Second Law of Thermodynamics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What happens with the internal energy when a system is returned to its initial state
There is no change
What is a heat engine
A device that converts heat into work
Over the whole cycle what does a heat engine do with heat energy
Absorb and reject
How does a Carnot cycle operate
Reversibly between two temperatures
Draw the Carnot cycle diagram
x
Draw the Carnot cycle graph
x
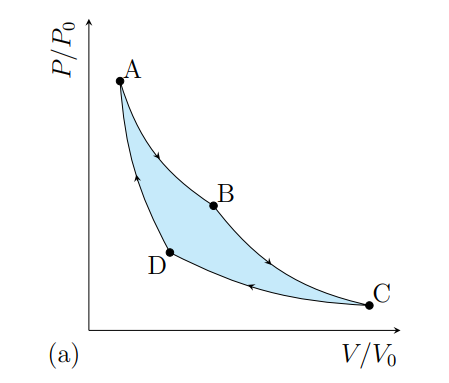
What happens from A to B
The gas expands isothermally at T1 and absorbs heat Q2
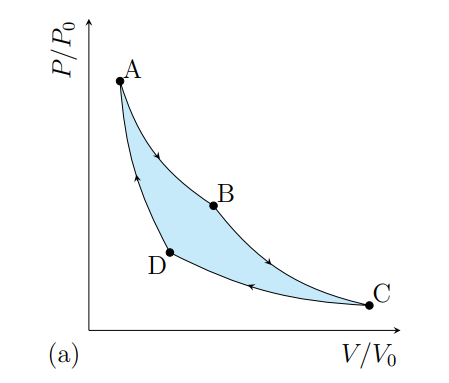
What happens from B to C
The gas cools adiabatically from T1 to T2
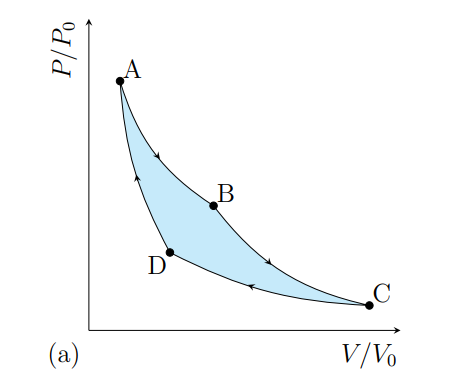
What happens from C to D
The gas contracts isothermally and T2 and rejects heat Q2
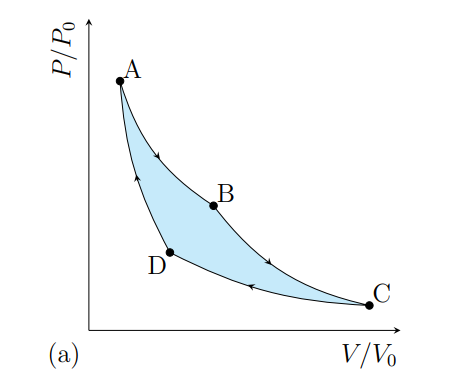
What happens from D to A
The gas heat adiabatically from t2 to t1
What processes does a Carnot cycle have
Two reversible isothermal and two revisable adiabatic
What can the Carnot cycle be reversed to make happen
Extract heat from Q2 at T2 and reject heat Q1 at T1
What is a heat pump/refrigerator
A device that uses work to continuously transfer heat from a hotter reservoir
What is the working substance in a refrigerator called
Refrigerant
What is need to extract heat from a colder reservoir to a hotter reservoir
Work
What coefficient of performance does a Carnot cycle yield
Ideal
What is Kelvin Statement
It is not possible to construct a thermodynamic system whose net effort is the complete conversion of heat into work
What is Clausius statement
No thermodynamic system is process is possible whose net effect is the transfer of heat from a colder body to a hotter body
What can the 2nd Law be defined by
Kelvin or Clausius statement
What is Carnot’s Theorem
No heat engine operating between two thermal reservoirs can be more efficient that a Carnot engine operating between the same reservoirs
What model is used for real engines
Air Standard
What is the working fluid of an air standard engine and what is it taken as
Air taken as an ideal gas
What is the Otto cycle
Simplified real petrol engine
What is the Otto Cycle made up of
Two adiabatic processes linked with two isochoric processes combined with a fluid injection and exhaust stoke
Draw an Otto Cycle
x
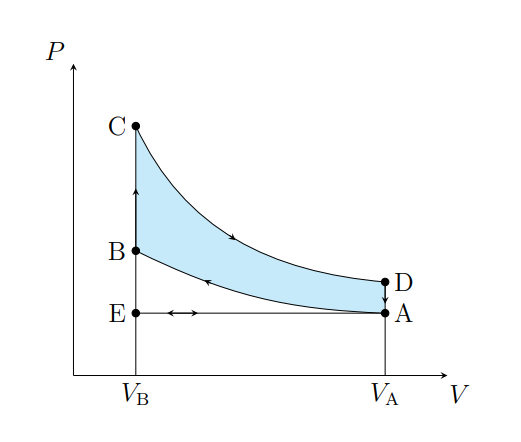
What Cycle is this
Otto
What is happening from E to A
Air is drawn into the piston chamber isobarically
What does A to E model
Fuel intake stroke of a real petrol engine
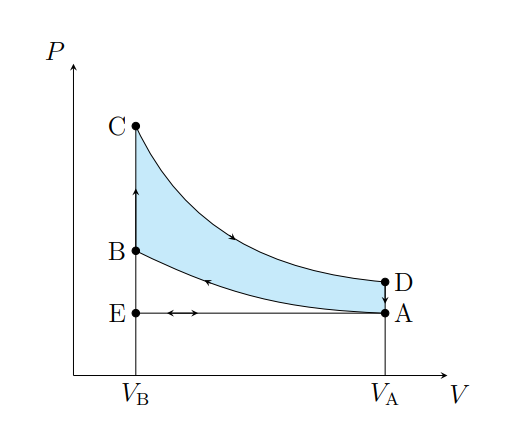
What does A to B show
Air is compressed adiabatically and heats from T1 to T2
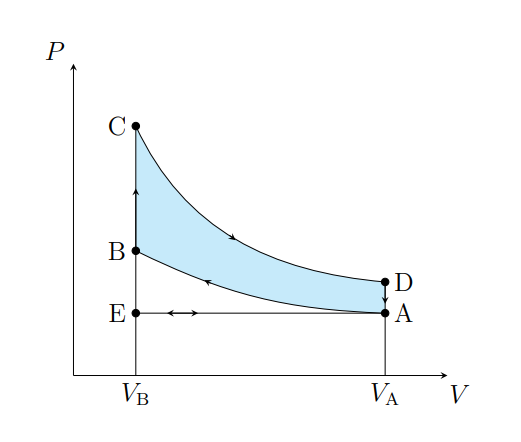
What is A does B model
Fuel compression stroke
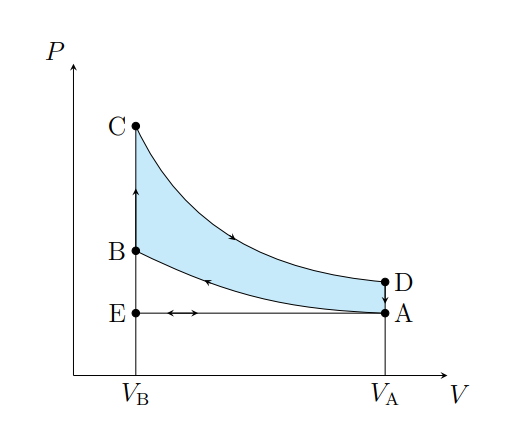
What does B to C show
The pressure of the air increases isochorically due to heat entering the system
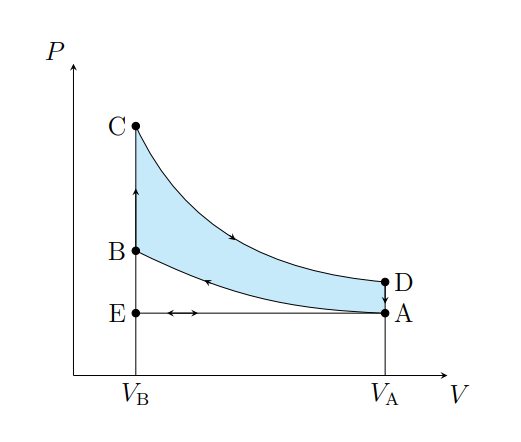
What does B to C model
Fuel ignition stage
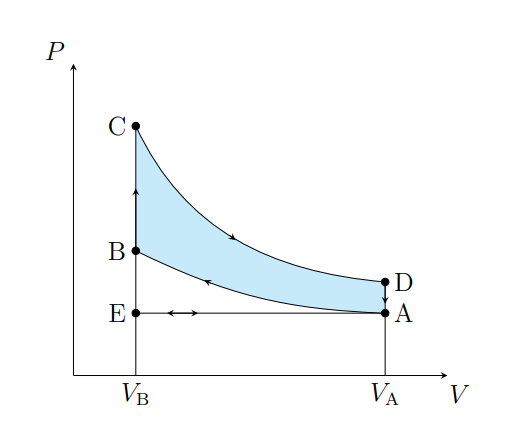
What does C to D show
The air expanding adiabatically and cools
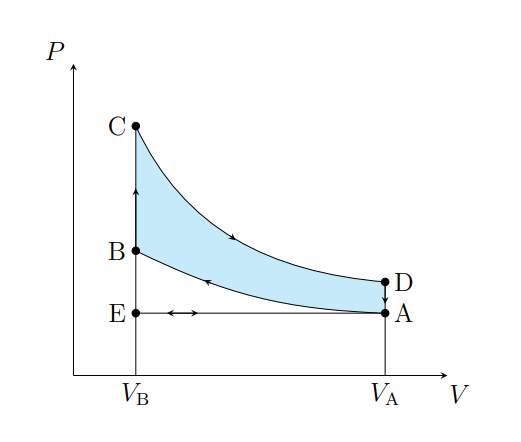
What does C to D model
Power stroke
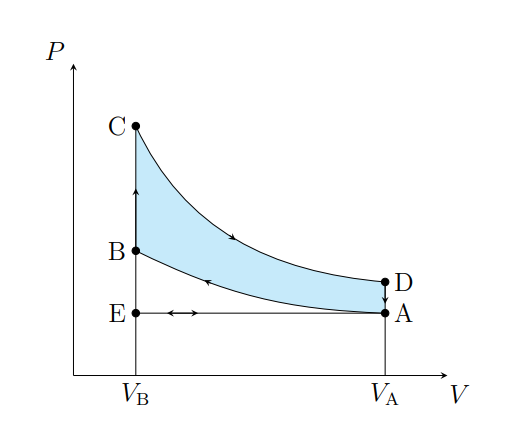
What does D to A show
The pressure of the air decreasing isochorically
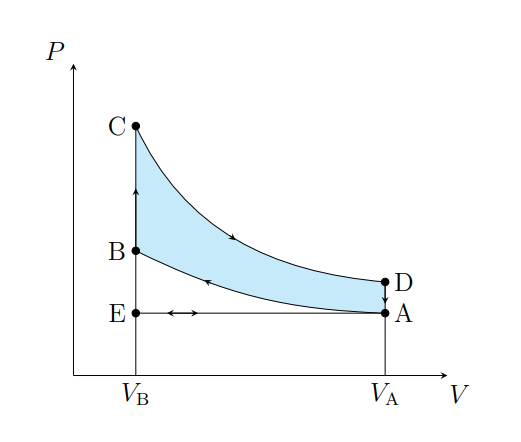
What does D to A model
Valve exhaust
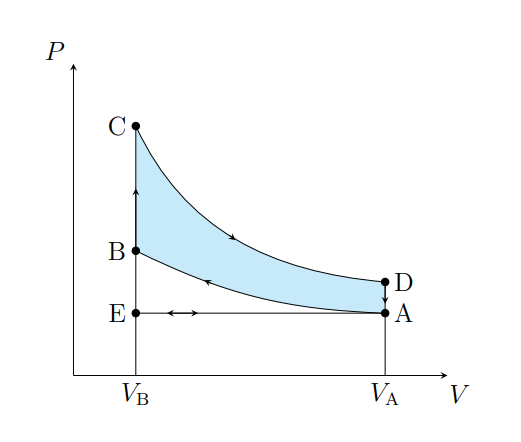
What is A to E
Air expelled from the piston chamber isobarically
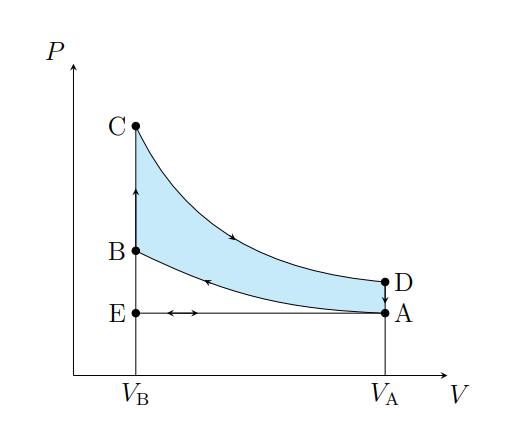
What does A to E model
Exhaust stroke
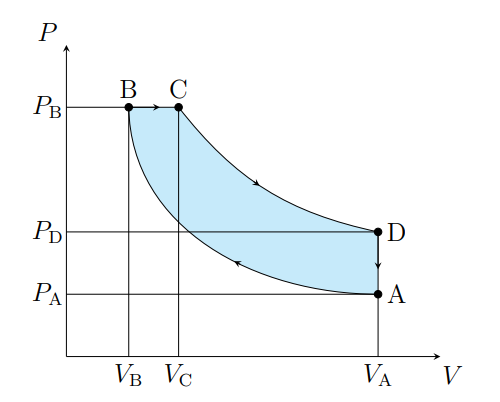
What is the diesel cycle made up of
Two reversible adiabatics an isobar and isochore
What is this cycle
Diesel
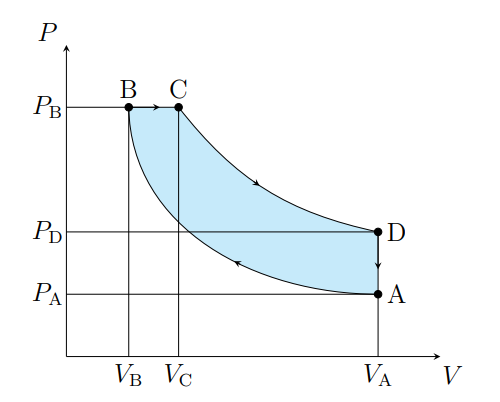
Draw a diesel cycle
x
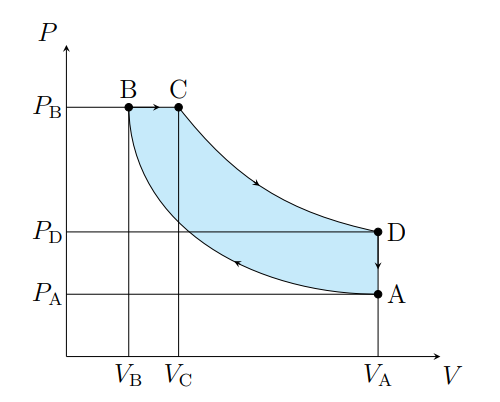
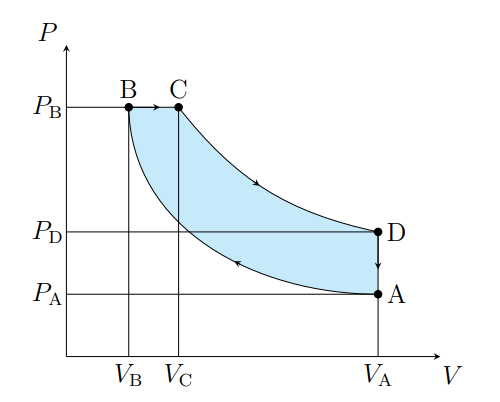
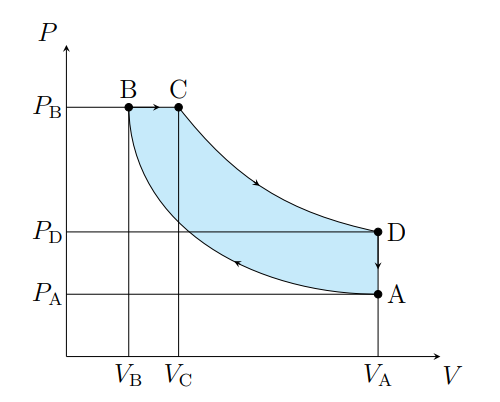
What does A to B show
The air is compressed adiabatically and heats
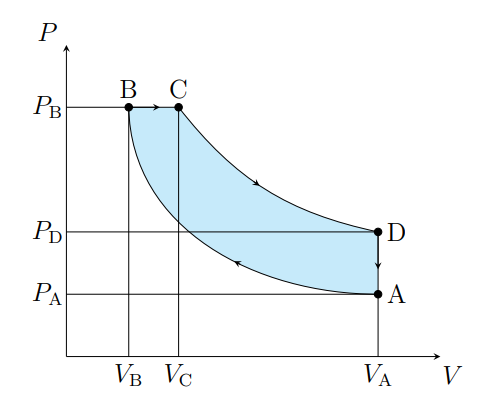
What is A to B modeled as
Compression stoke
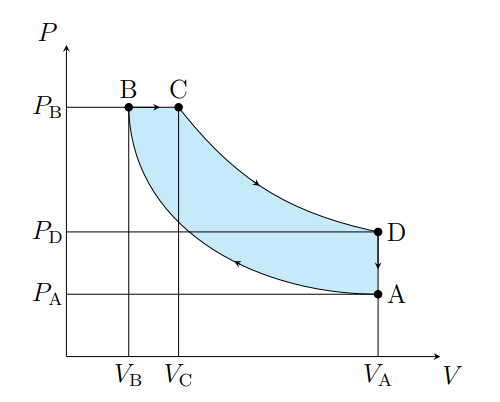
What does B to C show
The volume increases isobarically due to heat entering the system
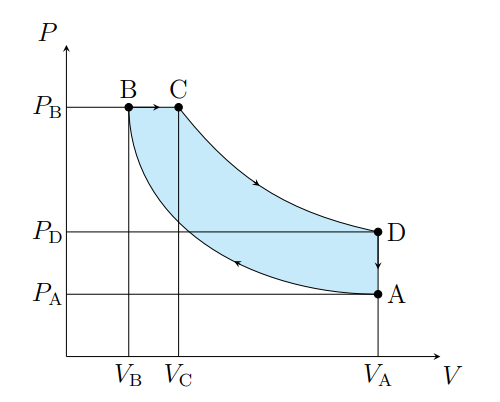
What is B to C modeled as
Fuel ignition
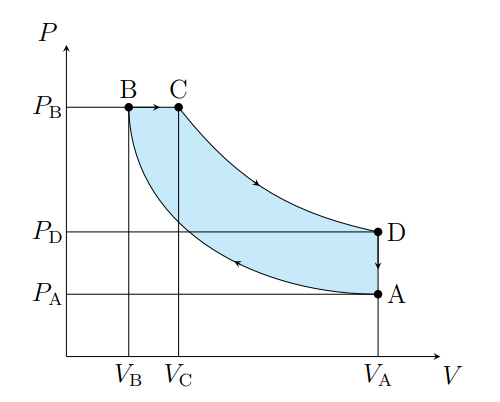
What does C to D show
Air expanding adiabatically and cooling
What is C to D modeled as
Power stoke
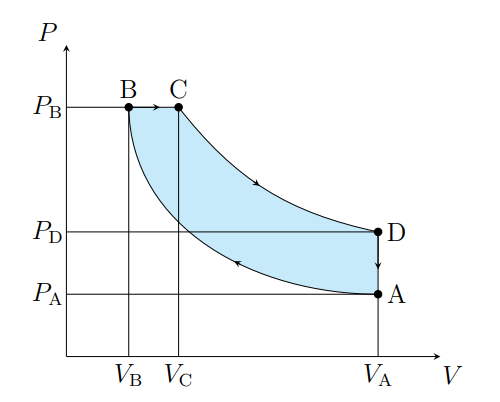
What does D to A show
Pressure decreasing isochorically due to heat leaving
What does D to A model
Valve exhaust
What do Stirling engines use as heat
Two thermal reservoirs
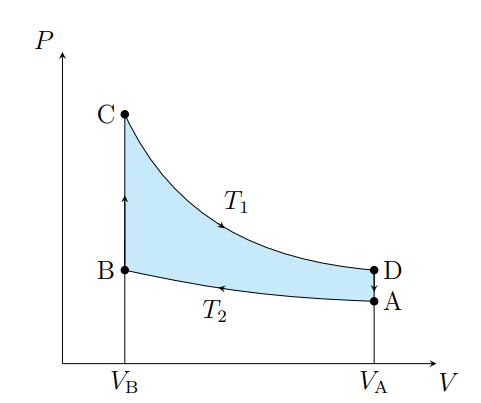
What is this graph
Stirling
Draw a Stirling Graph
x
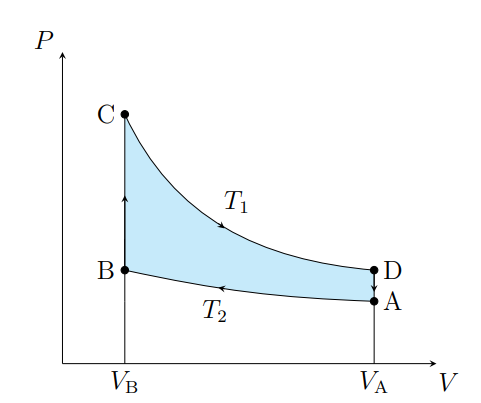
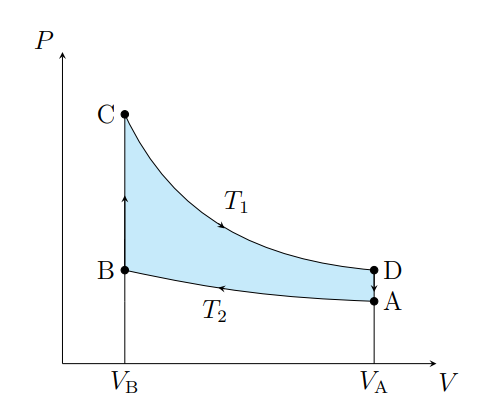
What are the cycles in a Stirling cycle
Two isotherms and two isochores
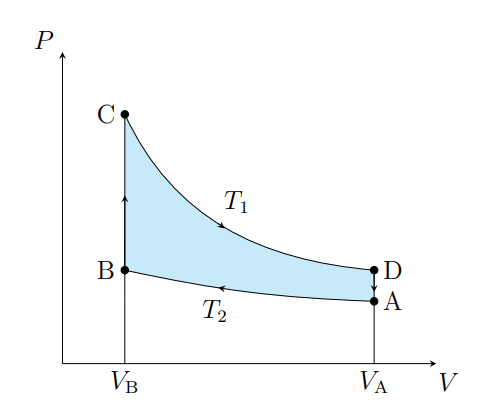
What happens from A to B
The air contracts isothermally and rejects Q2
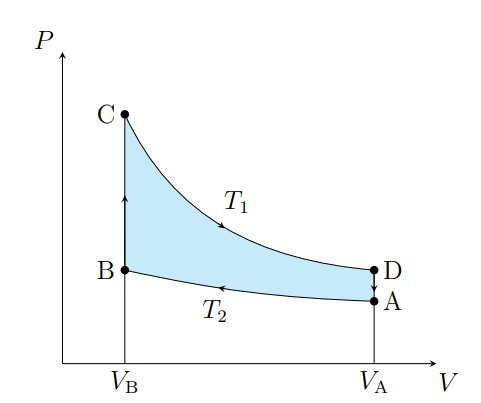
What happens from B to C
Air absorbs the regenerator heat and the temperature increases isochorically
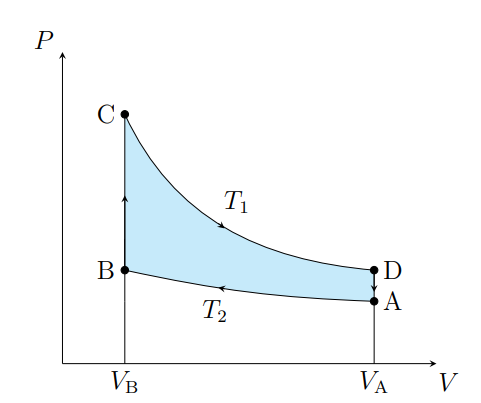
What happens from C to D
The air expands isothermally and absorbs Q1 from the surroundings
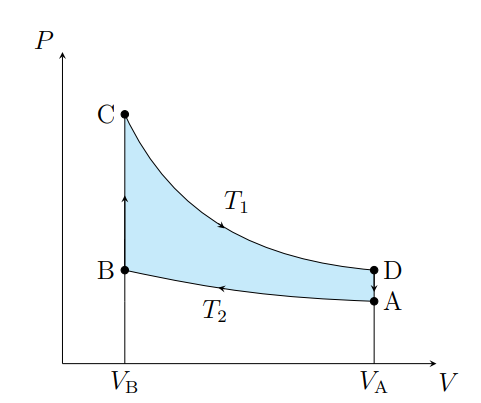
What happens from D to A
The air deposits the regenerator heat and its temperature decreases
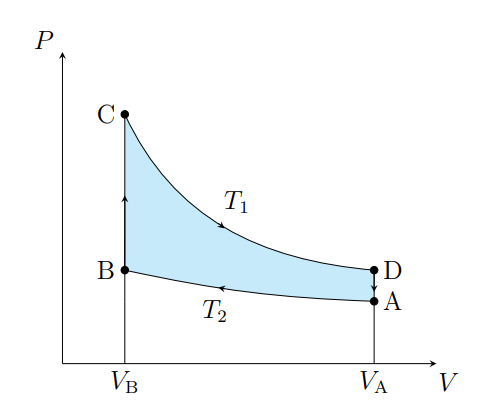
What is an ideal Stirling cycle
A carnot