Quiz 1 (copy)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
B. Physical, because the molecules have been re-arranged without any change in their type or number
Ice melts and forms water. Identify if the change is physical or chemical.
A. Physical, because the molecules have been broken into pieces
B. Physical, because the molecules have been re-arranged without any change in their type or number
C. Chemical, because a new substance – liquid water – has formed
D. Chemical, because the atoms have been re-arranged
D. Intensive properties are inherent to the substance itself, such as density and boiling point, whereas extensive properties are dependent on the amount of substance, such as mass and volume.
Which of the following best describes the difference between intensive and extensive properties of matter?
A. Intensive properties depend on the amount of substance present, while extensive properties do not.
B. Extensive properties are those that do not change with the amount of substance, while intensive properties change proportionally with the amount of substance.
C. Extensive properties are related to the chemical composition of the substance, while intensive properties are related to the physical state of the substance.
D. Intensive properties are inherent to the substance itself, such as density and boiling point, whereas extensive properties are dependent on the amount of substance, such as mass and volume.
C. Composition of matter
Table salt is made up of 1 sodium atom and 1 chlorine atom. This is an example of....
A. structure of matter.
B. interaction between matters.
C. composition of matter.
D. properties of matter.
C. The formation of a new substance with different properties from the original substances.
Which of the following is a characteristic of a chemical change?
A. A change in size or shape without altering the chemical composition.
B. A change in the state of matter, such as melting or freezing.
C. The formation of a new substance with different properties from the original substances.
D. The dissolution of a substance in water, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
B. The melting of ice into liquid water.
Which of the following processes is an example of a physical change, but not a chemical change?
A. The oxidation of iron to form rust.
B. The melting of ice into liquid water.
C. The combustion of gasoline in an engine.
D. The fermentation of sugars to produce ethanol.
D. Volume
If we took a ruler and measured the length x width x height of a block of wood. What measurement was we getting?
A. weight
B. density
C. mass
D. volume
A. Flammability
Which of the following is a chemical property of matter?
A. flammability
B. melting point
C. boiling point
D. density
C. density
Which of the following is a physical property of matter?
A. corrosiveness
B. pH (acidity)
C. density
D. flammability
A. mass
Which of the following is an example of extensive property?
A. mass
B. density
C. temperature
D. color
B. Oil is less dense than water so floats on top
Oil and water can be separated using flotation because:
A. Oil is more dense than water so floats on top
B. Oil is less dense than water so floats on top
C. Oil is more dense than water so sinks to the bottom
D. Oil is less dense than water so sinks to the bottom
C. Volume
Which of the following is not an example of intensive property?
A. melting point
B. conductivity
C. volume
D. density
D. I, II, III, and IV
Chemistry is a branch of science to study
(I) Interactions between matter
(II) Structure of matter
(III) Composition of matter
(IV) Properties of matter
A. I, II, and III
B. I, II, and IV
C. II, III, and IV
D. I, II, III, and IV
A. Combination of chemistry and metal work, combined with physics, medicine, and spirituality
What is alchemy?
A. Combination of chemistry and metal work, combined with physics, medicine, and spirituality
B. Same thing as chemistry
C. A made-up science
D. Solid liquid and gas
A particular soil is a mixture of sand, dead plant matter, water and air. The states of matter in this mixture are
A. Solid and liquid only
B. liquid and gas only
C. Solid only
D. Solid, liquid and gas
C. interaction between matters.
Magnesium reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide. This is an example of....
A. structure of matter
B. composition of matter.
C. interaction between matters.
A. True
One of the first goals of alchemy was to find the "elixir of life"
A. True
B. False
C. a mixture is physically combined and can be physically separated while a substance is chemically bonded
What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture?
A. a substances are made of many different things while mixtures are just made of 1
B. a substance has one type of particle while a mixture has 2 or more types
C. a mixture is physically combined and can be physically separated while a substance is chemically bonded
D. a mixture is chemically bonded together while a substance is physically combined
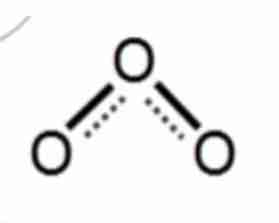
B. structure
The picture beside shows the __________of an ozone.
A. properties
B. structure
C. interaction of matter
B. Physical Chemistry
Which branch of chemistry combines chemistry with physics principles?
A. Organic chemistry
B. Physical chemistry
C. Inorganic chemistry
D. Biochemistry
B. To find the Philosopher's Stone, which was believed to turn base metals into gold
What was one of the primary goals of alchemy during the medieval period?
A. To discover the atomic structure of elements
B. To find the Philosopher's Stone, which was believed to turn base metals into gold
C. To develop modern chemical theories and principles
D. To create synthetic polymers for industrial use
A. Studying chemical processes in living organisms
What is the primary focus of biochemistry?
A. Studying chemical processes in living organisms
B. Analyzing chemical components
C. Exploring energy and chemical reactions D. Developing new materials
A. Mercury and lead
Which of the following substances were alchemists historically trying to transform into gold?
A. Mercury and lead
B. Carbon and sulfur
C. Hydrogen and oxygen
D. Sodium and potassium
B. Organic chemistry
Which branch of chemistry is responsible for studying compounds containing carbon-hydrogen bonds?
A. Inorganic chemistry
B. Physical chemistry
C. Organic chemistry
D. Analytical chemistry
C. Arabic; "alchemy" meaning "the art of the transmutation of base metals"
The term "alchemy" originates from which language, and what was its initial meaning?
A. Latin; "alchemy" meaning "the art of transformation"
B. Greek; "alchemy" meaning "the art of gold-making"
C. Arabic; "alchemy" meaning "the art of the transmutation of base metals"
D. Sanskrit; "alchemy" meaning "the study of ancient minerals"
C. properties, matter
Chemistry is the study of the _____________ and behaviors of ______________.
A. size, mass
B. energy, matter
C. properties, matter
D. characteristics, life
D. gas
The state of matter in which a substance does not have a definite shape or volume.
A. liquid
B. solid
C. compound
D. gas
12. J. J. Thomson - K. plum-pudding model
13. James Chadwick - E. neutron
14. Neil Bohr - J. solar system model
15. Roger Bacon - A. inductive method
16. Ernest Rutherford - B. nucleus and proton
17. Robert Boyle - H. PV relationship I gases
18. Democritus - D. atomos
19. Amedeo Avogadro - G. mole concept
Answer the following numbers:
