Psychophysiological Effects of Sport-Induced Concussions
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Concussion
Heterogeneous brain injuries from biomechanical forces.
Symptoms of concussion
Dizziness, headaches, confusion, memory deficits, nausea.
Acute symptoms
Symptoms occurring minutes to hours post-injury.
Late symptoms
Symptoms occurring days to weeks post-injury.
Concussion prevalence
Falls > road accidents > sports injuries.
Age risk factor
Youth aged 10-19 have highest concussion risk.
Emergency room data
2.7 million children treated for head injuries.
NCAA injury rate
Varies by sport, measured per 1000 exposures.
High school injury rate
Reported per 10,000 athletic competition exposures.
Major risk factors
Type of sport, position, technique, exposure time.
Sport types with highest risk
Rugby, hockey, and football lead in concussions.
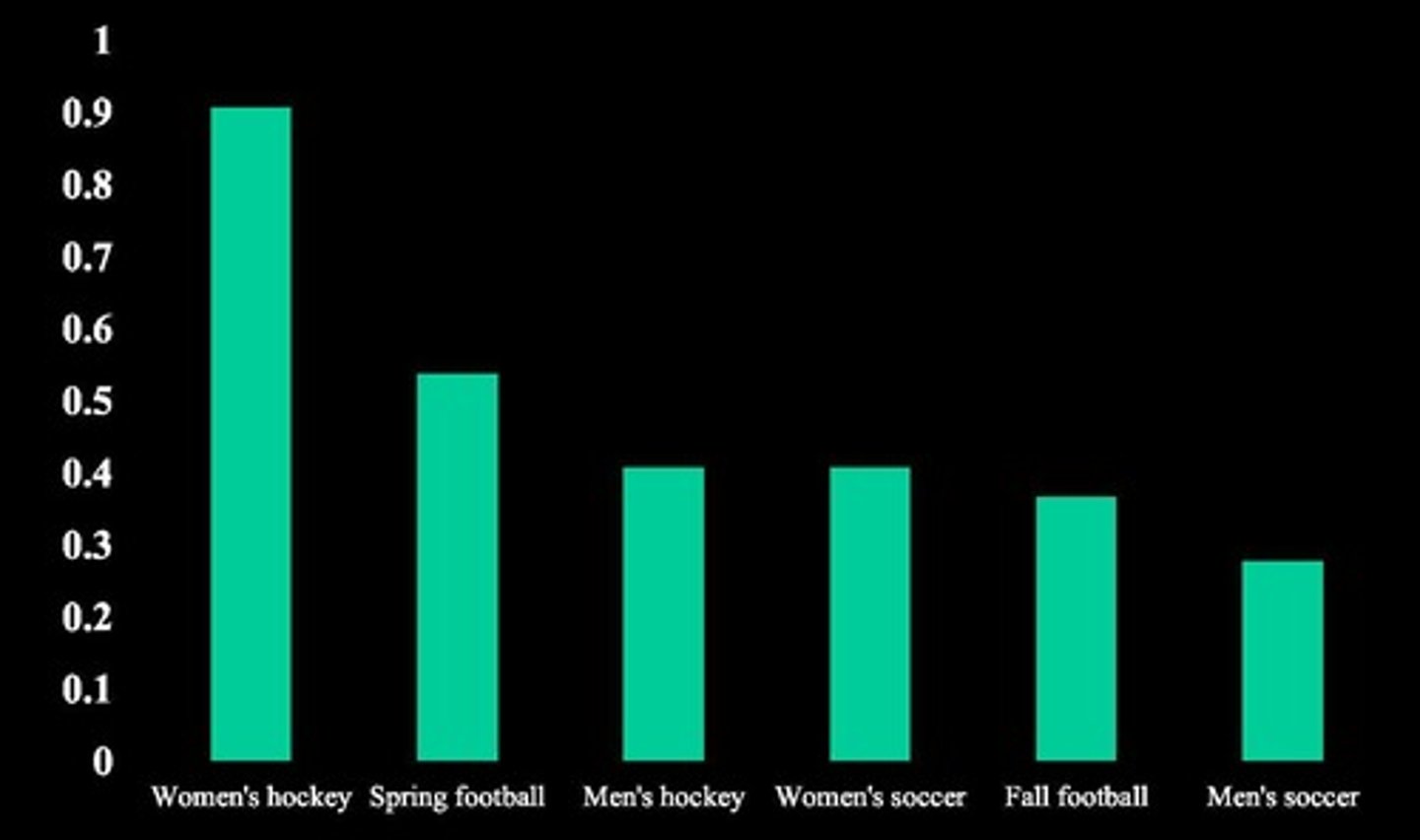
Position risk in football
Linemen face lower force impacts; receivers higher.
Technique risk
Head down position increases injury risk.
Competition risk
Higher risk of concussions in games than practice.
Gender risk
Females have higher concussion rates than males.
Concussion history
Prior concussions increase risk of future injuries.
Animal research
Studies suggest mechanisms for concussion effects.
Diffuse axonal injury
Twisting and stretching disrupts glia and axons.
Ionic pump activity
Increased need for glucose due to dysregulation.
Neuroinflammation
Inflammation and degeneration occur post-concussion.
Blood-brain barrier dysregulation
Larger molecules can enter brain post-injury.
S100B protein
Elevated post-concussion, indicates glial cell damage.
Fruit fly model
Used to study concussion effects in research.
High impact trauma
Severe brain/body injury causing immediate effects.
Genome-wide association study
Identifies gene variants predicting survival in flies.
Blood-brain barrier
Protective barrier regulating substances entering the brain.
Glucose dysregulation
Impaired glucose metabolism affecting brain injury recovery.
Metformin
Medication that improves glucose control in humans.
Ketogenic diet
High-fat, low-carb diet potentially aiding brain recovery.
Psychophysiological consequences
Mental and physical effects following brain trauma.
Neurophysiological effects
Long-term brain function changes post-injury.
Cognitive performance
Mental ability to process information and tasks.
Neuropsychological test battery
Set of tests assessing cognitive functions.
Executive functioning
Cognitive flexibility and memory inhibition abilities.
Acute exercise effects
Short-term boost in attention and memory post-exercise.
Graded symptom checklist (GSC)
Assessment tool for concussion symptoms and recovery.
Standard assessment of concussion (SAC)
5-minute test for memory and orientation post-injury.
Age as moderator
Age influences recovery duration after concussion.
Sleep problems
Increased risk of issues in concussed athletes.
Delayed recovery
Prolonged recovery linked to pre-injury sleep issues.
Verbal memory performance
Ability to recall spoken information post-injury.
Short-term effects
Immediate symptoms occurring weeks after concussion.
Long-term effects
Persistent symptoms lasting months to years post-injury.
Natural experiment
Observational study comparing effects of boxing matches.
Quasi-experimental evidence
Research design assessing concussion effects in football.
Multi-site study
Research involving multiple locations for broader data.
Acute psychological response
Increased symptoms like headache and dizziness.
Symptom resolution time
7 days for adults, 15 for high school athletes.
Cognitive change
Memory deficits show largest acute changes.
Cognitive test changes
Attention and processing speed show moderate changes.
Cognition resolution time
2-5 days for adults, 7 days for high school athletes.
Sport-induced insomnia
Common sleep issue after concussions.
Daytime sleepiness
Frequent symptom following sport-related concussions.
Recovery moderators
Factors slowing recovery include age and prior concussions.
Chronic neurophysiological deficits
Long-term cognitive effects from repeated concussions.
Event-related potential
Measures brain response to auditory stimuli.
P300 component
Related to attention, reduced in aging and disorders.
Clinical depression risk
Increases with recurrent concussions in retired NFL players.
Dementia-related syndromes
May begin after repetitive cerebral concussions.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
Change in one cognitive domain, not full dementia.
Dementia definition
Impairment in two or more cognitive domains.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)
Progressive neurodegenerative disorder from repeated head trauma.
Phosphorylated tau
Protein linked to neurofibrillary tangles in CTE.
Neurofibrillary tangles
Hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, formed by tau.
Amyloid plaques
Protein clumps associated with Alzheimer's disease.
PET radiotracers
Used to image tau distribution in the brain.
NCAA-DoD Care Consortium
Study aiming to improve data on head injuries.
Punch drunk syndrome
Historical term for dementia from boxing-related head trauma.
Boxer brain study
Research on brain damage in boxers by Corsellis.
NFL post-mortem CTE diagnosis
High prevalence of CTE in former NFL players.