3.5 Genetic Modification and Biotechnology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
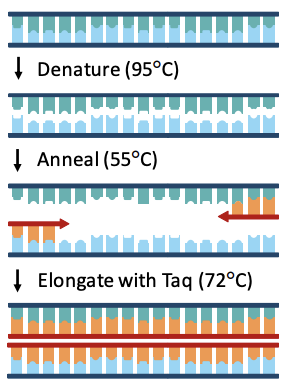
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
**Artificial** method of replication used to rapidly **amplify DNA sequences.** Involves three key steps (which are repeated):
* **Denaturation** – Heat separates strands (no helicase).
* **Annealing** – Primers designate copying sequence.
* **Elongation** – Taq polymerase copies the sequence
* **Denaturation** – Heat separates strands (no helicase).
* **Annealing** – Primers designate copying sequence.
* **Elongation** – Taq polymerase copies the sequence
2
New cards
Gel Electrophoresis
Separates **proteins** or **fragments** of DNA according to their size.
* DNA fragments are placed in an agarose gel.
* Proteins are placed in a polyacrylamide gel.
* DNA fragments are placed in an agarose gel.
* Proteins are placed in a polyacrylamide gel.
3
New cards
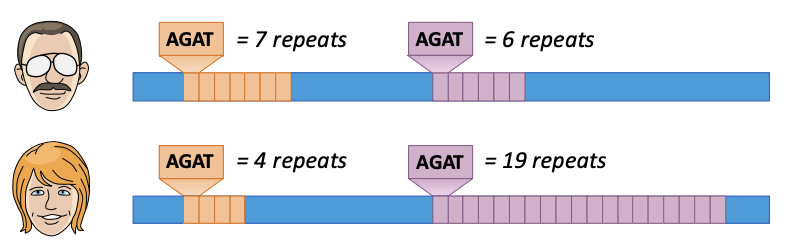
DNA Profiling
Comparison of DNA
4
New cards
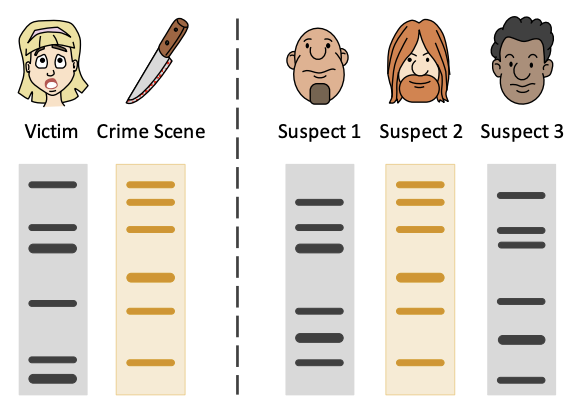
DNA Profiling: Forensics
* DNA sample collected.
* STR loci selected.
* **PCR amplification.**
* **Gel electrophoresis.**
\
Suspect and sample should be a complete match
* STR loci selected.
* **PCR amplification.**
* **Gel electrophoresis.**
\
Suspect and sample should be a complete match
5
New cards
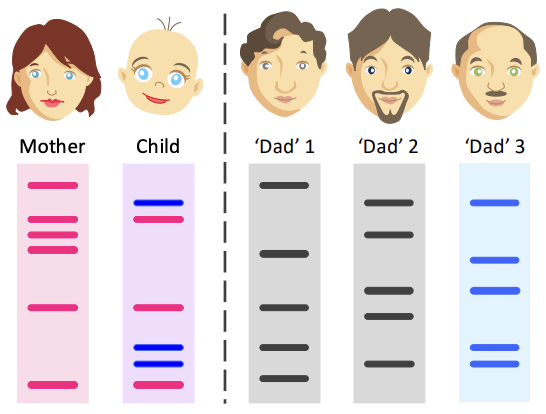
DNA Profiling: Paternity
Children inherit DNA from **both parents**, all of the **child’s bands** should match to either the mother or father (i.e. **combination of parents**)
6
New cards
Gene Transfer
Process by which genes from one organism are inserted into another organism (i.e. horizontal gene transfer).
* Genetic code is *universal.*
* Genetic code is *universal.*
7
New cards
What is a **vector**?
Molecular **vehicle** used to artificially **carry genetic material into a host cell.**
* Plasmids: **Circular DNA** molecules capable of **autonomous gene expression.**
* Viruses: **Inject** their **genetic material** directly into **host cells.**
* Plasmids: **Circular DNA** molecules capable of **autonomous gene expression.**
* Viruses: **Inject** their **genetic material** directly into **host cells.**

8
New cards
Gene transfer key steps
**Four** key steps:
* **DNA extraction** – **Gene** of interest **and vector** (*virus or plasmid*) are ==**isolated.**==
* **Digestion** – Gene and vector are **cut** with restriction endonucleases.
* **Ligation** – **Gene** of interest is **placed into the vector.**
* **Transformation** – Recombinant vector **inserted into host cells.**
* **DNA extraction** – **Gene** of interest **and vector** (*virus or plasmid*) are ==**isolated.**==
* **Digestion** – Gene and vector are **cut** with restriction endonucleases.
* **Ligation** – **Gene** of interest is **placed into the vector.**
* **Transformation** – Recombinant vector **inserted into host cells.**
9
New cards
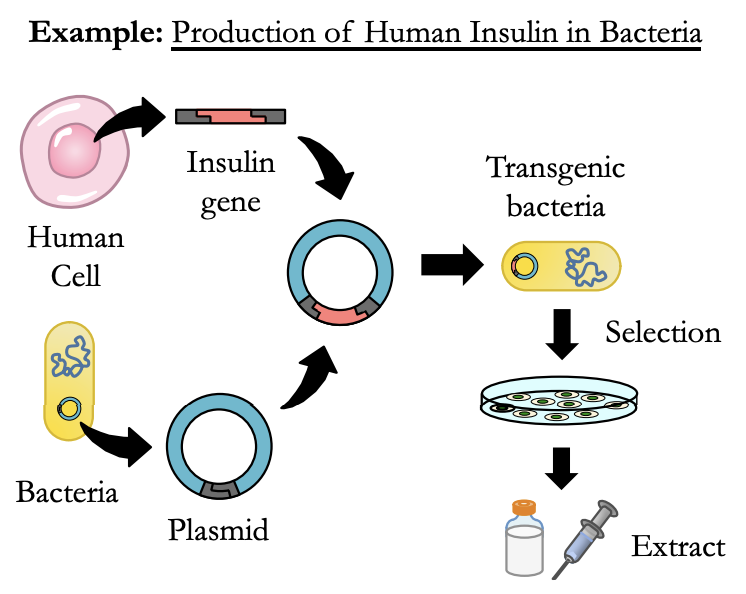
Step 1: DNA Extraction
* Gene of interest **isolated** from organism.
* Gene is amplified using **PCR** (along with a plasmid).
* Gene is amplified using **PCR** (along with a plasmid).
10
New cards
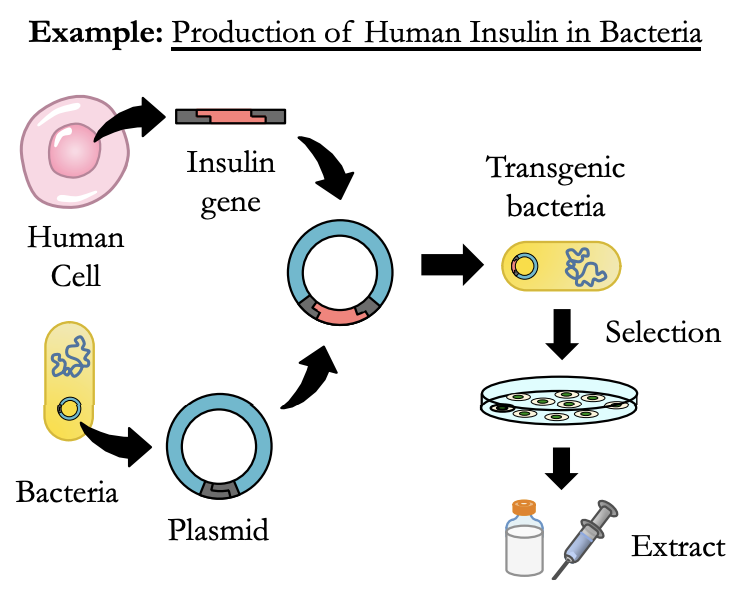
Step 2: Digestion and Ligation
* **Plasmid** and **gene** **cut** with a specific restriction enzyme.
* Gene is spliced into plasmid vector by **DNA ligase**.
* Gene is spliced into plasmid vector by **DNA ligase**.
11
New cards
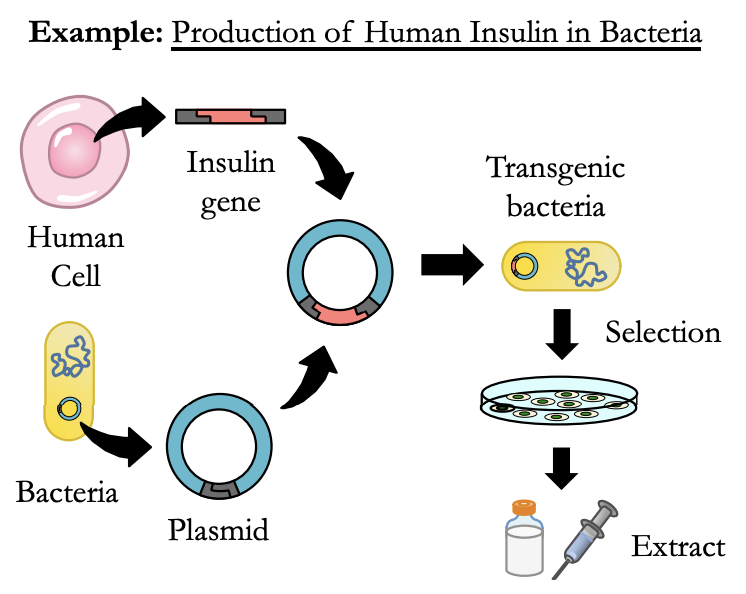
Step 3: Transformation and Expression
* **Recombinant plasmid** is **inserted into a host cell.**
* Antibiotic selection may be used to select for successful transgenic cells (if plasmid has an antibiotic resistance gene).
* **Transgenic cells express new protein** (for extraction / use)
* Antibiotic selection may be used to select for successful transgenic cells (if plasmid has an antibiotic resistance gene).
* **Transgenic cells express new protein** (for extraction / use)
12
New cards
Clones
Groups of **genetically identical** organisms (derived from **single parent cells**).
* **Naturally** via ==__**a**__sexual reproduction.==
* **Artificially** via ==embryonic division== or **somatic** cell nuclear transfer.
* **Naturally** via ==__**a**__sexual reproduction.==
* **Artificially** via ==embryonic division== or **somatic** cell nuclear transfer.
13
New cards
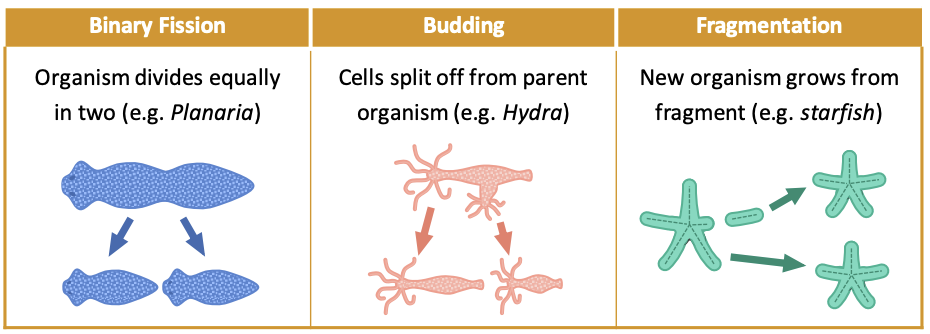
Natural Cloning: Animals
Certain species of animals can clone **themselves**.
1. Binary fission: **divides** **equally** in two.
2. Budding: cells **split off** from parent organism.
3. Fragmentation: new organism **grows** from fragment.
1. Binary fission: **divides** **equally** in two.
2. Budding: cells **split off** from parent organism.
3. Fragmentation: new organism **grows** from fragment.
14
New cards
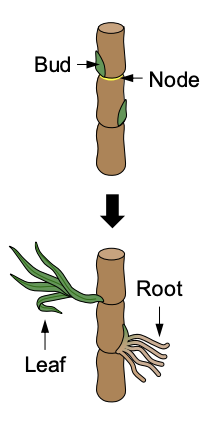
Natural Cloning: Plants
Plants have the capacity for **vegetative propagation**, small parts of the plant **grow independently.**
* **Stem cuttings** are separated portions of plant stems that can **regrow into new, independent clones.**
* **Stem cuttings** are separated portions of plant stems that can **regrow into new, independent clones.**
15
New cards
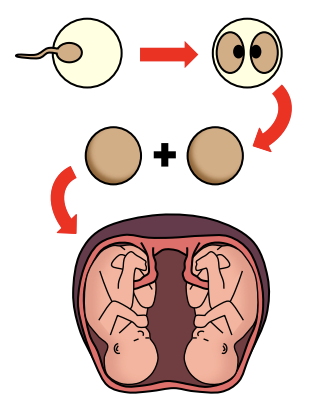
Natural Cloning: Humans
Identical twins (**monozygotic**) are created when a **fertilised egg splits into two** separate cell groups
16
New cards
Artificial Cloning
Using differentiated adult tissue called **somatic cell nuclear transfer (**@@**SCNT**@@**)**
* **Reproductive** cloning – Produces **new** __**organisms**__ (%%repopulate%% endangered species)
* **Therapeutic** cloning – Produces **new** __**tissue**__ (%%transplantations / disease treatments%%)
* **Reproductive** cloning – Produces **new** __**organisms**__ (%%repopulate%% endangered species)
* **Therapeutic** cloning – Produces **new** __**tissue**__ (%%transplantations / disease treatments%%)
17
New cards
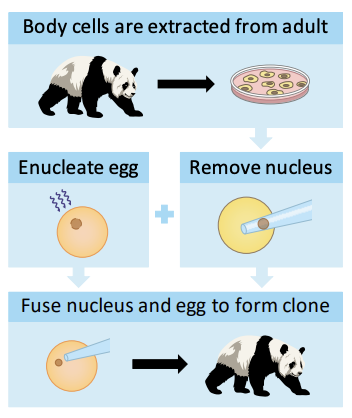
Artificial Cloning: SCNT
Cloning **embryos** from **differentiated adult tissues:**
* Nucleus is removed from adult body cell.
* Egg cell nucleus destroyed by UV radiation.
* Body cell nucleus fused to enucleated egg.
* Electrical current stimulates egg to divide.
* Developing embryo implanted in surrogate.
* Embryo develops into a cloned animal.
* Nucleus is removed from adult body cell.
* Egg cell nucleus destroyed by UV radiation.
* Body cell nucleus fused to enucleated egg.
* Electrical current stimulates egg to divide.
* Developing embryo implanted in surrogate.
* Embryo develops into a cloned animal.