Income Taxes IAS12
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is the definition for current tax?
The amount of income taxes payable in respect of the taxable profit for a period.
What are the two forms of income taxes?
Current tax
deferred tax
What is taxable profit?
The profit (or loss) for a period determined in accordance with the rules established by the taxation authorities, upon which income taxes are payable.
What is accounting profit?
Profit (or loss) for a period before deducting tax expense (aka profit before tax)
What is deferred tax?
It is the tax that you pay or save in the future because of temporary differences between the asset or liability’s carrying amount and its tax base.
Why do timing differences rise?
Because the timing of accounting recognition (of income and expenses) in the P&L differs from that of their ‘tax points’ (when it becomes taxable or deductible)
Deferred tax is created since the difference is only in timing and will eventually reverse
How is deferred tax created?
There is a mismatch between P&L recognition period and tax point period creates a temporary timing difference which leads to deferred tax because tax catches up later.
What is taxable profit?
The profit amount that a company must pay tax on, according to tax authority rules.
Starts with accounting profit and is then adjusted to follow tax law
What are the two main reasons why taxable profits are different from accounting profits?
Permanent differences: Some accounting income (or expenses) are not chargeable (or deductable) for tax purposes. These ‘permanent differences’ will not reverse in the future accounting accounting period.
Timing/Temporary differences: Some income/expenses are recognised in one period but are taxed or deductible in a different period. These timing/temporary differences will reverse in the future.
What is the formula to get from accounting profit (before tax) to taxable profit?
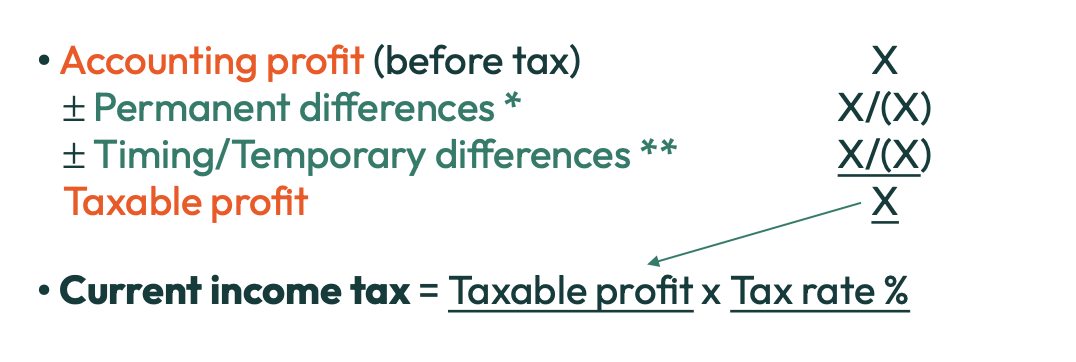

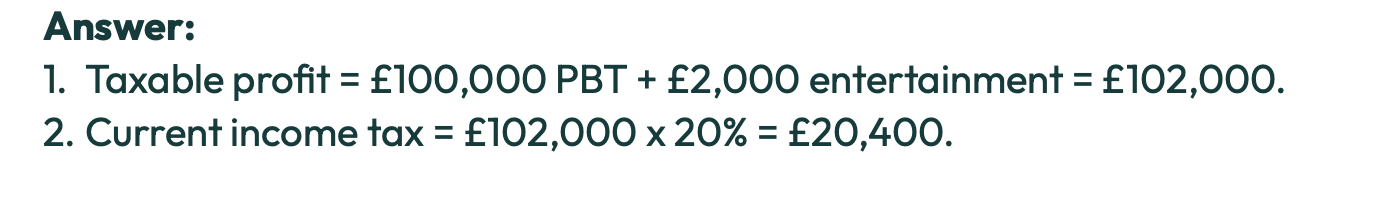
What is an overprovision ?
If the estimated current income tax> actual tax payable
What do we do if we have an overprovision?
We reduce the income tax of the following year
For financial reporting purposes do accountants have to estimate the amount of income tax for the current year?
Yes
The actual amount of tax payable is later confirmed by the tax authority
What is an under provision?
If estimated current income tax< actual tax payable
What do we do if we have an underprovision?
Increase income tax of the following year

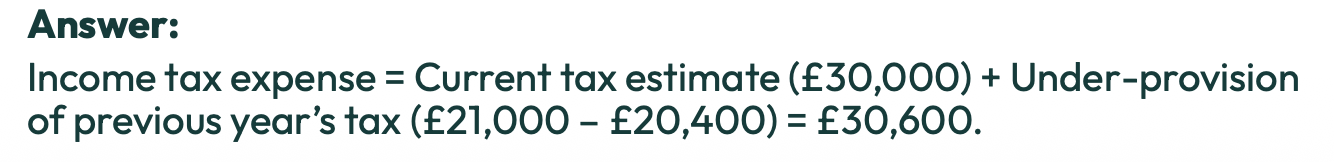
Why are taxable profits different from accounting profits? (main reason)
Timing/temporary differences
They arise because the timing of accounting recognition (of income and expenses) in the P&L differs from that of their ‘tax points’ (the points they become chargeable or deductible for tax purposes)
What are “tax points”?
The moments when a transaction becomes taxable or tax deductible under tax authority rules
Why do tax points matter?
They can occur in a different period than accounting recognition, which creates timing/temporary differences which creates deferred tax.


What is deferred tax?
‘accounting adjustments’ designed to resolve the distortion effects of timing/temporary differences
When do we create a deferred tax liability?
If temporary differences cause accounting profits> taxable profits, increase income tax expense by creating a DT liability
When do we create a deferred tax asset?
If temporary differences cause taxable profits> accounting profits, decrease income tax expense by creating a DT asset
What are the steps to compute deferred tax adjustments?
Compare Accounting’s carrying amount vs tax’s tax base for both assets and liabilities (differences between CA and TB = Temporary differences)
Determine if the TDs are taxable or deductible and compute DTL or DTA
Compute the period changes in DT liabilities/assets. The changes are the deferred tax adjustments.
How do we determine if the TDs are taxable or deductible and compute DTL or DTA?
if assets CA>TB - taxable TDs - DT liabilities
if assets CA<TB - deductible TDs- Dt assets
When do we have a taxable TDs?
If A’s CA>TB
leads to deferred tax liability
When do we have deductible TDs?
If A’s TB>CA
leads to deferred tax asset

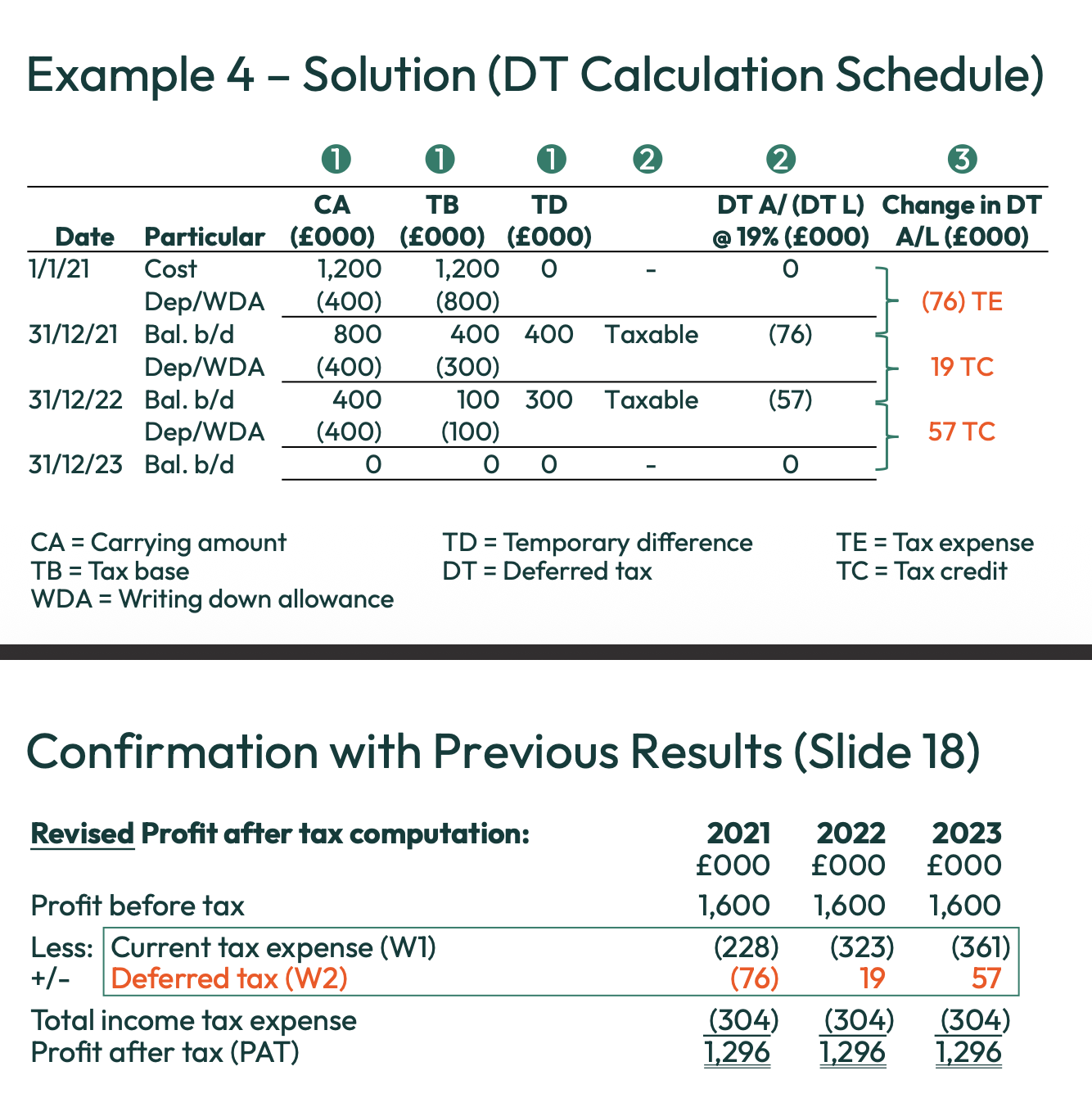
What are the two types that a tax base is split into?
Assets that give rise to taxable future economic benefits
Assets that do not
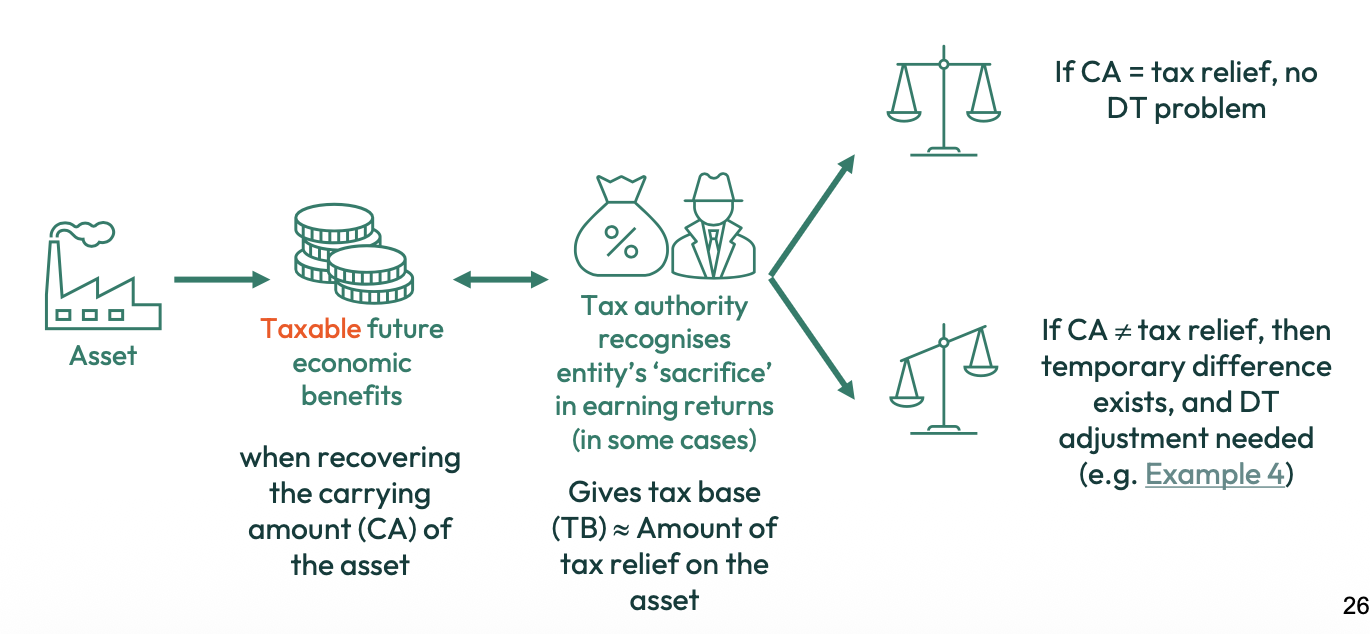
What is the tax base of assets (taxable future benefits)
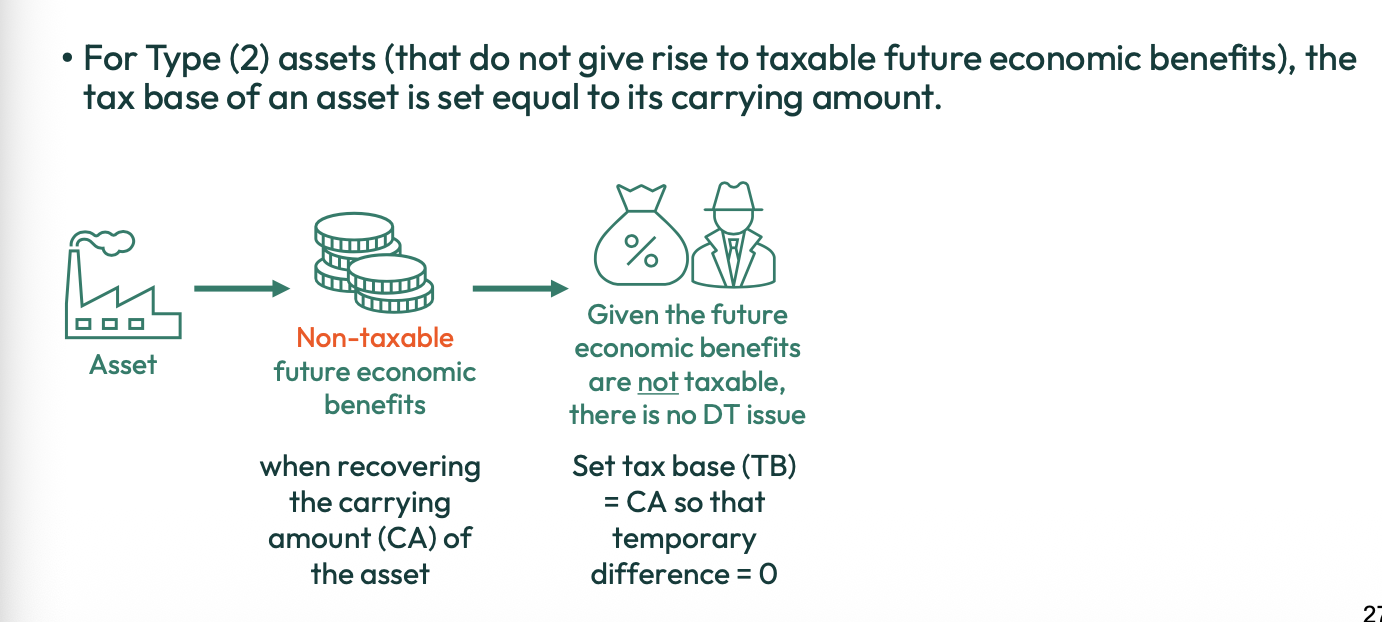
What is the tax base of assets (non taxable future benefits)?
What can temporary differences (TDs) be defined as?
The differences between the carrying amount of an asset or liability in the SFP and its tax base
What are permanent differences?
They arise when items affect accounting profit but will never affect taxable profit or vice versa. Because these differences do not reverse in future years they do not give rise to deferred tax.
What are temporary differences?
Temporary differences arise because certain income and expenses are recognised in different accounting periods for financial reporting and tax purposes.
These differences reverse over time and therefore create deferred tax assets or liabilities
What does reversal mean?
The timing difference between accounting and taxable profit will be eliminated in a future period as tax and accounting eventually recognise the same total income or expense.
Would permanent differences pose any accounting problems?
No, since they will not reverse in the future
What do we do when temporary differences cause taxable profits to be less than accounting profits?
The company is paying less tax now but will pay more tax later when the temporary differences reverse
The company must increase the income tax expense today by creating a deferred tax liability.
How is a deferred tax liability created?
When accounting profits> taxable profits
How is a deferred tax asset created?
When taxable profits> accounting profits
Are accounting and tax rules the same?
They are not the same. So profit under each system is different in many periods.
Because accounting and tax rules are not the same profit under each system is different, what does this difference create?
Permanent differences- do not reverse
Temporary differences- reverse later- create deferred tax