Brain Imaging
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MRIQuiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
The brainstem includes all of the following EXCEPT:
putamen
The _ passes through the Sylvian fissure
middle cerebral artery
The mesencephalic duct, aka aqueductus mesencephali, aqueduct of Sylvius or the cerebral aqueduct, contains CSF is within the midbrain and
connects the third ventricle in the diencephalon to the fourth ventricle, which is in between the pons and cerebellum
When performing MRI to rule out brain tumors, the weighted images acquired to evaluate the extent of lesion involvement, after injection of gadolinium, are
T1
How do the vertebral arteries enter the cranium?
foramen magnum
To best visualize the pituitary gland in MRI, high resolution T1 weighted images in the __________ planes pre and post contrast are optimal.
Thin slice sagittal and coronal (3 mm or less)
If a brain exam is being perfomed and the request is made to rule out globe tumor due to symptoms of diplopia, a protocol with thin cuts through the ____________ should be performed including fat supression pre/post contrast
Orbits/Optic Nerves
____________ is a condition in which part of the cerebellar tonsil is displaced through the foramen magnum.
Chiari Malformation
The hippocampus is located in the medial temporal lobe, and is best seen is what plane?
coronal oblique
If a brain exam is being performed and the request is made to rule out acoustic neuroma, a protocol with thin cuts through the _ should be performed
IAC (VII or VIII cranial nerves)
3mm Axial and Coronal T1 pre/post contrast
heavily T2 weighted 3D Volume for optimal VII and VIII cranial nerve assessment are useful
If a brain exam is being performed and the request is made to evaluate cranial nerves VII and VIII due to the patient's symptoms of tinnitus, a protocol with thin cuts through the ____________ should be performed.
IAC
A depression in the base of the skull where the pituitary gland is located is called the ___________.
Sella turcica
How many cranial nerves are there?
12
When performing an MRI to confirm a suspected pituitary microadenoma, contrast is injected and imaging is performed:
Rapidly because lesions appear as low signal intensity compared to the enhanced pituitary gland
The _____________ imaging plane would be the most optimal slice orientation for evaluation of Arnold Chiari Malformation and its inferior cerebellar tonsillar herniation.
sagittal
if the third ventricle is dilated, but the fourth ventricle is not, there would then be pathology associated with:
aqueduct of sylvius
_______ sequences are performed to suppress CSF (cerebro-spinal fluid) and aid in the detection of demyelination.
FLAIR
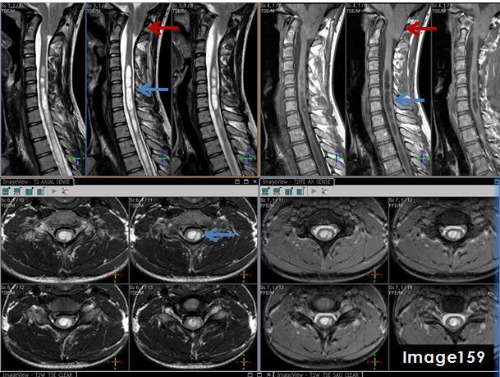
The pathology identified by the blue arrows in Image 159 is a syrinx, displaying T1 _____________ signal and T2 _______________ signal relative to the spinal cord.
hypointense; hyperintense
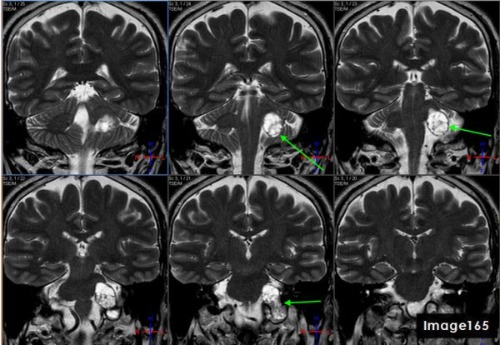
The green arrows in Image 165 point to what pathology?
Vestibular schwannoma aka acoustic neuroma
Which fissure divides the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobes?
sylvian fissure
the right and left optic nerve joint at the
optic chiasm
MRI findings of a low volume corpus callosum and increased white matter lesions can be indicative of a diagnosis of:
multiple sclerosis
The insular cortex is primarily responsible for:
motor control, cognitive function, perception, self-awareness, and interpersonal experience
When imaging a hemorrhagic infarct in the brain, which pulse sequence would demonstrate the magnetic susceptibility effects better?
gradient echo
When positioning a patient for a brain MRI, the centering should be placed at what anatomical landmark?
Nasion
The stalk of the pituitary gland is also known as the:
Infundibulum/pituitary stalk
Which dural venous sinuses drain from the confluence of sinuses (by the internal occipital protuberance) to the mastoid portion of the temporal?
transverse sinuses
On a T2 weighted image, CSF appears bright because it has a __________ relaxation time.
Long T2
Which area of the brain is typically affected in patients with a history of epilepsy?
temporal lobe and/or hippocampus
In the TMJ’s, the articular disc lies between what two anatomical structures?
Mandibular fossa and mandibular condyle
The medial and lateral rectus muscles are located in the:
eyes
Which structure lies adjacent to the head of the caudate nucleus?
anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
Which cranial nerve is responsible for Bell's Palsy?
7th Cranial nerve VII-the facial nerve
The __________________ runs the length of the falx cerebri.
superior sagittal sinus
What would be the most useful sequence for evaluation of an acute stroke?
DWI
A FLAIR sequence with a long TI is utilized to:
null the signal from CSF
If a brain exam is being perfomed and the request is made to rule out microadenoma due to elevated prolactin levels, a protocol with thin cuts through the ____________ should be performed.
Pituitary gland
To accurately depict the VII and VIII cranial nerves, the patient would centered at the level of the:
external auditory meatus
The dural venous sinuses that drain into the internal jugular vein are the:
sigmoid sinus
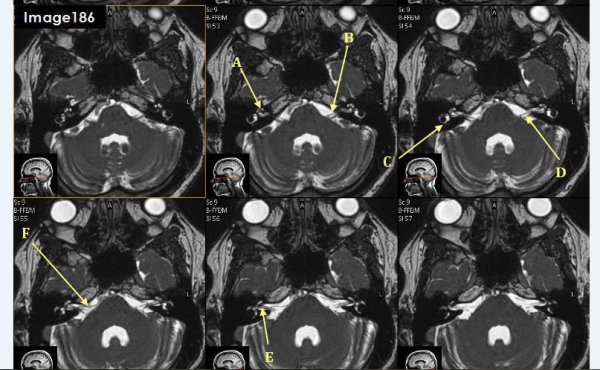
Letter A in Image 186 is pointing to:
cochlea
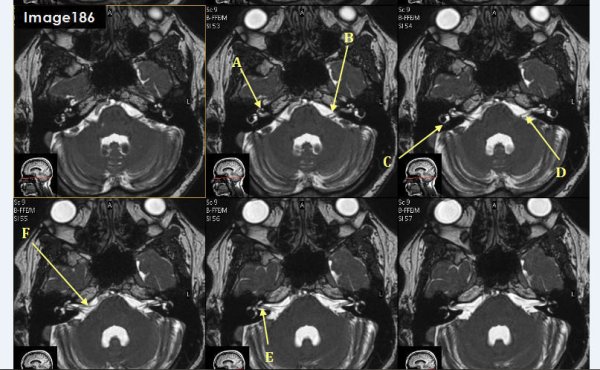
Letter B in Image 186 is pointing to which cranial nerve:
left facial nerve-CN VII
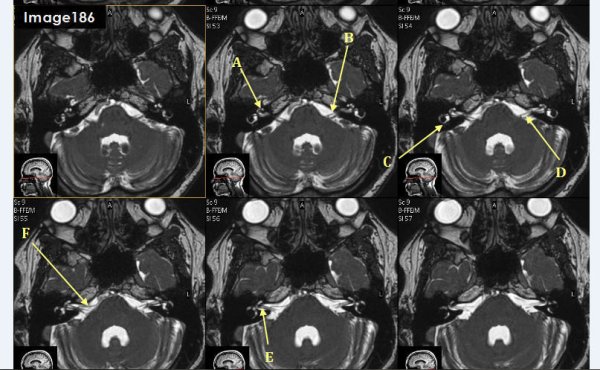
Letter C in Image 186 is pointing to:
semicircular canal
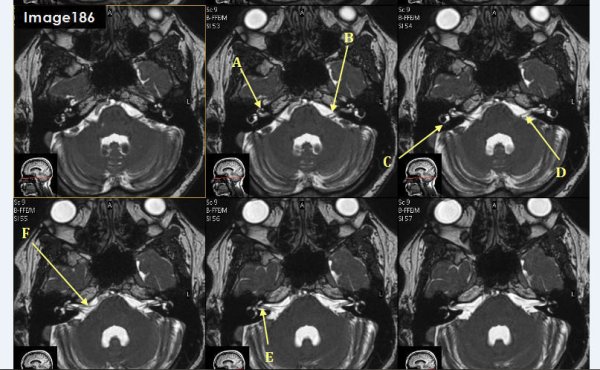
Letter D in Image 186 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
Cranial nerve 8- left vestibulocochlear nerve
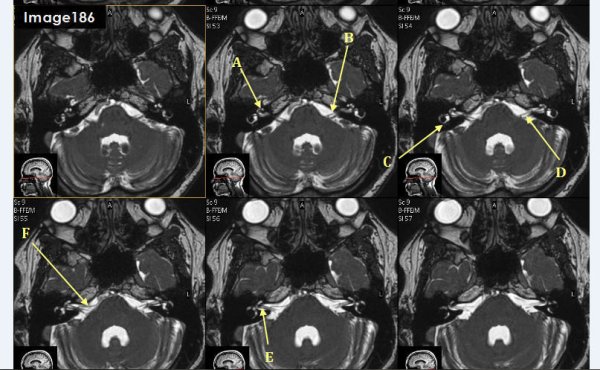
Letter E in Image 186 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 8-right vestibulocochlear nerve
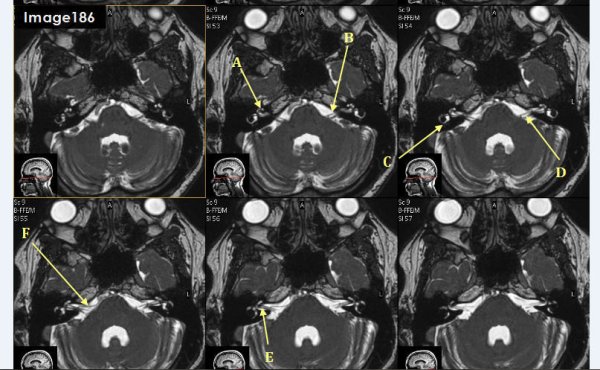
Letter F in Image 186 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 7- right facial nerve
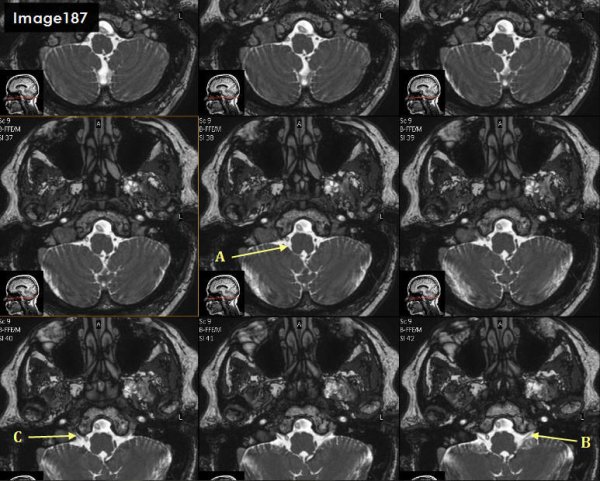
Letter A in Image 187 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 10- right vagus nerve
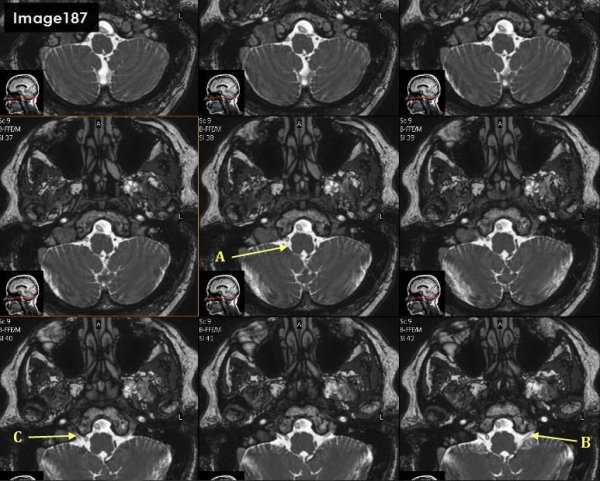
Letter B in Image 187 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
Cranial nerve 9- left glossopharyngeal nerve
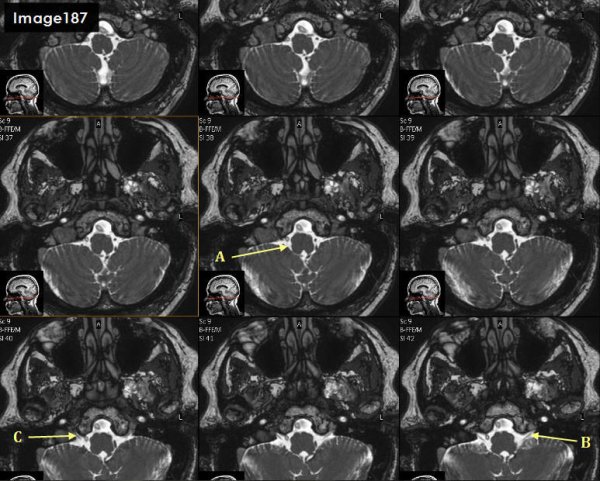
Letter C in Image 187 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 9-right glossopharyngeal nerve
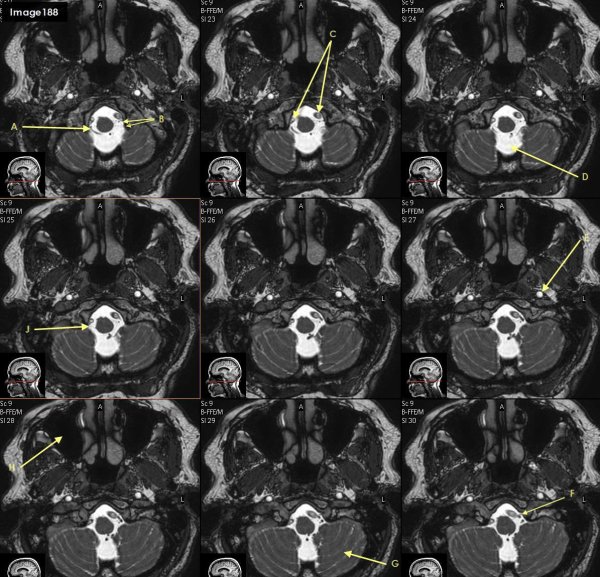
Letter J in Image 188 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 12- right hypoglossal nerve
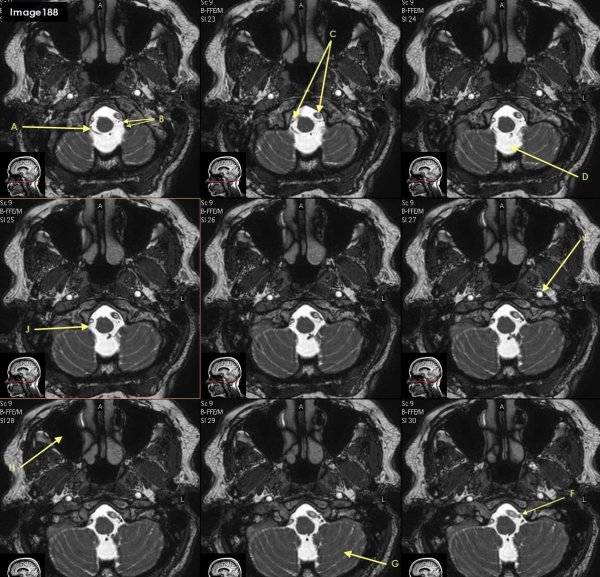
Letter F in Image 188 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 12-left hypoglossal nerve
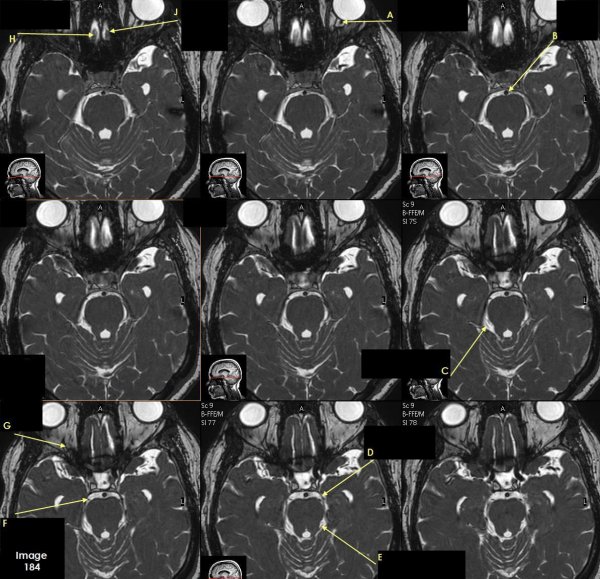
Letter A in Image 184 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 2-left optic nerve
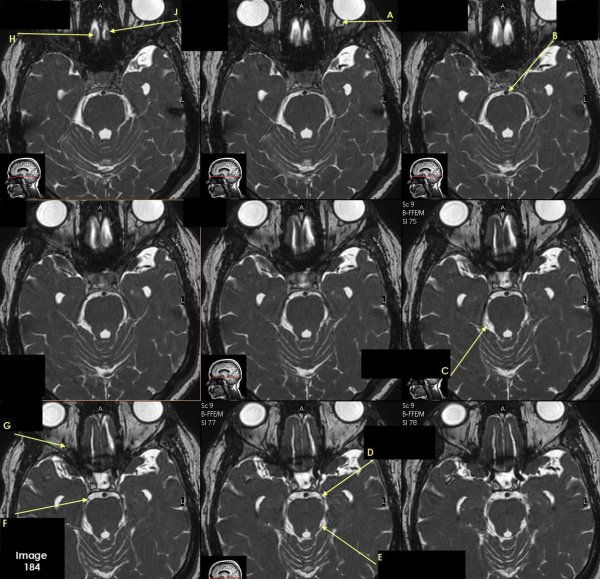
Letter B in Image 184 is pointing to:
Basilar artery
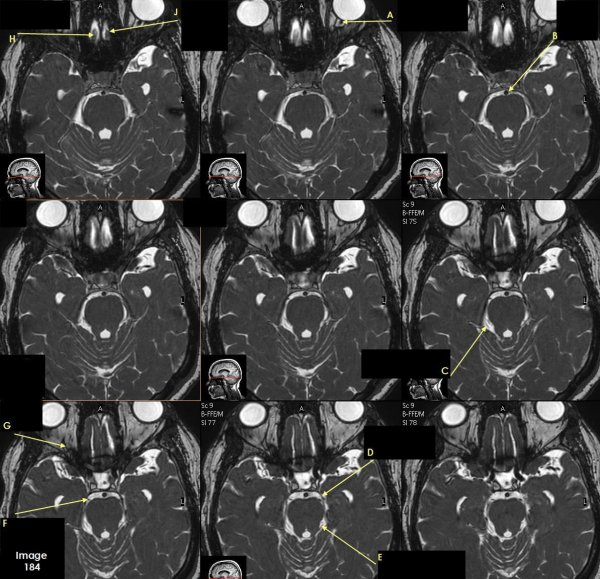
Letter C in Image 184 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 4-right Trochlear nerve
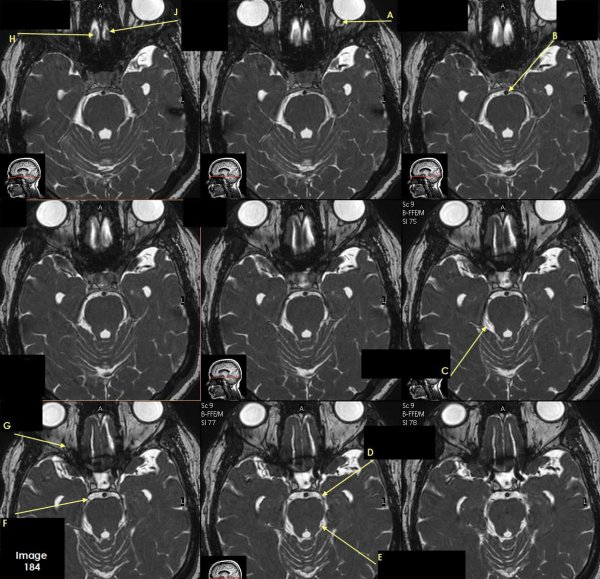
Letter D in Image 184 is pointing to:
cranial nerve 3-left oculomotor nerve
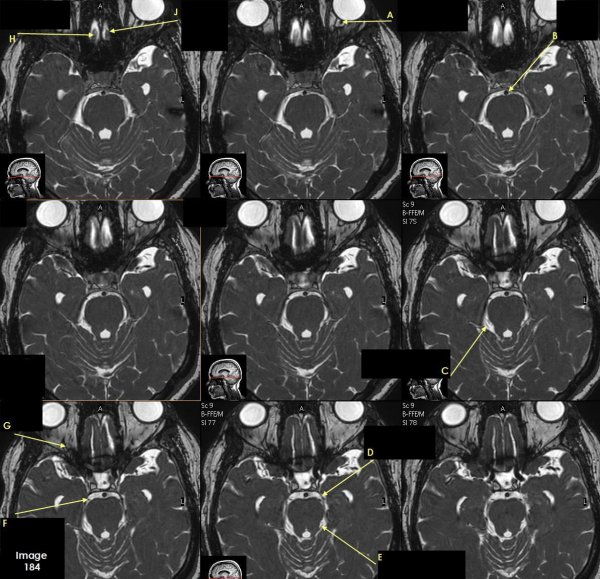
Letter E in Image 184 is pointing to:
cranial nerve 4- left Trochlear nerve
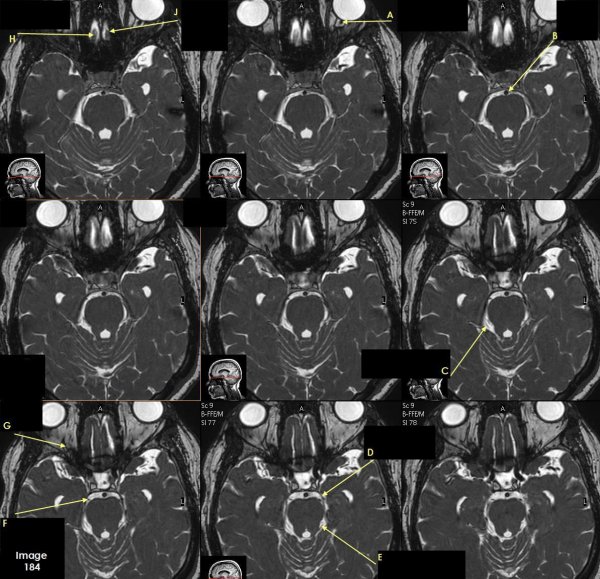
Letter F in Image 184 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 3-right oculomotor nerve
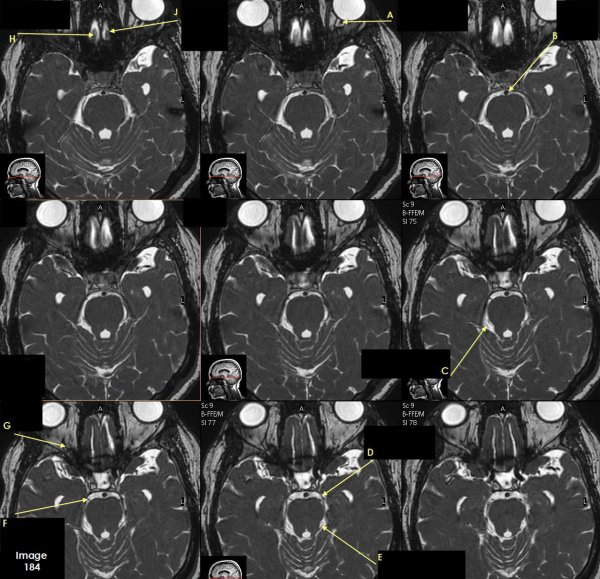
Letter G in Image 184 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 2-right optic nerve
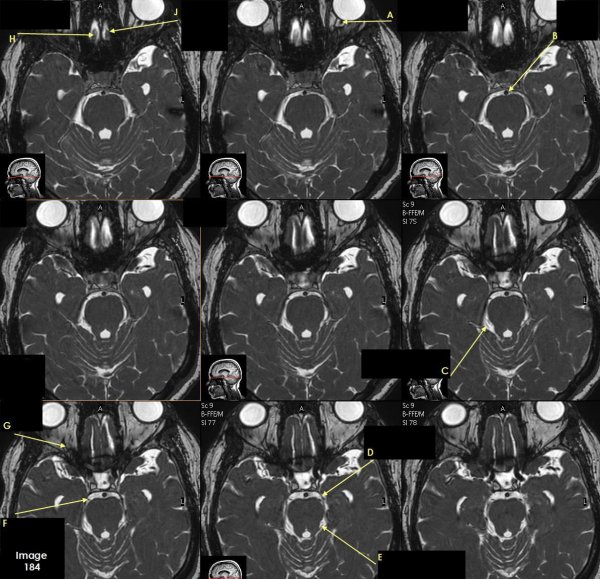
Letter H in Image 184 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 1-right olfactory nerve
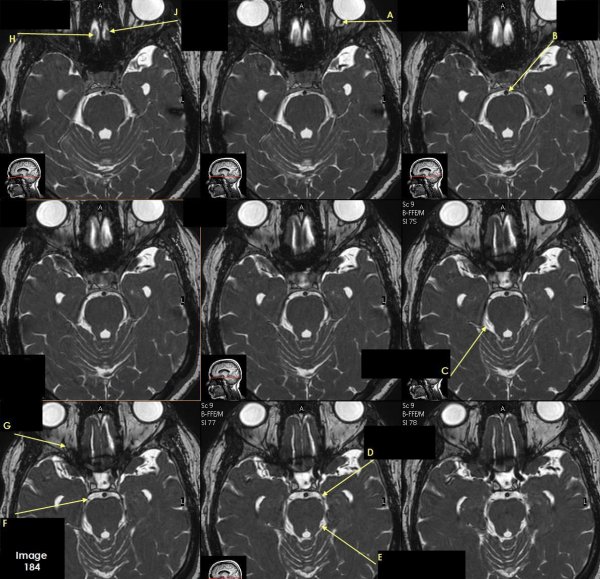
Letter J in Image 184 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 1-left olfactory nerve
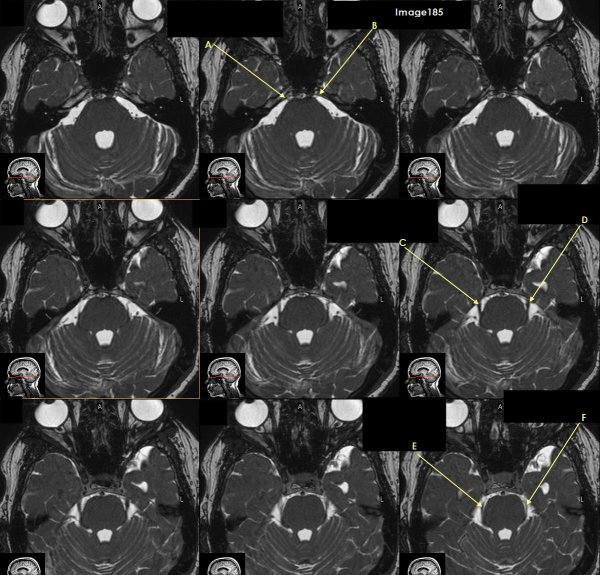
Letter A in Image 185 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 6-right Abducens nerve
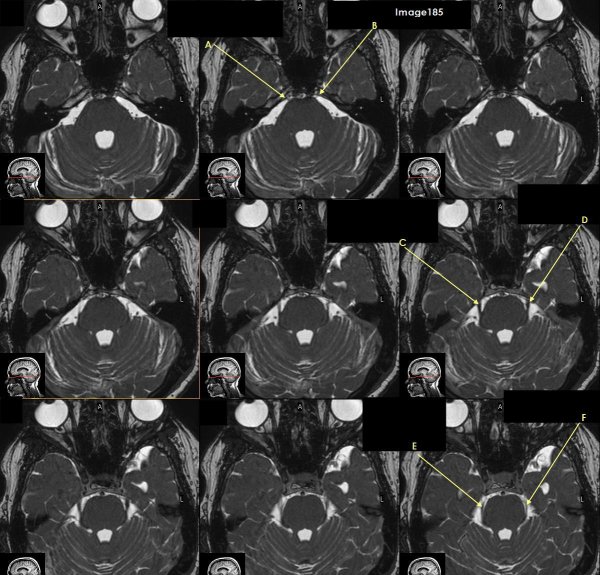
Letter B in Image 185 is pointing to:
cranial nerve 6-left Abducens nerve
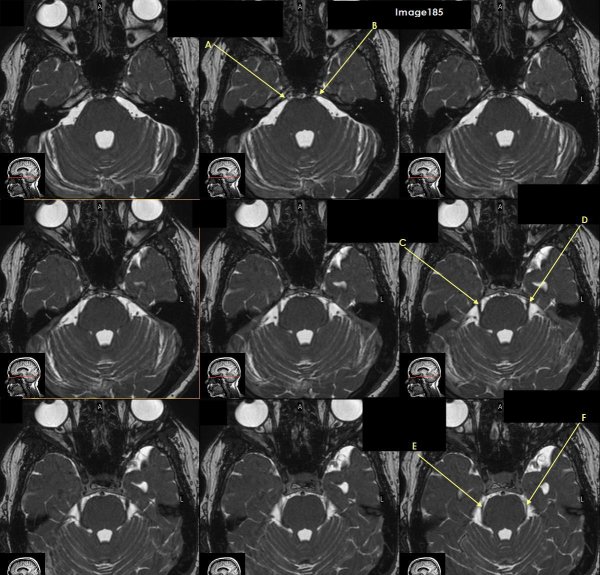
Letter C in Image 185 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 5-Right trigeminal nerve
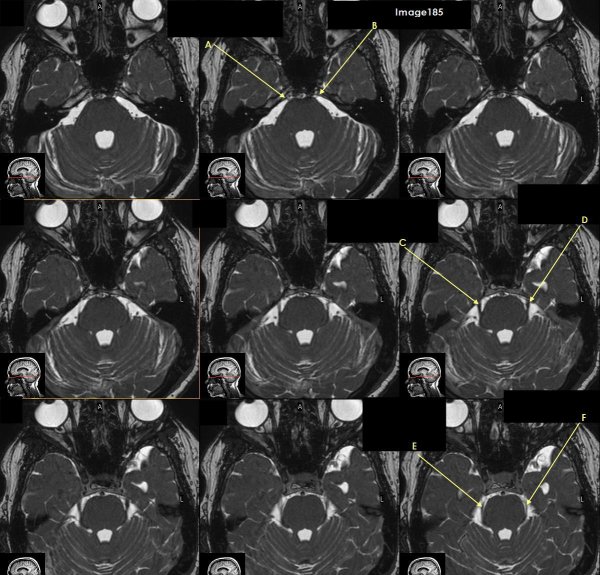
Letter D in Image 185 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 5-left trigeminal nerve
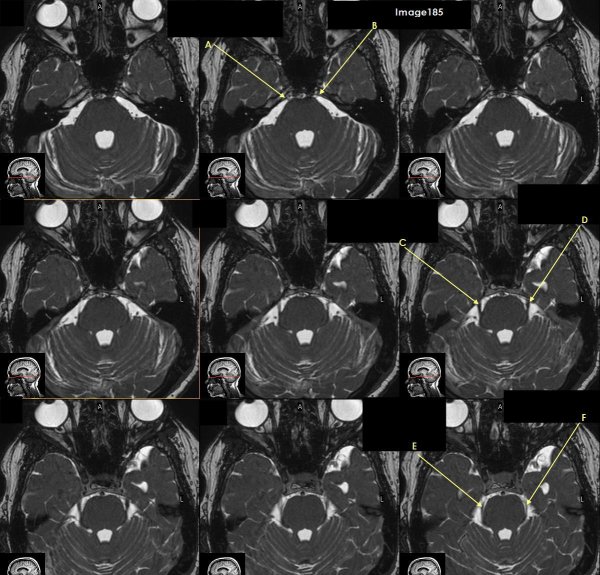
Letter E in Image 185 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 4-right trochlear nerve
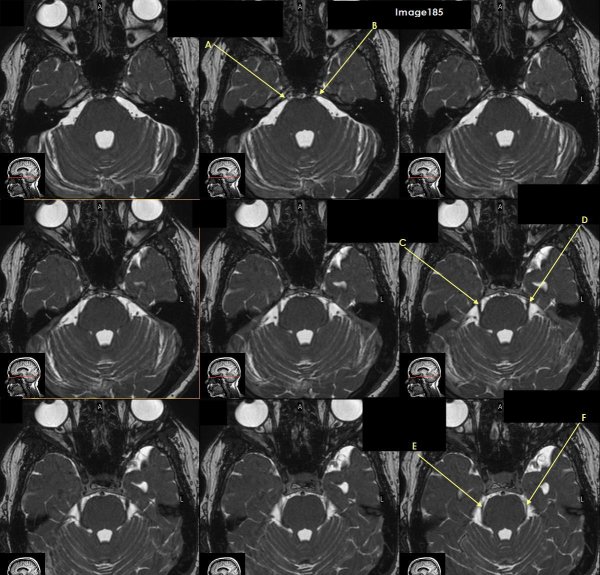
Letter F in Image 185 is pointing to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 4-left trochlear nerve
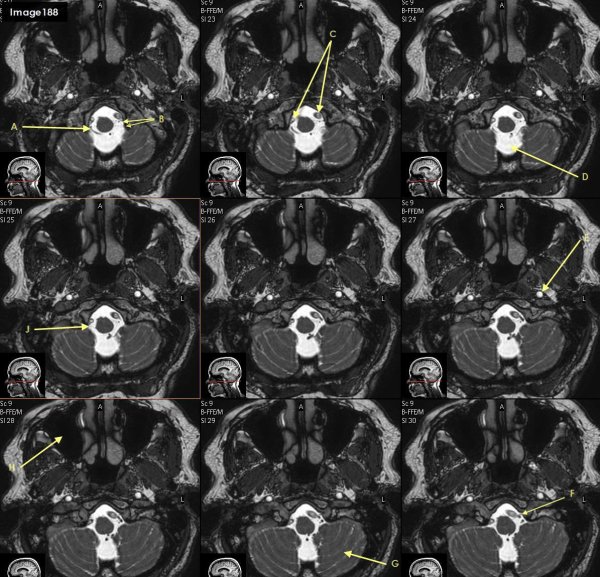
Letter B in Image 188 is poinitng to which cranial nerve?
cranial nerve 11-Spinal accessory nerve
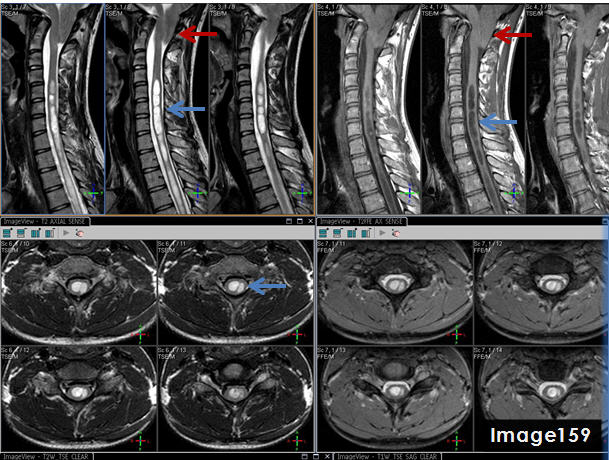
The blue arrows in Image 159 point to what pathology?
syrinx
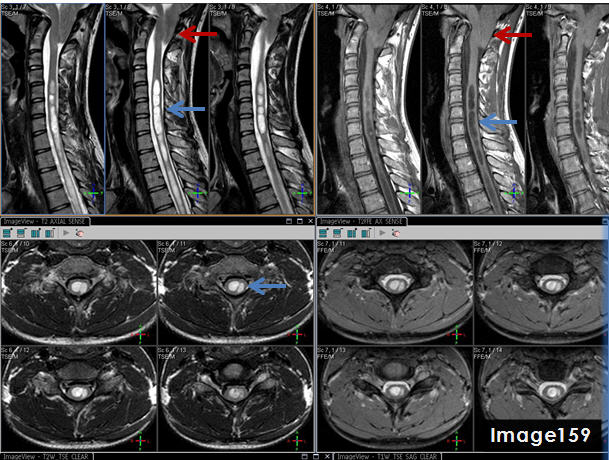
The three images in the top right quadrant of Image 159 identify which MRI pulse sequence?
T1 sagittal
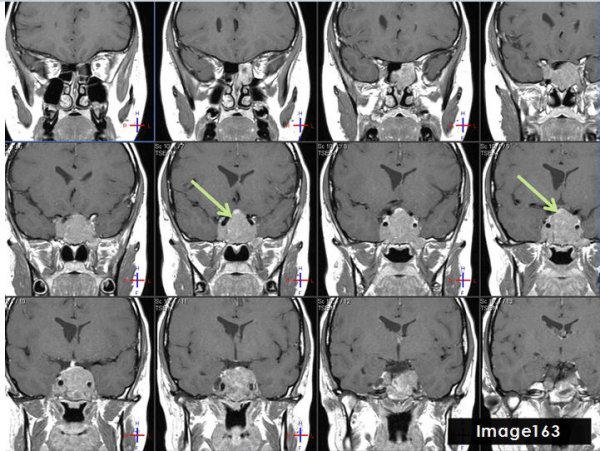
The green arrows in Image 163 point to what pathology?
pituitary tumor
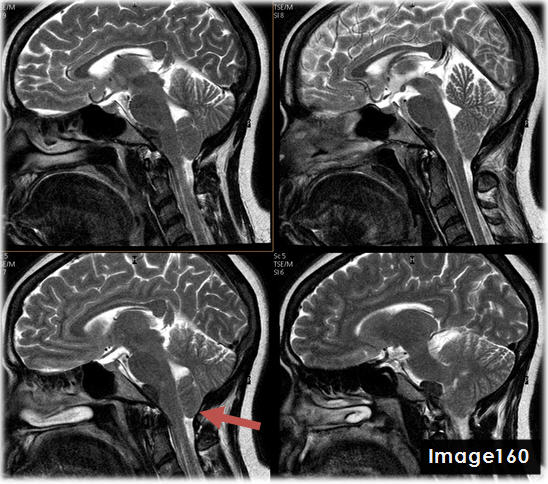
The red arrow in Image 160 points to what pathology?
Chiari malformation
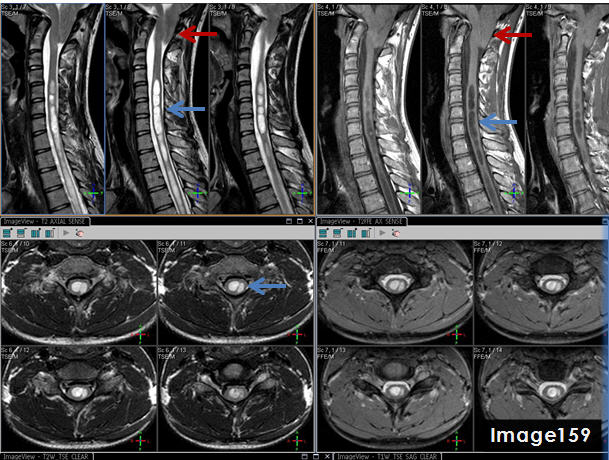
The three images in the top left quadrant of Image 159 identify what pulse sequence?
T2 sagittal
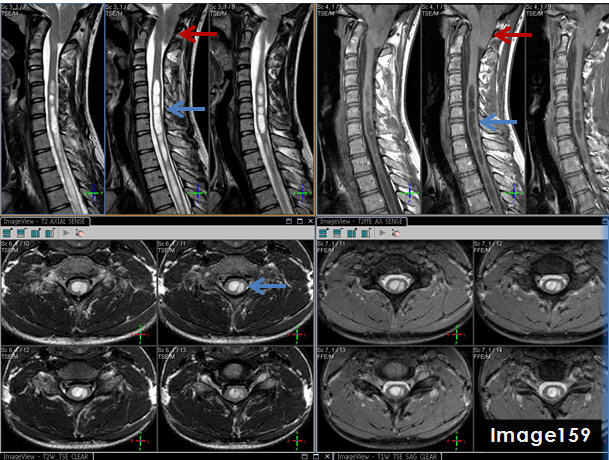
The red arrows in Image 159 point to what pathology?
chiari malformation