35. Diseases of the elbow joint. Elbow dysplasia. Screening ED. Short radius and short ulna. Aetiology, symptoms and therapy.
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What type of joint is the elbow?
Complex hinge joint (flexion and extension in the sagittal plane)
Describe the anatomy of the humerus regarding the elbow.
Distal (lower) end of humerus forms part of elbow joint.
Condyle of humerus consists of medial & lateral epicondyles.
Trochlea articulates with ulna, & capitulum articulates with radius.
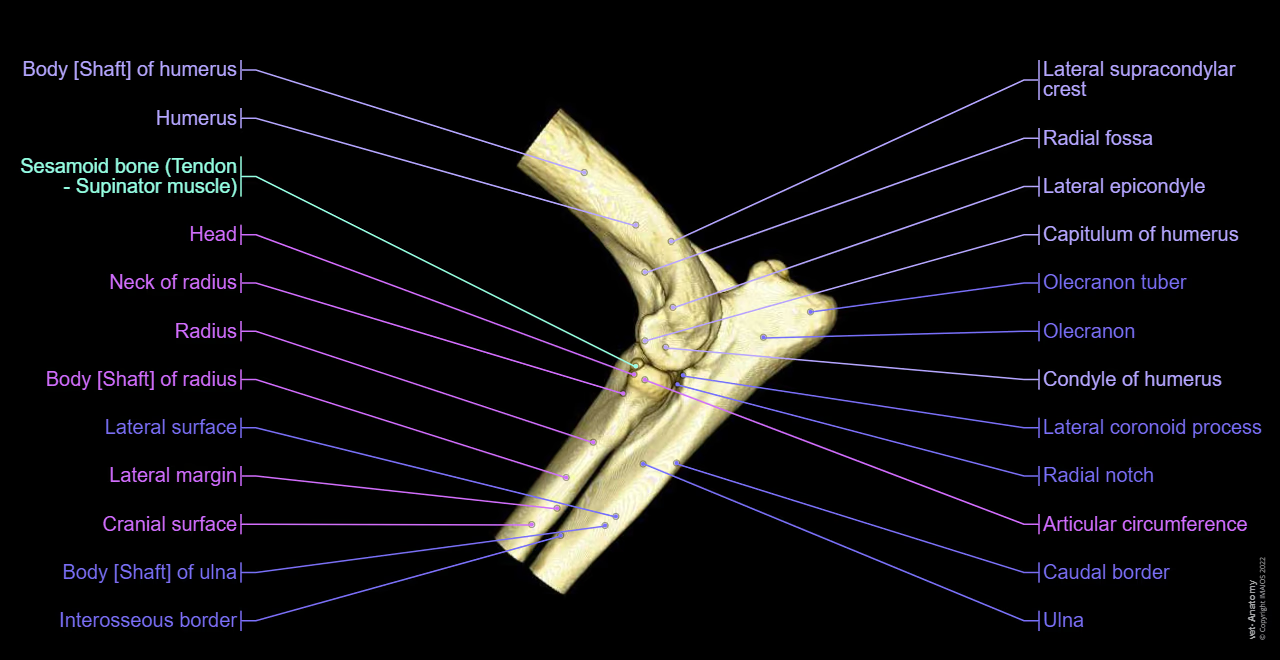
Which part of the ulna articulates with the humerus?
Proximal end articulates with humeral capitulum
Which bone provides structural support to the elbow?
Ulna
What are the important structures of the ulna for the elbow?
Olecranon process
Trochlear notch
Which process of the ulna forms the point of the elbow?
Olecranon process. Attachment site for muscles e.g. triceps brachii
Why is the trochlear notch of the ulna important?
Articulates with humeral trochlea
What is the joint capsule of the elbow?
Surrounds elbow joint, providing stability & containing synovial fluid for lubrication
Which ligaments are associated with the elbow?
Medial collateral ligament
Lateral collateral ligament
Annular ligament
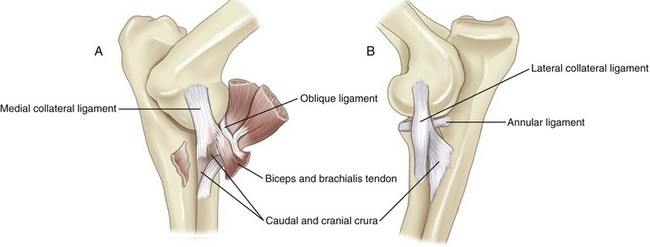
What is the function and attachment of the medial collateral ligament?
Stabilises medial side of the joint
Attached proximally to medial humeral epicondyle and inserts with two parts of the radius and ulna
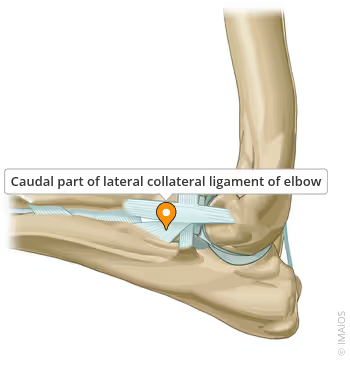
What is the function and attachment of the lateral collateral ligament?
Stabilises lateral side.
Attached proximally to lateral humeral epicondyle & distally it divides into cranial (insert on radius) & caudal (insert on ulna)
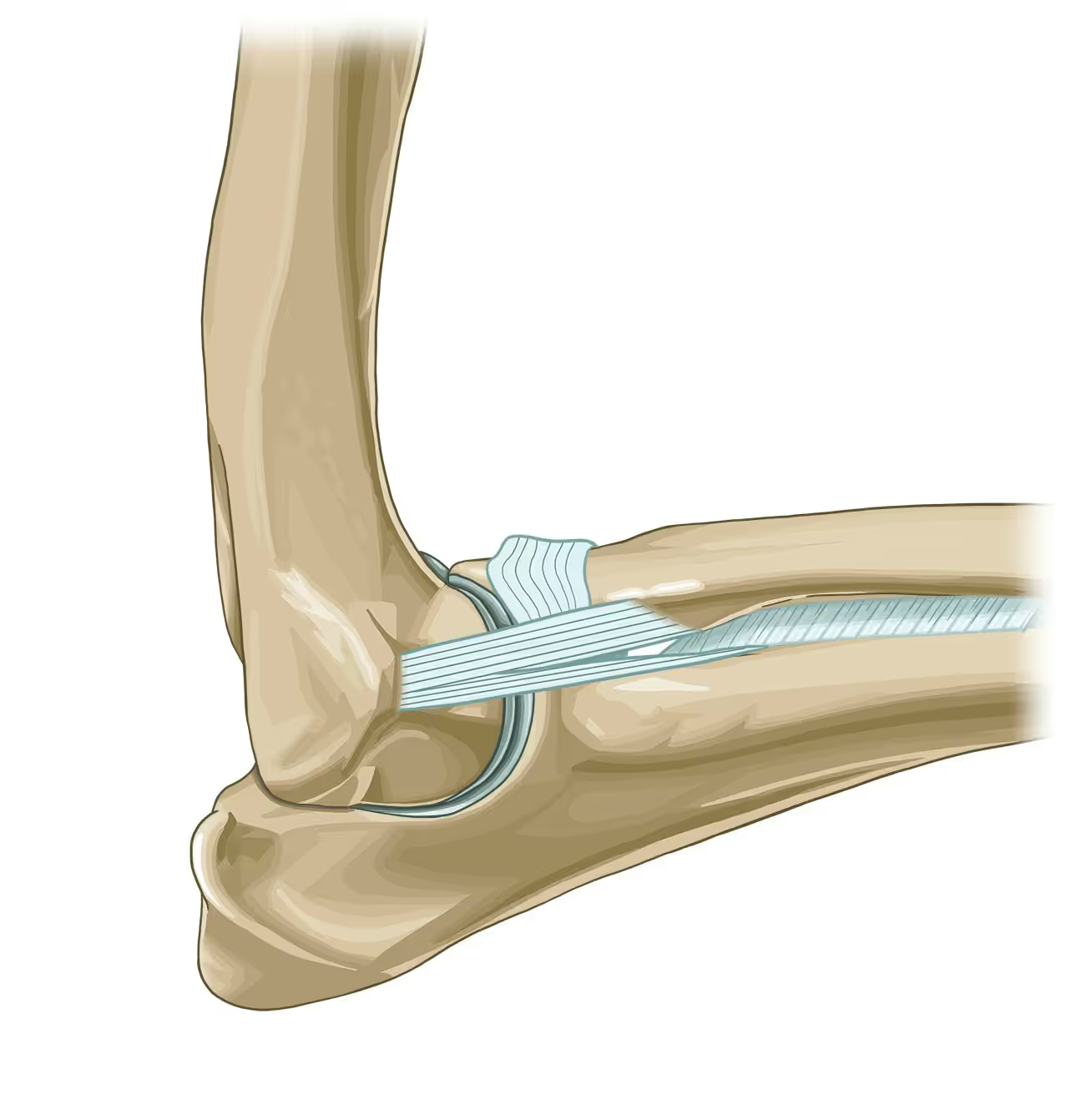
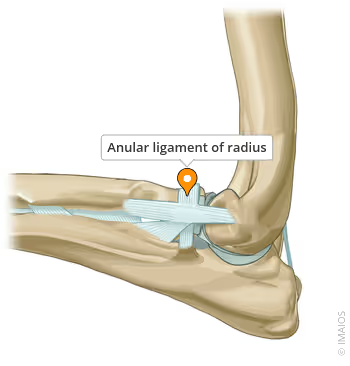
What is the function of the annular ligament of the elbow?
Supports radial head & holds it in place against ulna
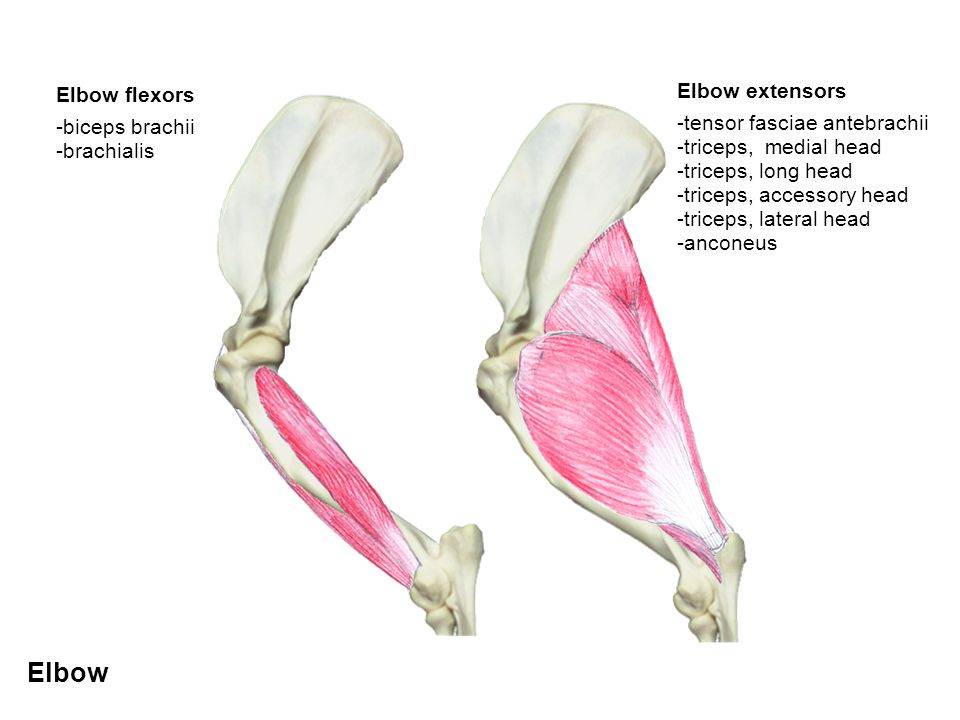
Which muscles are associated with the elbow joint?
m. triceps brachii (responsible for elbow extension)
m. biceps brachii & m. brachialis (responsible for flexion)
What are examples of elbow diseases?
Traumatic luxation
Congenital luxation
Short radius/ulna
Elbow dysplasia
Why are most elbow luxations lateral?
The medial epicondyle prevents medial movement of the ulna. When medial subluxation occurs, it is accompanied by severe ligamentous damage
What occurs in lateral elbow luxation?
The rounded shape of lateral epicondyle permits the anconeal process to clear the lateral epicondylar crest when elbow is flexed more than 90 degrees
How is an elbow luxation diagnosed?
History, clinical signs, X-ray (cranio-caudal, latero-medial)
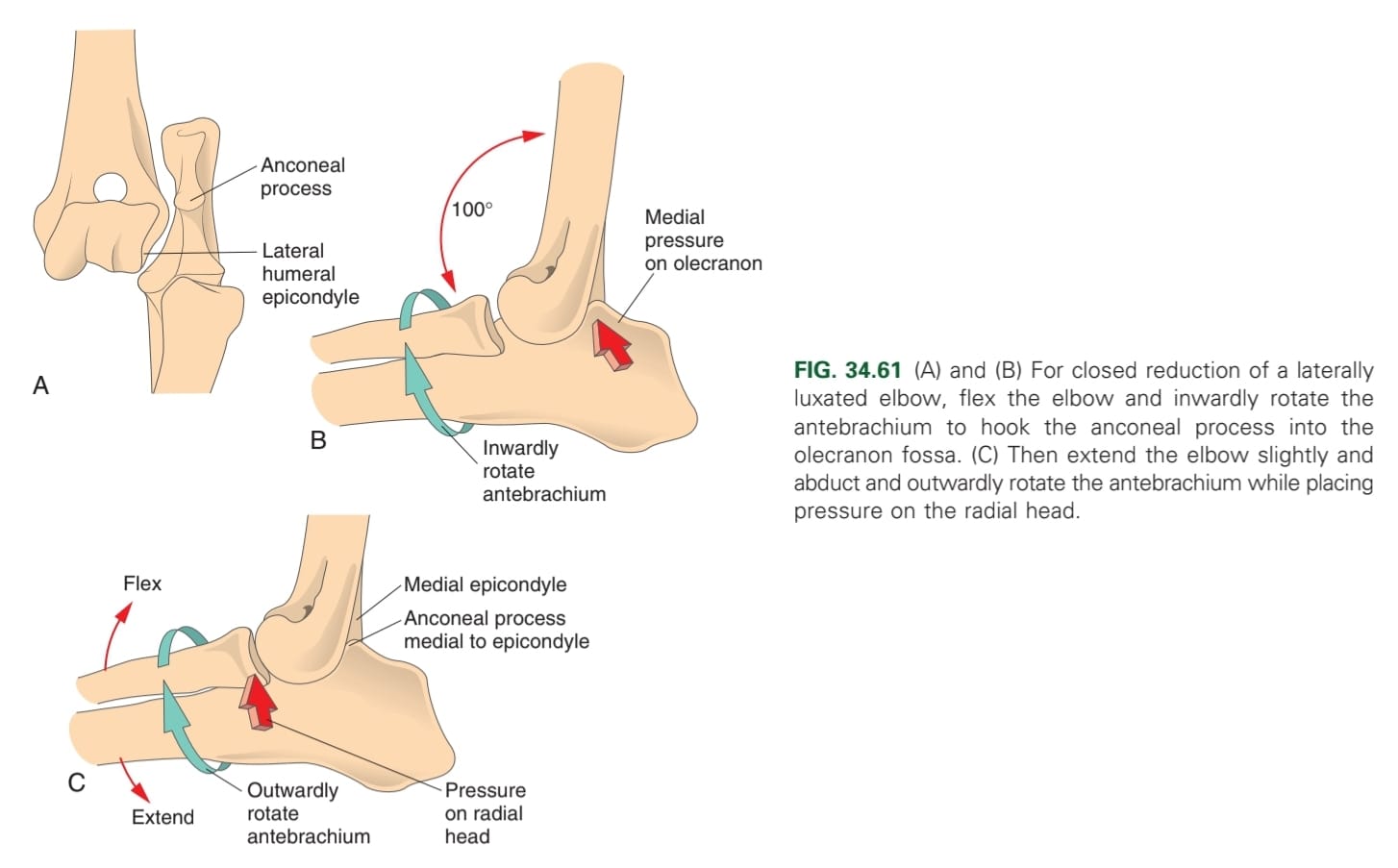
How is closed reduction of the elbow carried out?
Animal under general anaesthesia, & firm palpation is used to position humeral condyles relative to radius & ulna.
Pressure of reduction is based on position of anconeal process, medial to lateral epicondylar crest (medial pressure on olecranon while flexion), lateral to lateral epicondyle (flexion, antebrachium twisted inward, extend joint & flex while medial pressure on radial head)
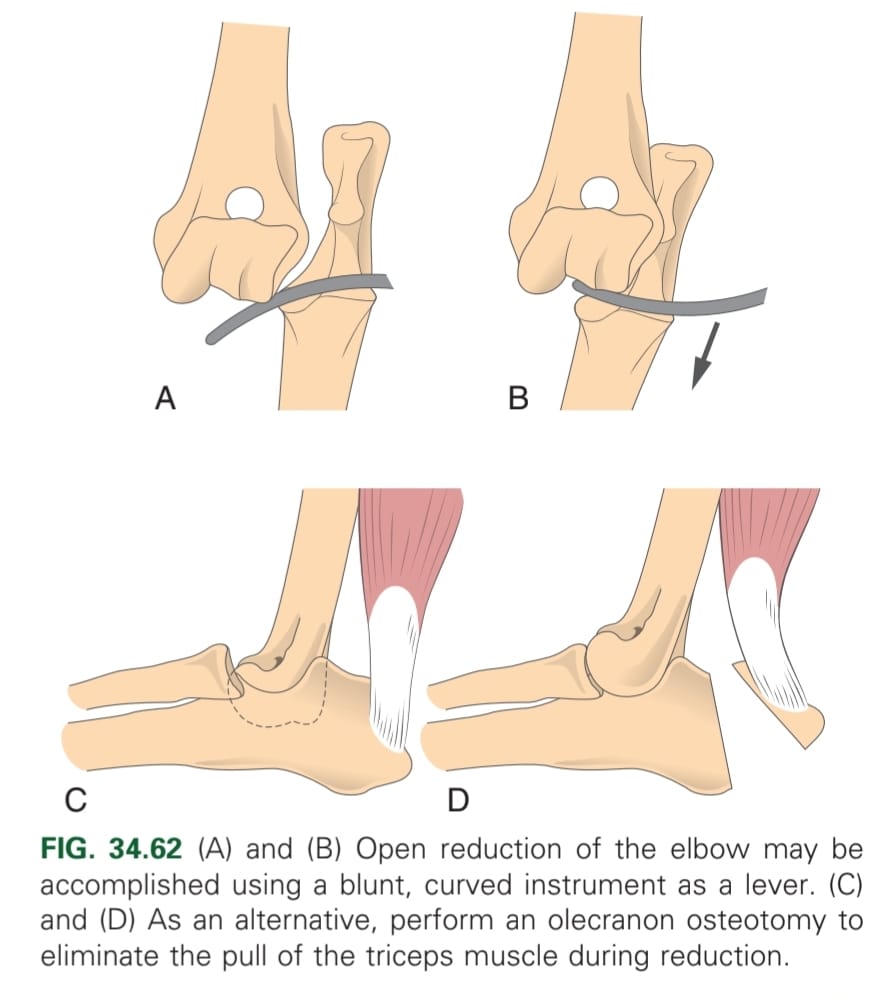
How is open reduction of the elbow joint carried out?
Incise & reduce, & flush joint afterwards. NB: check stability.
Which other surgical procedures can be carried out for a elbow luxation?
Arthrodesis and arthrotomy
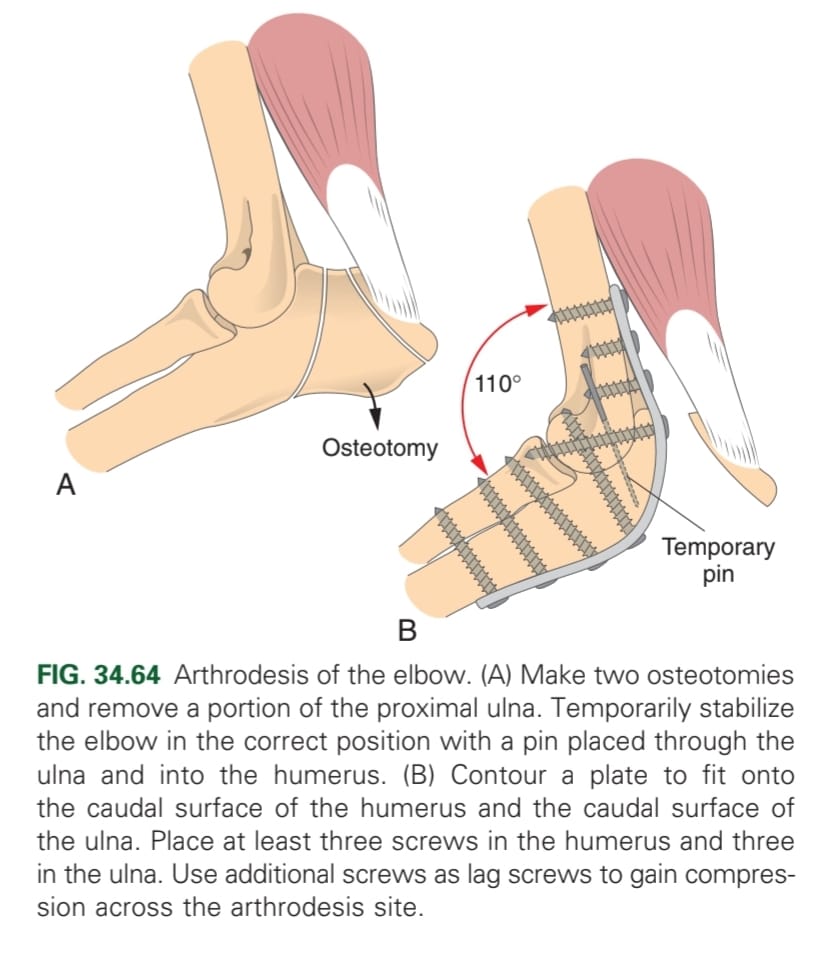
What should be checked during elbow luxation surgery?
Collateral ligaments
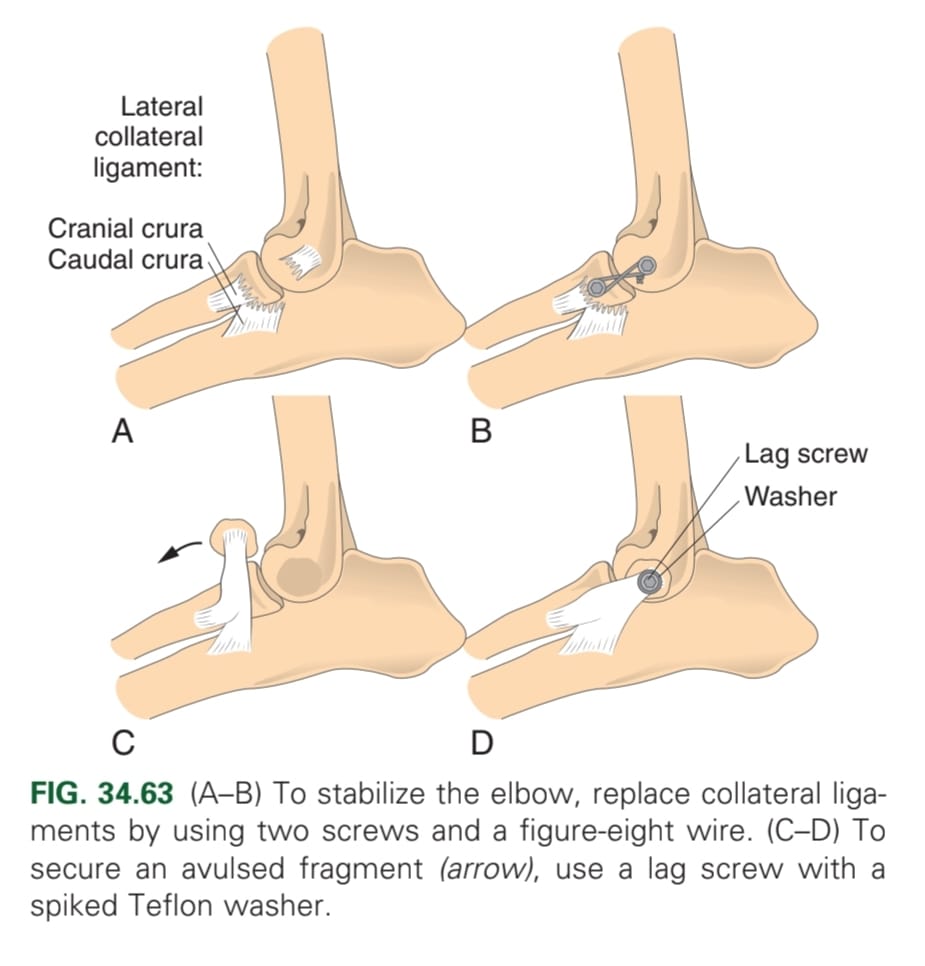
What are the three types of congenital elbow luxation?
Type 1 (radial head)
Type 2 (humeroulnar)
Type 3 (both radius and ulna)
What are the clinical signs of congenital elbow luxation?
2-4 months old. Lameness, elbow swelling, carpal valgus, elbow varus, crepitus
How is congenital elbow luxation diagnosed?
Physical exam (deformities, crepitus)
X-ray (subluxated radial head is more lateral than normal, ulna may be bowed)
What are the treatment options for congenital elbow luxation?
Closed reduction, surgical osteotomy (shortening of radius, should be done early in life, stabilise radial head w/ pins or plate)
What are the causes of short radius/short ulna?
Growth failure, premature physis closure, hereditary, osteochondrosis, trauma to physis (Salter-Harris), overnutrition in large breeds
What are the clinical signs of short radius/short ulna?
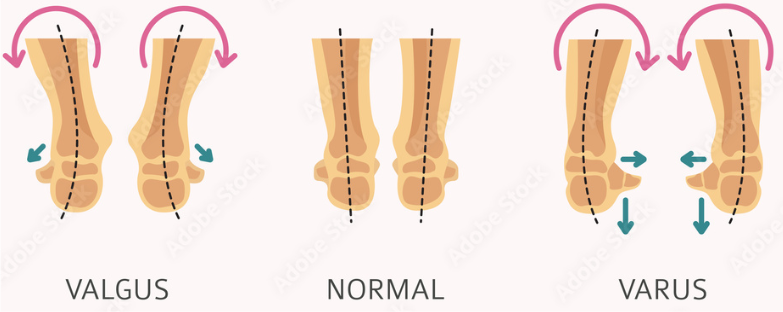
Lameness, synovial effusion, limb rotation (valgus/varus)
Short radius: Varus Leg: rotated outwards
Short ulna: Valgus Leg: rotation inwards (most common) → Causes radius to bend as it continues to grow
What are the treatment options for short ulna?
Transverse or short oblique osteotomy of proximal ulna and pin placement
Short oblique osteotomy of distal third of the ulna
Biplanar long oblique osteotomy of ulna
What are the treatment options of short radius?
Biplanar long oblique osteotomy
Bone plating with bone grafts to lengthen radius
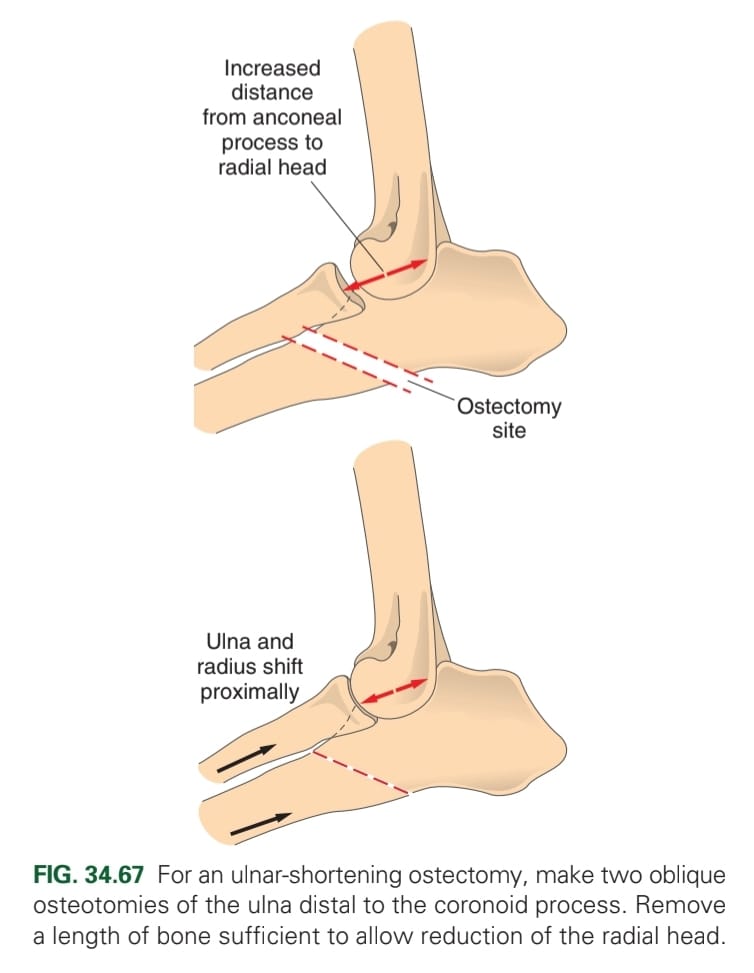
What are the developmental conditions that cause elbow dysplasia?
Ununited anconeal process (UAP)
Fragmented medial coronoid process (FCP)
Osteochondrosis dissecans (OCD)
Elbow incongruity
How does FCP occur?
Unequal growth rates of radius and ulna → uneven pressure of medial coronoid process → cracks or fragments of coronoid process → pain during movement and arthritis
What does FCP often occur with?
OCD of humeral condyle
What are the clinical signs of FCP?
Mostly bilateral. Pain on flexion/extension and lateral rotation, joint effusion, crepitus
How is FCP diagnosed?
Radiologically: Osteophytes on anconeal process. Surgical exploration may reveal FCP
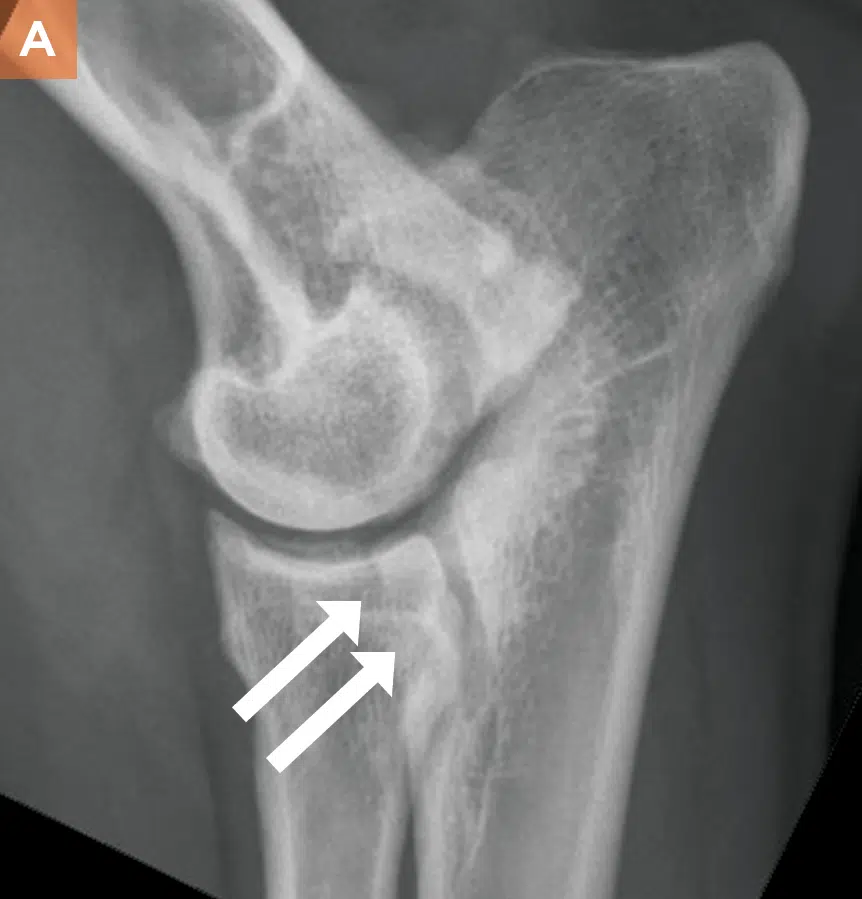
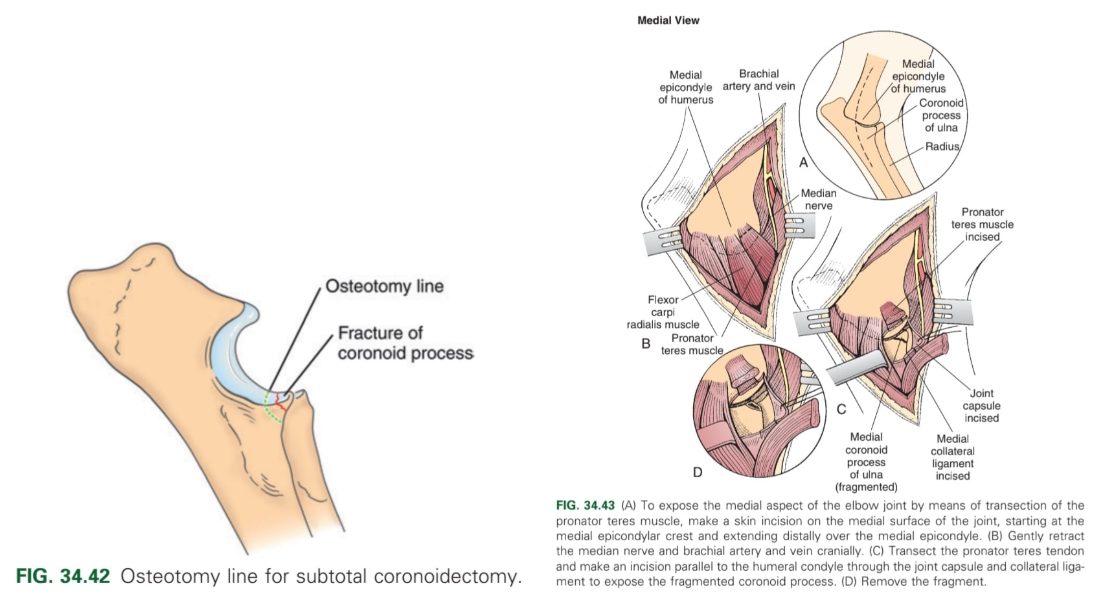
What is the treatment for FCP?
Arthroscopy: subtotal osteotomy of medial condyle (MCP microfracturing (to allow blood flow to the area) → fibrocartilage fills the area over time. Need tenotomy of biceps tendon and pronator teres muscle via incision of medial collateral ligament to improve view).
Arthrotomy: total osteotomy of medial condyle of humerus → remove coronoid fragment from the ulna → lag screw insertion
What is OCD of the elbow?
OCD affects the medial condyle of the humerus, sometimes bilaterally → avascular necrosis → fragmentation of bone and cartilage → lameness, arthritis
What are the clinical signs of OCD of the elbow?
Foreleg lameness or stiffness & stilted gait between ages of 5-8 months. Lameness is often exercise induced. Joint swelling, may be valgus of carpus on standing, Crepitus often present in dogs older than 1 year. Pain on hyperflexion/extension
How is OCD of the elbow diagnosed?
Radiologically: Triangular subchondral defect can be seen on medial aspect of humeral trochlea in craniocaudal projection. Sclerosis of medial condyle.
Surgical exploration of joint (arthroscopy) confirms definitive diagnosis when a flap is present.
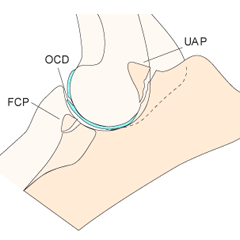
What is ununited anconeal process?
Failure of the ossification centre of the anconeus to fuse with the olecranon by 5 months
How does UAP lead to elbow dysplasia?
UAP → instability → articular cartilage damage → lameness, arthritis
How is UAP diagnosed?
Radiography: In young dogs there is a thin, linear radiolucent (black) space between the anconeal process and the rest of the olecranon. In older dogs the anconeal process is often completely detached
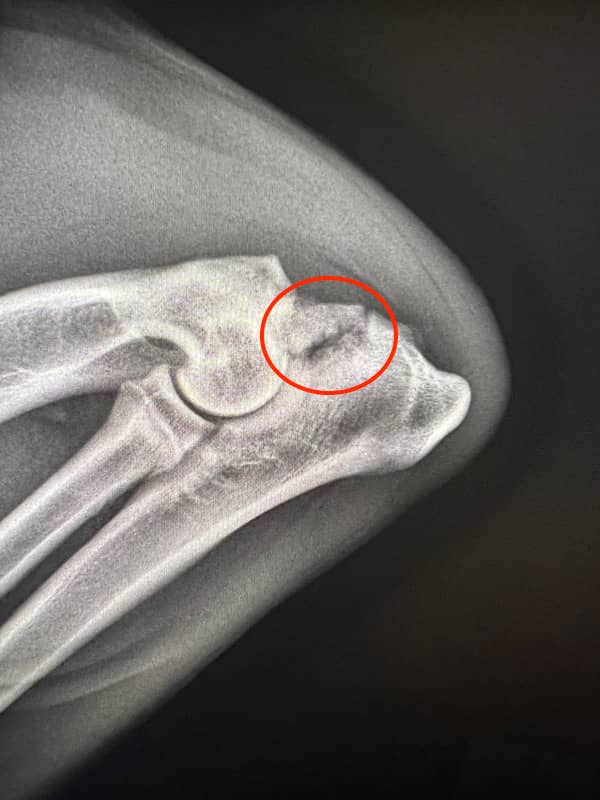
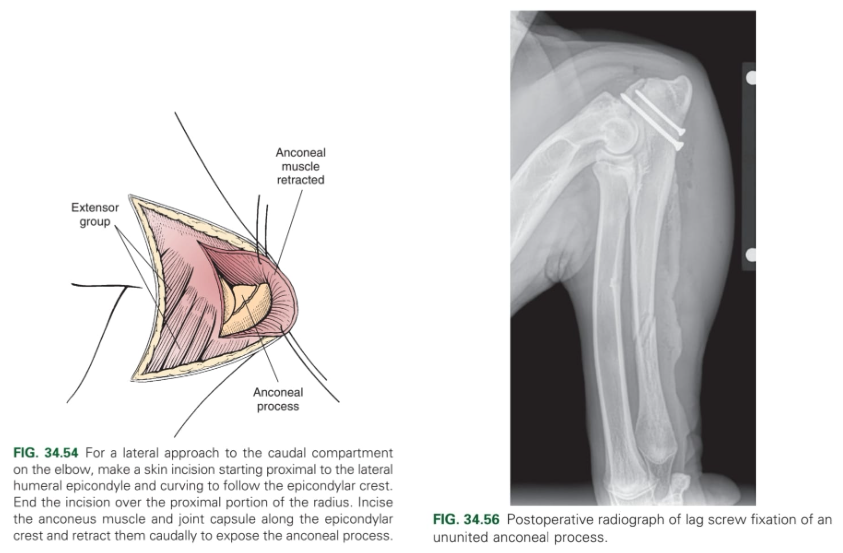
What are the treatment options for UAP?
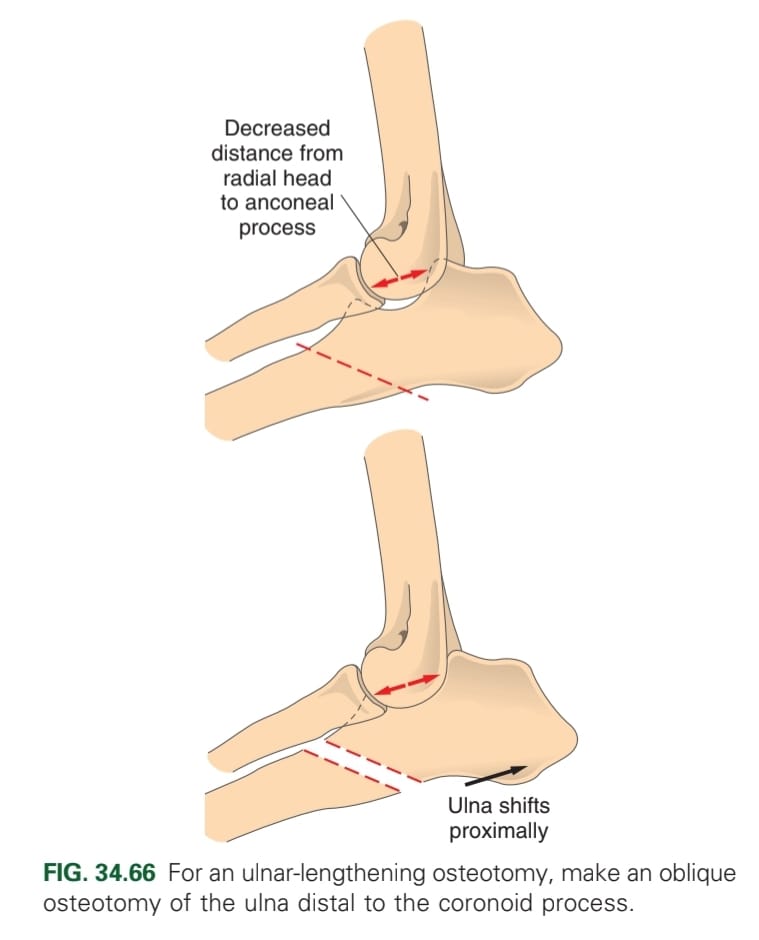
Surgical excision of anconeal process → screw fixation (lag screw)
Ulna osteotomy (lengthening osteotomy of the proximal ulna to reduce pressure of the anconeal process).
What is elbow incongruity?
Most commonly radioulnar incongruity. Elevation of the coronoid above the level of the radial head
What are the clinical signs of elbow incongruity?
Limb rotation, lameness, pain, synovial effusion, joint swelling
How is elbow incongruity diagnosed?
X rays in standard views will see osteophytes formation; evaluated in mm: the disproportion between the size of the trochlear notch of the ulna, the condyles of the humerus, and the fossa olecrani (increased radioulnar joint space seen as radiolucent area)
What are the treatment options for elbow incongruity?
Conservative: Chondroprotectives, NSAIDs
Surgery (anconeal process removal/reattachment, coronoidectomy, osteotomy, biceps tendon release)
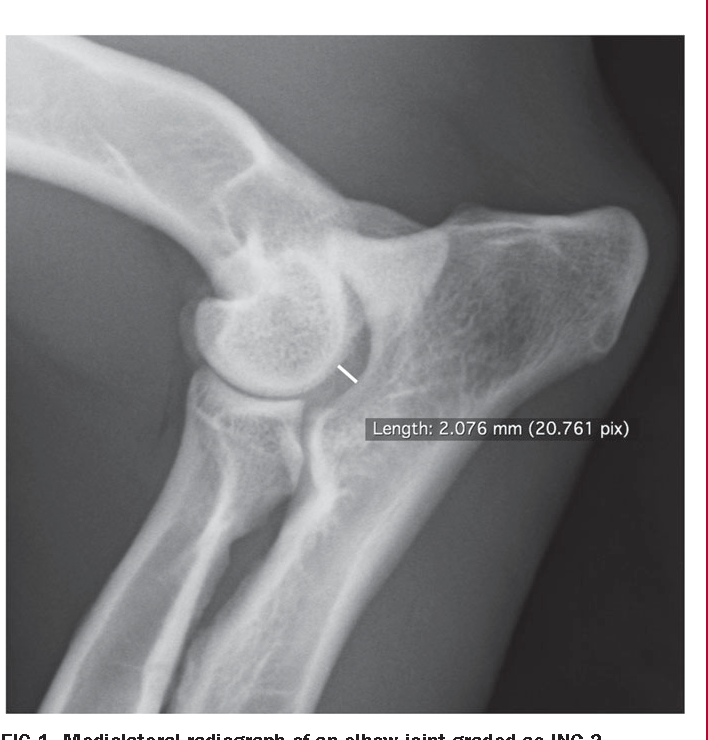
What characterises grade 0 elbow dysplasia?
Normal elbows. No osteoarthritis or primary lesions (osteophytes, OCD, UAP, FCP)
What characterises mild elbow dysplasia (grade 1)?
Osteophytes <2mm, sclerosis, with/out incongruity
What characterises moderate elbow dysplasia (grade 2)?
Osteophytes 2-5mm
What characterises severe elbow dysplasia (grade 3)?
Osteophytes >5mm, primary lesions present (UAP, FCP, OCD)