Kidney Transplant Basics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
survival of transplant v dialysis
-transplant > dialysis
-QOL transplant > dialysis
-cost transplant > dialysis
earlier transplant =
-better survival
waitlist eligibility in the US
-on dialysis or not on dialysis but GFR/eGFR </= 20 AND no contraindications to transplant
contradictions to transplant
-absolute (make transplant dangerous or futile): active malignancy, active infection, contraindication to surgery, non-kidney organ failure (and not listed for dual organ transplant) or other condition with very short life expectancy
-relative (subjective and contribute to disparities): active substance abuse, lack of insurance coverage, inadequate support, medical nonadherence, severe/uncontrolled psychiatric illness, condition that will markedly reduce allograft longevity
getting to transplant
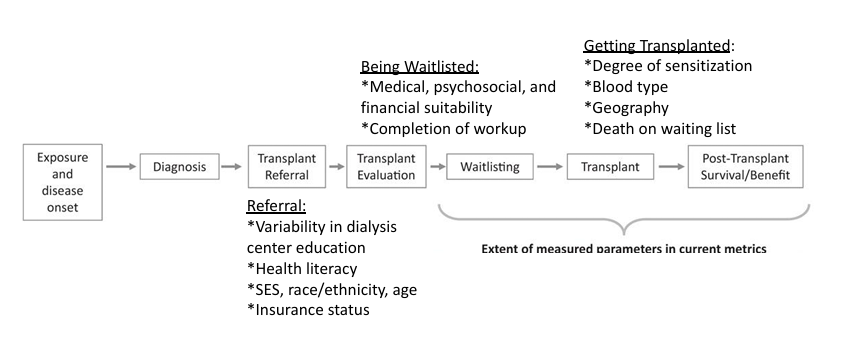
disparities in referral/waitlisting
-racial minority
-lower SES
-lower educational attainment
-non-English speaking
-female
-obesity
-distance from transplant center
assigning waitlist priority
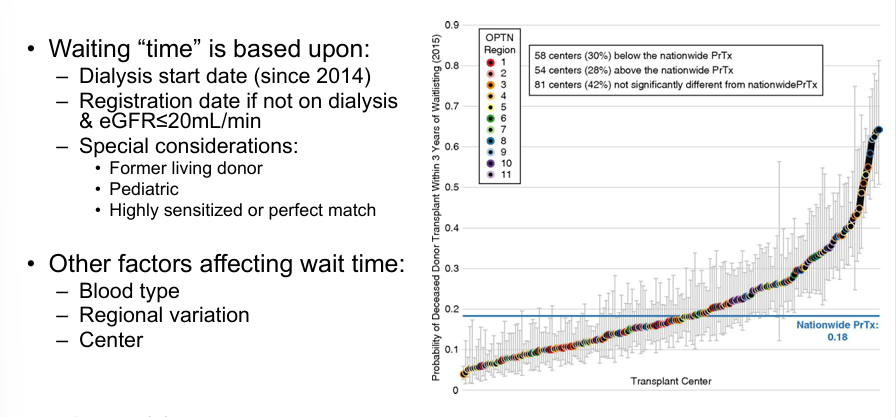
organ-recipient longevity matching

kidney allocation
-CPRA: calculated panel reactive antibodies
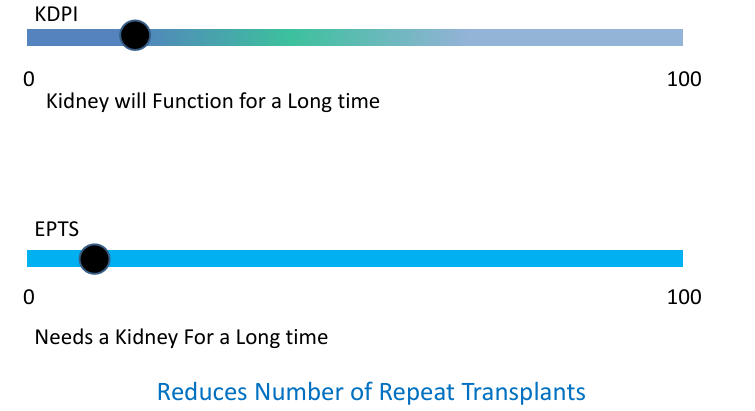
-KDPI: kidney donor profile index; estimated how long a given kidney may function once transplanted
-EPTS: estimated post transplant survival score; estimates how long a given candidate is likely to benefit from a kidney
kidney donor profile index
-medical match: age/height/weight/ethnicity, how the donor died, high bp/diabetes/hep C, donor’s creatinine
-time waiting
-distance between hospitals
KDPI and EPTS
-pediatric recipients <18 do not receive an EPTS score
-pediatric candidates have 1st offer <KDPI 35
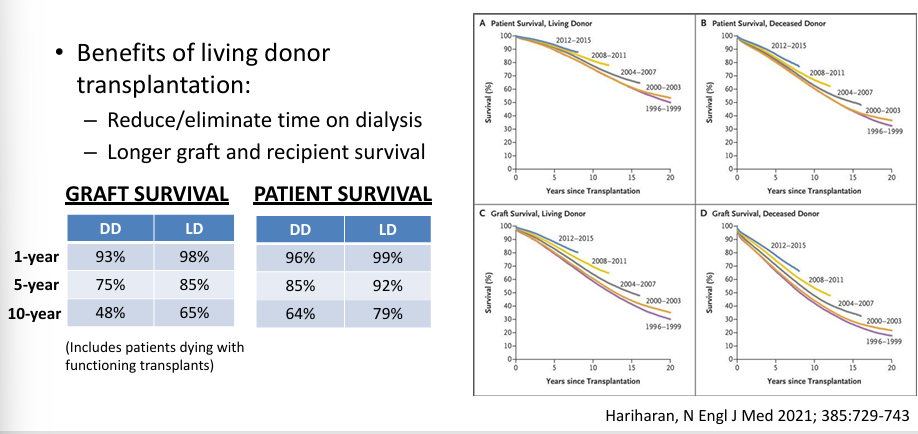
donor source- living or deceased
what is a “mismatch”?
-ABO blood group antigens- “ABO compatible”
-HLA antigen mismatch: class I (HLA A, B- all nucleated cells), class II (HLA DR- APCs, B cells, endothelial cells, renal tubular epithelial cells)
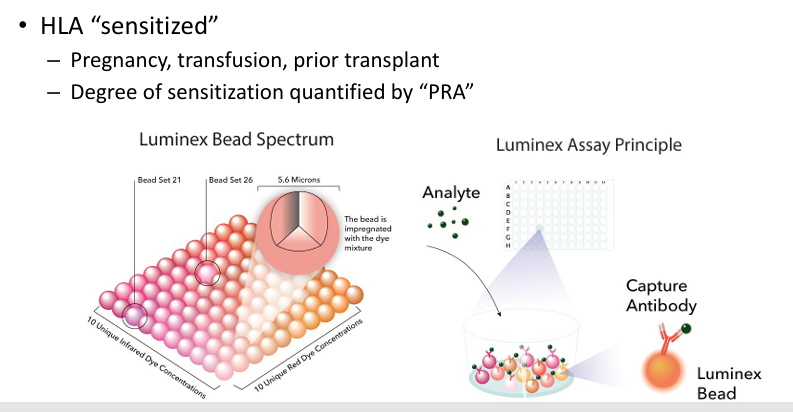
pre-transplant antibodies to HLA molecules
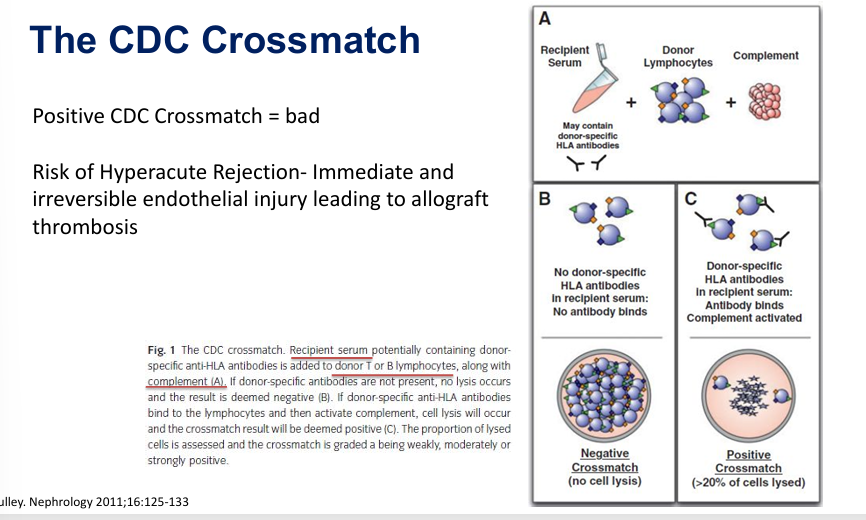
CDC crossmatch
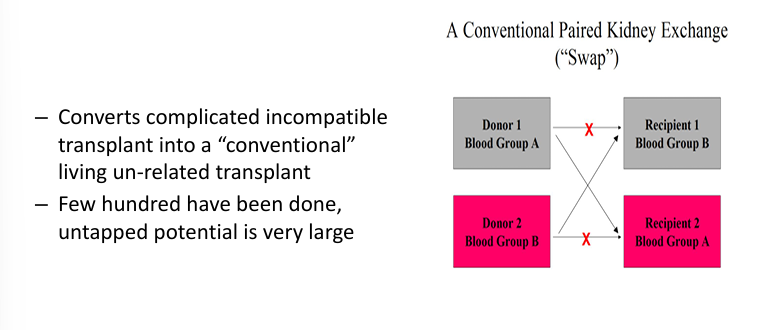
increasing live donor kidney transplants- paired kidney exchanges (“swaps”)
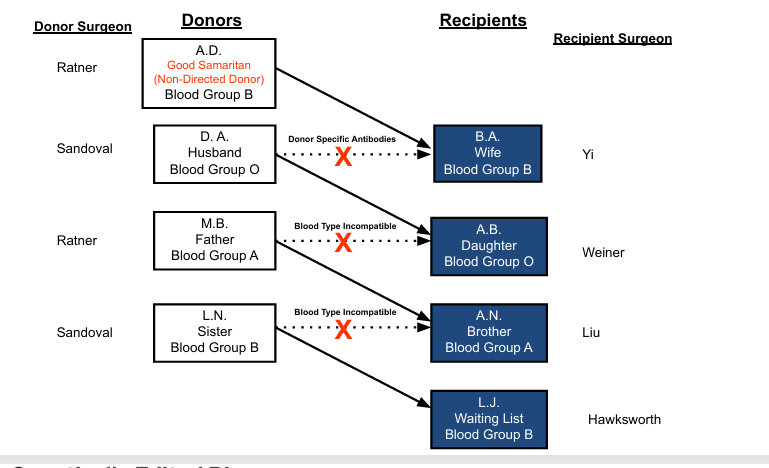
paired kidney exchanges- chains
current state of xenotransplant
-primarily done via FDA expanded access pathway, NOT via clinical trials- ethical concerns
kidney transplantation
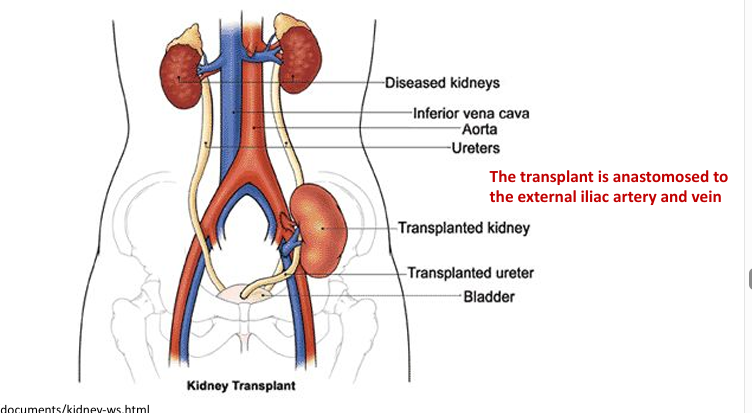
special cases
-dual kidney transplant
-en-bloc kidney transplant
-retransplant
induction immunosuppression
-intense immunosuppression given in first week after transplant
-can be lymphodepleting or non-lymphodepleting agent (plus corticosteroids)
-goal: to reduce risk of acute rejection
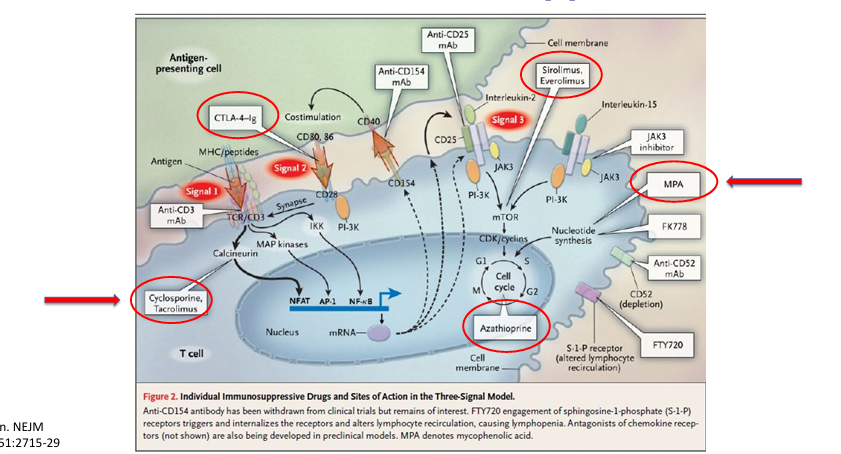
choice of maintenance immunosuppression

maintenance immunosuppression
allograft function and surveillance

kidney transplant rejection

hazards of chronic immunosuppression
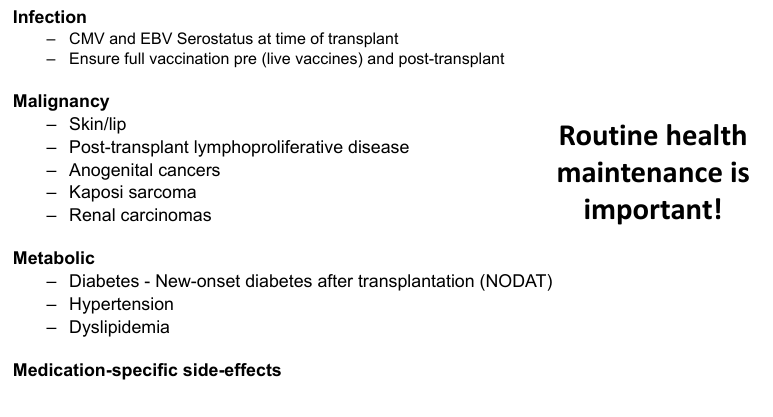
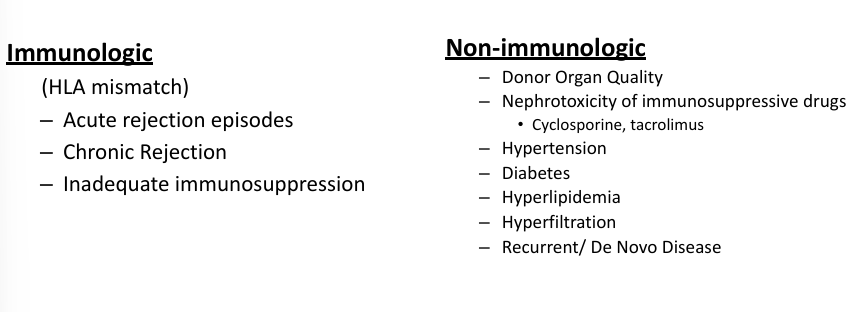
challenges to long-term success
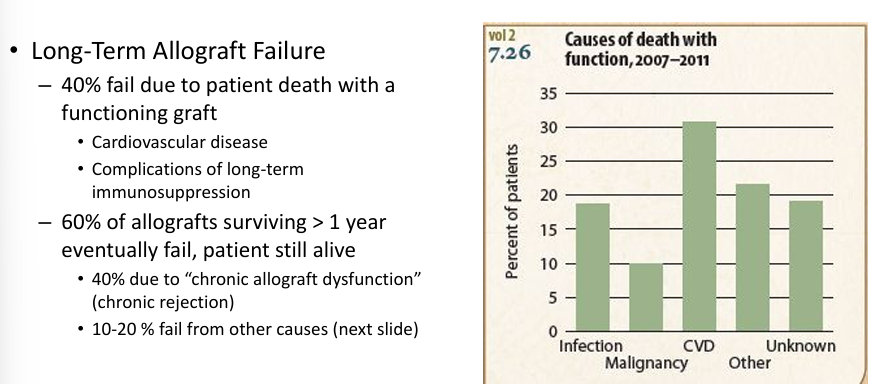
why do transplants fail long-term?
the future
-better understanding and diagnosis of the rejection process- understand mechanisms leading to allograft injury/protection at the molecular level
-new/improved immunosuppressive agents- reduce alloantibody production
-improved organ donation rates
-xeno-transplantation
-tolerance induction
-tissue/organ culture- generate/repair
take home points
