Bio paper 1
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
What is a triglyceride
Glycerol and three fatty acids joined by ester bonds
What is starch made from
alpha glucose
Amylose (1,4) (coiled) and Amylopectin (1,4) (1,6) (Branched)
What is glycogen
A polysaccharide (1,4) (1,6)
What type of melting point do saturated fats have
a high melting point
Why is the dipole nature of water so important
because it allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other
Dna replication
Semi-conservative, Uses DNA bases, Uses DNA polymerase, Creates double stranded DNA
What enzymes are used for cutting DNA into fragments in gel electropheresis
Restriction Enzymes
What are Nitrate ions used for
Required to make amino acids and DNA
What are calcium ions used for
Calcium pectate for the middle lamellae
What are phosphate ions used for
ADP, ATP, DNA and RNA
What are magnesium ions used for
Needed for chlorophyll
Structure of Cellulose
Polysaccharide of B glucose Microfibrils held together by hydrogen bonds. Arranged in a criss cross pattern (1,4 bonds)
Tissue
Group of many cells that work together for a common function
How can we ensure a practical is valid
Control: both biotic and abiotic
Repeats
Same method used
what are lipids made of
Hydrophilic head containing a glycerol and a phosphate group
Hydrophobic fatty tails
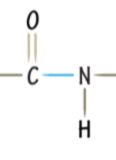
Draw a peptide bond
What size are ribosomes in different types of cells
Eukaryotes: 80s Prokaryotes: 70s
What does the RER do
Fold polypeptide chains into secondary/tertiary structures
What cells are centrioles found in
Only animal cells
What are the general stages of the cell cycle
Interphase
-(G1, G2, S)
Mitosis
Cytokenesis
What happens in cytokenesis
The cytoplasm fully divides creating new cells
What happens in G1 phase
The organelles in the cell double and the cell grows in size
What occurs in the S phase
DNA replication occurs
What occurs in G2
Further growth and DNA checking for mutations
What occurs in Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible
Centrioles appear
Nuclear envelope begins to disintegrate
What occurs in metaphase
Chromosomes line up on the equator
Spindle fibres attach to the centromere on the chromatids
What occurs in anaphase
Spindle fibres begin to separate
Splits chromosomes
(Requires ATP)
What occurs in Telophase
Chromosomes are now at each pole of the cell and begin to become longer and thinner again
Nuclear envelopes begin to reform
Spindle fibres break down
What stain would you use in the root tip practical
Acetic orcein
Rough steps of the root tip practical
Place roots in warm Hydrochloric acid
Take out and rinse with water
Stain root tips with acetic orcein
Heat in water bath
What is crossing over and when does it occur
Swapping sections of DNA
Prophase 1
Adaptions of sperm
Many Mitochondria
Shape
Acrosome
Flagellum
Haploid nucleus
Why does the sperm release enzymes
comes into contact with zona pellucida
causing acrosome to rupture
What fuses to create a triploid endosperm
one male gamete and two polar bodies
What is the formation of sperm order
Spermatagonia
Primary spermatocytes
secondary spermatocytes
spermatids
Spermatazoa
Effects of antibodies
Agglutination (Microbes clump together making phagocytosis easier)
Lysis (Bursting of bacterial cells)
Opsonation (Coat bacterial cells essentially marking them form phagocytosis)
Precipitation ( Soluble toxins made Insoluble)
What is the final electron acceptor in the light dependent reaction
NADP
Endemic
Native to a specific location and not found anywhere else
How are seeds selected for the seed bank
X-rayed for viability and a range of seeds selected for genetic variation
Stud books
Help in breeding programmes increasing genetic diversity
Inbreeding Vs Intebreeding
Interbreeding: Breeding 2 different species Inbreeding: Two individuals of the same species with similar genetics
Why are some animals better protected in protected reserves
Less stressful for the animal
May require large ares
Less susceptible to disease
Wider gene pool
Natural diet available
In situ conservation
Education programmes
Nature reserves
How does gel electrophoresis work
Multiple copies of DNA made using PCR
Restriction enzymes used to cut into fragments
Loaded into Into Agarose gel
Current applied
Use of fluorescent tag
3 Domains
Archae, Bacteria, Eukarya
Why might two species not breed
DIfferent breeding times
Do not recognise courtship displays
Physically incompatible
Genetic diversity
Variety of alleles in a gene pool
How does natural selection occur
Selection pressure
Results in selection for an advantageous phenotype
Advantageous alleles passed on through reproduction
Change in genotypes over generations
Ecological niche
The role an organism plays in an ecosystem with regards to its interactions with other species and where it lives (trophic level as well)
How does a heart attack occur
Blood clot in coronary artery
causing the heart to be starved of oxygen
meaning no aerobic respiration can occur
this will cause the cells to die in the heart
Myogenic
Stimulation generated from within the muscle
This results in depolarisation
Why would regular exercise decrease risk of developing CVD
Regular exercise would decrease blood pressure
Order of heartbeat control
SAN initiates wave of depolarisation in the right atrium
Atria contracts
Region of non conducting tissue confines depolarisation to the atrium
Stimulates the AVN
This passed a wave of depolarisation into the bundle of his with a delay
Bundl of his splits in two called the purkyne fibres
causes contraction from the bottom of the ventricle
Plasmodesmata
How are mammals adapted for gas exchange
Large surface area through capillaries, alveoli
Difference in concentration gradient through ventilation of lungs and mass circulation system
Length of diffusion pathway: Thin capillary and alveoli walls
How does gas exchange occur in insects
Spiracles- allow air in
Air travels down the trachea which is lined with chitin
Then air diffuses into tracheloes which are permeable
How are insects adapted for gas exchange
Can remove water from tracheole ends by causing a lactic acid buildup
Chitin rings keep the tracheole tubes strong
Some insects can ventilate their air systems by mechanical ventilation
How does gas exchange occur in fish
Mouth opens and operculum closes
Mouth closes which causes operculum to open
water rushes over the gills
How are fish adapted for rapid gas exchange
High surface area, many lamella on many Gill filaments
Countercurrent flow in the lamella
Large capillary network
Xylem
Cellulose
lignified in spirals
Pits in the side
Pectin in the cell wall
Why does tissue fluid return into the capillaries
More protein in plasma than tissue fluid
As plasma proteins are too large to pass out of capillary
Oncotic pressure greater than hydrostatic
Summarise the mass flow hypothesis
Sugar loaded into sieve tubes via active transport
Lowers water potential causing water to move in from xylem
Hydrostatic pressure causes sugars to move
Evidence for mass flow hypothesis
Sap is released when a stem is cut therefore there must be a high pressure in the phloem
There is a higher sucrose conc. in the leaves than the roots
Phloem structure
Consists of sieve tubes made of many cells joined together to to create a long tube
Sieve plates
Companion cells
Evidence against the mass-flow hypothesis
Not all solutes move at the same speed
There is bidirectional movement in the sieve tubes
Where does glycolysis take place
The cytoplasm
Where does the link reaction take place
Mitochondrial matrix
Where does the Krebs cycle occur
Mitochondrial matrix
Where does ETC take place
Inner membrane of the mitochondria
How can anaerobic respiration release energy
ATP may already be present
ATP can be produced from glycolysis which is rapid
Some aerobic respiration will occur
NAD recycled
Lactate tolerance
What happens to lactate after anaerobic respiration
Broken down in the liver
into pyruvate
Involving production of NADH
which is then used for respiration
How is pyruvate formed
Through the process of glycolysis
Hexose molecule (glucose) phosphorylated
Breakdown to glycerate 3 phosphate
Production of ATP and NADH
How is pyruvate converted to Acetyl coA
Link reaction
Pyruvate converted to Acetate
CoA added to make Acetyl CoA
What does the Krebs cycle do
Completely oxidises Acetyl coA
To release as much energy as possible
To generate ATP directly
Producing reduces coenzymes
So ATP can be produced in the electron transport chain
What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain
Oxygen to produce water
Anaerobic respiration in plants
fermentation of glucose to produce ethanol and co2
Carbon fixation
CO2+RUBP= GP
Catalysed by RUBISCO
What does a chloroplast not have
A matrix
Instead it has a stroma
what is the channel protein that is used to make ATP in oxidative phosphorylation
ATP synthase
final electron acceptor in photosynthesis
Reduced NADP
How does glycolysis operate in anaerobic conditions
NADH used to convert pyruvate into lactate
instead of being sent to the electron transport chain
Streak plate Vs spread plate
Streak plate is when three streaks of culture, rotated by 90 degrees
Spread plate is when culture is poured on plate and then spread around with a spreader
Benefits of broth over agar
Broth can provide anoxic conditions but with oxygen closer to the surface
You can get a much larger volume of bacteria
Can’t get discrete colonies
Order of microorganism growth
Lag phase
Log phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
Lag phase
Microorganisms adapting to their environment
Reproduction increase slowly
Log phase
Microorganisms grow at max rate
Stationary phase
Death rate = reproduction rate
This is due to buildup of waste products and lack of nutrients
Death phase
Deaths exceed new reproduction rate
Cell count
Use a haemocytometer
Only counts viable cells
slow and expensive
Turbidimetry
Measure absorbance using a colorimeter
Quick and can be conducted in the field
counts dead cells
Dilution plating
Works on the principle that every colony is grown from a single viable microorganism
colonies counted and then multiplied by dilution rate to find original cell count
DOesnt require expensive or complex equipment
slow as incubation period needed
Gram negative bacteria
Extra lipopolysaccharide layer
Contain endotoxins
ie Salmonella
Gram positive bacteria
No lipopolysaccharide layer
No endotoxins
Staphylococcus which release exotoxins
Penicillin
Bacteriocidal
Tetracycline
Bacteriostatic
Puccinia graminis (stem rust fungus)
Wind carries spores and infected fragments left in the ground
Spores germinate in water on plants
producing hyphae which grow into mycelium which surround plant tissue
Which digest the plant
Weakens the plant
Steals water and nutrients
reduced transpiration
Influenza
Droplet infection
Infects ciliated epithelial cells
plasmodum spp. (protozoa) (malaria)
Transmitted through anopheles vector
Parasite transmitted via mosquito
Travels to liver, infects red blood cells
reproduces asexually in red blood cells
blood bursts every 2-3 days
can be treated with antimalarial drugs ie quinine
Problems of controlling endemic diseases
Disease is often widespread
Difficult to remove all sources
treatment can be expensive
ie for malaria
Preventing mosquito bites
Controlling mosquito population