BIOL 3000 Final AUBURN
1/255
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
256 Terms
pangenesis
particles carry genetic information from different parts of the body to the reproductive organs; "in my hand are tiny versions of my hand"
epigenesis
somatic cells vs. gametes; only the information in the egg/sperm is passed on to the next generation
preformationism
genetic information is passed down from mother OR father only
germ-plasm theory
cells in the reproductive organs carry a complete set of genetic information
transmission genetics
encompasses basic principles of heredity and how traits are passed down from one generation to the next
molecular genetics
chemical nature of the gene itself; how genetic information is encoded, replicated, and expressed
population genetics
genetic makeup and dynamics over space and time (i.e. evolution) of entire populations
cytogenetics
chromosomal biology, including structure, function, variability, and disease
genomics
content, organization, structure, and function of entire genomes
interphase
extended period of growth and development between cell division
G1
cell grows and proteins are synthesized
S phase
where DNA is replicated
G2
more cell growth and additional biochemical events
M phase
cell undergoes division; cell's chromosomes separate and divide (mitosis)
haploid number
single set of chromosomes (reproductive cells)
diploid number
two sets of genetic information (body cells)
prophase
chromosomes condense and become visable; each chromosome has 2 chromatids; spindle forms
prometaphase
nuclear membrane disintegrates; spindle enters nuclear region; microtubule from one of the centrosomes anchors to the kinetochore of the sister chromatids
metaphase
chromosomes are aligned in the middle
anaphase
connection between sister chromatids breaks down and sister chromatids move toward opposite spindle poles
telophase and cytokinesis
chromosomes arrive at spindle poles, nuclear membrane reforms and cytoplasm divides
prophase I
chromosomes form homologous pairs; crossing over takes place; chromosomes condense; nuclear membrane breaks down and spindle forms
metaphase I
homologous pairs of chromosomes align along metaphase plate
anaphase I
separation of homologous chromosomes
telophase I
chromosomes arrive at spindle poles and cytoplasm divides
prophase II
chromosomes recondense; spindle reforms; nuclear envelope breaks down
metaphase II
individual chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate
anaphase II
kinetochores of sister chromatids separate, and chromatids are pulled to opposite poles
telophase II
chromosomes arrive at poles; nuclear envelope reforms; cytoplasm divides
crossing over
homologous chromosomes exchange genetic information
chiasmata
points where crossing over is occurring
recombination
creating new combinations of alleles on a chromatid
genotype
set of alleles that an organism possesses
phenotype
manifestation or appearance of a characteristic
heterozygote
two different alleles
homozygote
two identical alleles
alleles
different versions of a gene
gene
inherited factor that determines a characteristic
locus
specific place on a chromosome where particular gene and alleles are found
Mendel's "recipe for success"
-made sure he could clearly identify different 'forms' among the progeny.
-counted each generation separately to correctly deduce ratios and allow for backcross.
-did large number of crosses and also reciprocal crosses.
-used summary statistics to compare observed vs. expected ratios.
the principle of segregation (Mendel's 1st law)
During gametogenesis, pairs of alleles separate (segregate). Each gamete receives one or the other randomly. There is an equal chance that the copy from the individual's mother or father is present in a gamete. -- happens in anaphase I
the principle of independent assortment (Mendel's 2nd law)
alleles at separate loci segregate independently from one another -- alleles at different loci combine randomly in gametes -- metaphase 1?
assuming no recombination has occurred, what stage of meiosis explains the principle of segregation?
anaphase I
assuming no recombination has occurred, what stage of meiosis explains the law of independent assortment?
metaphase I
Mendel's big six
-AA x AA = all AA
-aa x aa = all aa
-AA x aa = all Aa
-Aa x Aa = 1AA : 2Aa : 1aa
-Aa x aa = 1Aa : 1aa
-AA x Aa = 1AA : 1Aa
dihybrid F1 phenotype (Aa x Aa)
3:1
double homozygote phenotype
all same
dihybrid dominant backcross phenotype (Aa x AA)
all show dominant trait
dihybrid recessive backcross phenotype (Aa X aa)
1:1
addition rule
the probability of two or more mutually exclusive events is calculated by adding the probability of these events
*add within a cross
multiplication rule
the probability of two or more independent events is equal to the product of their individual probabilities
*multiply between crosses
backcross
cross between an F1 individual and one of the parental; used for determining dominance
testcross
cross between an individual with an unknown genotype and an individual with a homozygous recessive gene; used for determining an unknown genotype
reciprocal crosses
pair of crosses which the phenotypes of the male and female parents are reversed
chi-squared & degree of freedom equations
- X^2 = ∑(observed-expected)2/expected
-df = n-1
complete dominance
one trait is completely dominant over the other and normal mendelian ratios are observed
incomplete dominance
heterozygote is a mix of both traits (1:2:1 ratio)
co-dominance
heterozygote expresses both traits fully and simultaneously (1:2:1 ratio)
pleiotropy
multiple phenotypic effects resulting from a single gene
penetrance
the proportion of genotypes that actually express the diseased phenotype
expressivity
individuals with the same genotype show different degrees of the same phenotype
dominant lethal vs. recessive lethal
dominant lethal can only last one generation; recessive lethals can be carried and you must have two recessive alleles
semi-lethal
an allele whose expression makes death more probable
semi-sterile
an allele whose expression makes reproduction less probable
conditional lethal
lethal alleles whose expression is dependent on environmental conditions
delayed expression
the expression of a trait is not expressed until later in life; how dominant lethals can be passed on
recessive lethal heterozygous cross
2:1 (1/4 will die)
dominant lethal heterozygous cross
1 (only the homozygous recessive will live)
haplodiploidy
ploidy determines sex (i.e. bees)
dosage compensation
small X in females makes up for difference in males (X inactivation)
sex linkage
mode of inheritance resulting from loci being located on the same sex chromosome
what kind of cross would you do to test for sex linkage?
reciprocal cross
sex limited inheritance
a trait that is expressed in only one sex even though both sexes carry the alleles; found on autosome; males and females will have the same genotype, but different phenotypes
sex influenced inheritance
traits are expressed differently in males and females; found on autosome; trait has a higher percentage in one sex
epistasis
interaction between two or more loci that affect a single trait
-when an allele at one locus masks the effects of alleles at one or more loci
-when two or more loci interact to create new phenotypes
-when an allele modifies
linkage group
gene located together on the same chromosome; travel together in meiosis, are not expected to assort independently
coupling (cis) configuration
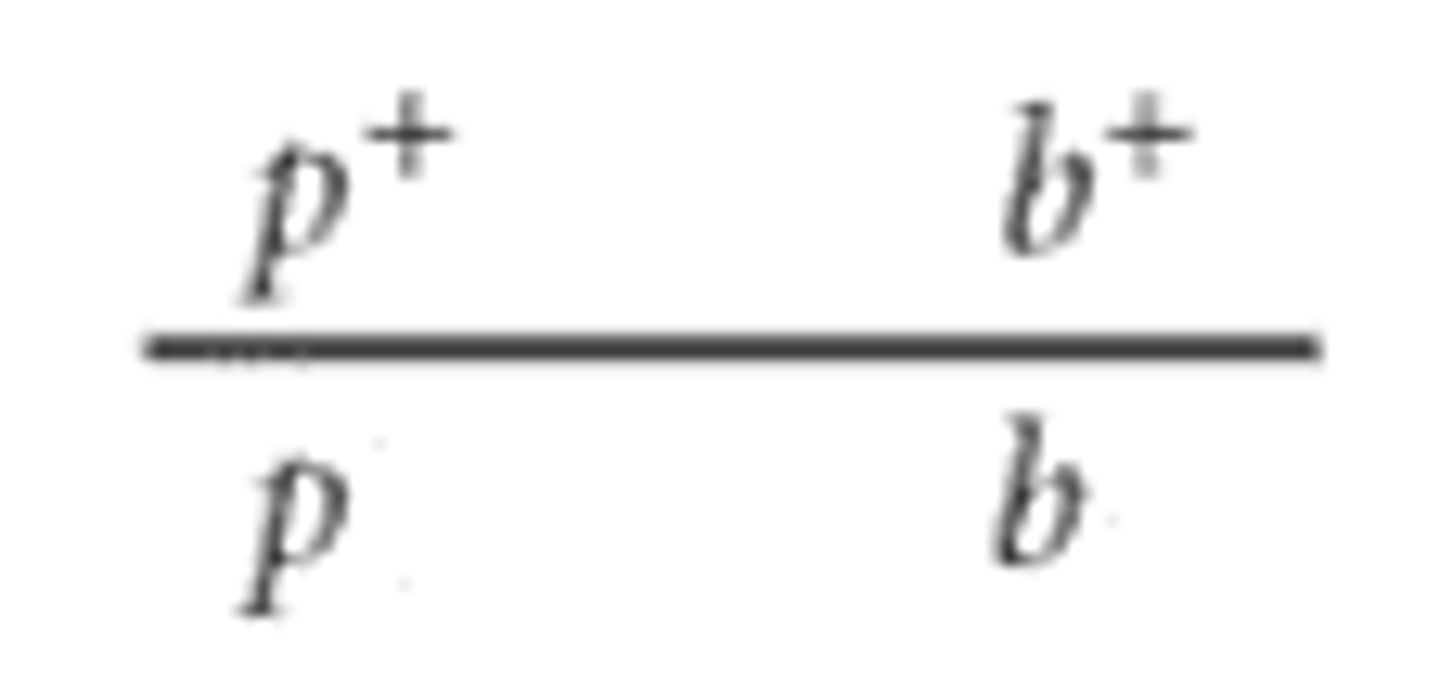
repulsion (trans) configuration
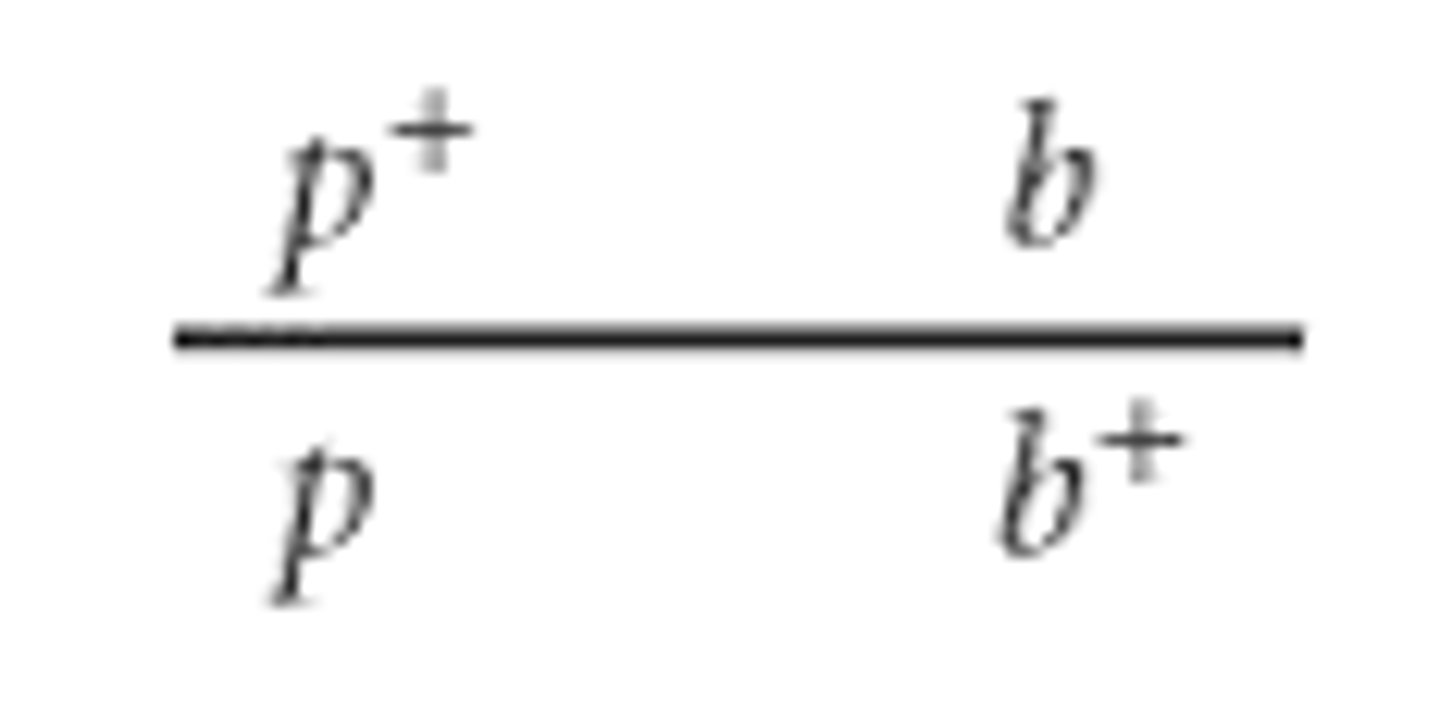
why does calculating the proportion of recombinant gametes yield information about distance?
the frequency of recombination can give us an idea about how far away they are from each other; what are the odds at this distance, they will cross over
how to calculate MU
(# of recombinants/total progeny) x 100
how do you identify your NCOs?
2 most common phenotype
how do you identify your DCOs?
2 least common phenotype
what information to you need to determine order?
compare the NCO to DCO and see which one changed, that is what is in the middle
what information do you need to determine distance
single crossover ratio + double crossover ratio
what are you going to add together, divide by, etc
to determine ratios, add the NCO/DCO/single crossovers that match and divide by the total progeny
karyotype
complete set of chromosomes possessed by an organism
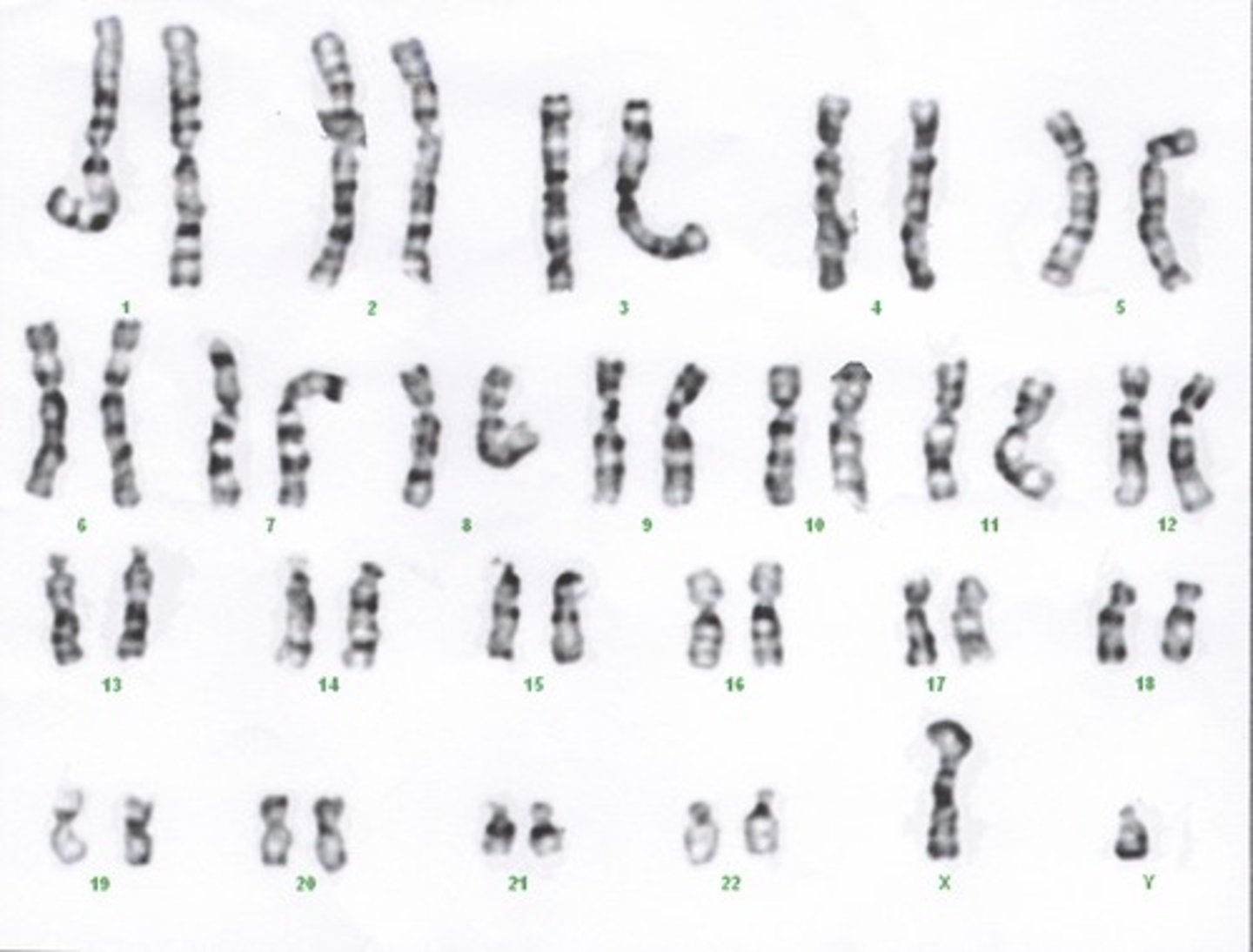
karyogram
chromosome stained and arranged for viewing -- analyze a karyogram to see if it's a karyotype
ideogram
a schematic depiction of the characters size, centromere position, and banding proteins

cytogenic location
chromosome #, p or q, region, band, subunit
euploidy
different multiples of entire sets of chromosomes
aneuploidy
an abnormal number of chromosomes, usually a gain or loss of one chromosome
monoploid (x)
number of chromosomes in a unique set
autopolyploid
duplication of the same genome; 1 ancestor
allopolyploid
duplication resulting from uniting of two different gametes at the species level or higher; more than one ancestor
cause of abnormal euploidy
-errors in fertilization
-unreduced gametes (due to nondisjunction)
-hybridization between species)
sex chromosome aneuploids
phenotypes generally result from wrong dosage of genes which escape X-inactivation
why is sex aneuploid more common?
-X chromosome inactivation
-few genes on Y
turner's syndrome
XO; monosomy X; 2n-1=45
klienfelter's syndrome
XXY; trisomy; 2n+1=47
trisomy X
XXX; 2n+1=47