MICR5831 L2: Genetic Machinery Transcription 7/21/25
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What RNA is this?
-Carries genetic code instructions for how to create new proteins
mRNA (Messenger)
What RNA is this?
-Decodes mRNA into proteins
tRNA (Transfer)
What RNA is this?
-Subunits of ribosomes (machine that synthesise proteins)
rRNA (Ribosomal)
Which DNA strand is written 5' to 3'?
Coding/sense strand
Which DNA strand is read by RNAPol 3' to 5' from Promoter to Terminator?
Template strand
True or False: mRNA is transcribed and written in the 3' to 5' direction
False, it is 5' to 3'
What does mRNA translation begin with?
Ribosome recognizes RBS (binding site), aka Shine Dalgarno Sequence
How do tRNAs donate amino acids to the growing peptide?
Recognize three-base codon
What Transcription step is this?
-Initiation
RNAPol binds promoter and begins transcription at transcription start point (tsp)
What Transcription step is this?
-Elongation
Successive addition of ribonucleosides (RNTPs) to RNA strand
What Transcription step is this?
-Termination
Hairpin loop is reached, completed mRNA transcript released
What makes RNA transcription different from DNA replication?
Only one strand is copied during RNA transcription
What does enzymatic RNA synthesis require?
1) Four ribonucleoside 5' triphosphates
2) Magnesium (Mg)
3) DNA template
4) RNAPol
True or False: RNA transcription does not require primers, only a DNA template
True
What cation is required to synthesize RNA?
Magnesium (Mg2+)
What is this?
-Gene
Entire nucleic acid sequence necessary for expression of a gene product
What makes DNA different from RNA?
DNA: Double stranded, 2' carbon has a hydrogen, Thymine
RNA: Single-stranded, 2' carbon has a hydroxyl, Uracil
What direction will this DNA strand be?
-Coding strand
-NOT the strand being transcribed
5' to 3'
What direction will this DNA strand be?
-Template strand
-Transcription based on this
3' to 5'
What direction will this mRNA strand be?
-Complementary mRNA strand
-Complementary to Template DNA strand
5' to 3'
What four ribonucleotide 5' triphosphates are necessary for RNA synthesis?
5' ATP, GTP, CTP, or UTP
Why is Mg so important?
-It helps a lot of enzymes to work
-Without it, hard to sleep
What is the overall reaction for RNA synthesis?
NMP + XTP -> XMP—NMP + PPi
NMP = Peptide chain that receives new nucleotide
XTP = Triphosphate, first nucleotide added to peptide
Ppi = Pyrophosphate, byproduct that is cleaved off
What sugar is present in RNA that has a hydroxyl (OH) instead of a hydrogen at the 2' carbon?
Ribose
How many alpha, beta and sigma units does the RNA polymerase have?
2 alpha
2 Beta
1 sigma factor
What does the RNA polymerase do?
-Bind to promoter region (DNA)
-Unravel/unzip DNA helix, similar to helicase
-Recruit ribonucleotide triphosphates (RNTPs)
-Match RNTPs to DNA template (5' to 3') base pairs
Which unit of the RNApol is this?
-Initiation factor
-Binds to specific sequences near -10, -35 box
-Recognizes TATA box
Sigma 70 Factor
Where does the Sigma 70 factor interact with the template strand of DNA?
Promoter
Which unit of the RNApol is this?
-Controls the frequency of initiation of transcription
Alpha
Which unit of the RNApol is this?
-Polymerizes NTPs during pyrophosphate reaction
-Transcribes DNA
Beta1, Beta Prime
What does Sigma factor form when it binds reversibly to RNApol?
RNA polymerase holoenzyme
What does RNA polymerase holoenzyme do after Sigma factor binds to RNApol?
-Selectively binds DNA promoter (-10, -35)
-Unravels, unzips DNA
-Initiates mRNA transcription at tsp (+1)
-Releases Sigma factor to allow elongation
What is this?
-Major sigma factor
-Recognizes TATA box promoter (-10 sequences of TATAAT)
Sigma 70
What are some possible physiological signals that could cause minor sigma factors to be expressed?
-Starvation
-Temperature change
-Growth phase
True or False: Each sigma factor recognizes a different promoter, so RNApol will transcribe different genes based on what physiological signals are present
True
What does it mean for RNA to be self-complementary after RNApol reaches the termination sequence?
-Binds to itself when it exits RNApol
-mRNA forms hairpin loop and is released
-RNAPol can dissociate
What formation does mRNA make after the termination sequence, allowing it to be released from RNApol?
Hairpin loop
Where would you find the hairpin loop?
3' UTR (Untranslated region)
True or False: Amino acids can directly recognize the mRNA codons
False, they need tRNAs as adaptors
What is this?
-tRNAs
-Small adaptor molecules
-Align specific amino acids with triplet codons in mRNA during translation
Name some example of bases besides A, C, U, G that could be found in tRNA due to post-transcriptional modification
-Inosine (modified adenine)
-Dihydrouridine
-Pseudoiridine
What creates the cloverleaf structure associated with RNA?
Internal complementary base pairing
What is this?
-3 base sequence
-Determines mRNA codon binding
Anticodon
Where does the amino acid attach to tRNA?
3' end
What are some examples of modified bases in tRNA?
-Dihydrouracil
-Pseudouridine
True or False: The 3D shape of a tRNA determines which amino acid is attached by aminoacyl-tRNA syntheases
True
What is this?
-Couples a particular amino acid to its corresponding tRNA
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
What happens during amino acid activation?
1) Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase couples amino acid to its tRNA
2) tRNA whose anticodon forms base pairs with mRNA codon
Where does the energy for linking amino acid to tRNA come from?
ATP is hydrolyzed to create the high energy bond
True or False: The bond formed between the tRNA and amino acid is a low energy bond
False, ATP must be hydrolyzed to provide enough energy
True or False: For each amino acid, there are several aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that all correspond to the same single amino acid
True
What enzymes are responsible for attaching the correct amino acid (as specified by the anticodon) to the tRNA 3' end?
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases
What synthetase attaches leucine to tRNAleu?
What synthetase attaches alanine to tRNAAla?
Leucyl-tRNA
Alanyl-tRNA
What is it called when the correct amino acid is attached to its tRNA?
-Charged/acylated
-tRNA becomes amino acyl tRNA
What is it called when an incorrect amino acid is attached to the tRNA?
Mischarging
True or False: Ribosomes are an integral part of ribosomal structures and important parts of protein synthesis machinery
True
Which rRNA is found in prokaryote Large Ribosomal Subunit (50S)?
5S
23S
Which rRNA is found in prokaryote Small Ribosomal Subunit (30S)?
16S
How is rRNA transcribed?
-Two DNA genes are each transcribed by RNApol
-Tandem repeats
-Terminal ribosomes at ends of rRNA
True or False: During optimal growth, 80% of RNA synthesis can be dedicated to rRNA and tRNA transcription
True
What percent of the genome do rRNA and tRNA genes represent?
1 percent
What are the features of a gene required for transcription? (slide 4)
-Promoter
-Shine Dalgarno sequence
-ORF
-Start and stop codons
-Transcription start and termination points
What is the composition of RNA? (slide 5)
-Ribose sugar
-A, C, G, U
-Single strand
What are the three types of RNA and what are their roles? (Slide 6)
-Messenger RNA: Carries genetic code instructions for how to create new proteins
-Transfer RNA: Decodes mRNA into proteins
-Ribosome RNA: Subunits of ribosomes (machine that synthesize proteins)
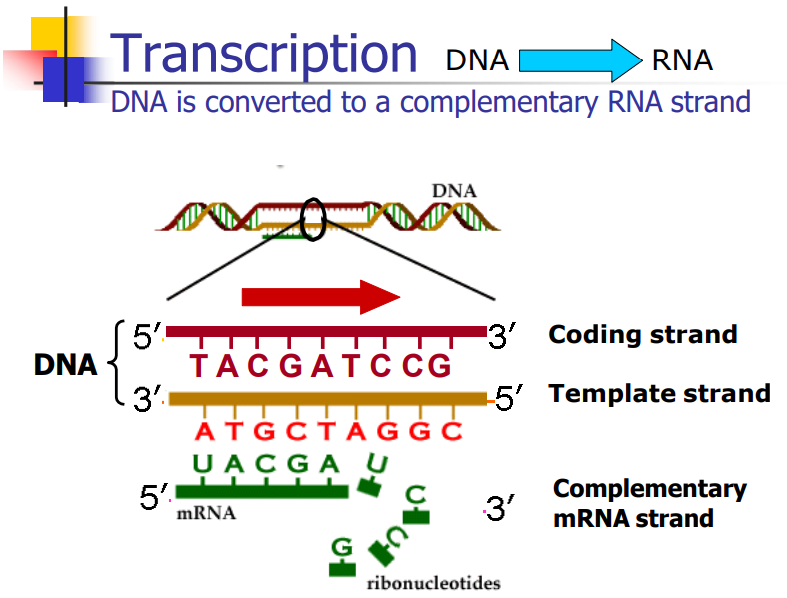
What are the conventions for DNA during transcription? (you will be given an unlabeled figure to annotate) (slide 7 and 8)
-DNA sequences are written in the 5' to 3' direction
-Coding/sense DNA is 5'->3'
-Template strand is 3' to 5'
-Transcribed mRNA is 5' to 3'
-mRNA translation starts with RBS (ribosome binding site) recognition
-tRNAs donate amino acids by recognizing three base codon
What are the necessary components for transcription?
Note: NOT features of a gene, actual ingredients
(slide 10)
1) Four 5’ RNTPs (5' ATP, GTP, CTP and UTP)
2) Magnesium (Mg2+)
3) DNA template (no primer required, not DNA replication)
4) RNAPol (initiation, elongation, termination)
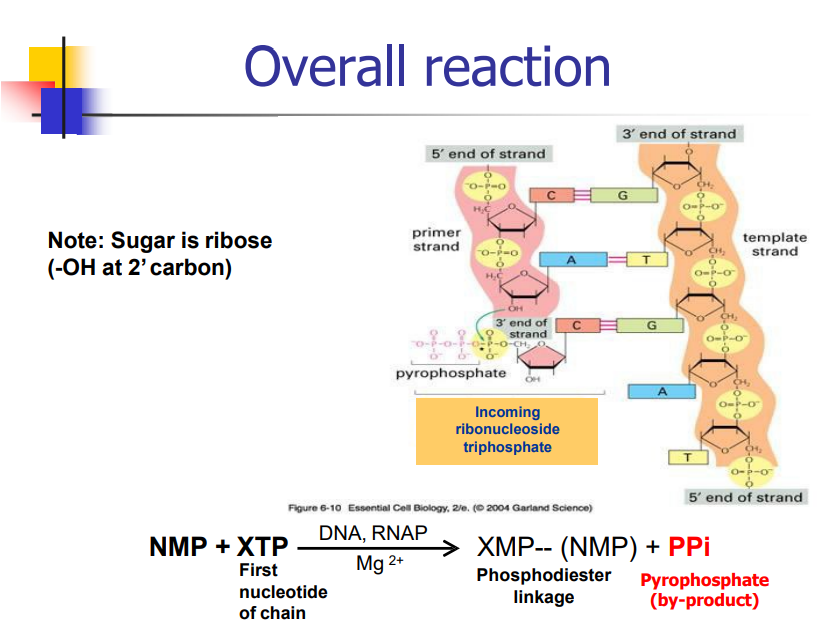
What is the overall reaction for transcription? (slide 11)
NMP + XTP -> XMP--(NMP) + PPi
XMP and NMP are linked via phosphodiester
XTP: First Nucleotide of the chain
Ppi: Pyrophosphate byproduct
What are the components of RNA polymerase (NOT ribosome)? (slide 12)
-Multi subunit complex
-2 alpha: aI, aII
-2 beta: B, B'
-1 sigma factor
How does RNA polymerase generate RNA from DNA? (slide 12
-Binds to promoter (Shine-Dalgarno is translation, not transcription)
-Unravels and unzips DNA, recruits ribonucleoside triphosphates (RNTPs)
-Matches them to DNA template (5' -> 3') via base pairing
Describe the first four steps in transcription initiation (slide 13)
1) Sigma factor binds reversibly to RNApol to form holoenzyme
2) Selectively bind promoter region (-10 and -35)
3) Unravels/unzips DNA helix like helicase
4) Initiates mRNA transcription at tsp (+1)
What are the roles of the sigma factor in transcription initiation (slide 14)
-Forms holoenzyme with RNApol
-Unwinds and unzips DNA helix (like helicase in replication)
-Recognizes TATA box promoter
What causes transcription termination? (slide 15)
-RNApol reaches the termination sequence
-mRNA forms hairpin loop (self-complementary region)
-Newly synthesized mRNA
-RNApol dissociates from DNA
What features of the mRNA are required for translation? (slide 17)
-Shine Dalgarno sequence
-Start and stop codon
-5' and 3' UTR
What is a tRNA? (slide 18)
-Adaptor small molecules
-Align specific amino acids opposite their triplet codon in the mRNA molecule during translation
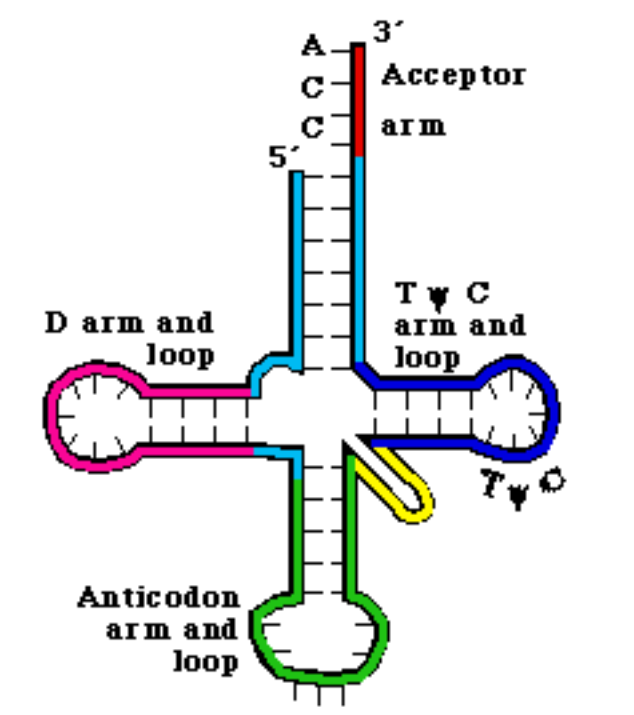
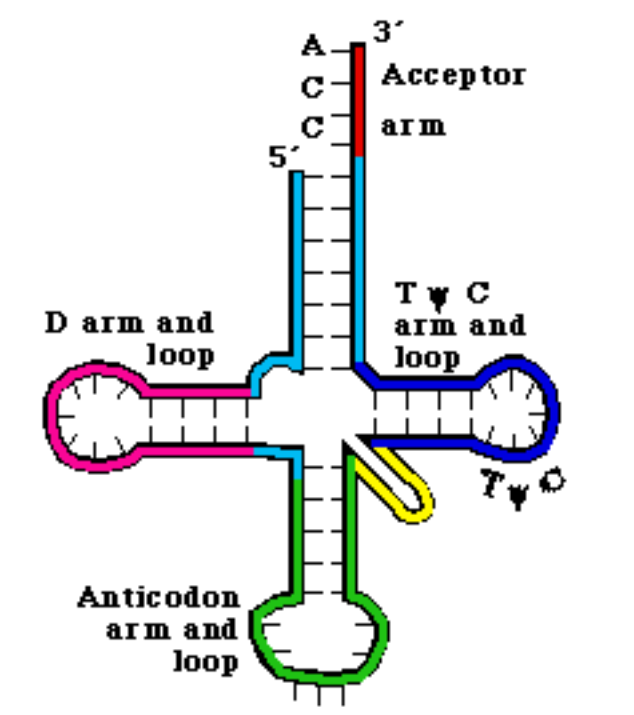
Draw and label the structure of tRNA. (Slide 19)
-Clover leaf structure
-Anticodon sequence of 3 bases (at bottom) determines mRNA codon binding
-D loop, T loop (connected to acceptor stem)
-3' end at top with acceptor stem, longest end
-5' end bound to acceptor stem and 3' end
Describe how the structure of tRNA is formed? (slide 19)
-Internal complementary base pairing of RNA
-Gives clover leaf structure
Name two modified bases found in tRNA (slide 19)
D = dihydrouracil
Ψ = pseudouridine
How are amino acids linked to tRNAs (slide 21)
-Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase couples a particular amino acid to its corresponding tRNA
-tRNA anticodon forms base pairs with mRNA codon
What is the composition of a ribosome (slide 23).
Large 50S Subunit: 5S, 23S
Small 30S Subunit: 16S
How is a ribosome formed? (slide 24)
-Transcribed, folded, modified in tandem repeats by RNApol
-Ribosomal proteins bind together, form 30S and 50S subunit
-Increased transcription during optimal growth along with tRNA