JW 1-2. Intro & Electrophilic aromatic substitution
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What are the three rules of aromaticity?
4n + 2pi electrons
Planar molecule for the overlap of p orbitals
Fully conjugated pi-system
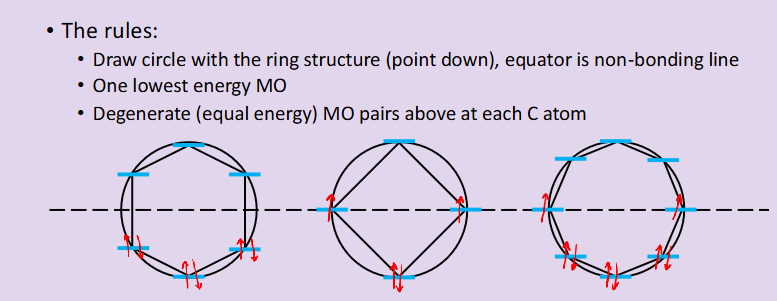
What is a Frost-Muslin Diagram? How are they constructed?
shows the bonding and anti-bonding and non-bonding molecular orbitals in cyclic structures
along the dotted line draw the molecules ring structure with the point facing down, there will always be one lowest energy MO on this bottom point
an MO space will sit on every corner of the structure
How to fill them: e.g. benzene has six pi-bonds
What are the requirements for an anti-aromatic system?
cyclic and conjugated molecule
With only 4n electrons
When is something planar?
When there is sp2 hybridisation
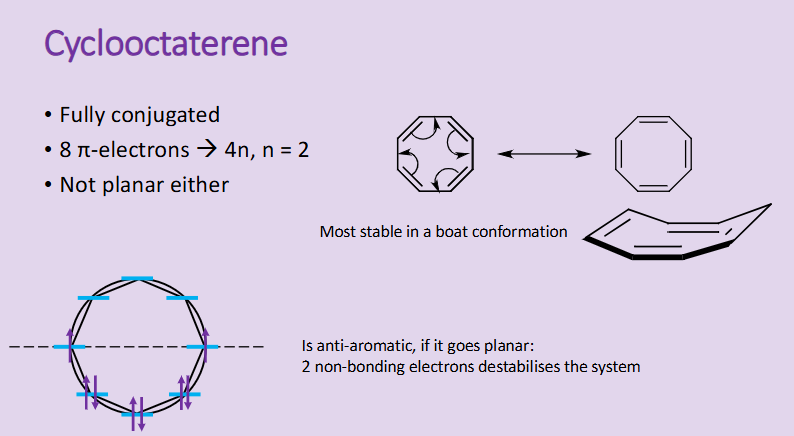
What can cause a structure (like cyclooctaterene) to not be aromatic even though it looks like it would follow all the rules of aromaticity?
although its fully conjugated with 4n +2 pi electrons
It is not planar as it is more stable in its boat conformation
When constructing the Frost-Muslin diagram for it, there are 8 electrons to be placed on, however two of these land on non-bonding lines and are not paired, this destabilises the system forcing it to be more stable in boat conformation.
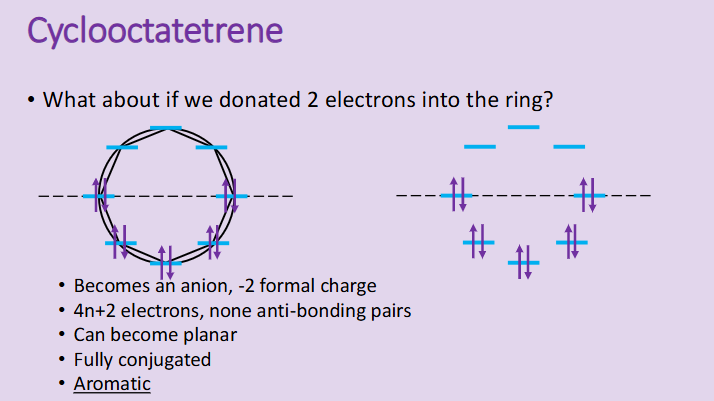
How can we force some cyclic structures into aromaticity?
by forming aromatic anions with negative charges
the addition of 2 electrons often causes structures to be able to be aromatic as it adds the possibilities of resonance and conjugation to the ring
Even cycloocaterene can have two electrons donated into the ring to become cycloocatetrene which is now planar and fully conjugated.
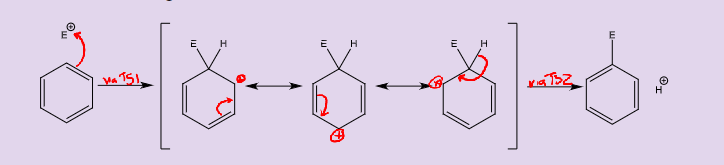
What is the general mechanism with Wheland intermediates for electrophilic aromatic substitution?