Human Nutrition Chapter 4,5,6
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
205 Terms
Where can you find carbohydrates?
In the plant-based food
What are the type of plat-based food where you can find carbohydrates.
grains
vegetables
fruits
nuts
legumes
What is the most desirable form of energy for body?
Glucose
Brain and RBC especially rely on ____ for fuel source.
Glucose
What is the process where plants convert the sun’s energy into glucose?
Photosynthesis
During the photosynthesis, plants use the ____ enzyme in their leaves to absorb the energy in sunlight.
Chlorophyll
_____ is most abundant carbohydrate in nature.
Glucose
What carbohydrate is used as energy by plants or combined with minerals from soil to make other compounds, such as protein and vitamins?
Glucose
Glucose units are linked together and stores in the form of ____.
Starch
_____ are the carbohydrates that contain one or two sugar units.
Simple carbohydrates
What are the types of simple carbohydrates that contain one or two sugar units.
Monosaccharides and disaccharides
What are the three types of monosaccharides? (IMP)
Glucose, fructose, galactose
What are the type of disaccharides?
Maltose, sucrose, lactose
Glucose + glucose makes?
Maltose
Glucose + fructose makes?
Sucrose
Glucose + galactose makes?
Lactose
What are the complex sugar known as?
Polysaccharides
What are the example of polysaccharides?
Starch, fiber, and glycogen
_____ is the storage form in plants.
Starch
What are the types of starch?
Amylose and amylopectin
Straight chains of glucose units is known as?
Amylose
What is the branched chains of glucose units known as?
Amylopectin
_____ is a nondigestible polysaccharide.
Fiber
What is the type of fiber that is naturally found in foods?
Dietary fiber
What is the type of fiber that is added to foods for beneficial effect?
Functional fiber
Cellulose, hemicellulose, logins, gums, pectin is the example of?
Fiber
T/F: Humans lack digestive enzyme needed to breakdown fiber.
True
Psyllium is an example of?
Functional fiber
Dietary fiber + functional fiber is equal to?
Total fiber
____ is the fiber that dissolve in water and is fermented by intestinal bacteria.
Soluble fiber
T/F: Soluble fiber are viscous and have thickening properties and it also move slowly through GI tract.
True
Pectin in fruits and vegetables, beta-glucan in oats and barley, gums in legumes, psyllium is an example of?
Soluble fiber
Cellulose, Hemicellulose, lignins are the example of what type of fiber?
Insoluble fiber
T/F: Insoluble fiber move very slowly though the GI tract and have laxative effect.
False: It moves more rapidly
Where can you find insoluble fiber?
In bran of whole grains, seeds, fruits, vegetable
____ is the storage form of glucose in animals.
Glycogen
Where is glycogen stored?
Liver and muscle cells
Where do you digest carbohydrates?
Mouth and intestines.
Saliva contains ___ enzyme.
amylase
Which enzyme starts breaking down amylose and amylopectin into smaller starch units and maltose.
Amylase
Where does the pancreatic amylase breaks down and remaining starch converts into maltose?
In small intestine
Maltose is absorbed into?
blood
Maltose and disaccharide are broken down to ____
Monosaccharides.
Fiber continues to the _____, where some is metabolize by ___ in the ___ and majority eliminated in your stool.
large intestine, bacteria, colon
____ is the principle carbohydrate (disaccharide) found in dairy products.
Lactose
People with a deficiency of the enzyme ___ cannot digest lactose properly.
Lactase
People with what condition can still consume dairy and should not eliminate it from their diets.
lactose malabsorption
What is this condition when lactose malabsorption results in nausea, cramps, bloating, diarrhea, and flatulence within two hours of eating or drinking foods containing lactose?
Lactose intolerance
____ regulates the amount of glucose in your blood.
Hormones
Which hormone is released from he pancreas and regulates glucose in your blood.
Insulin
Insulin is released from where in the body?
pancreas
What is the process known as when direct conversion of glucose into excess of immediate energy needs into glycogen in liver and muscle cells.
Glycogenesis
Rest of excess glucose converted to ___.
Fat
when blood glucose begins to drop, pancreas releases the hormone ____ to raise blood glucose levels.
Glucagon
Directs relate of glucose from stores glycogen in liver is known as what process?
Glycogenolysis
Making glucose from noncarbohydrate sources, mostly protein is known as which process?
Gluconeogenesis
______ also helps in the stimulation of glycogenolysis and increase blood glucose levels.
Epinephrine
Without glucose, fat can’t be broken down completely and acidic ____ are produced.
Ketone bodies
____ is the the process elevated Teton levels after fasting about two days.
Ketosis
How much of carbohydrate do you need on daily basis?
130 grams
What are the three edible parts of grains?
Bran, endosperm, germ
Milling removes bran and germ that is known as?
Refined grains.
Folic acid, thiamin, niacin, riboflavin, and iron added to restore some of the lost nutrition. These are the what types of grains?
Enriched grains
What are the grains that has all three parts of kernel?
Whole-grain
_____ are the type of sugar that is found in fruits and dairy.
Naturally occurring sugars
____ are the sugar that is added by manufacturers and are often empty calories.
Added sugars
What are the calories that provide little nutrition.
Empty calories
Cheese is rich in protein, calcium, and phosphorus, and calcium can assist in _____ of your teeth.
Remineralization
Honey should not be given to children younger than one year of age in order to prevent _____ spores that cause botulism.
Clostridium botulinum.
Less than 10 percent of your total daily calories should
come from added sugars. What is the source of it?
Dietary Guidlines for Americans
What is this condition? Individual has high blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin or insulin resistance.
Diabeters mellitus
Define the term: Glucose can’t enter ells because the cells of not respond to insulin.
Insulin resistance
This is an autoimmune disease that usually begins in childhood or early adult years.
Type 1n diabetes
____ is the type of diabetes that is seen in people who have become insulin resistant.
Type 2 diabetes
____ is known as the precursor to type 2 diabetes?
Prediabetes
____ is the condition known as when the blood glucose appear higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Prediabetes
What is the condition when blood glucose level is below than 70 mg/dl
Hypoglycemia
Hunger, shakiness, and dizziness are the symptoms of?
Hypoglycemia
_____ ranks food’s effects on blood glucose compared with equal amount of pure glucose.
GI (Glycemic index)
_____ adjust GI to take into account the amount of carbohydrate consumed in a typical serving.
GL
Saccharin, aspartame, and neotame are the example of which type of sweetener?
Calorie-free sweetener
_____ pressure in the colon causes weak spots in the colon to bulge out, forming _____.
Increases, Diverticula
Define the term: Infection of the diverticular.
Diverticulitis
Stomach pain, fever , nausea, vomiting, cramping, and chills are the symptoms of which condition
Diverticulitis
T/F: Lipids are hydrophilic.
False. They are hydrophobic
Fat is the common name for just one type o lipid, known as a _______.
Triglyceride
T/F: Energy storage, insulation, transport of compounds in blood, and cell membrane structure are the functions of fats.
True
T/F: Triglycerides (fats), phospholipids, and sterols are the type of lipids in your body.
True
What is the basic unit of triglycerides and phospholipids?
Fatty acid
_____ is the chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms with acid group.
Fatty acids.
What is the acidic group at the end of a fatty acids?
COOH
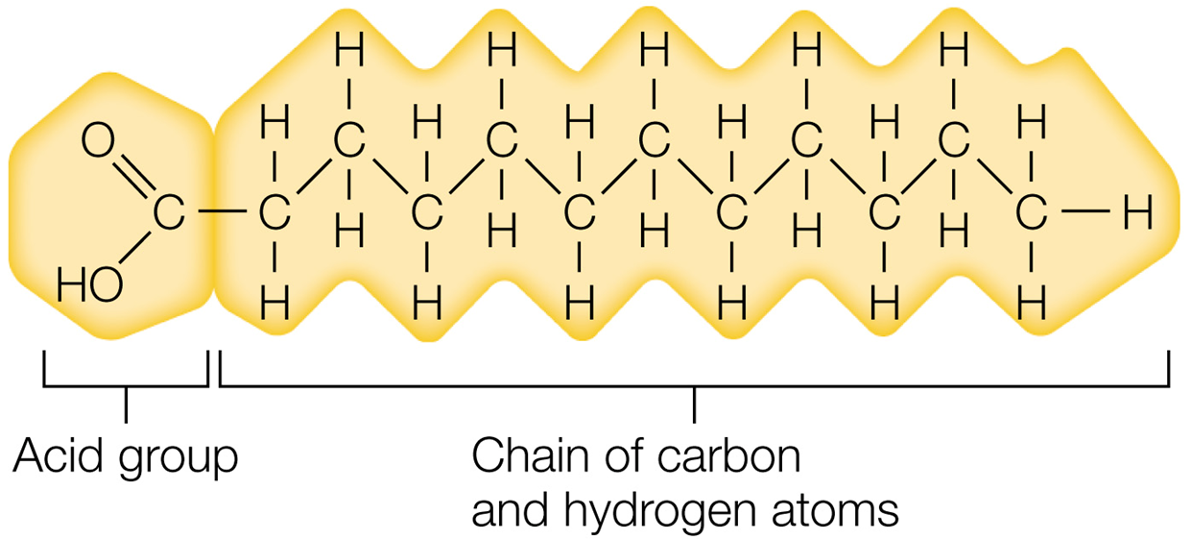
What is this structure of?
Fatty acid
What type of fatty acid is this, where all carbons bonded to hydrogen.
Saturated fatty acids
What type of fatty acid is that where one double bond is present.
Monounsaturated fatty acids
What type of fatty acid has more than one double bond.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
Essential fatty acids linoleum acid and alpha-linolenic acid is an example of what type of fatty acid?
Polyunsaturated
What is it called when three fatty acids connected to glycerol “backbone”
Triglyceride
_______ have glycerol backbone, but two fatty acids and phosphorus group.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids have _____ backbone, but two fatty acids and a phosphorus group.
Glycerol
Phosphorus-containing head is _____
Hydrophilic