geography - river
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
3 major stores where water on earth is held
atmosphere, ocean & land
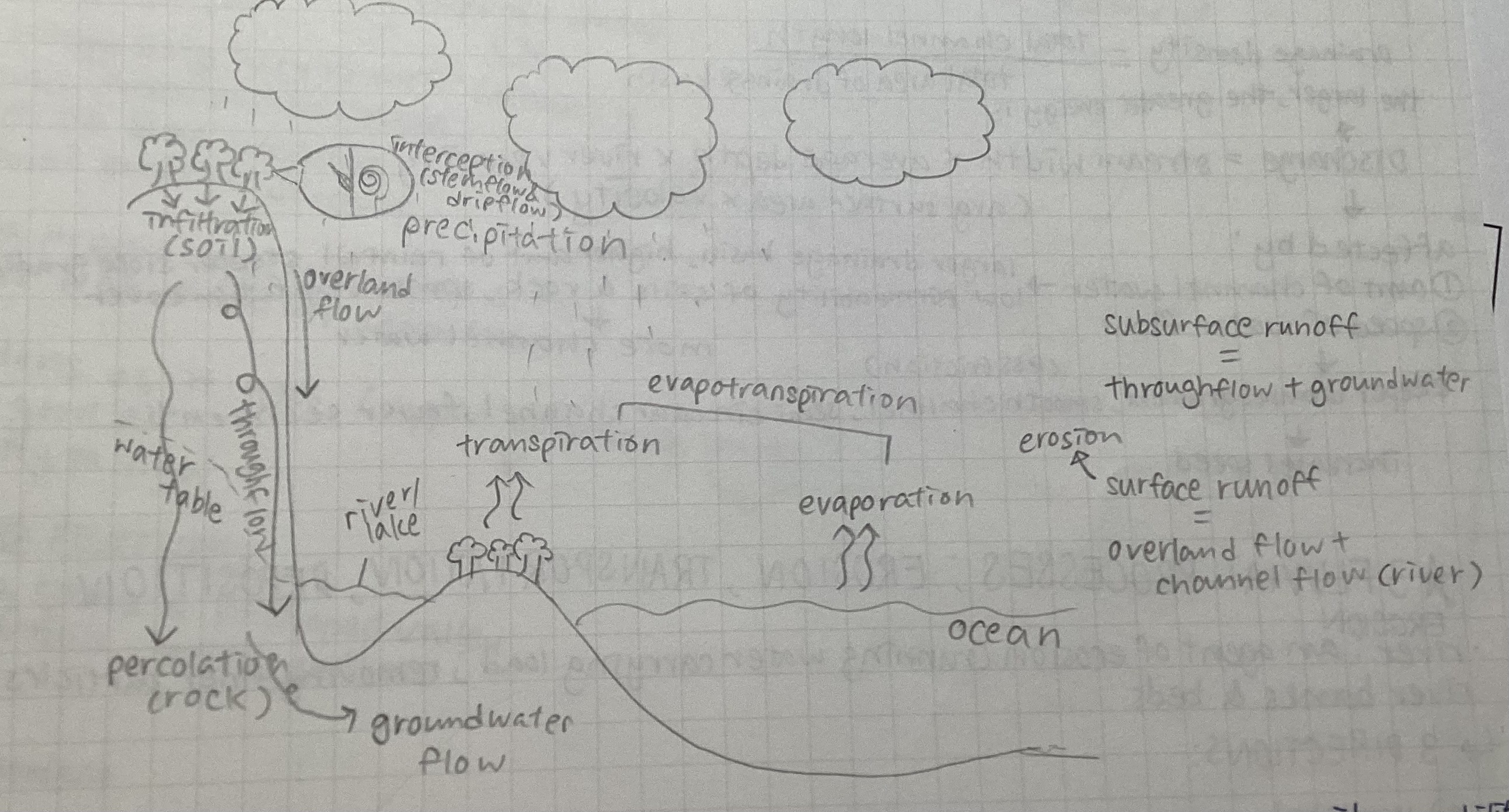
water cycle
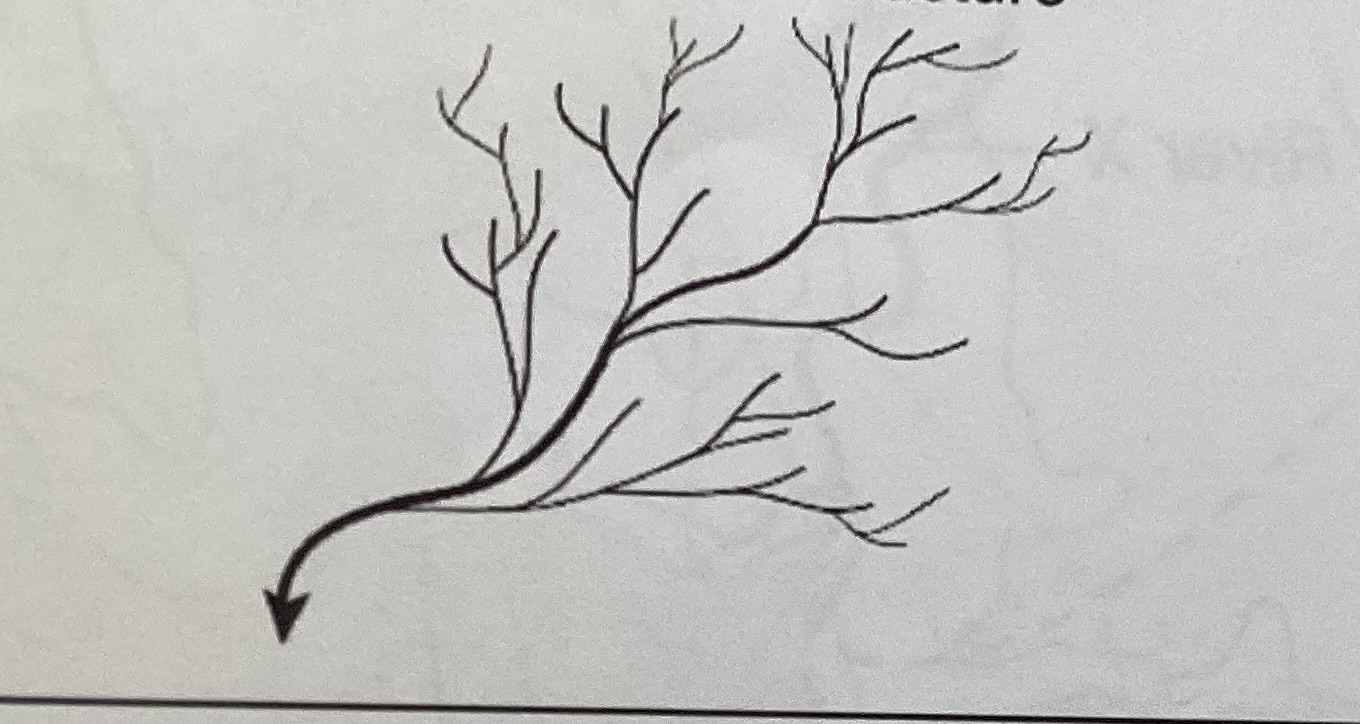
dendritic pattern
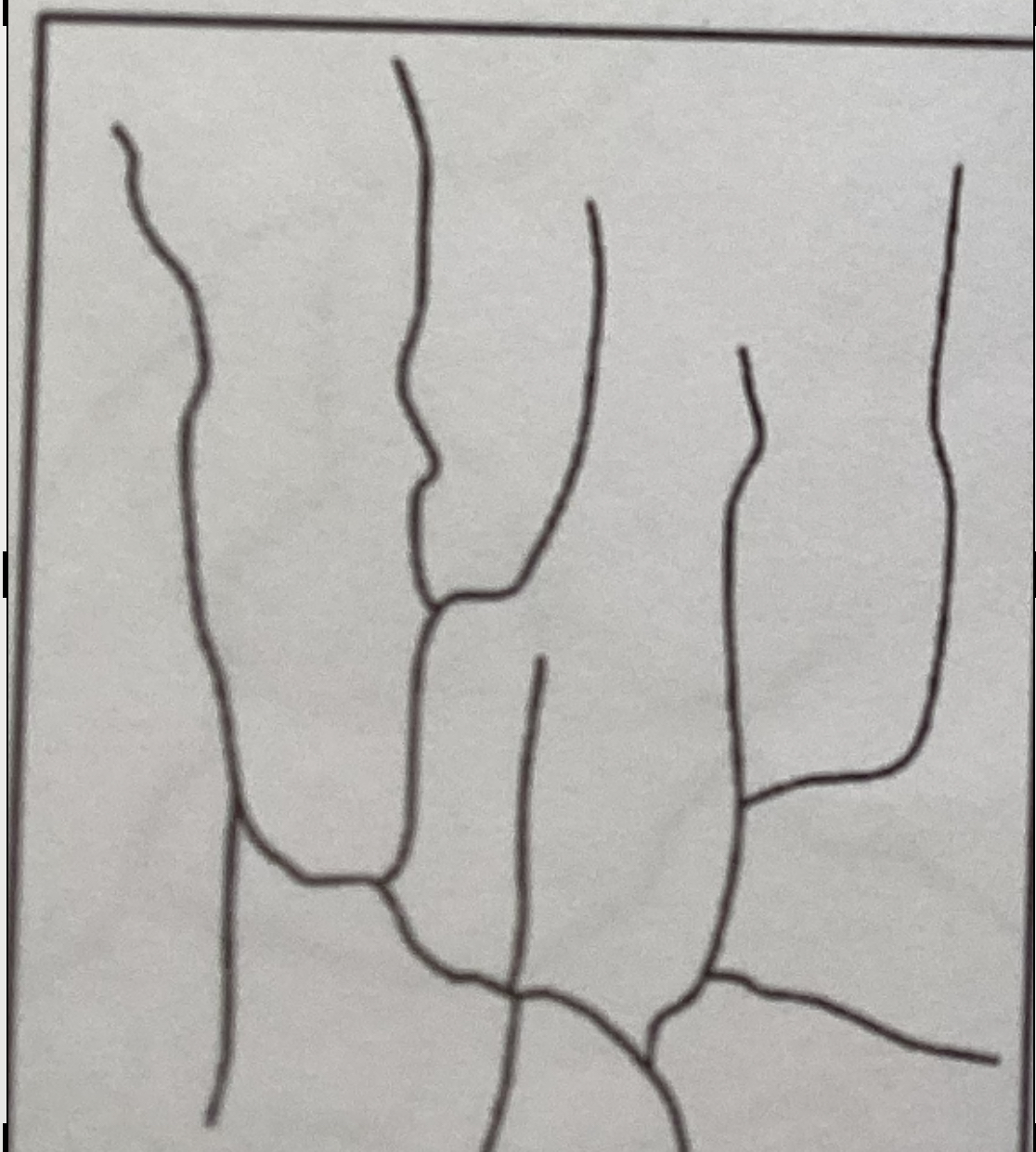
trellis pattern
source of river
where a river starts, normally high up in the mountains where rain collects or a spring is found
tributary
a small stream that flows into the main channel
confluence
where two streams meet
watershed
the boundary of a drainage basin. it is an imaginary line joining the high grounds (ridges & spurs) separating adjacent drainage basins
mouth of a river
where a river enters the sea
distributary
a stream that branches off and flows away from mainstream channel
1st order stream
river source, smallest stream, no tributaries
2nd order stream
when 2 1st order streams join together
3rd order stream
when 2 2nd order streams join together
drainage density
total channel length/total area of drainage basin
discharge calculation formula
stream width x average depth x river velocity
typical conditions for high drainage density
high annual rainfall
steep basin slope
impermeable rock layer at the surface
bare land surface
2 factors that affect the energy of a river
amount of channel water & speed of water flow
3 fluvial processes in a river channel
erosion, transportation, deposition
fluvial erosion
running water carrying load to remove fine particles from the river bank or beds
vertical erosion
deepens the river channel, occurs at upper course
lateral erosion
widens the river channel , occurs in middle and lower courses
headward erosion
lengthens the river, occurs at river source
4 types of fluvial erosion
solution
attrition
abrasion
hydraulic action
transportation
downstream movement of river load
how deforestation affects the rate of fluvial erosion
less vegetation cover → more overland flow → more rocks & stones washed into river → more tools for erosion
4 types of transportation
suspension
traction
saltation
solution
fluvial deposition
when a river loses energy, it drops its load. this load will be deposited on the river bed as sediment
v-shaped valley
vertical erosion is active at the upper course. over time, a narrow steep sided V-shaped valley is formed
interlocking spurs
continuing from the formation of v-shaped valleys, on the other hand, the river water is unable to remove the obstacles (spurs) and it flows side to side around the obstacles forming interlocking spurs
rapids
when a land of more resistant and less resistant rock lies horizontally, vertically, or obliquely across a river, erosion (abrasion) will be concentrated at the less resistant rock. small steps develop due to fluvial erosion, forming rapids
waterfall
when there is continuous erosion (abrasion) on less resistant rock, great differences are created in water level between the hard and soft rocks, forming a waterfall
gorges
the strong hydraulic action enlarges the notch at the back of the waterfall. without support, the overhanging rock collapses and when the process repeats overtime, the waterfall recedes. this forms a well-developed gorge, a valley with narrow, deep and very steep side channels
plunge pools
once waterfalls form, the force of running water can undercut the cracks at the base and back of the waterfall, forming a plunge pool by hydraulic action
example of gorges
sanxia in china
examples of plunge pools
bride’s pool in tai po
pot holes
when a river flows over an uneven surface, it causes turbulence in the water. the turbulence causes rocks or pebbles to drill holes on the river bed, forming potholes