Indirect taxation 1.2.9
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Indirect tax
A tax on expenditure/ consumption e.g. VAT
Imposed by gov that increases the supply costs of producers but can be transferred to consumers via high prices
Unlike direct taxes, indirect taxes are typically collected by businesses at the point of purchase/consumption
Most indirect taxes are either specific taxes or ad valorem taxes
Direct tax
A tax on income e.g. corporation tax
Tax revenue
Revenue received by gov from the tax (tax per unit x quantity)
Producer revenue
Income from sales (price x quantity)
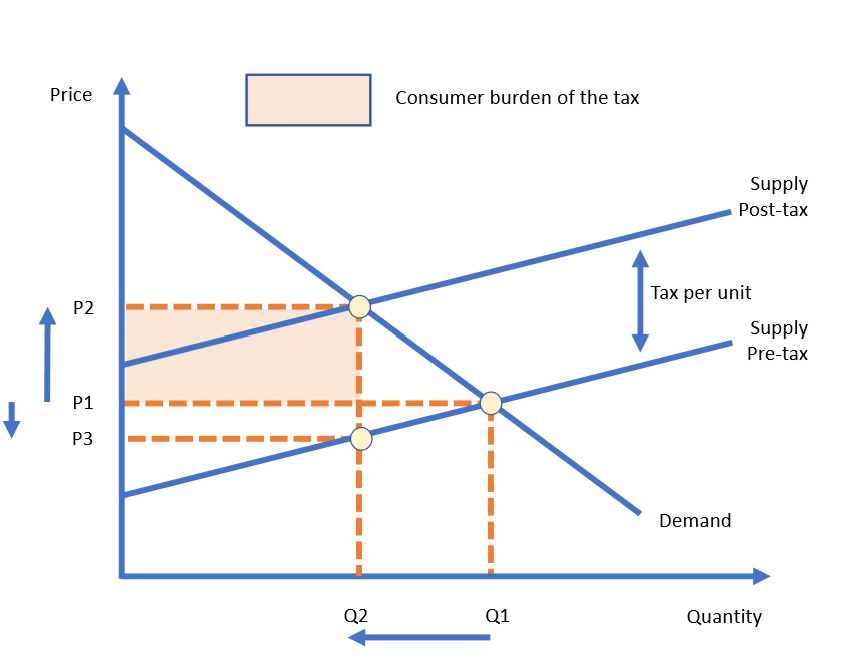
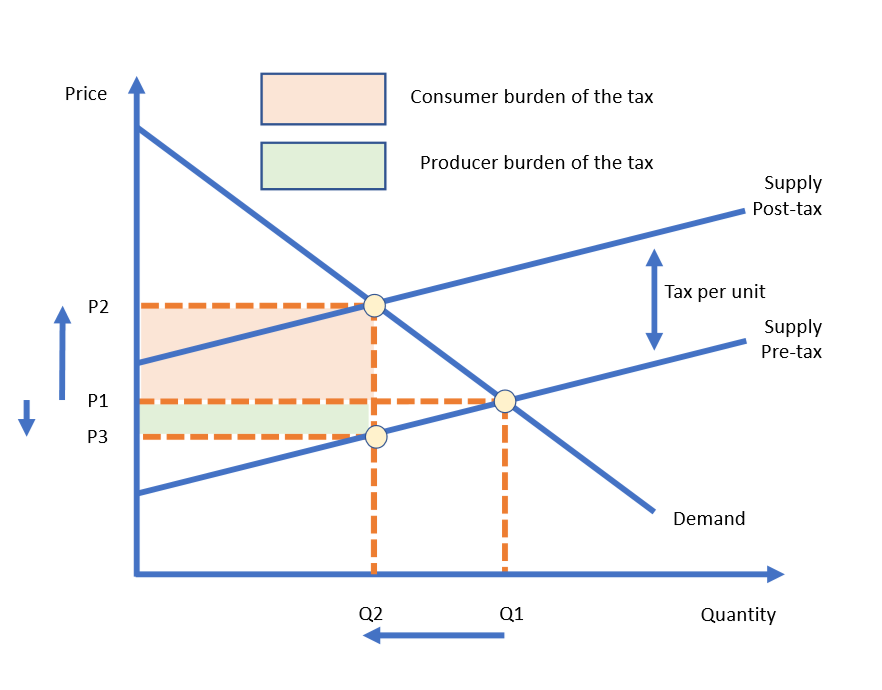
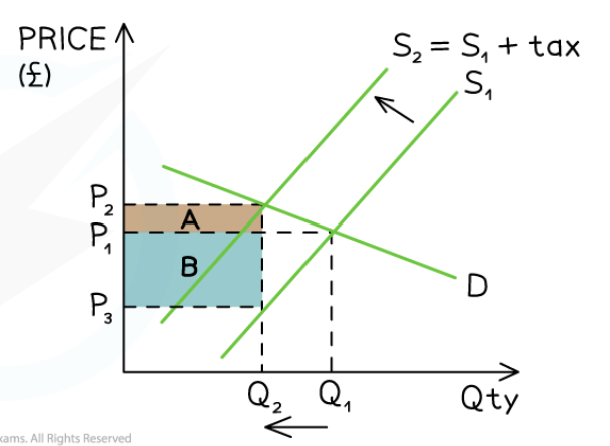
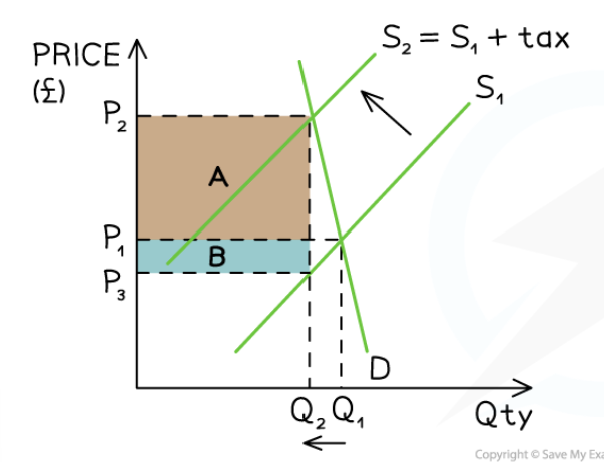
Consumer tax burden
Difference between original market price and new market price x quantity
Producer tax burden
Tax revenue minus consumer tax burden
Specific tax
A fixed tax per unit regardless of price
E.g. all wine has a specific tax of £2 per bottle
Ad valorem / percentage tax
A tax which is a % of the price, the higher the price the higher the tax
Why do we have taxes?
To fund public services e.g. NHS
To curb consumption of ‘demerit'' goods e.g. cigarettes because they are bad for society
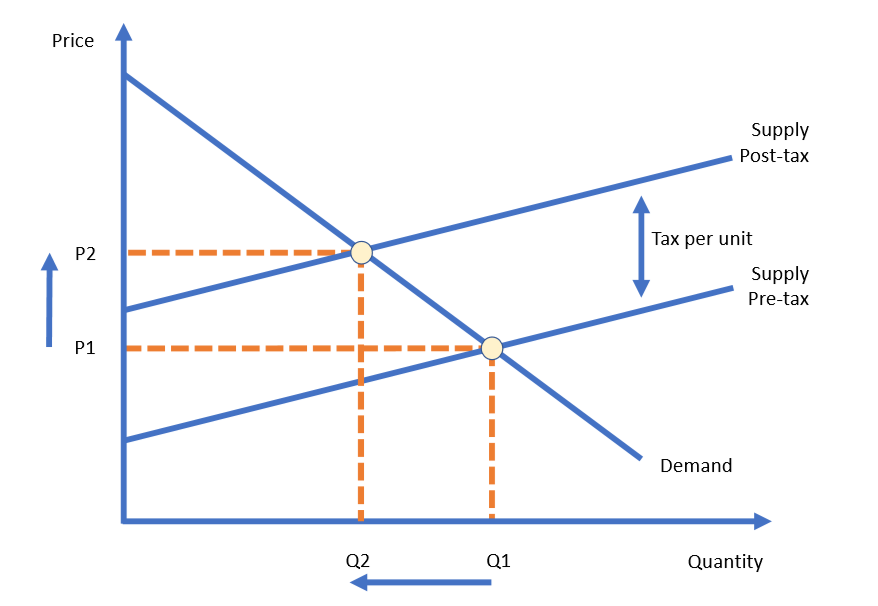
How is tax shown on a diagram?
By the vertical distance between pre- and post-tax supply curves
Because of the tax - less will be supplied to the market at each price level
Are VAT + Ad valorem the same thing?
No - VAT is a specific type of ad valorem tax + VAT is a direct tax - ad valorem is indirect
So all VATs are ad valorem but not vice versa
Examples of main indirect taxes in UK?
Air passenger duty - environmental impact
Alcohol duties
Tobacco duties
Soft drinks industry levy - sugar tax
What are excise duties?
Indirect taxes levied on 3 major categories of goods - alcoholic drinks, tobacco products + road fuels
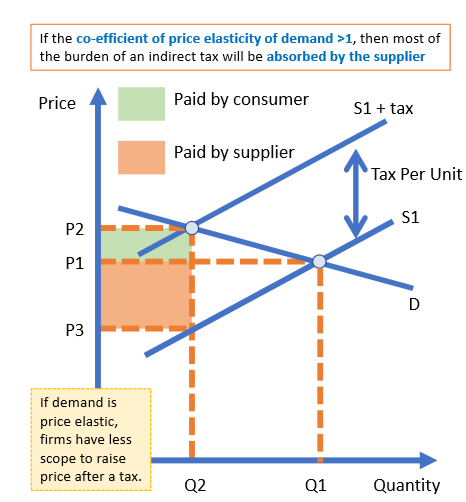
If PED>1 then most of the burden of an indirect tax will be absorbed by? demand
The supplier/producer
If demand is price elastic - firms have less scope to raise price after a tax - producers pass on a much smaller proportion of the tax to consumers (+ pay the rest themselves)
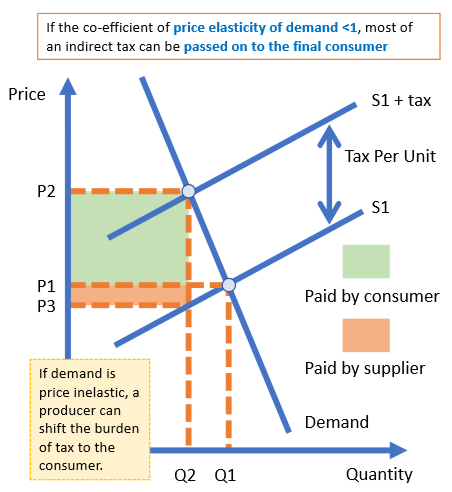
If PED<1 then most of the burden of an indirect tax will be absorbed by? demand
The final consumer
If demand is price inelastic - producers pass on a much higher proportion of the tax to consumers (+ pay the rest themselves) e.g. cigarettes
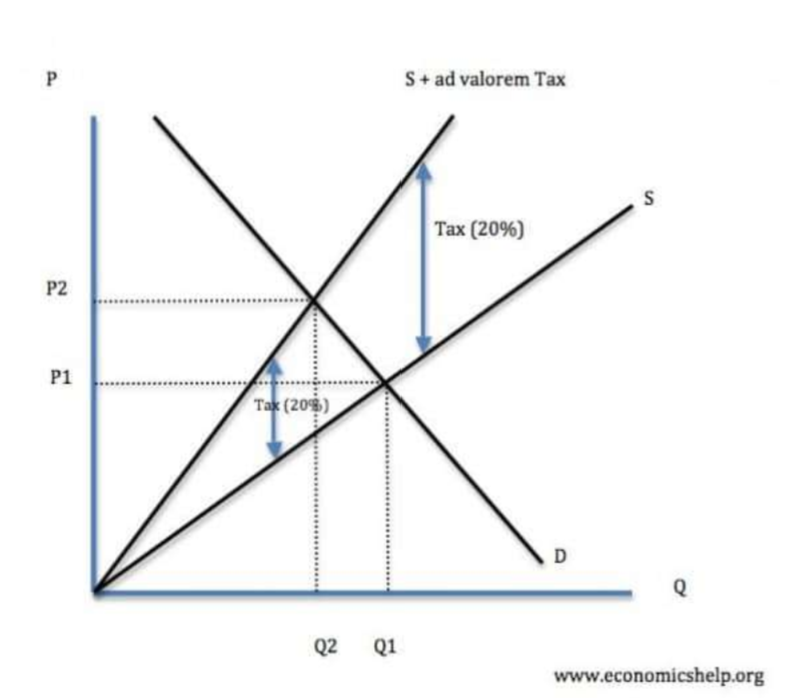
How does an ad valorem indirect tax differ from a specific tax?
Ad valorem - depends on its value - usually expressed as a percentage
Specific tax - regardless of the price tax stays the same
But are both indirect taxes
How do you represent ad valorem tax on a diagram?
Must pivot curve to show that the higher the price, the higher the tax
How do you show specific tax on a diagram?
Shift supply curve left or upwards (same thing)
This shows that it doesn’t matter how many bottles of wine you purchase - they all have the same tax of £2 per bottle
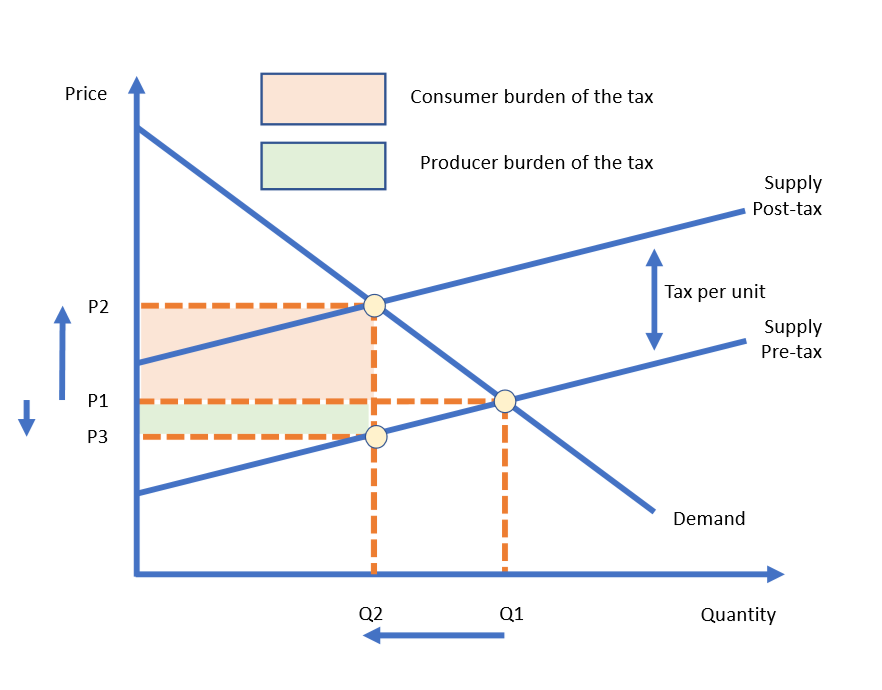
What does a specific indirect tax look like on a graph?
This
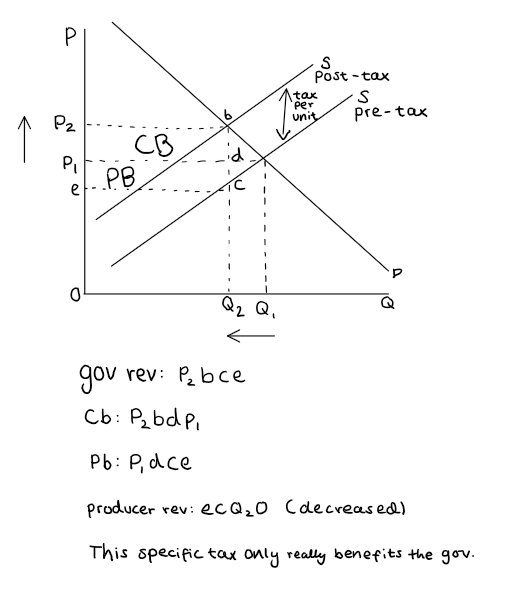
If PES>1 then most of the burden of an indirect tax will be absorbed by? supply
Consumers bear more of the tax
When supply is elastic - firms can easily adjust production levels
This means that firms can pass most of the tax to consumers by raising prices
If PES<1 then most of the burden of an indirect tax will be absorbed by? supply
Producers bear most of the tax
When supply is inelastic - firms can’t easily change their production levels
Since consumers are still somewhat responsive to changes in price - firms absorb most of the tax as they can’t instantly adjust supply