WHAP: Bullet Points 2 - Developments in Europe
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Shift in population Europe and China face in 12th and 13th century? What accounted for these shifts?
Both Europe and China faced rapid population growth during the 12th and 13th centuries
In 1200, China’s population exceeded Europe’s population by 2 to 1
In 1300, both China’s and Europe’s population increased by about 80 million
However, from 1100 to 1445, China’s population fell due to the Mongol conquest, while Europe’s population doubled
The Three-Field System
The three-field system replaced the two-field system
For the three-field system, farmers grew crops on two-thirds of their land each year, alternating wheat and rye with oats, barley, or legumes, but the third field was left fallow.
Why “God’s Wrath” strike most people as a better explanation for the Black Death
People in Europe weren’t aware that the cause of the Black Plague was their lack of sanitation, causing church leaders to gain power during this time.
The Chronology Table
13th Century
Environment
1200s - Widespread use of crossbows and windmills(envi)
Culture
1210s - Teutonic Knights, Franciscans, Dominicans
1225–1274 - Philosopher-monk Thomas Aquinas
Politics and Society
1200s Champagne fairs flourish
1204 Fourth Crusade
1215 Magna Carta issued
14th Century
Environment
1315–1317 Great Famine
1347–1351 Black Death
Politics and Society
1337 Start of Hundred Years’ War
1381 Wat Tyler’s Rebellion
15th Century
Environment
Culture
Politics and Society
Hanseatic League in 1241
The Hanseatic League was an economic and defensive alliance of the free towns in northern Germany
It was the most powerful in the fourteenth century
How changes in the textile industry help initiate change in European economics
Changes in the textile industry increased competition, which then promoted the spread of manufacturing and encouraged new specialties
Civic life of Jews in Europe from 1200-1450 and a trend that continued later in European history
Jews with manufacturing and business skills were welcomed in by commercial cities
However. despite protections by certain Christian princes and kings they endured violent religious persecutions or expulsions
Ex. In 1492, all jews were expelled by Spanish monarchs
Baptism was a trend of theirs that continue later on in the European history
How guilds bring economic changes in Europe? What Italian city rose to prominence and later become the center of the Renaissance?
Guilds brought together all craft specialists working in a particular trade to regulate business practices and set prices
They also trained apprentices and promoted members’ interests with the city government
Guilds protected the interests of families that already belonged to them but denied memberships to outsiders and Jews
The Great Western Schism (1378 & 1415)
The Great Western Schism was a division in the Latin Christian Church caused by rival popes
This crisis broke the pope’s ability to challenge the rising power of monarchs
Feudalism
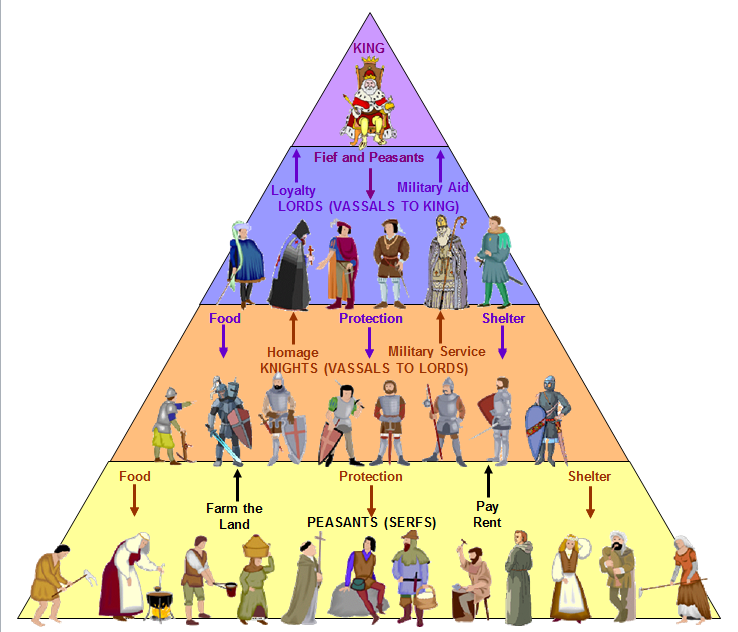
Describe the relationship between the Church and Monarchs in the 14th century
The relationship between the church and monarchs in the 14th century wasn’t friendly because both churches and monarchs seek to consolidate more power than the other.
How the Hundred Years’ War brought an end to traditional medieval methods of war
The 100 Years War grew out of a marriage alliance between Princess Isabella of France and King Edward II of England
The war introduced new war technologies:
Canons
Longbow
Due to the war, armies now depended on bowmen, pikemen, musketeers, and artillerymen rather than knights
Magna Carta in 1215
The Magna Carta was signed by King John. This was to subject all monarchs to yield to established laws and guaranteed the nobles’ hereditary rights
How new monarchies in France, England, and Spain represent a shift in power
The rise of new monarchies in France and England, centralized states with fixed “national” boundaries and stronger representative institutions
Ex. the English monarch consolidated control over territory within the British Isles
Ex. the French monarch consolidated control over powerful noble families in Burgundy and Brittany.
The Reconquest of Iberia
The Reconquest of Iberia was the taking back of territories of Portugal and Spain from the Muslims
What the Ottoman Soldiers called, and their military specialty?
The soldiers in the Ottoman empire were Janissaries. Their military specialty was fighting on foot with guns.
Scholasticism and the founder
Scholasticism is the synthesizing reason and faith. It was founded by Thomas Aquinas
Scholasticism upset many traditional thinkers
The Renaissance
The Renaissance was a transformative cultural, intellectual, and artistic movement
Greeks and Arabs manuscript were aquired like:
Works of literature by Plato and Aristotle
Greek treatises on medicine, mathematics, and geography, as well as scientific and philosophical writings by Muslim writers
Latin translations of Iranian philosopher Ibn Sina also known as Avicenna had great influence because of their sophisticated blend of Aristotelian and Islamic philosophy
Who developed the printing press in the 15th century
Johann Gutenberg