TEAS CHEM
1/497
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
498 Terms
Extensive property
a property that depends on the amount of substance in a sample
Intensive property
a property that does not depend on the amount of substance in a sample
elasticity: physical or chemical property?
physical property of matter
volume: physical or chemical property?
physical property of matter
mass: physical or chemical property?
physical property of matter
color: physical or chemical property?
physical property of matter
Weight definition
is a measure of the force that gravity exerts on an object.
Mass definition
is a measure of the amount of substance within an object.
Volume definition
is a measure of the amount of space an object occupies.
Temperature
is a measure of how fast molecules are moving in a substance
Heat
is a measure of energy transfer - it's the amount of energy transferred from one substance to another.
Density
is the measure of the amount of mass per unit of volume.
(ratio between mass and volume of substance) ex: m/v
density
Melting Point
is the temperature and pressure at which a solid turns into a liquid
Boiling Point
is the temperature and pressure at which a liquid turns into a gas
Specific Heat Capacity
is the amount of heat needed to change the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by a certain unit of temperature.
intensive property examples
density, temperature, melting point, malleability, boiling point, specific heat capacity, and luster.
density, Intensive or Extensive
intensive
temperature, Intensive or Extensive
intensive
malleability - intensive or extensive
intensive
boiling point intensive or extensive
intensive
specific heat capacity intensive or extensive
intensive
Luster (intensive or extensive)
intensive
length (intensive or extensive)
extensive
mass (intensive or extensive)
extensive
heat intensive or extensive
extensive (If you double the amount of water in a pot, you'll need twice as much heat to raise the temperature by the same amount)
volume intensive or extensive
extensive
Density Formula
D=m/v
Relative Density formula
mass of any volume of a substance/ mass of an equal volume of water
Volume formula for Cube
V= a³
Volume formula for Rectangular Prism
a x b x c
Volume formula for Cylinder
V = πr²h
Volume formula for Sphere
V=4/3πr³
Volume formula for Cone
V = 1/3πr²h
Volume formula for Triangular Pyramid
V=a² x H/3
Volume displacement Formula
v=Vf-Vi
Conversion formula for cm^3 to m^3 (using 1000cm^3)
1000cm³x(1m/100cm³)=0.001m³
Weight Formula and Unit of Measurement
W=mg Newton
ex: box is 10kg, gravity on planet earth is 9.8m/s²
(10kg)x(9.8m/s²)= 98N
Heat capacity Measurement
J/K or J/C°
Which has a higher heat capacity Wooden handle or Iron Handle
an iron handle heats up more rapidly than a wooden one, which means iron has a lower heat capacity than wood, so it will require less heat for its temperature to rise.
Specific Heat Capacity Measurement
J/kg°C or J/kgK
Measurement for Energy
Joules (J)
equation that relates the heat energy to the specific heat capacity
Define each Variable
Q=mCΔT
Q=heat energy (in J)
M=the mass of the substance
C=the specific heat capacity of the substance
ΔT=the change in the substance's temperature.
A student must use 225 mL of hot water in a lab procedure. Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 225 mL of water from 20.0 /C to 100.0 /C.
q= heat (in joules, J)
m = mass of the water (in grams, g)
c = specific heat capacity of water = 4.18 J/g·°C
ΔT = change in temperature (°C)
Step 1: Convert volume to mass
Since the density of water is approximately 1.00 g/mL, 225 mL of water has a mass of:
m=225mL×1.00g/mL=225g
Step 2: Calculate temperature change:
100-20= 80
Step 3: Plug values into the formula
Q(?)= 225g x 4.18 × 80 = 75240 J or 75.2 kJ
75.2 kJ (Divide by 1000 to convert J to kJ)
Calculate the specific heat capacity of a new alloy if a 15.4 g sample absorbs 393 J when it is heated from 0.0/C to 37.6 /C.
c = 0.679 J/g C/C
Calculate the specific heat capacity of titanium if a 43.56 g sample absorbs 0.476 kJ as its temperature changes from 20.13/C to 41.06/C.
(0.522 J/g C/C)
kJ to J conversion
kJ x 1000=J
A 175 g piece of iron and a 175 g piece of aluminum are placed in a hot water bath so that they are warmed to 99.7/C. The metal samples are removed and cooled to 21.5/C. Which sample undergoes the greater heat change?
Iron:0.450 J/g·°C
Aluminum: 0.897 J/g·°C
(Al; -12.3 kJ Fe; - 6.08 kJ)
specific heat capacity equation
C=Q/mΔT
The burning of a sample of propane generated 104.6 kJ of heat. All of this heat was use to heat 500.0 g of water that had an initial temperature of 20.0/C. What was the final temperature of the water?
water heat cap: 4.18 J/g°C
Step 1: Convert heat from kJ to J
q=104.6kJ = 104600J
Step 2: Plug known values into the formula
104600=500.0⋅4.18⋅(Tfinal−20.0)
Step 3: Solve for Tfinal
104600=2090⋅(Tfinal−20.0)
50.05≈ Tfinal−20.0
Tfinal−70.0∘C
(70.0/C)
If 700 g of an unknown metal requires 6.30 kJ of heat to raise its temperature by 10.0 °C, what is the metal's specific heat capacity in J/kg°C?
Step 1: Convert quantities
q=6.30kJ=6300J
m=700g=0.700kg (The question asked for heat capacity in J/kg °C) So you have to convert to kg
Temperature change:
ΔT=10.0∘C “raise its Temp by 10 degrees” is heat change already.
Step 2: Solve for specific heat capacity c
6300=0.700⋅c⋅10.0
6300=7.0⋅c
c=6300/7.0 = 900J/kg°C
900J/kg∘C
Steps when calculating a SHC, Ti or Tf, Heat, or heat change Problem
Identify whats being asked SHC, Tf, or HC
Figure out the equation for whats being asked
Plug in all varibles with units attached to sway confusion
Solve
Ensure the unit aligns with the question being asked
If 500 g of iron is at a temperature of 20.0 °C, how much heat will be required to raise its temperature to 45.0 °C if the specific heat capacity of iron is 475 J/kg°C?
Step 1: Convert g to kg because heat cap is in kg
500g = .500kg
Step 2: calculate heat capacity, Vf - Vi, 45-20= 25
Step 3: Plug in and solve
q= 0.500 ⋅ 475 ⋅ 25.0= 5937.5J
Q=5937.5J
Conduction definition
a process by which heat is transferred by direct contact between two bodies
Heat energy definition
the energy of movement of the particles of a substance
Thermal equilibrium Definition
a condition in which there is no net flow of heat between two bodies
Zeroth law of thermodynamics definition
if two thermodynamic systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then the two systems are in thermal equilibrium (if A=B and B=C, the A=C)
Conduction Example
the transfer of heat from the bottom of a hot pan to the food that is being cooked.
smallest unit of matter
atom
the center of the atom, which is made up of protons and neutrons
nucleus
a positively charged subatomic particle
proton
the number of gives an atom its identity; it is located in the nucleus at the center of an atom
protons
a neutrally charged subatomic particle
neutron
a negatively charged subatomic particle that moves around the outside of the nucleus of an atom along circular paths called orbitals
electron
the area around the nucleus of an atom that contains electrons traveling around the nucleus
Electron Cloud
imaginary paths surrounding the nucleus of an atom along which electrons travel
Orbitals
Left side of periodic table
metals (except hydrogen)
rows(horizontal) on the periodic table
periods
Columns(vertical) on the periodic table are called:
families
Center of the periodic table
transition metals
Right side of periodic Table
non-metals
valence electrons on periodic table
group number
The number in the tens place of the group number indicates
The number of outer electrons (Valence Electrons)
Fluorine's number of outer electrons (group #17)
7
octet rule
States that atoms lose, gain or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons
Atomic Number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic Mass
the number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Atomic Weight
the average weight of all a particular element's isotopes.
the average weight of all a particular element's isotopes.
Atomic Weight
the number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Atomic Mass
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic Number
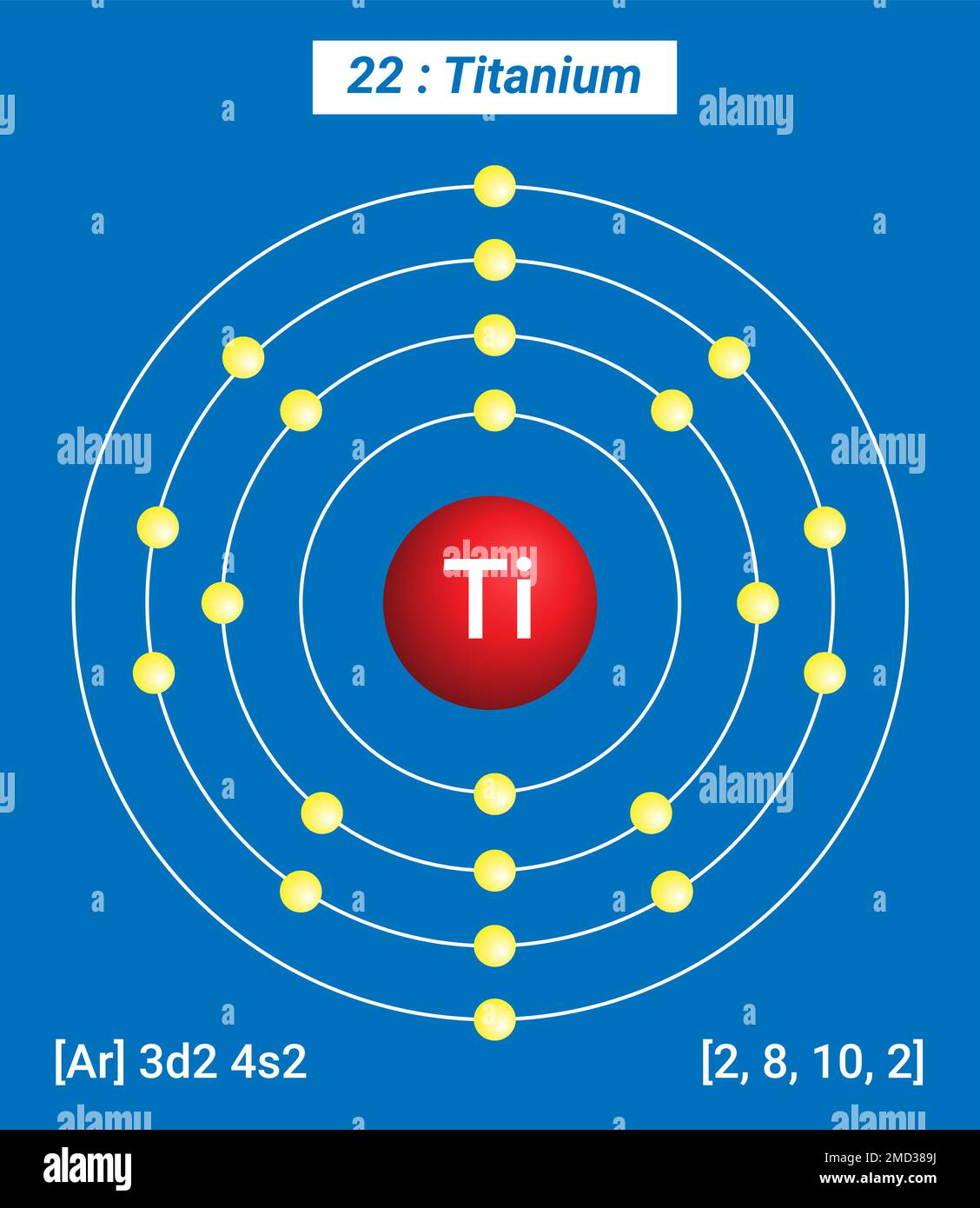
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
22
22
4
22
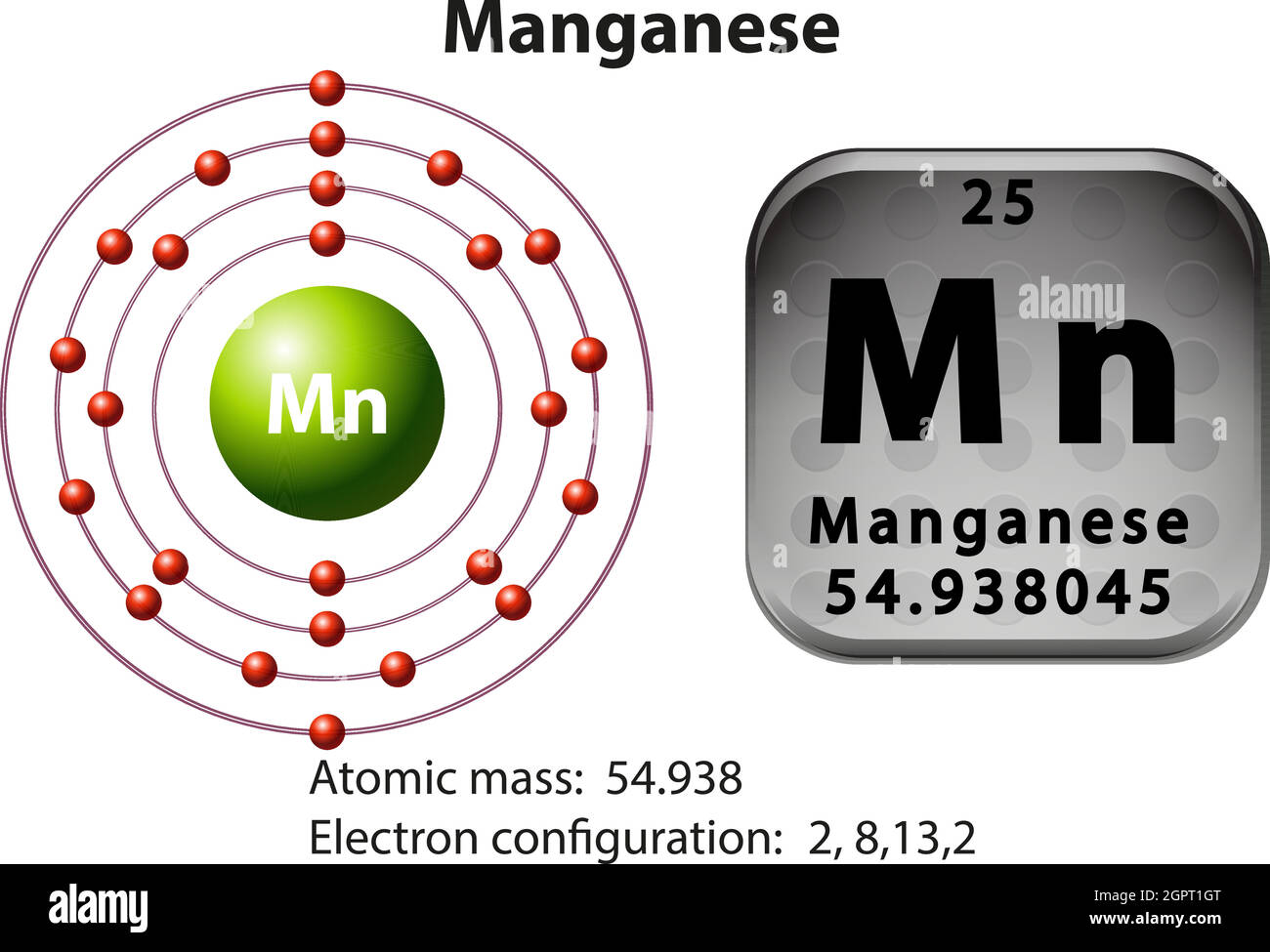
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
25
25
7
25
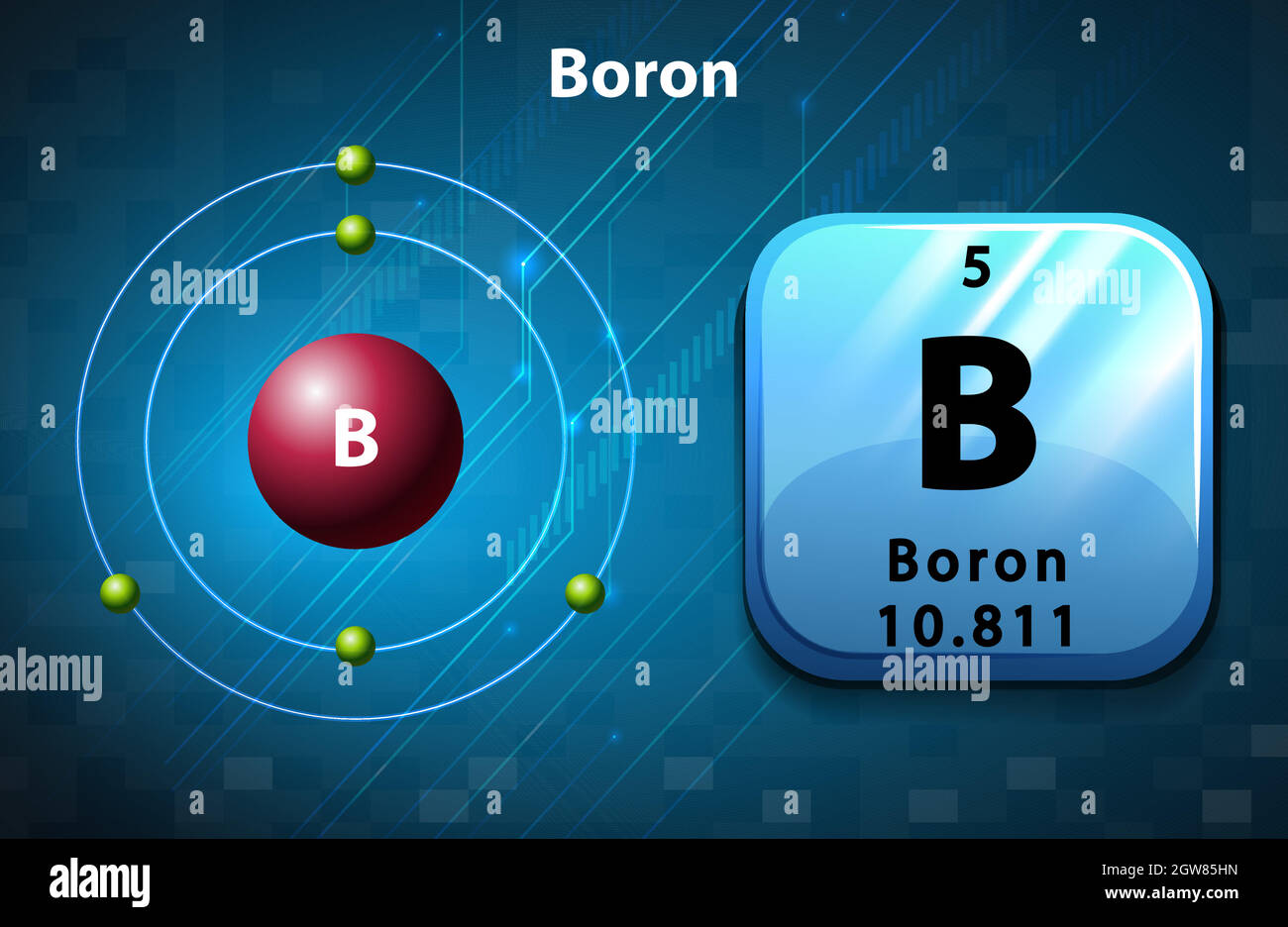
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
5
5
3
5
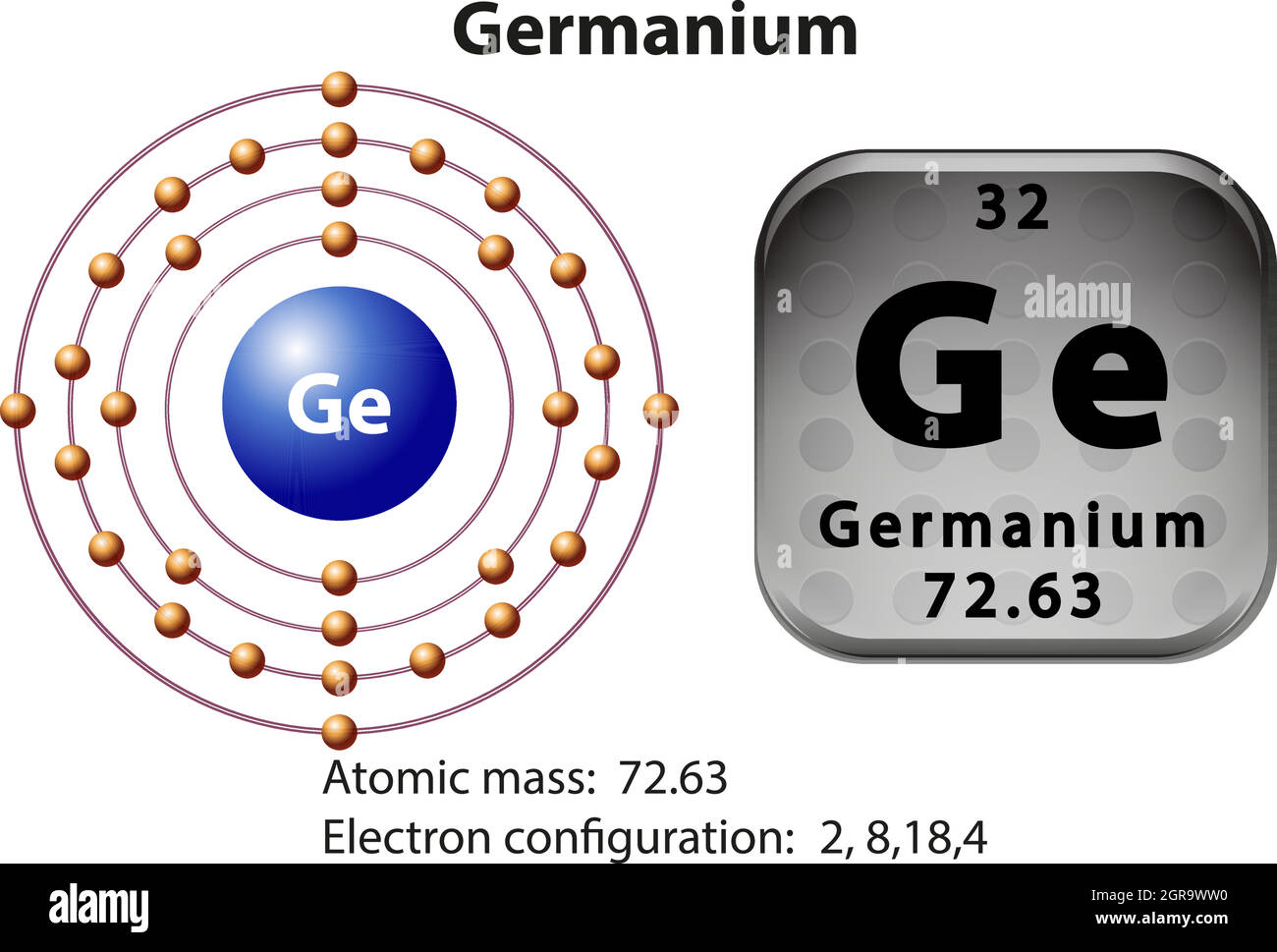
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
32
32
4
32
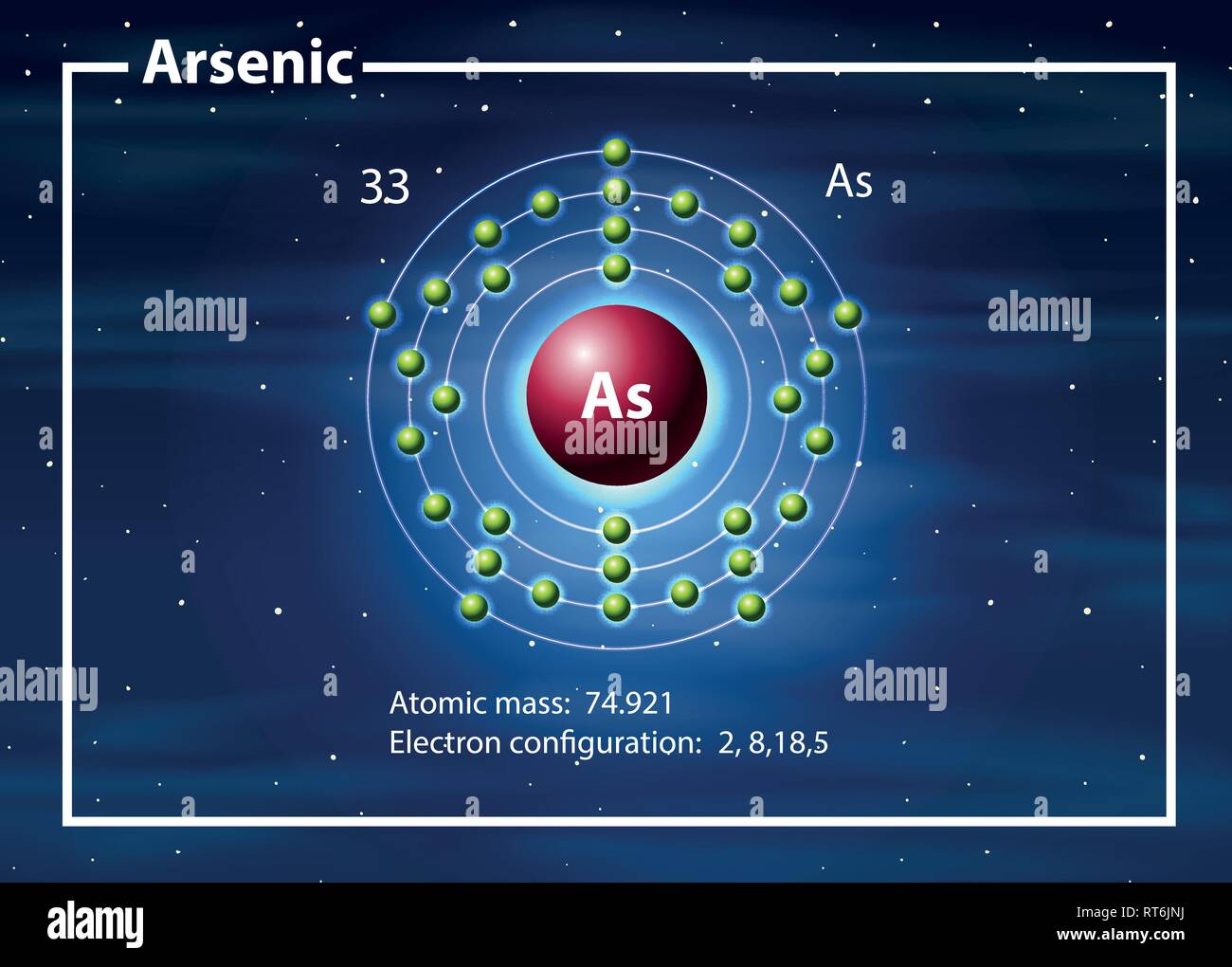
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
33
33
5
33
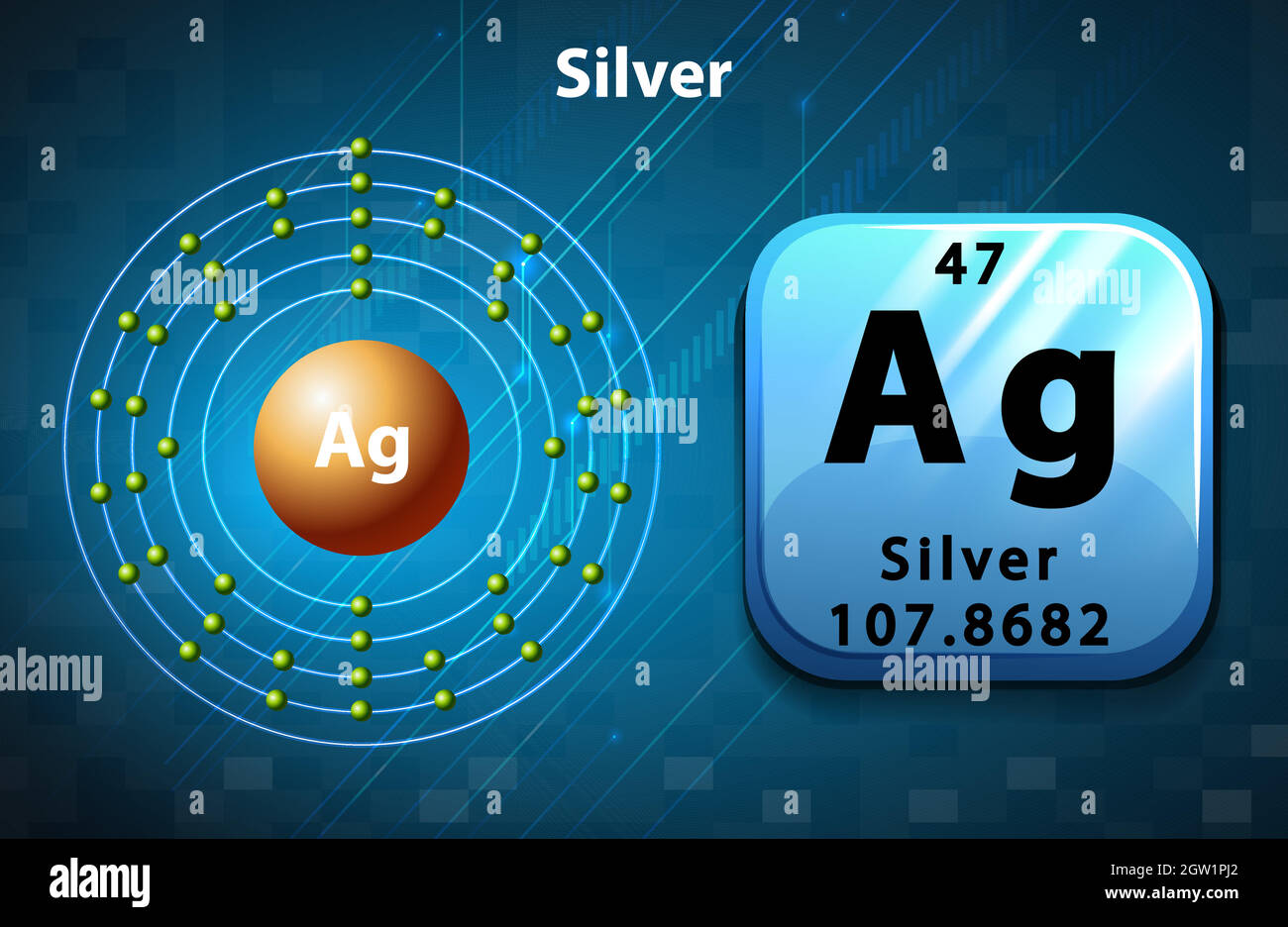
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
47
47
1
47
what do Valence Electrons Determine?
The chemical reactivity and bonding behavior of an atom, influencing how it interacts with other elements.
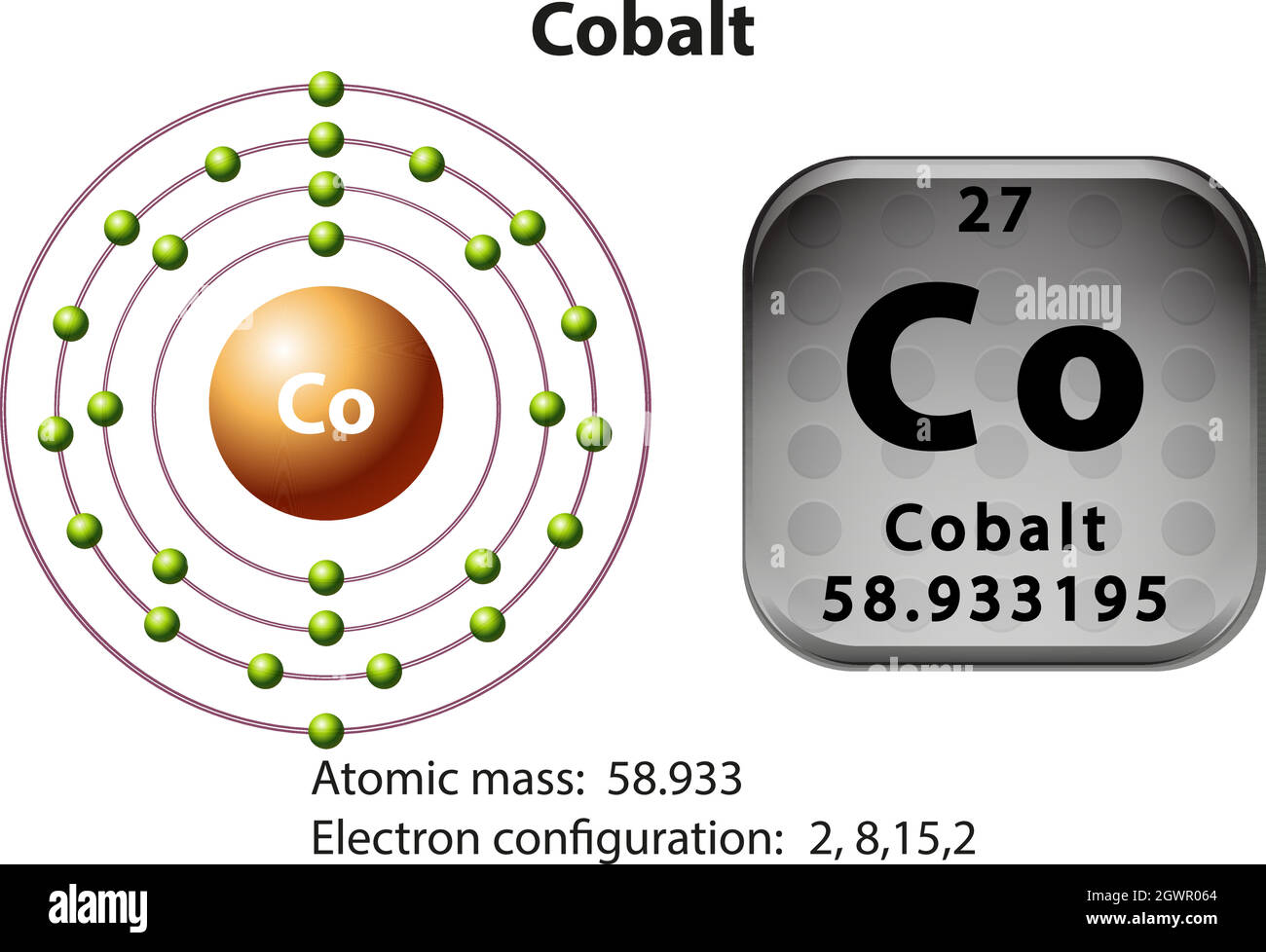
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
27
27
9
27
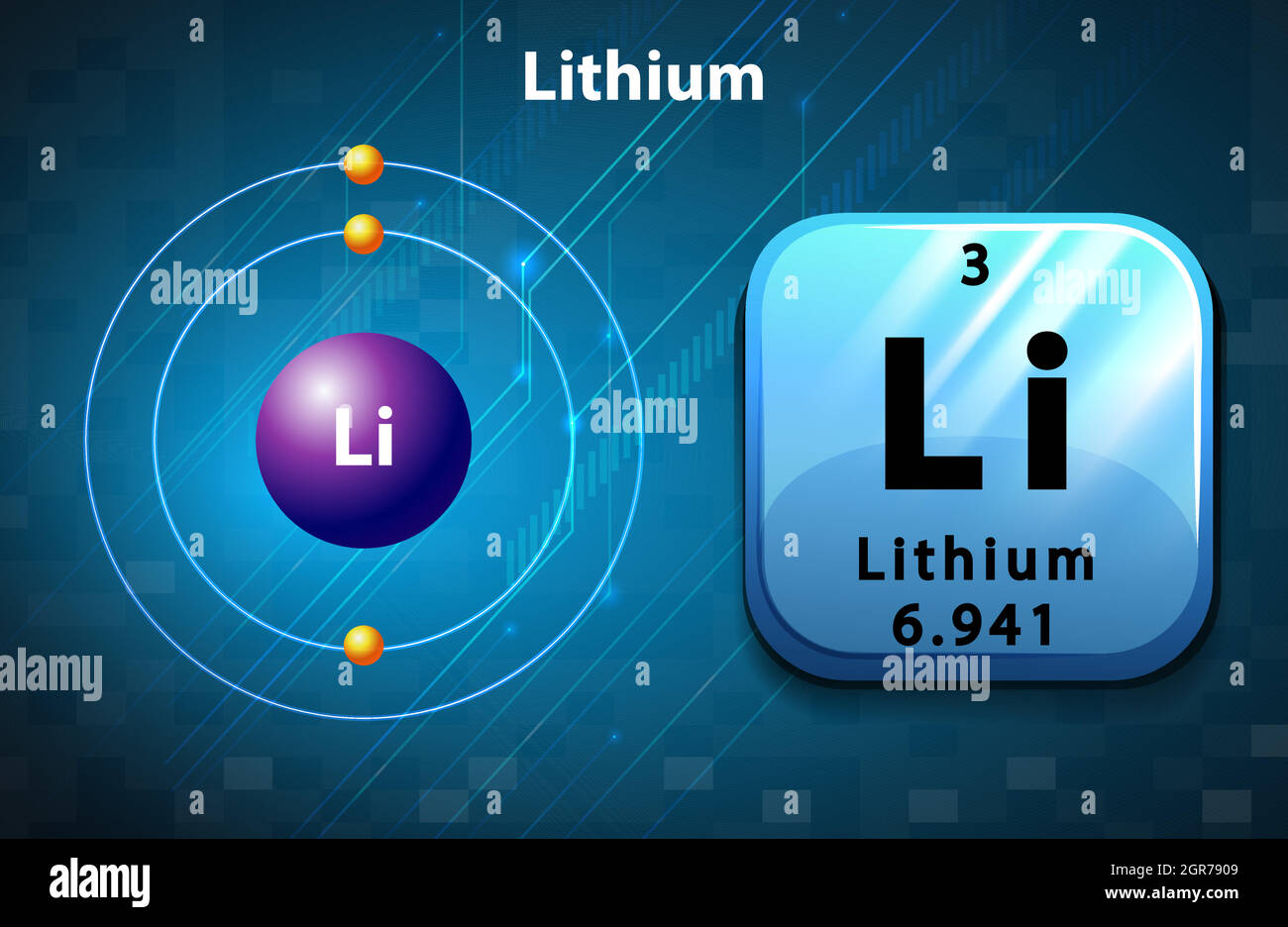
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
3
3
1
3
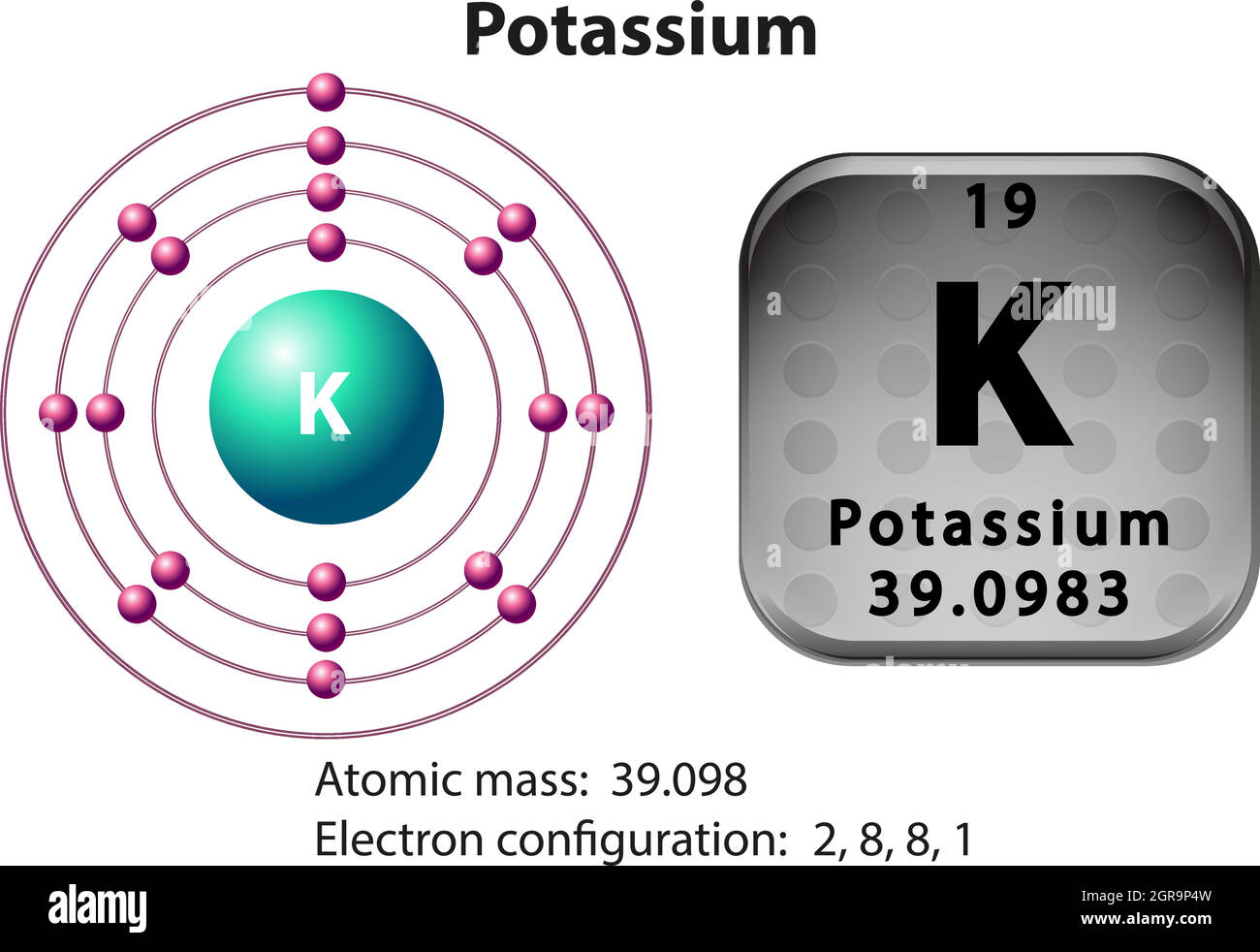
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
19
19
1
19
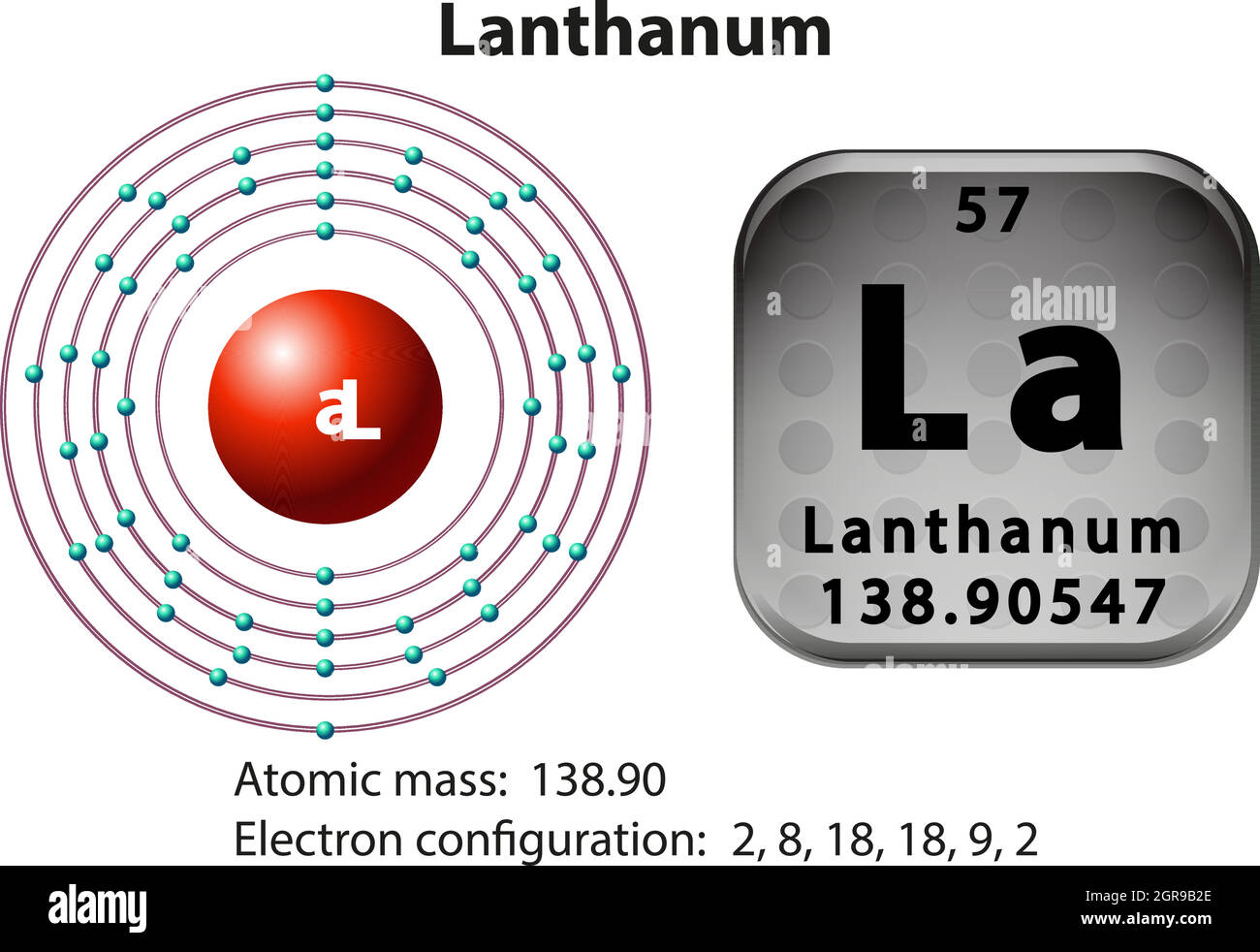
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
57
57
3 ( in group 3)
57
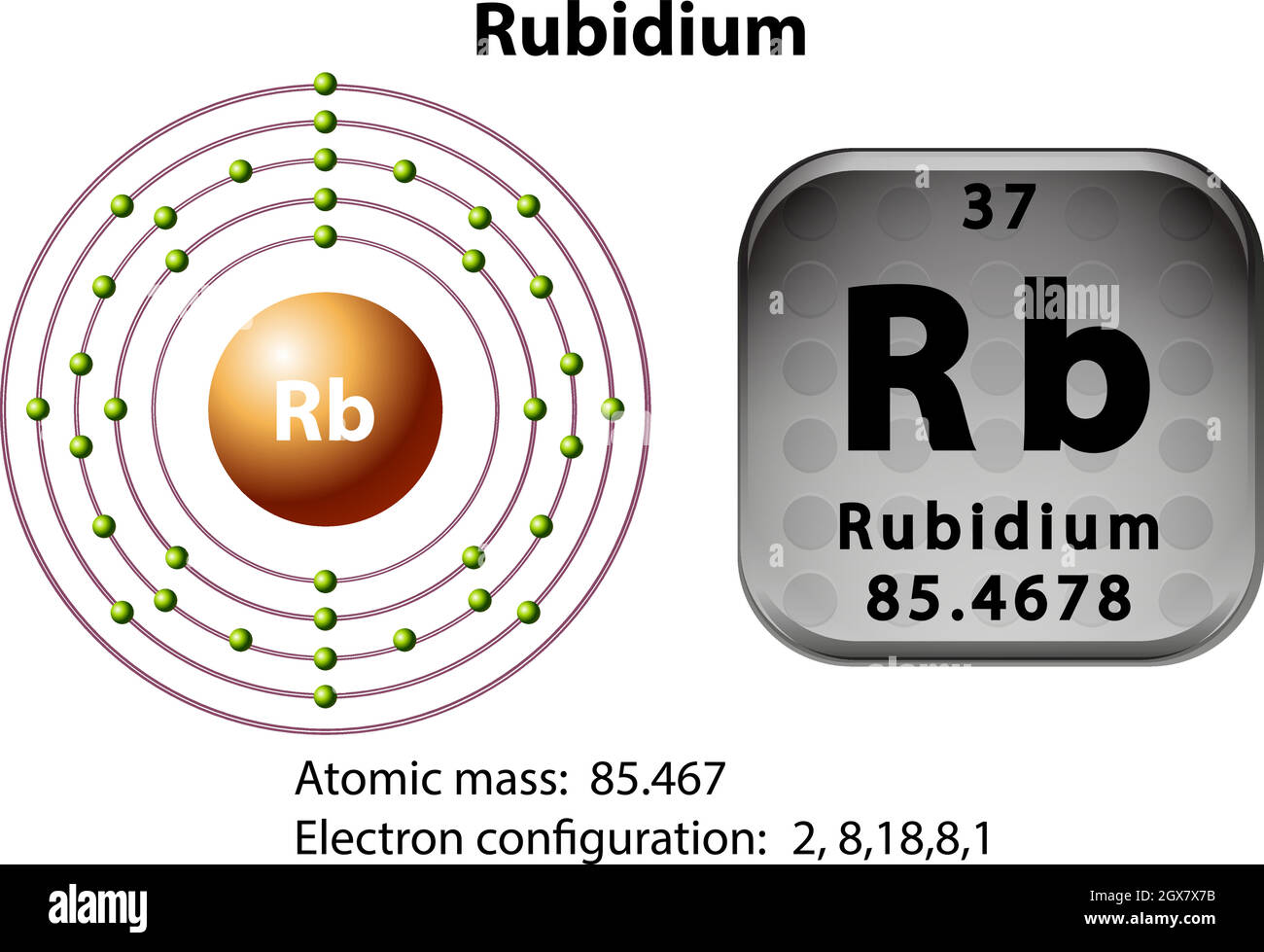
How many Protons in Nucleus?
How many Electrons?
How many Valence Electrons?
Atomic Number?
37
37
1
37
What is an isotope? and what is its result
An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons, resulting in a different atomic mass.
Name
#of neutrons in the isotope
Rb-87
Rubidium
50
13 more neutrons than a normal atom of Rubidium
Name
#of neutrons in the isotope
Zr-60
Zirconium
60-40=20 neutrons
Name
#of neutrons in the isotope
Pt-106
Platnium
106-78=28 neutrons
Name
#of neutrons in the isotope
Co- 93
Cobalt
93-27=66 neutrons