Session 10: Antibiotic Stewardship
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Antibiotic resistance
Resistance evolving rapidly in many species of prokaryotes due to overuse of antibiotics, especially in agriculture.
Resistance to antibiotics
Antimicrobial resistance
The ability of bacteria, viruses, and other microbes to resist the effect of drugs
Resistance to antimicrobials (antivirals, antifungals, antiparasitics, as well as antibiotics)
WHO list of urgently needed antibiotics
List of 12 priority pathogens that pose the greatest threat to human health.
This was created to help guide research/development of new antibiotics to address global resistance which is developing.

Antibiotic stewardship
The optimal selection, dosage and duration of antimicrobial treatment that results in...
- The best clinical outcome for treatment/prevention of infection
- Minimal toxicity to patient
- Minimal impact on subsequent resistance
Goals of stewardship
1) Health practitioners help each patient receive most appropriate antimicrobial with correct dose & duration
2) Prevent the overuse, misuse and abuse of antimicrobials
3) Minimize development of resistance. At the individual patient level and community level - the use of antibiotics changes susceptibility patterns.
Your task in antibiotic stewardship
1) Treat antibiotics responsibly
2) Follow guidelines
3) Update knowledge continuously
4) Educate patients/colleagues
General guidelines of antibiotic stewardship
- Prescribe antibiotics when needed
- If systematically unwell with symptoms/signs of serious disease, give antibiotics (always consider sepsis)
- Use simple generic antibiotics & avoid broad-spectrum
- Check guidelines
- Seek microbiology advice if uncertain
- Limit over-the-phone prescribing
What should you consider when communicating with patients about antibiotics
- Explain decision to patients
- Cause of condition & severity
- Why prescribing an antimicrobial may not be the best idea
- Alternative options to antibiotics
- Consider ICE
Sources for guidelines on antibiotic stewardship
- NICE CKS = Clinical Knowledge Summaries
- BNF = British National Formulary
- Local guidelines
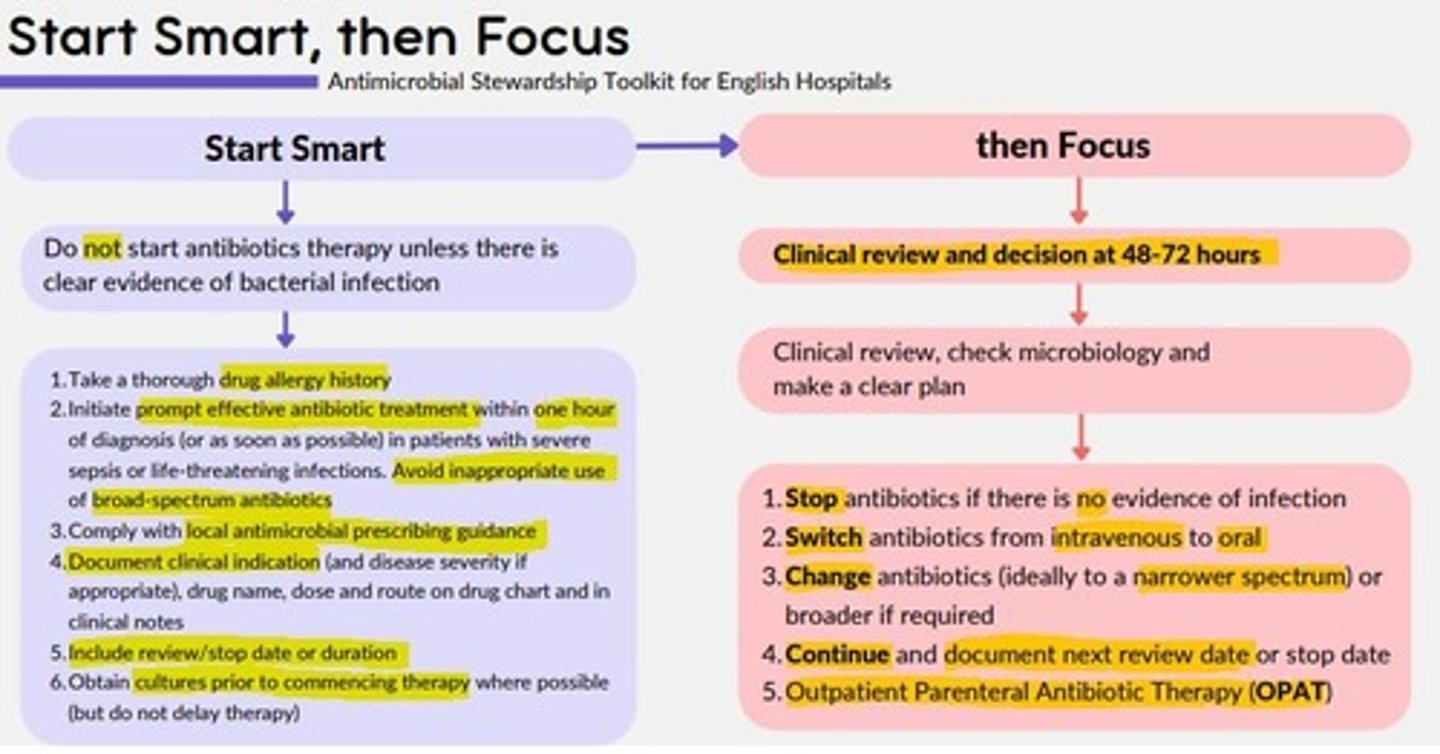
Start Smart, Then Focus
Antimicrobial Stewardship Toolkit for English Hospitals
The UK's five-year national action plan (2019-2024) for tackling antimicrobial resistance
1) Lower burden of infection = treatment of resistant infection & minimize transmission in communities, NHS, farms, environment & other settings
2) Optimal use of antimicrobials = good stewardship across all sectors, including access to safe and effective medicines that have been manufactured responsibly for all that need them, achieving usage levels, by sector as good as the best countries in the world where comparable data is available
3) New diagnostics, therapies, vaccines and interventions in use and full antimicrobial resistance and development pipeline for antimicrobials, alternative, diagnostics, vaccines and infection prevention across all sectors
AWaRe index
ACCESS
First and second choice antibiotics for treating the most common infections
e.g., Amoxicillin for Pneumonia
WATCH
Antibiotics with higher resistance potential that should only be prescribed in specific indications
e.g., Ciprofloxacin for complicated UTIs
RESERVE
Antibiotics that are last-resort options should only be used in severe circumstances, when other options have failed
e.g., Colistin and IV parenteral Fosfomycin

What is the primary recommendation for prescribing antibiotics in primary care?
Prescribe antibiotics only if there is a CLEAR clinical benefit
Which of the following is not recommended to reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance?
Prescribing antibiotics for self-limiting mild infections
What is the purpose of obtaining cultures in the context of antimicrobial stewardship?
To narrow down broad-spectrum therapy
Which is the best reason for avoiding the widespread use of topical antibiotics in primary care?
They increase the risk of Clostridium difficile infection