BIO 120: Quiz 5
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are carbohydrates?
macromolecules that include sugars
monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
provide energy
formula is (CH2O)n where “n” is the number of carbon atoms
Where are carbohydrates broken down?
Begins in the mouth then takes place in the small intestines
What enzymes are used to break down carbohydrates?
Starch and glycogen are broken down into glucose by amylase and maltase
Sucrose and lactose are broken down by sucrase and lactase.
When the body has excess ATP and glucose what happens to it?
glucose is stored in the liver as glycogen
What are calories?
A unit of measurement for energy that food provides
Define the basal metabolic rate (BMR)
the amount of energy (calories) the body requires at rest to maintain vital functions
How are carbohydrates converted into ATP energy?
Glycolysis: glucose is converted to pyruvic acid which converts into ATP in the mitochondria
Krebs Cycle: Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA and yields ATP
Glucose is an example of ___
monosaccharide
Sugar is stored in plants as ___ and in animals as ____
Starch (in seeds and roots) and glycogen (in liver/muscle cells)
Monosaccharides
are simple sugars (glucose) and exist as a linear chain or as ring-shaped molecules
Polysaccharides
a long chain of monosaccharides linked by covalent bonds (starch, glycogen, and cellulose)
Disaccharides
when two monosaccharides lose a water molecule (examples are lactose, maltose, and sucrose)
What is the primary role of salivary amylase in digestion?
Breaks down polysaccharides into disaccharides in the mouth
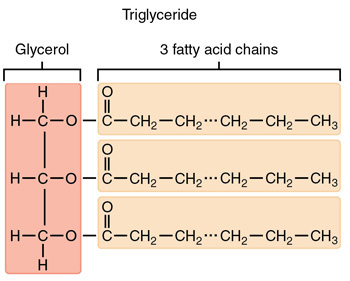
What is the structure of a fat molecule (triglyceride)?
Made up of glycerol (C3H3O3) and 3 fatty acid chains that are attached to the glycerol
Saturated Fats
Fatty acids with single bonds
saturated with hydrogen
usually solid at room temperature
typically from animals
Unsaturated Fats
Fatty acids with double bonds that prevent them from packing tightly
liquid form at room temperature
usually from plants but sometimes animals (fish oil)
ex: canola, avocado, olive oils
What is an essential fatty acid and what is the source?
Cannot be made by the body, must be consumed through food
What is the structure of a steroid?
Have a four, linked carbon rings and several steroids, like cholesterol, have a short tail.
Describe the process of lipid metabolism (lipolysis)
fatty acids undergo beta oxidation
glycerol goes under glycolysis
Forms acetyl-CoA
Enters the Krebs cycle to make ATP energy
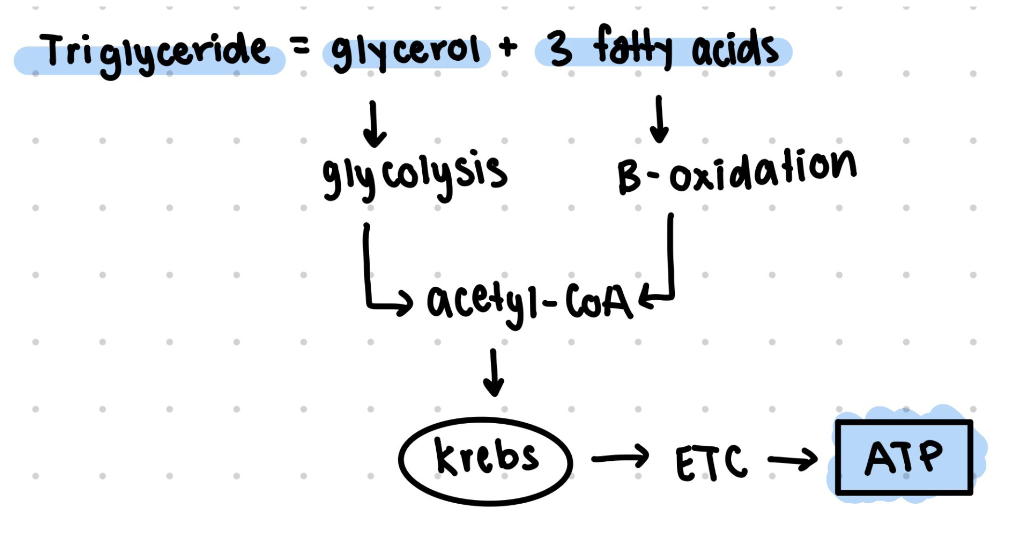
What are ketone bodies and what are they used for?
when there’s excessive acetyl CoA, the liver converts it to ketone bodies that serve as fuel if glucose levels get too low
What happens to fats after we eat them?
Broken down into fatty acids and stored in fat cells or used as energy via fatty acids.
What is the structure and functions of proteins?
most abundant organic molecule
diverse array of functions including transport, storage or membranes/enzymes
ex: hemoglobin, collagen, and actin
What is the structure of amino acids?
Monomers that consist of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino, carboxyl, hydrogen atom, and an R group
List all the essential amino acids
isoleucine
leucine
lysine
methionine
phenylalanine
tryptophan
valine
histidine
threonine
arginine
What traits do all lipids have in common?
Hydrophobicity, nonpolar, insoluble, and monomers
Which of the following best describes a saturated fat?
the fatty acid chain has the maximum number of hydrogens
What do cholesterol, estrogen, and testerone all have in common?
All are steroids
The process of breaking down and digesting fatty acids into acetyl CoA is called
beta oxidation
What are the monomeric units of proteins?
amino acids
Insulin is activated during which metabolic state?
absorptive state
Absorptive State
can last up to 4 hours after a meal
your body stores fats and builds glycogen
the rise of blood sugar levels activates insulin
Post-Absorptive State
the “fasting state” overnight or when you skip meals
when food has been digested, absorbed, and stored
the hormone glucagon is released from the pancreas
Starvation
the body uses ketones to function due to low blood sugar
uses Krebs cycle to make ATP
survival depends of the amount of fat and protein stored in the body
Where are lipids digested?
Begins in the stomach and mouth then goes to small intestines
What enzyme breaks down proteins?
pepsin
Which enzyme breaks down fat?
lipase
How are proteins digested?
first in the stomach with the enzyme pepsin then in the small intestines using pancreatic enzymes to break down the peptides
Which enzyme breaks down carbohydrates?
amylases
Where is insulin and glucagon synthesized?
both are made and released by the pancreas
When digesting fat, what is the role of bile?
emulsification large fat globs
which type of biomolecule is cholesterol?
Lipid
what’s an example of a saturated fatty acid?
Butter
What is the primary function of insulin in the body?
It decreases blood sugar levels by activating the GLUT transporter to allow sugar to enter the cell’s bloodstream
where in the body is cholesterol synthesized?
liver
Which of the following is not a natural source of carbohydrates?
meat products
Which is the correct order of how food gets processed in our body?
mouth, esophagus, small intestines, large intestines, rectum, stomach
why do fats yield more energy than carbohydrates during metabolism?
because fat molecules contain more carbon-hydrogen bonds, which store more chemical energy
What is the primary function of glucagon?
If blood sugar levels decrease too much, glucagon is a hormone released to make blood sugar levels rise
Why is emulsification important?
Because smaller lipid globs make it easier for pancreatic lipases to digest them
What kind of environment is optimal to digest proteins?
Acidic environment with a low pH helps to denature protein
Which of the following best describes ketogenesis?
Conversion of fatty acids into ketone bodies during starvation
What is the primary role of pancreatic amylase in digestion?
Break down polysaccharides into disaccharides in small intestines
What are 2 key differences between Type I and Type II diabetes?
Type I requires lifetime insulin injections while Type II often involves insulin resistance, but one may still have normal insulin levels
T1D is an autoimmune disease, while T2D is primarily metabolic
Glucose is broken down into pyruvate during which metabolic process?
glycolysis
What is characterized by insulin resistance?
Type II Diabetes
There are ___ total amino acids and ___ essential amino acids.
20, 10
After eating, an animals’s blood glucose levels…
Increase
What enzyme is NOT involved with protein digestion?
amylase
Which condition is characterized by an autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, typically developing in childhood or adolescence?
Type 1 Diabetes
What is the role of insulin in Type I and Type II diabetes?
In Type I, the body isn't making enough insulin whereas in Type II, the cells don't respond to insulin
Describe Type I diabetes
Cause: Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells → little to no insulin production.
Onset: Usually childhood or adolescence.
Management: Requires insulin injections for life.
Risk Factors: Genetic, autoimmune.
Describe Type II diabetes
Cause: Insulin resistance → body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin (levels decline gradually)
Onset: Usually adulthood
Management: Lifestyle changes, oral medication, sometimes insulin.
Risk Factors: Obesity, poor diet, lack of exercise, genetics.