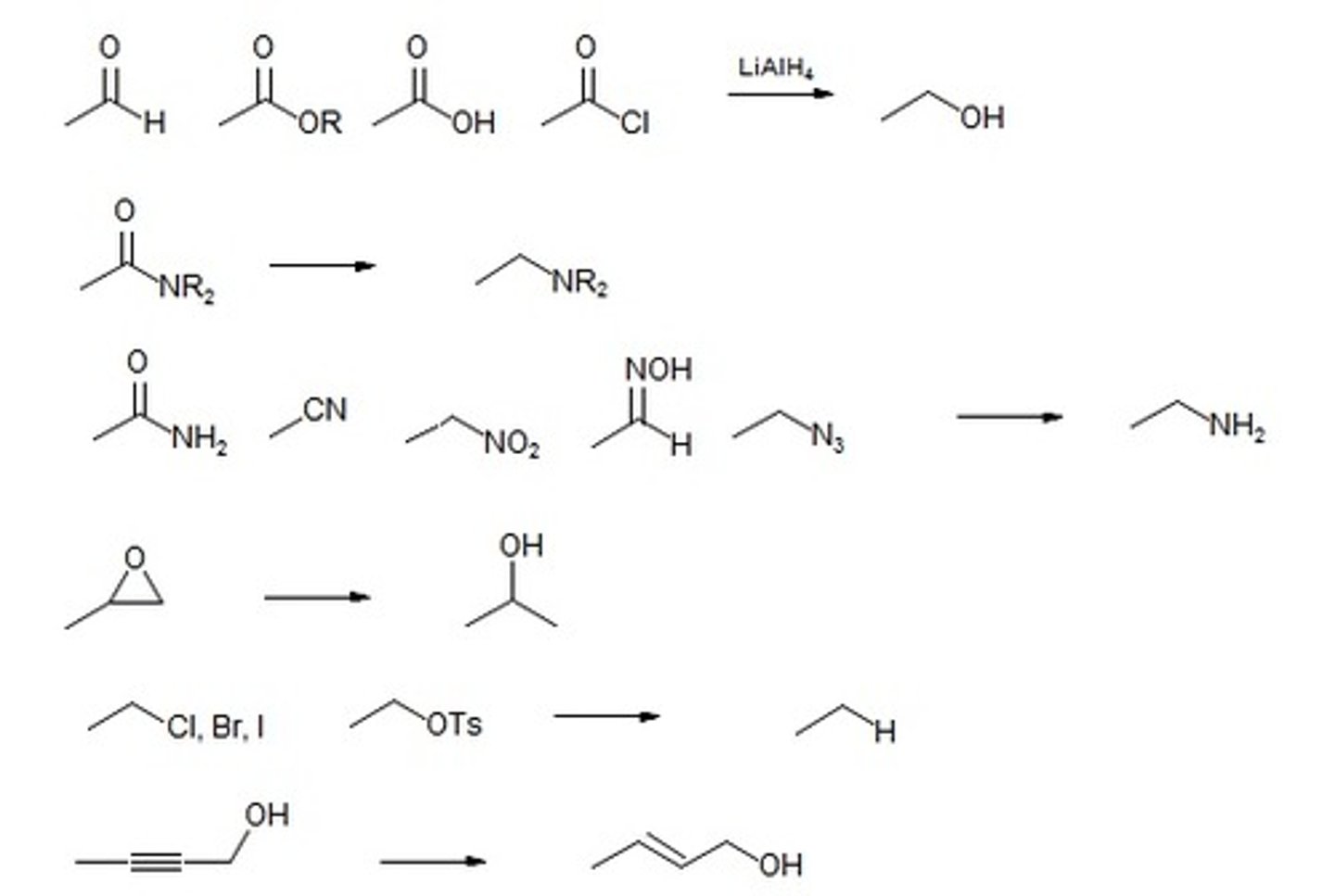
LAH (Lithium Aluminum Hydride)
STRONG REDUCING AGENT
Carboxylic acid - primary alcohol
All Carboxylic acid derivatives- primary alcohol
Aldehyde- primary alcohol(use NaBH4 rather)
ketone- secondary alcohol(use NaBH4 rather)
"Lets reduce everything"
CrO3 or H2CrO4
Oxidizing agent
"Crap lets oxidize everything"
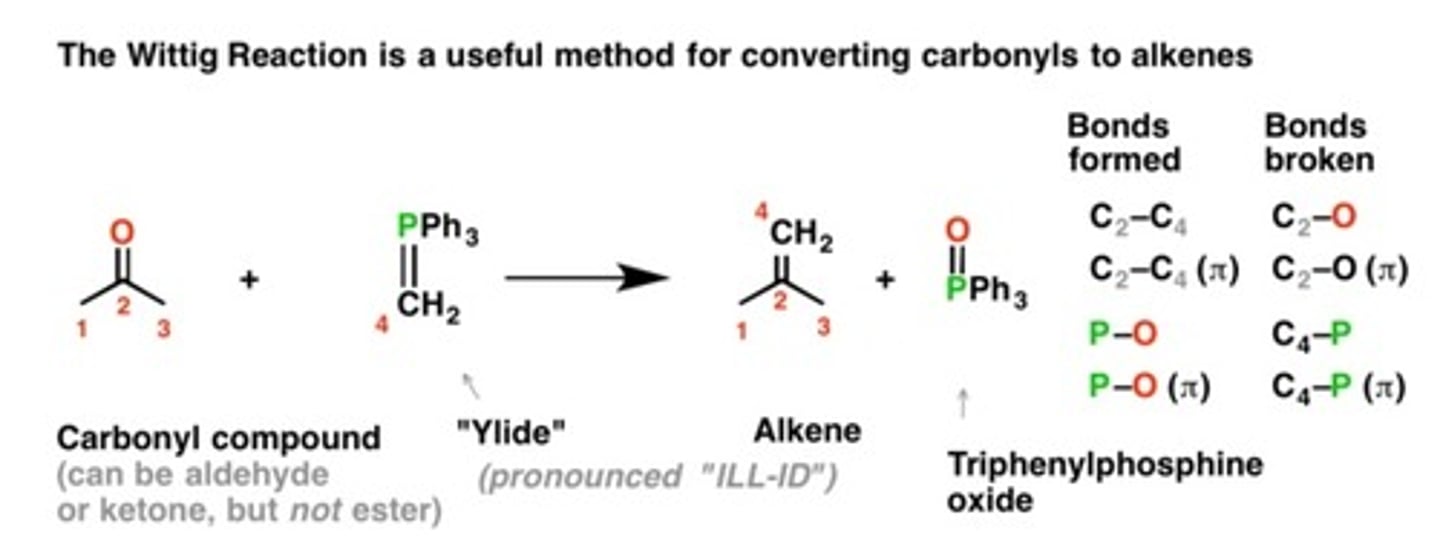
Ph3P=CH2
WITTIG REAGENT
Ketone or aldehyde- carbon to a double bond
"Please make the double bond"
**If you write this as a reagent: alkyl halide + Ph3P + n-butyl lithium
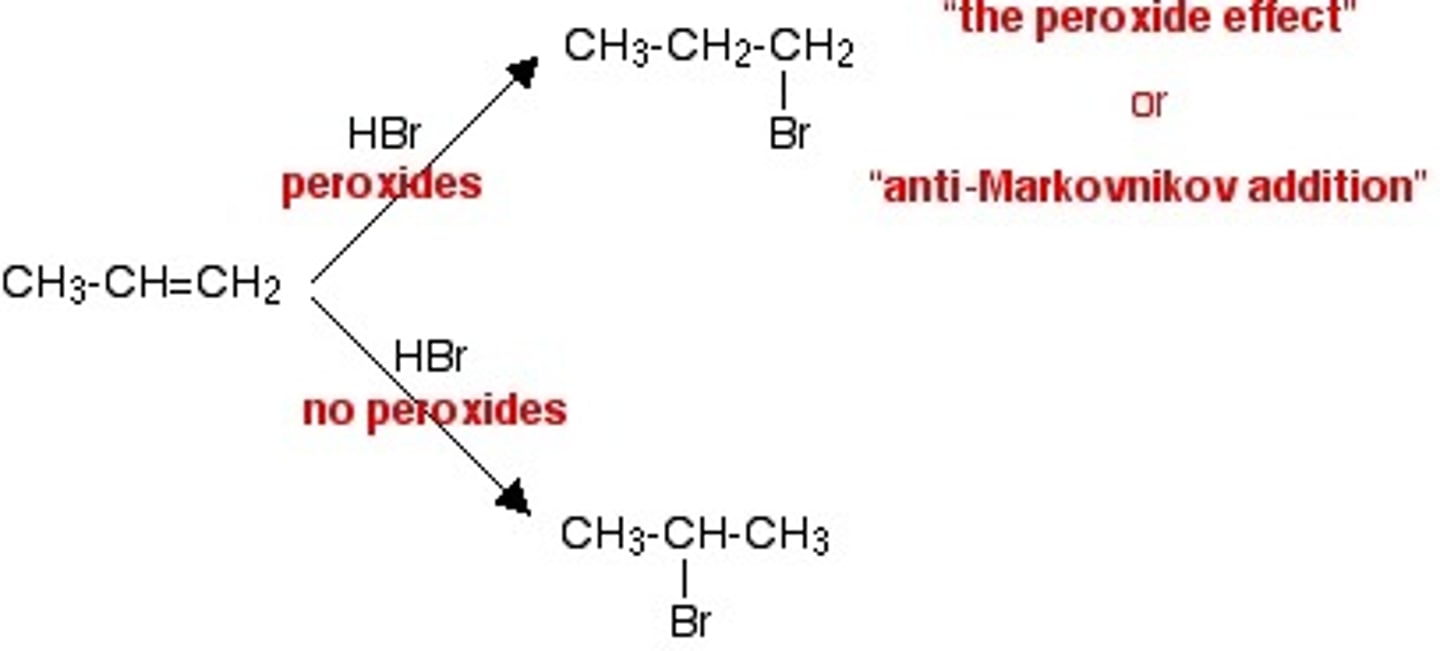
anti-Markovnikov
electrophile adds to the less substituted carbon, usually happens with a peroxide
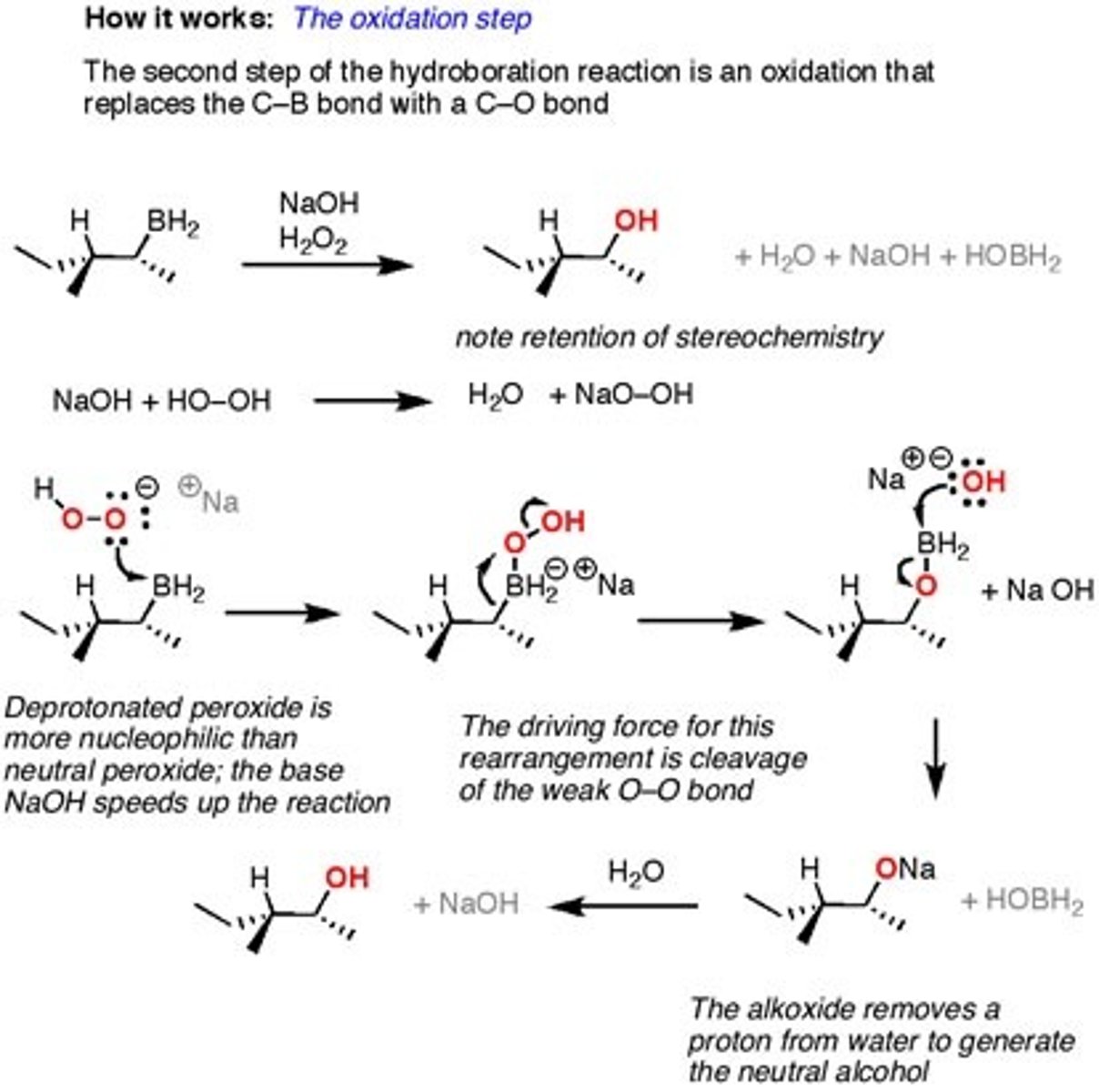
1.BH3
2.H2O2
Hydroboration
Alkene to an alcohol - alcohol
Anti-markovnikov
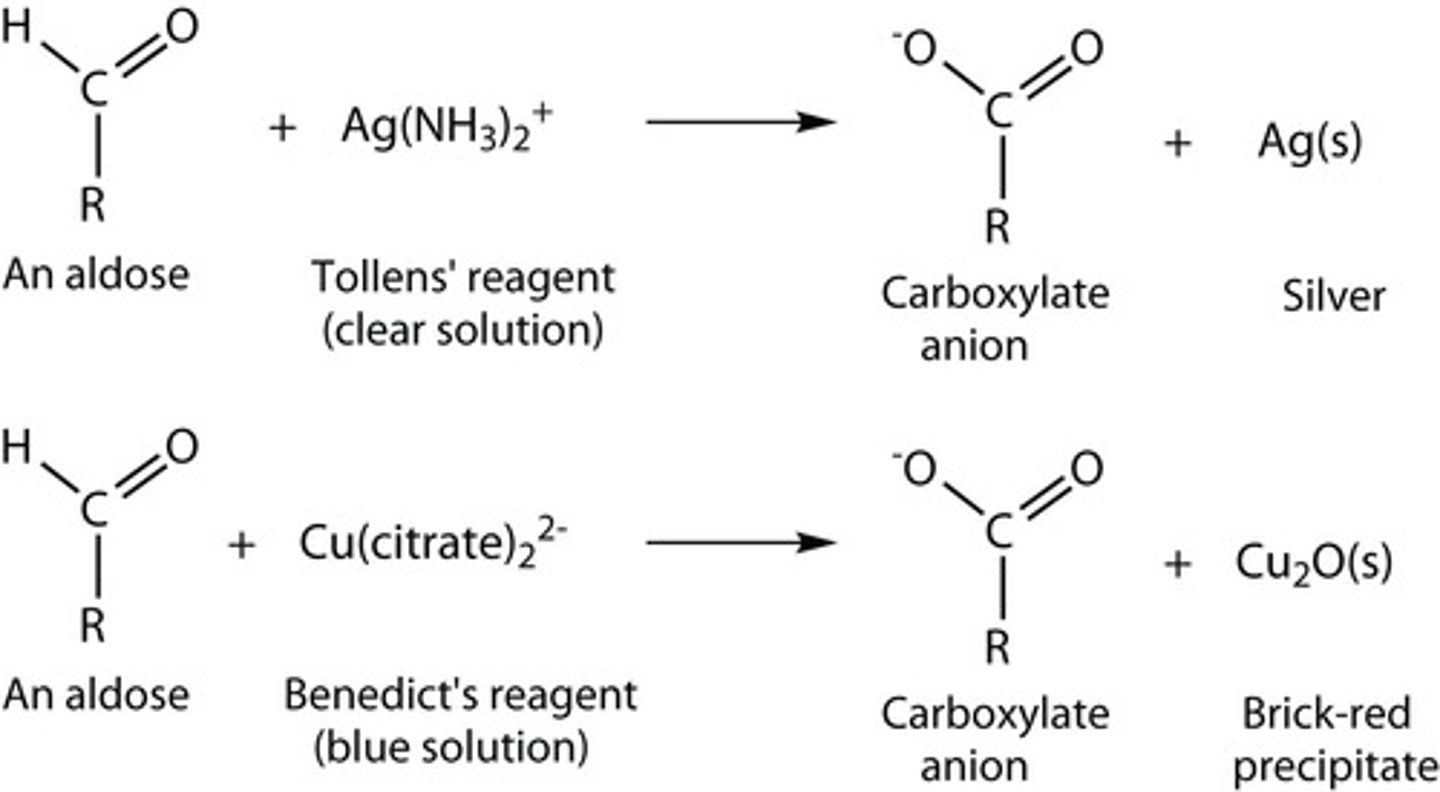
Ag(NH3)2+
Tollens reagent and aldehyde to a carboxylate
Ag2O
NaOH
Tollens test
Aldehyde to carboxylate

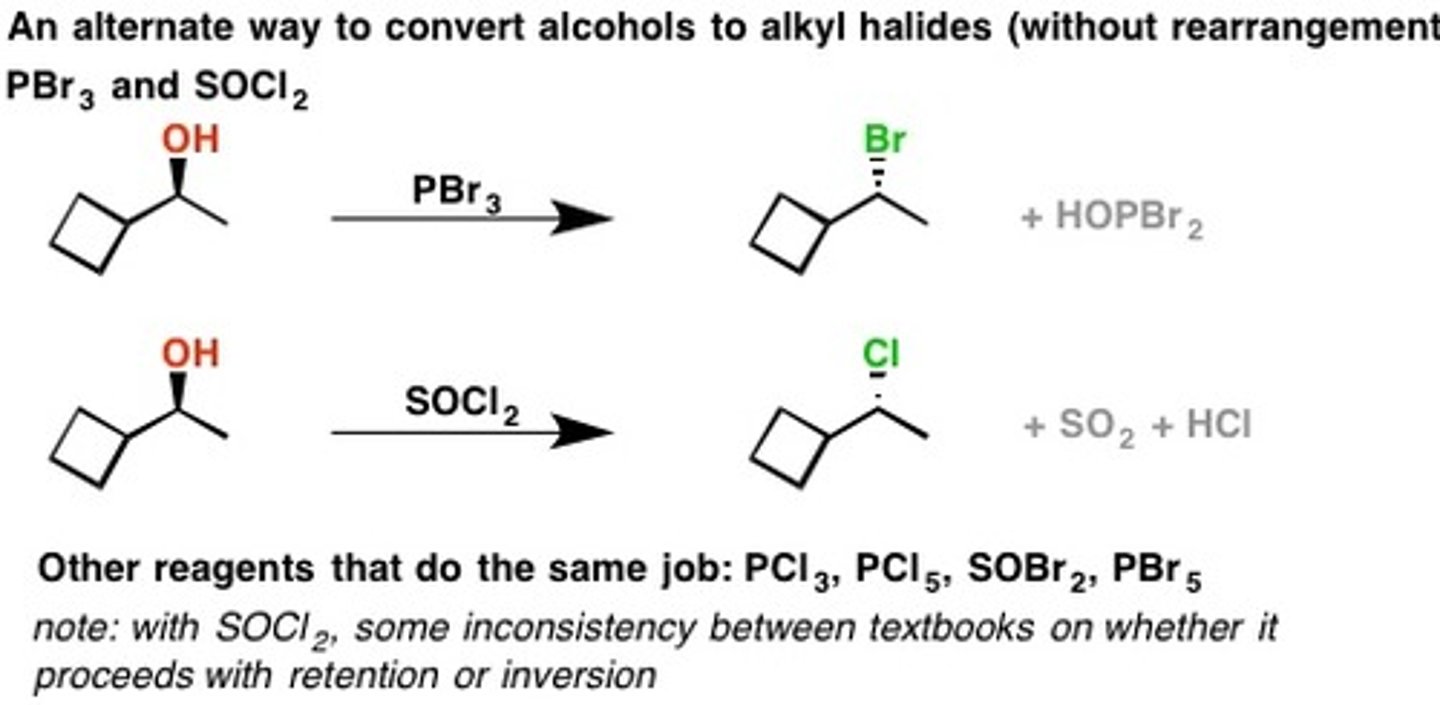
PBr3 (Phosphorus Tribromide) w/alcohol
Alcohol to alkyl halide without rearrangement
Ag2O
NH4OH
Tollens test with an "acidic work-up step"
Aldehyde to carboxylic acid
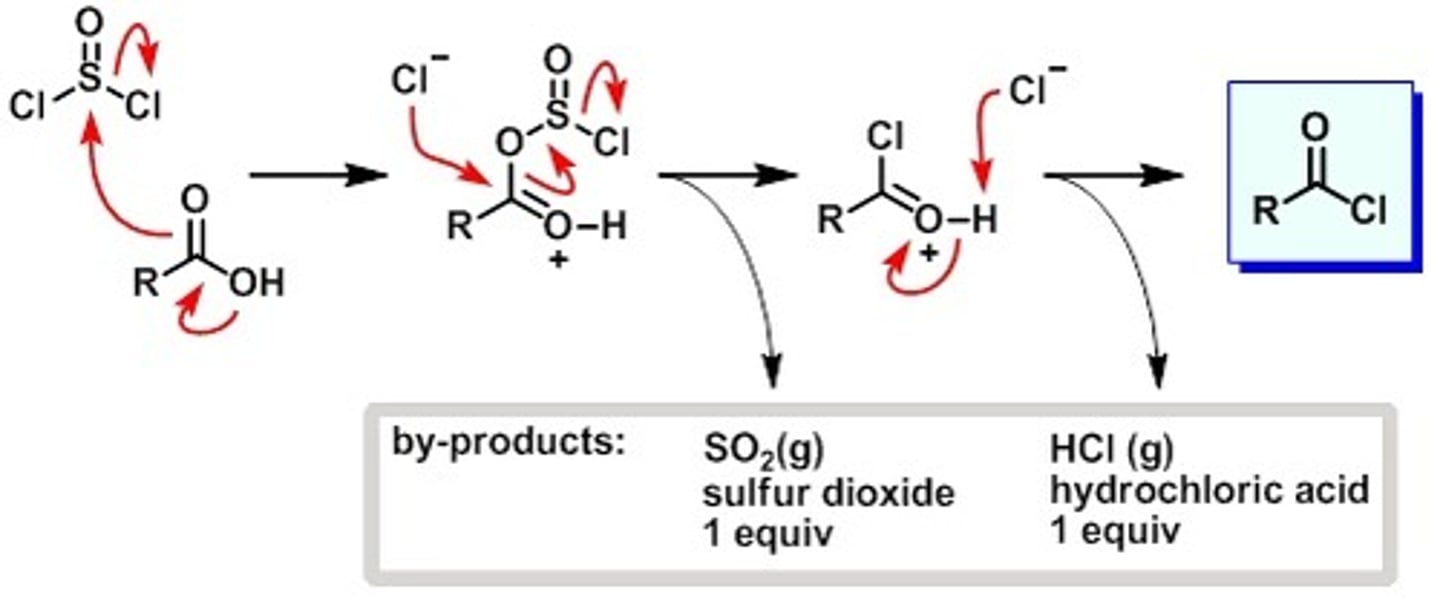
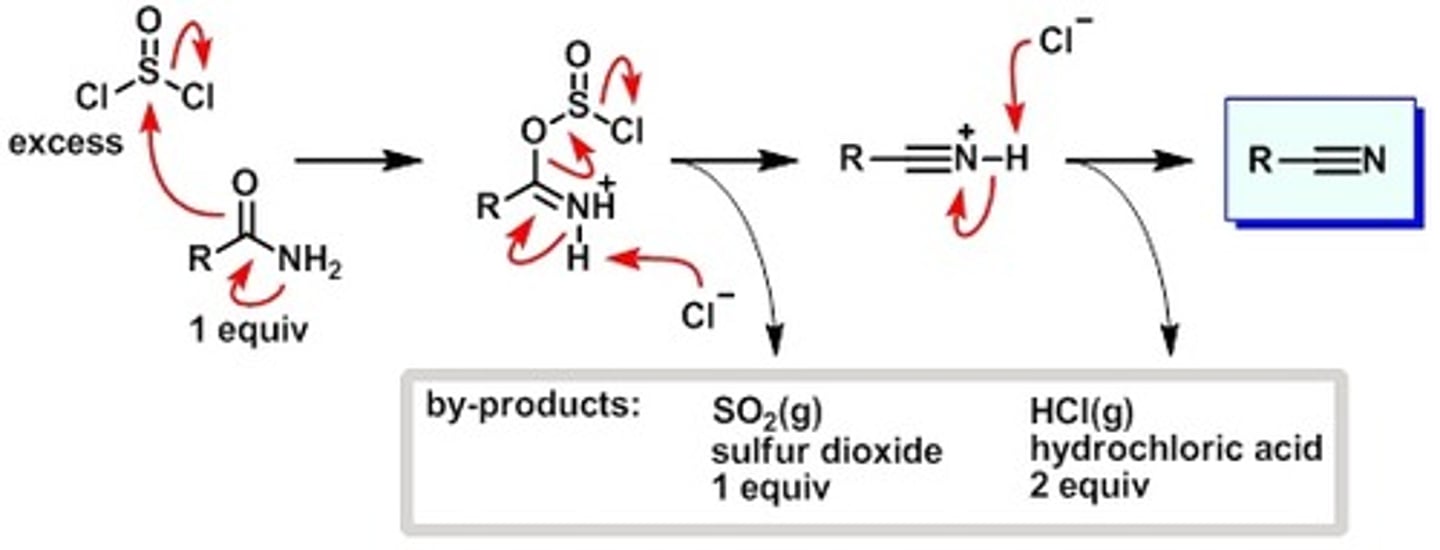
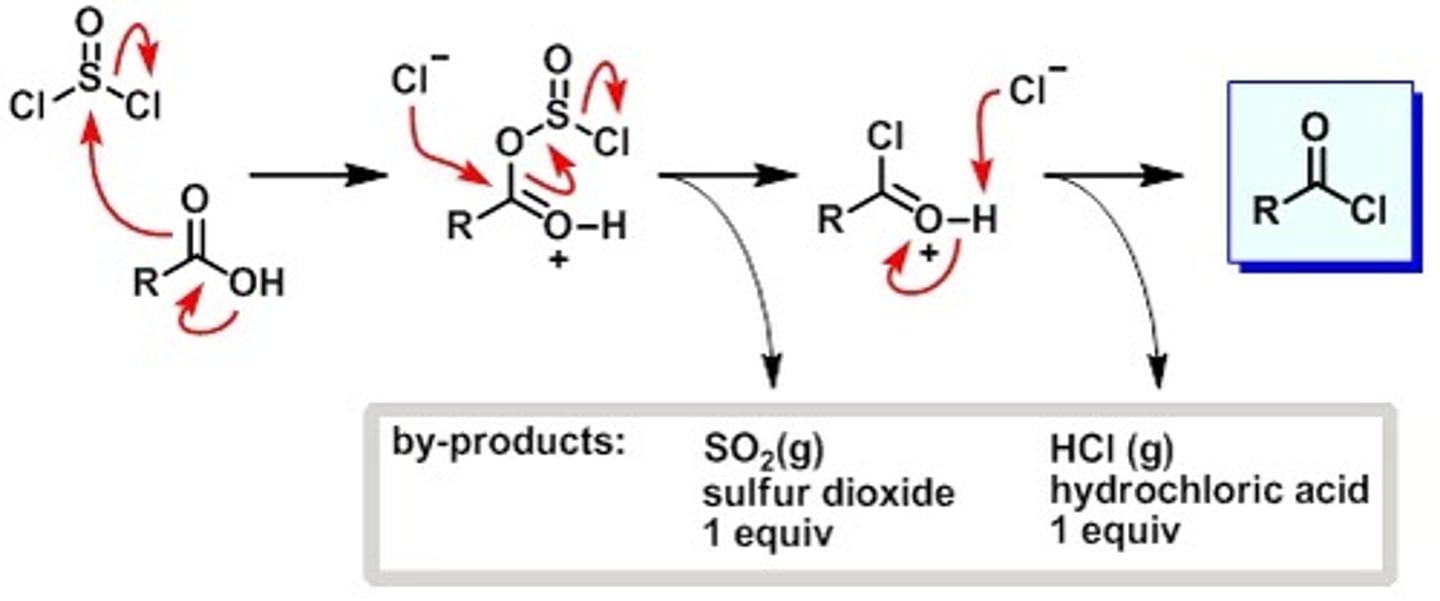
SOCl2 w/carboxylic acid
Thionyl Chloride
With Carboxylic acid
Makes for a good leaving group
Acyl Chloride from carboxylic acid + SOCl2 + pyridine
SOCl2(Thionyl Chloride) w/amide
Amide to Nitrile
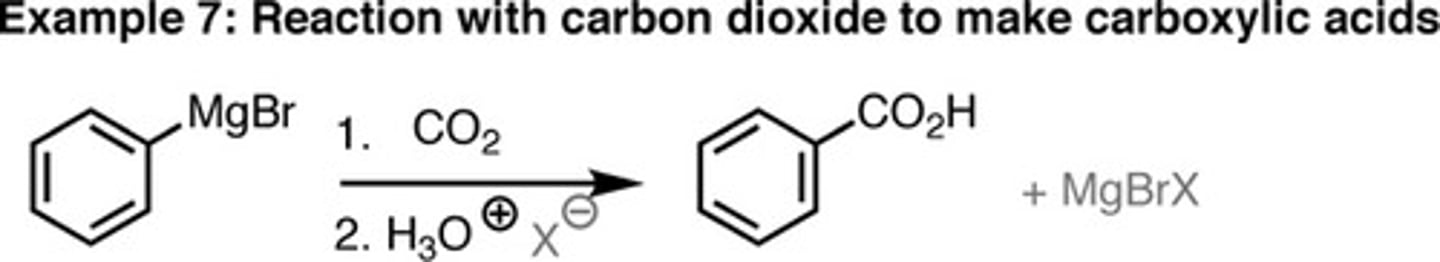
Grignard + 1. CO2 2. H3O+
Product = carboxylic acid
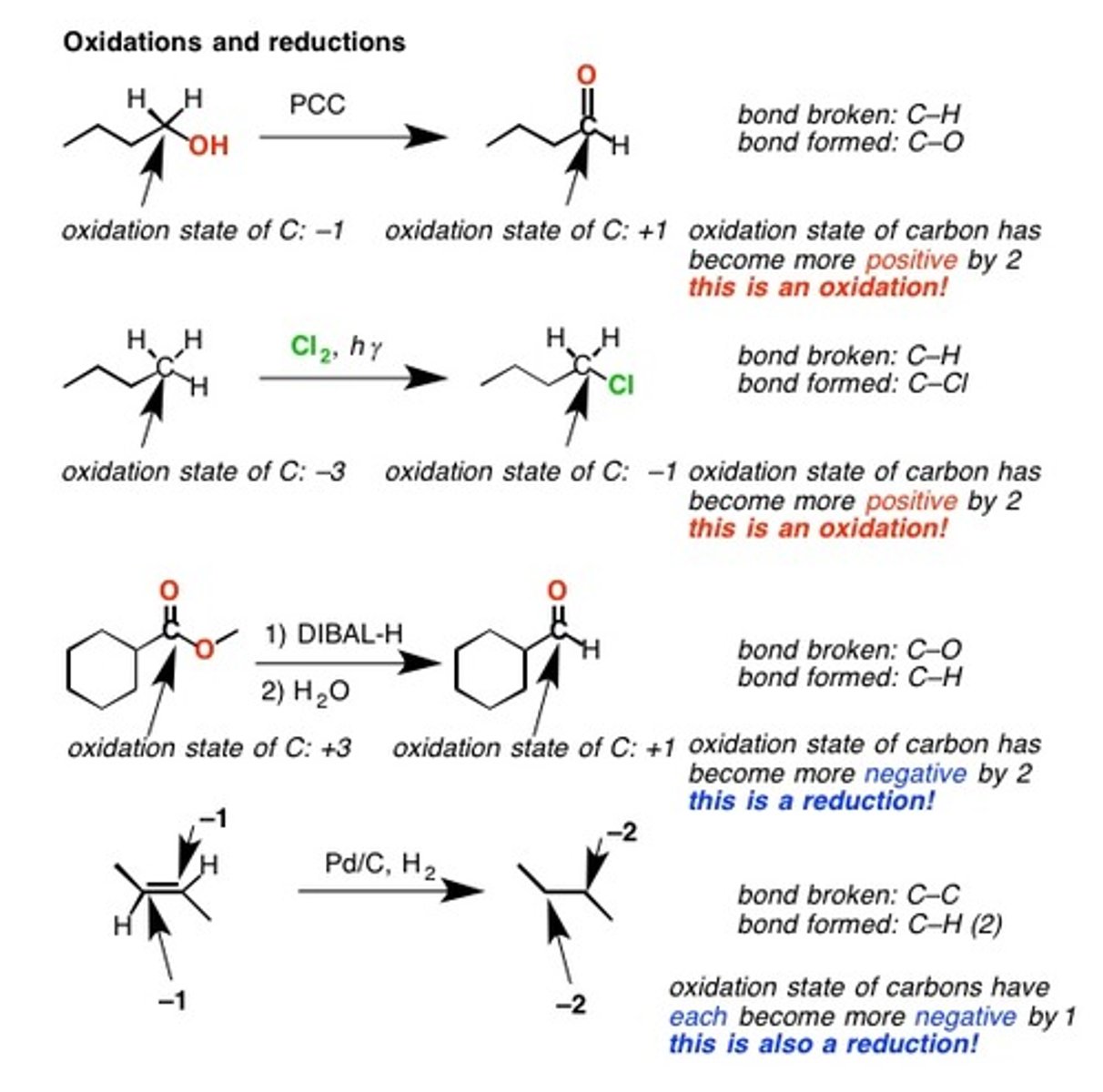
1.Oxidation and 2.Reduction
1.Removing electrons, oxidation state of the C becomes more positive
2.Gaining electrons, oxidation state becomes more negative
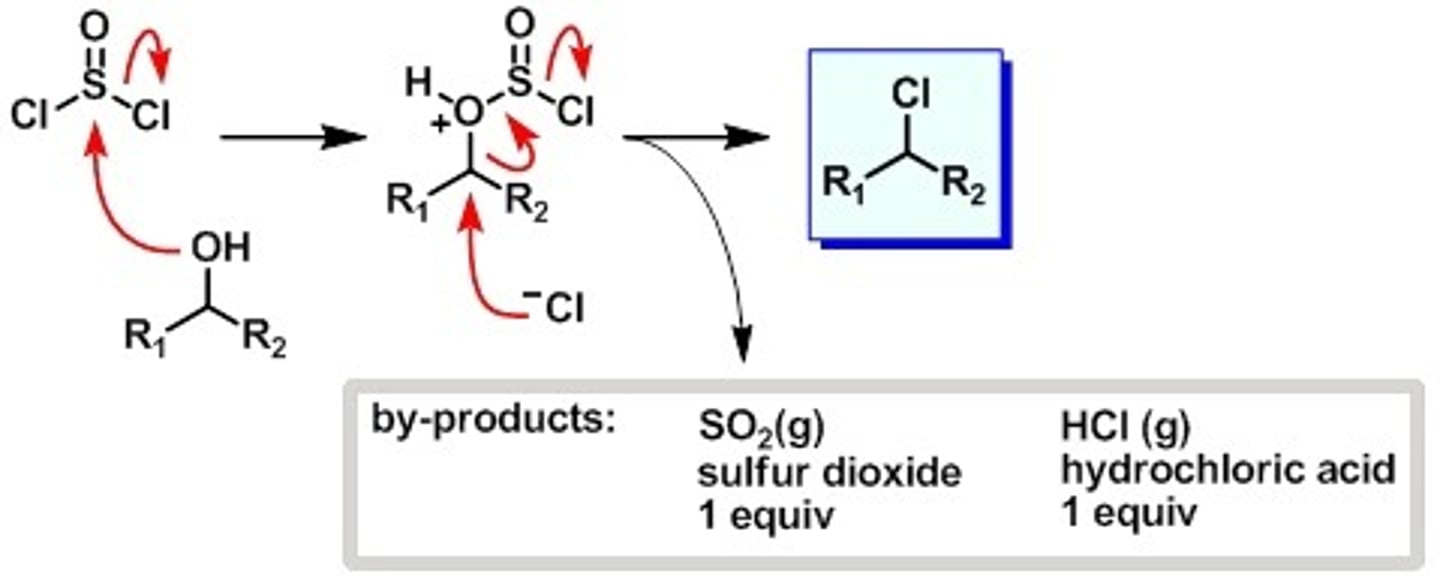
SOCl2+DMF (thionyl Chloride) w/alcohol
Alcohol to Chloride
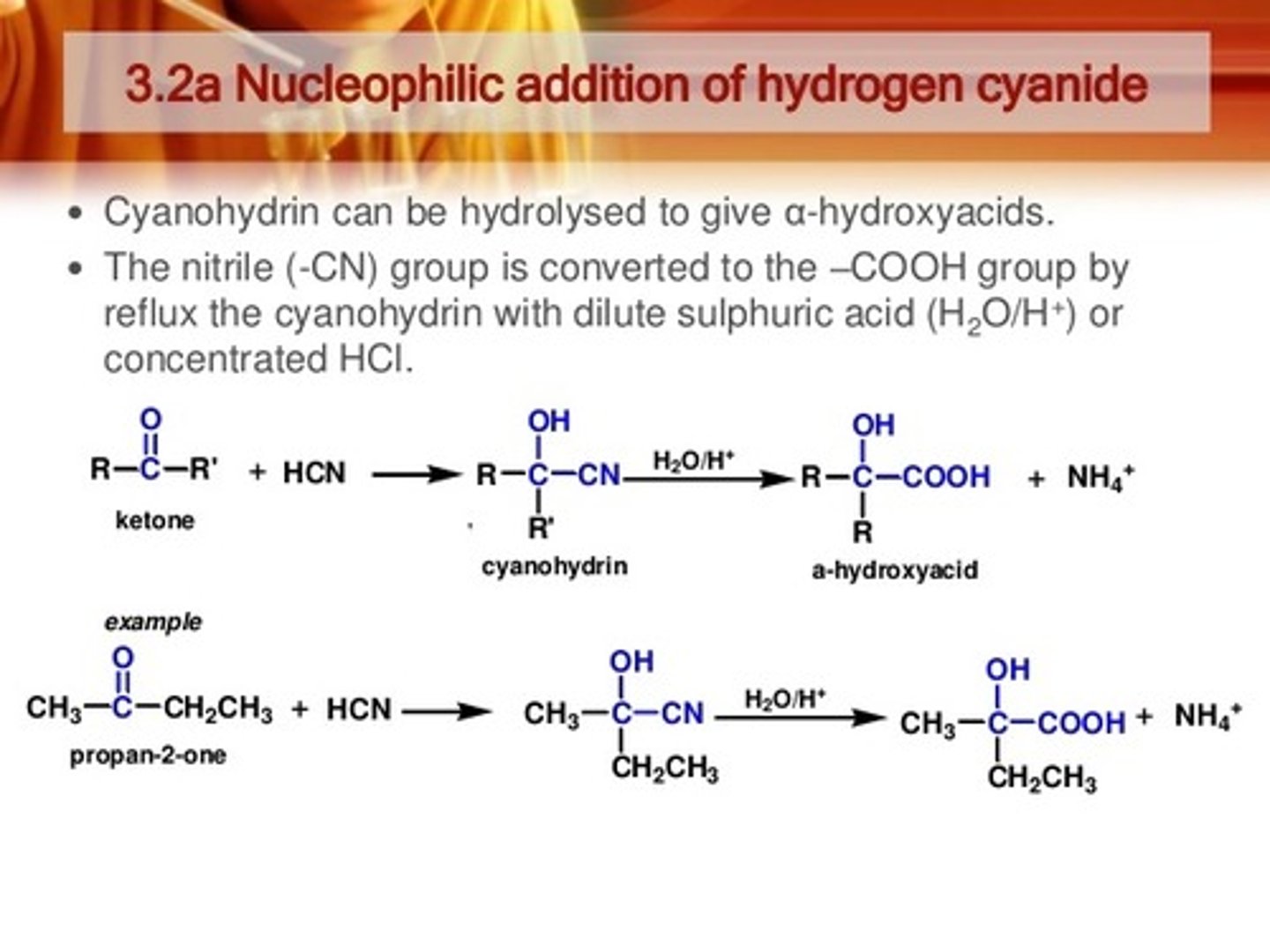
Ketone + 1.HCN (Cyanohydrin) 2.HCl, H2O, heat
Ketone gets hydrolyzed to carboxylic acid and then to alpha-hydroxy acid
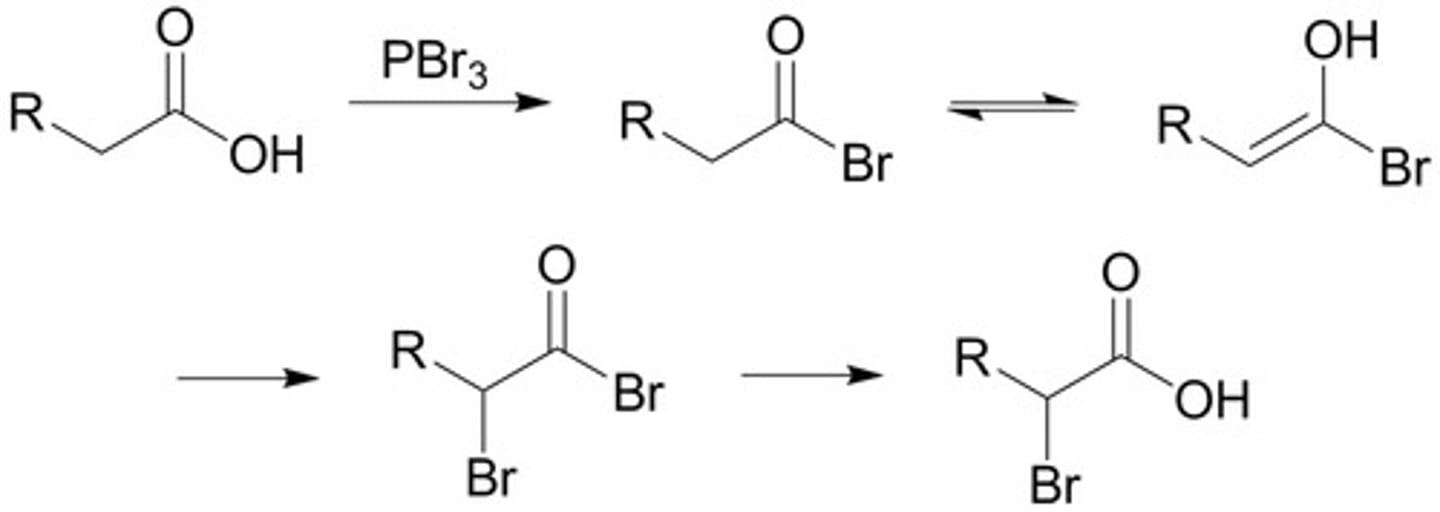
PBr3
With Carboxylic acid
Makes for a good leaving group
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation reaction- alpha position on carboxylic acid
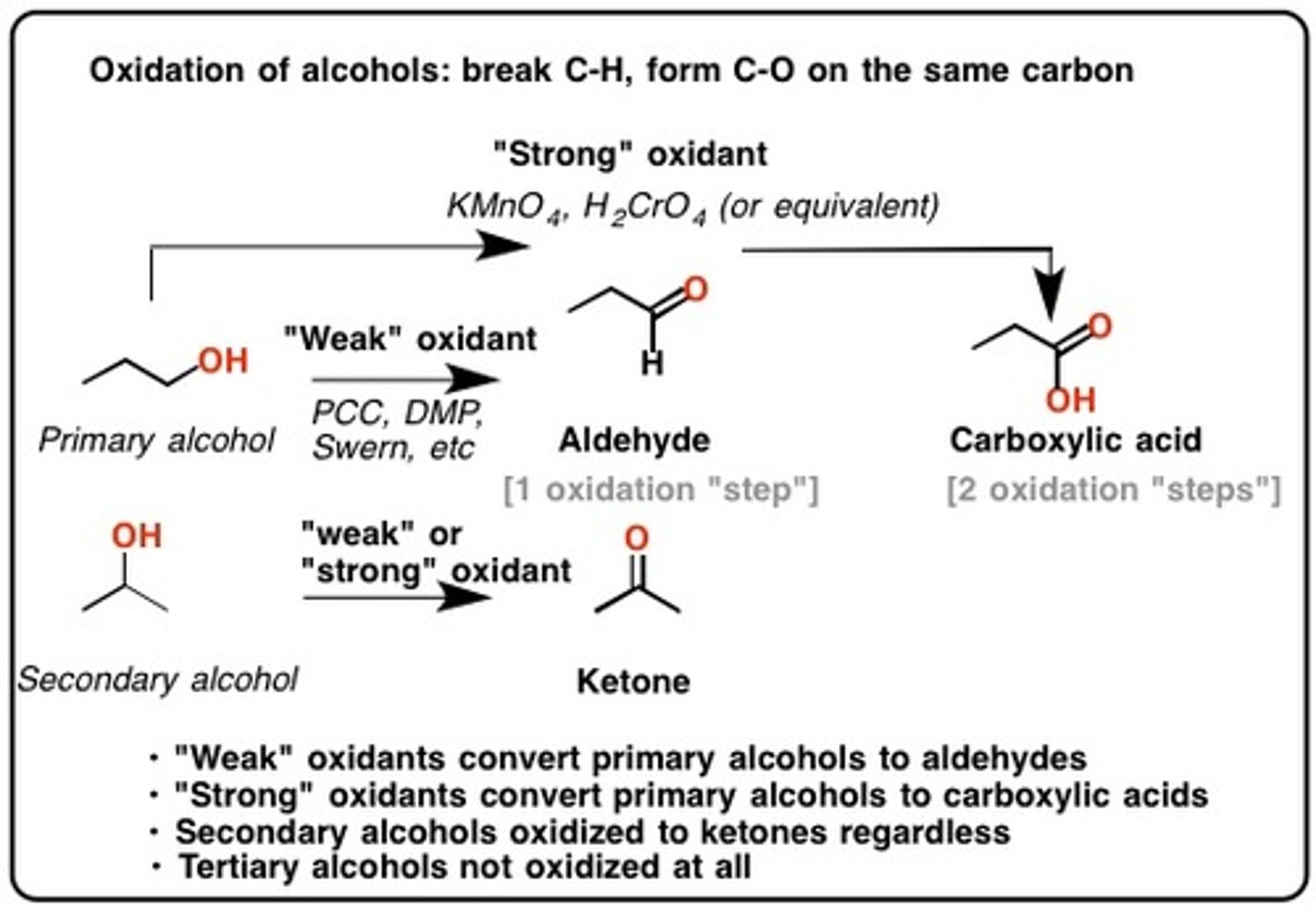
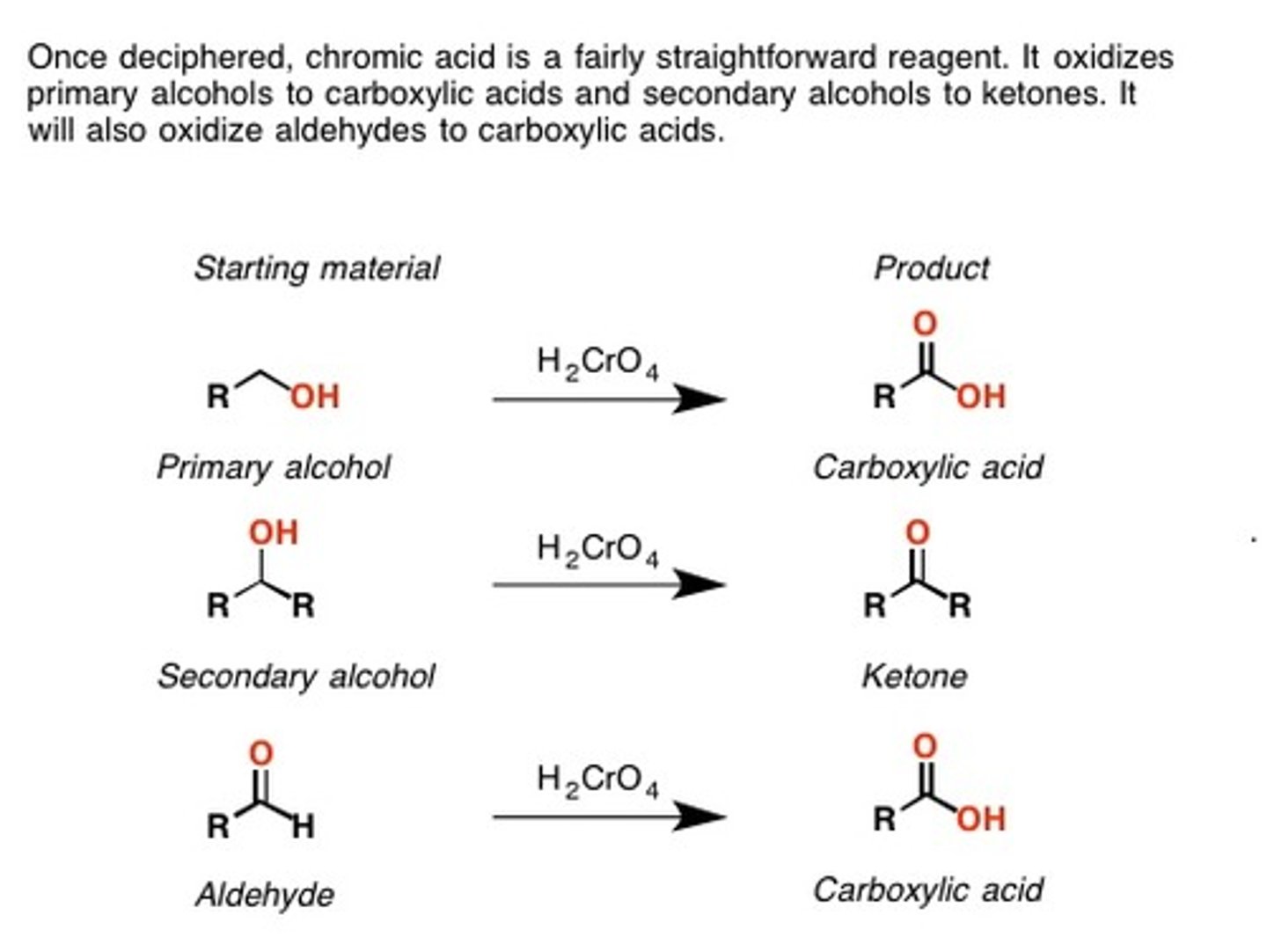
H2CrO4 (Chromic acid)
A VERY STRONG OXIDIZING AGENT.
Can use CrO3 "crap lets oxidize all the way"
Chromic acid or chromium trioxide will oxidize:
a primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
a secondary alcohol to ketone
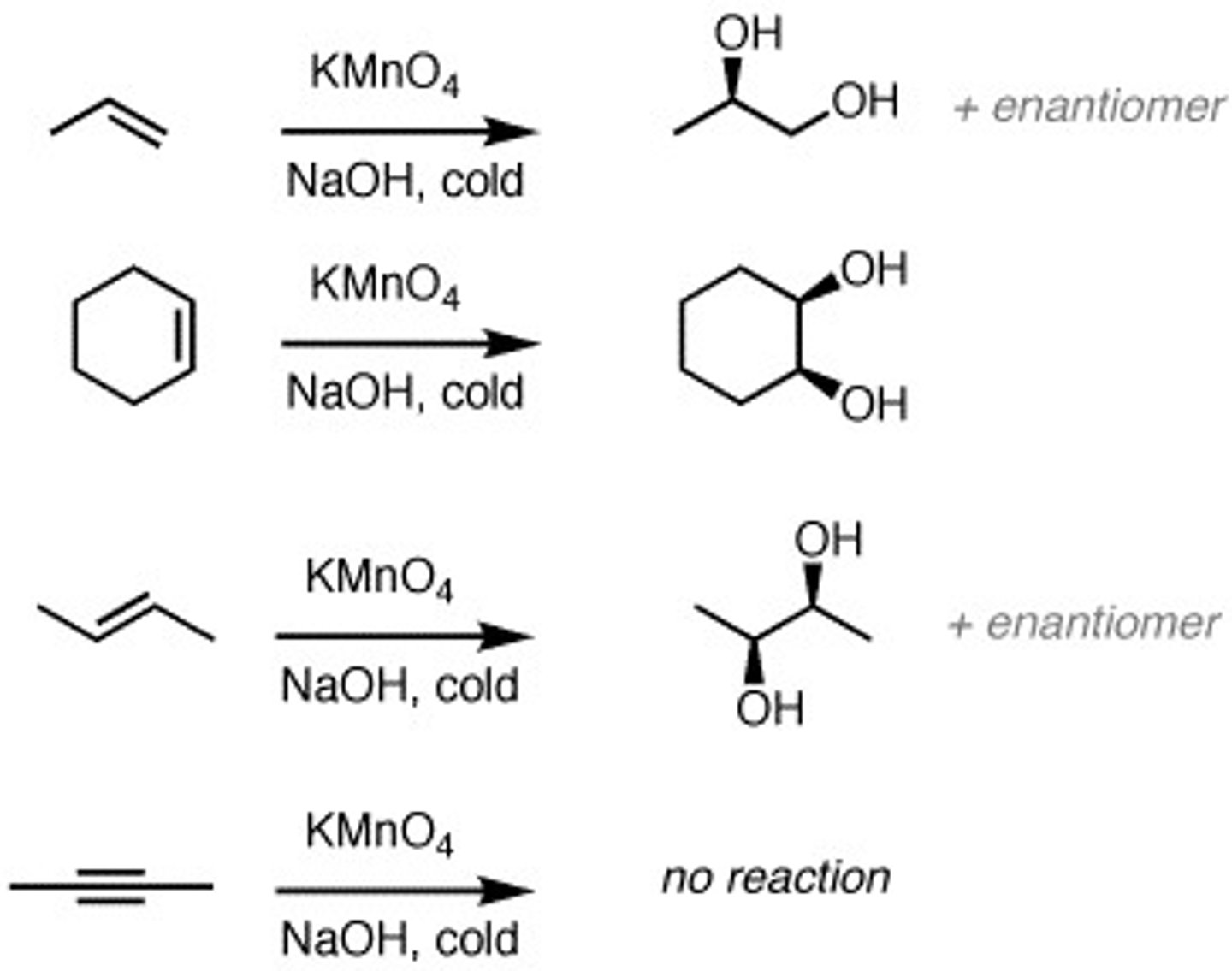
KMnO4 (potassium permanganate), cold +alkene
Potassium permanganate is an oxidizing agent but cold and hot will give different products.
Cold products- diol
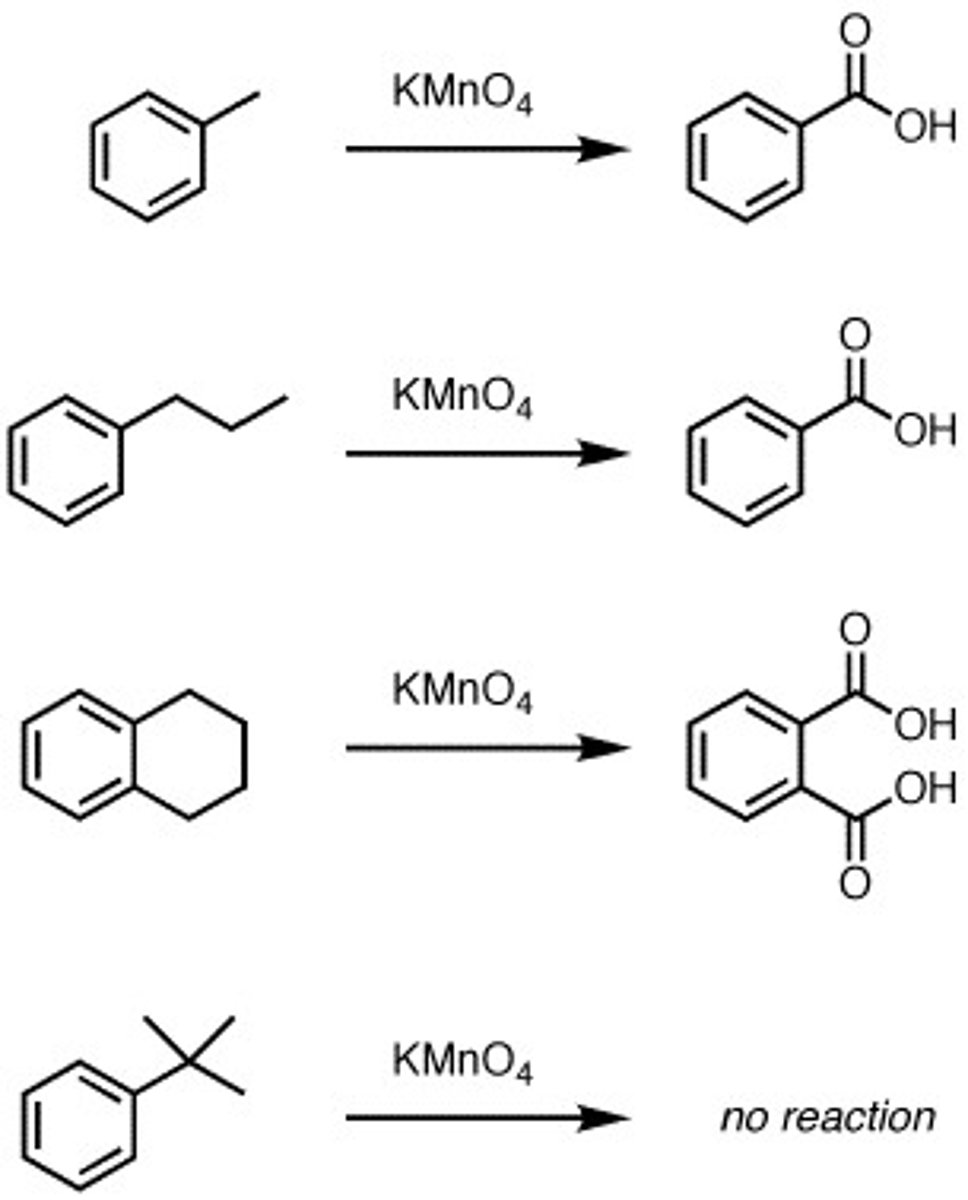
KMnO4 with aromatic alkane
Aromatic alkane give aromatic ring with carboxy acid (reaction only works if there is a hydrogen attach to the Carbon) **Carboxy acid attaches to the benzylic position (spot directly adjacent to the aromatic group)
K2CO3
A mild base that de-protonates readily available hydrogens
example: carboxylic acid to carboxylate
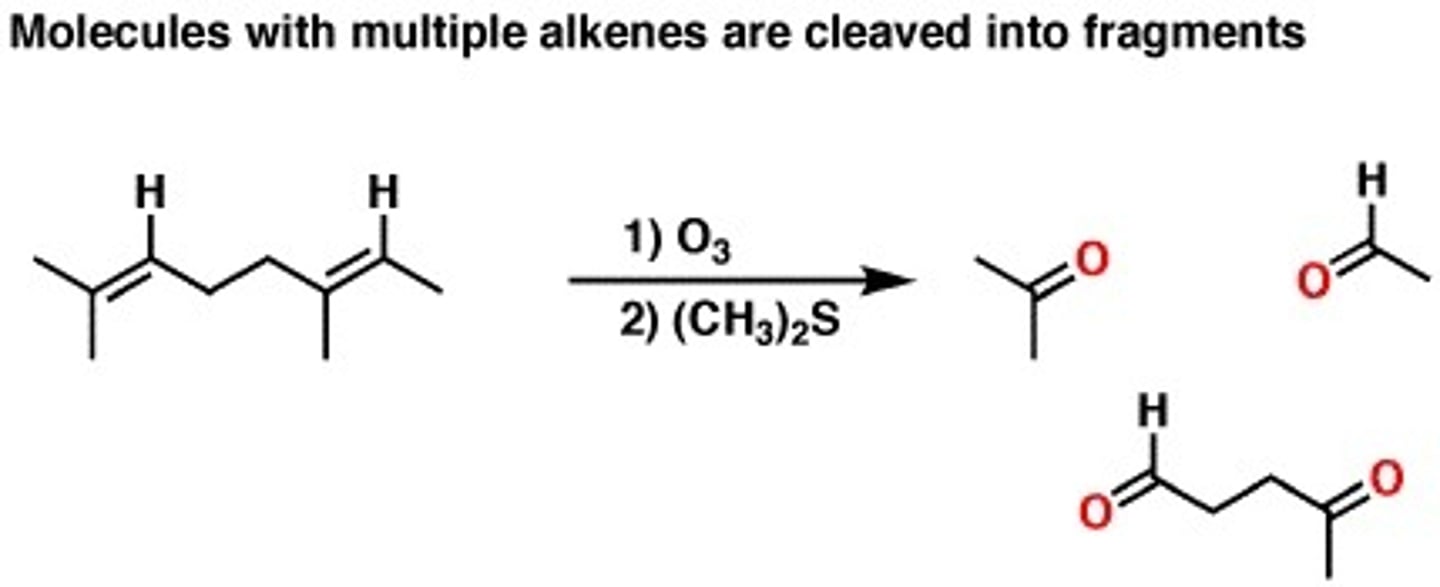
1.O3
2.DMSO +alkene
1.ozonolyis (oxidation)
2. Oxidation stops at aldehyde or ketone depending on how substituted the double bond is.
Ketone + 1.HCN (Cyanohydrin) 2. H2SO4, heat
Ketone gets hydrolyzed to alpha, beta-unsaturated acid. The difference from the alpa-hydroxy acid to alpha,beta- unsaturated acid is the acid strength. H2SO4 is a much stronger acid than HCl is.
Acid Chloride
This is the most reactive carboxylic acid derivative and as a reagent, it can synthesis less reactive carboxylic acid derivatives.
Carboxylic acid + Thionyl chloride (SOCl2) + pyridine
Acid Chloride , a carboxylic acid derivative
KMnO4 (potassium permanganate), acetone
-OH
A base. Will deprotonate any readily available hydrogens. If no hydrogens, will act like a nucleophile.
Anhydride + alcohol
Ester synthesis
With an acidic workup step - 2 esters
** side note: 2nd way to make ester is fischer esterification- carboxylic acid + alcohol
mCPBA +Ketone
OXIDIZING AGENT
Ketone + mCPBA = ester
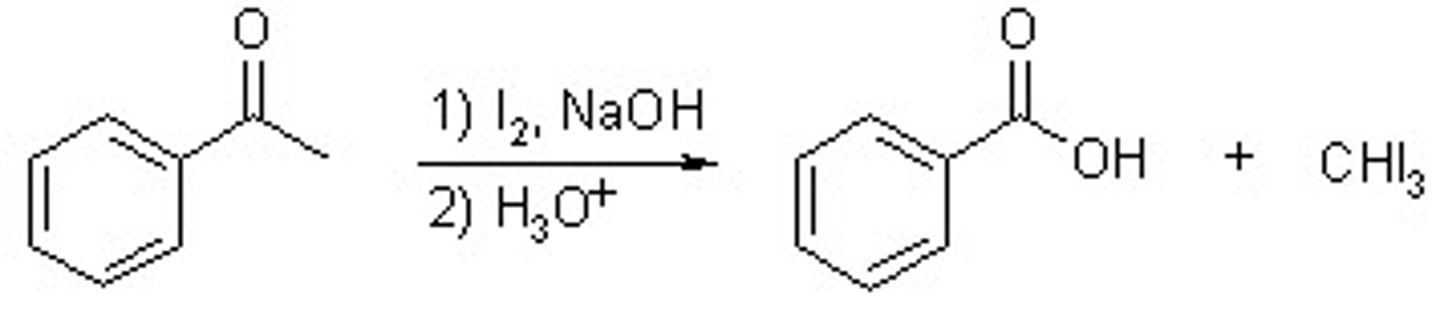
METHYL KETONE + NaOH & I2
Haloform reaction
Carboxylate & Haloform (o- & CHI3)
Carboxylic acid + 1.Br2,P 2.H2O
Hell-Volhard Zelinski Reaction
alpha- halo acid...leads to the selective alpha-bromination of carboxylic acids
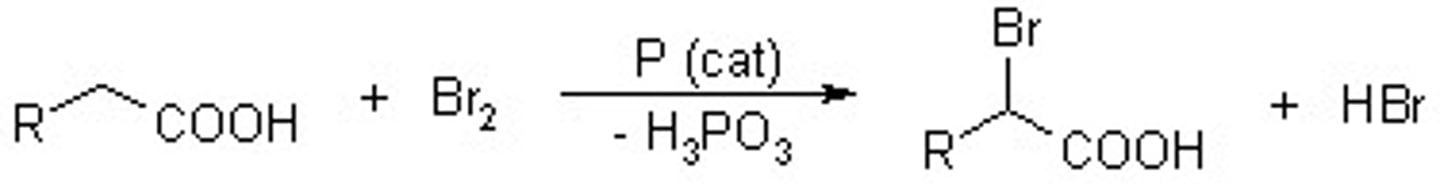
alpha-halo acid + 1.OH- 2.H3O+
HVZ product + basic hydrolysis = alpha-hydroxy acid.
alpha-halo acid + NH3
HVZ product +ammonia = amino acid at neutral pH and at pH of 9 = Zwitterion
Na+ -:C(C6H5)3
Will allow for an ester with ONLY ONE ALPHA HYDROGEN to undergo Claisen Condensation. It is a carbon with a negative charge and three phenyl groups attached which further increases its basicity.
n-butyl lithium + diisopropyl amine OVER THF
LDA synthesis
1.NaOH
2.H3O+
Saponification / basic hydrolysis
Carboxylic acid + NH3 (ammonia)
Amide
NaCN (Sodium cyanide)
A nucleophile
R-CN (Nitrile) + H3O+ heat
Nitrile is a carboxylic acid.
Acidic hydrolysis back to carboxylic acid
Alcohol + H3O+ and heat
Dehydration
B-dicarboyl + H3O+ and heat
Decarboxylation
**ALPHA AND BETA POSITION IS YOUR HINT**
Me2 (or R2)CuLi +alkyl halide
Corey posner whitesides-house synthesis (Lithium dialkylcuprate)
Adds carbons! Easiest way to add a carbon.
ALKENE + 1.KMnO4, HEAT
2. H3O+
Potassium permanganate is an oxidizing agent and when hot in temperature, alkenes are oxidized to aldehydes or ketones depending on how substituted the double bond is.
ALDEHYDE + 1.KMnO4, HEAT
2. H3O+
Aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylate without workup step and carboxylic acid WITH a workup step
Alkyl benzene (the first carbon with atleast one hydrogen) + 1.KMnO4, HEAT
2. H3O+
The alkyl group is oxidized to carboxylate WITHOUT workup step and carboxylic acid WITH workup step.
Alkene + X2( halogens)/ low concentration or high temperature
Allylic radical substitution
Halide on allylic position
(use for chlorine and NBS for bromine)
NBS/ Light or ROOR
or
Br2
Allylic radical substitution
Halide on allylic position
(Use for bromine and Cl2/ High temperature for Chlorine)
IF YOU USE NBS IN A MECHANISM, YOU MUST SHOW HOW NBS AND HBR REACT !!!!!
Diene (conjugated system) + H-Br/ 25 degrees celsius and lower
1,2- addition (Kinetic and markovnikov product)
Diene (conjugated system) + H-Br/ 60 degrees celsius and higher
1,4-addition (Thermodynamic product)
Diene (conjugated system) + dienophile (an alkene)
Ring synthesis (2 new sigma bonds and 1 pie bond formed)
Alkene + X2/ CCl4, LOW TEMPERATURE
2 halogens added across the double bond
Aromatic ring + Br2,
FeBr3
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reaction
Halogenation of benzene ring
Bromine on the aromatic ring = the product
Aromatic ring + HNO3,
H2SO4
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reaction
Nitration of benzene ring
Nitro group on the benzene ring = the product
Aromatic ring + SO3
H2SO4
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reaction
Sulfonation of benzene ring
Sulfuric acid group on the benzene ring = the product
Aromatic ring + R-X
AlCl3 (or FeBr3)
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reaction
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of benzene ring
Alkyl group on the benzene ring = the product
Aromatic ring + Acid chloride
AlCl3
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reaction
Friedel-Crafts Acylation of the benzene ring
Acyl group on the benzene ring = the product
Friedel-Crafts Acylation product + Zn(Hg), HCl
Clemmensons reduction of acyl group
Solves the rearrangement issue
REDUCES THE CARBONYL GROUP TO -CH2
USE IF MOLECULE IS SENSITIVE TO BASE!!!
Friedel-Crafts Acylation product + H2N-NH2 +KOH
Wolf-Kischner reduction of acyl group
Solves the rearrangement issue
REDUCES THE CARBONYL GROUP TO -CH2
USE IF MOLECULE IS SENSITIVE TO ACID!!!
Aromatic ring + Na*, NH3, EtOH
Birsch reduction of aromatic ring into 2 NON-AROMATIC, NON-CONJUGATED RINGS
PRODUCT = 2 CYCLOHEXADIENES
Ester + 1.DIBAL-H
2.H2O
Aldehyde
"Dear DIBAL, please stop reduction at aldehyde"
Acid Chloride + 1. DIBAL-H
2. H2O
Aldehyde
"Dear DIBAL, please stop reduction at aldehyde"
Nitrile + 1. DIBAL-H
2. H2O
Aldehyde
"Dear DIBAL, please stop reduction at aldehyde"
Ester + 1. LiAl(OtBu)3H
2. H2O
Aldehyde
*Works the same as DIBAL-H
Acid Chloride + 1. LiAl(OtBu)3H
2. H2O
Aldehyde
*Works the same as DIBAL-H
Alkyne + H2O
H2SO4
HgSO4
Tautomerization
Enol--> Keto
R-Li
Works the same as grignard
NaBH4 (Sodium Borohydride)
REDUCING AGENT.... WEAKER THAN LAH
Reduces Aldehydes and ketones to its respective alcohol.
Ketone + H3O+
Geminal Diol
Ketone + OH-
Geminal Diol
Ketone + R-OH
H3O+
Hemiacetal----> Acetal ( a protecting group for aldehydes and ketones)
Ketone + R-OH
OH-
Hemiacetal
To proceed to acetal (the protecting group), you need acidic conditions.
Aldehyde + R-OH
H3O+
Hemiacetal----> Acetal ( a protecting group for aldehydes and ketones)
Aldehyde + R-OH
OH-
Hemiacetal
To proceed to acetal (the protecting group), you need acidic conditions.
Ketone + primary amine & mild acid
Imine formation
Ketone + secondary amine
Enamine formation
beta- keto ester + 1.NaOR
2.R-X
3.OH-, H2O
4.H3O+, heat
The product is a longer ketone
This reaction can be performed with anything that is a di-carbonyl and has an ester
beta-dicarbonyl compound + KOtBu
Use for second alkylation or acylation!
Br-R-Br
Ring closure
Nucleophile + a conjugated system
Michaels addition
a)simple addition 1,2-addition
b)conjugated addition 1,4-addition AND THEN PRODUCT = ALPHA, BETA-UNSATURATED SYSTEM BECAUSE OF ENOL--->KETO
Cyanide + a conjugated system
Michaels addition (any nucleophile)
a)simple addition 1,2-addition
b)conjugated addition 1,4-addition AND THEN PRODUCT = ALPHA, BETA-UNSATURATED SYSTEM BECAUSE OF ENOL--->KETO
Amine + a conjugated system
Michaels addition (any nucleophile)
a)simple addition 1,2-addition
b)conjugated addition 1,4-addition AND THEN PRODUCT = ALPHA, BETA-UNSATURATED SYSTEM BECAUSE OF ENOL--->KETO
Di-carbonyl + a conjugated system
+ OH-
+ROH
Michaels addition (any nucleophile)
a)simple addition 1,2-addition
b)conjugated addition 1,4-addition AND THEN PRODUCT = ALPHA, BETA-UNSATURATED SYSTEM BECAUSE OF ENOL--->KETO