Midterm Investing for the future
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Inflation
The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, the purchasing power of currency is falling.
Compounding
Earning interest on your interest
CPI (Consumer Price Index)
Measures the average change of prices for consumer goods and services
PPI (Producer Price Index)
Measures the average change in prices over time for selling by producers
Rule of 72
A formula to estimate the number of year needed to double an investment at a given annual rate of return. Calculated as 72 divided by the annual rate of return
Good debt
Borrowing that is likely to increase your net worth or generate income over time like student loans or a mortgage
Bad debt
Borrowing that does not increase your net worth or generate income over time
How banks make money
Banks mainly make money through interest on loans and credit products, fees for services like account maintenance, and ATM use
Banks
For-profit institutions that offer a wide range of services to the public
Credit Unions
Not-profit insitutions owned by members who share a common bond. They often offer better interest rates and lower fees but have more limited services
How credit scores are used

Lenders use credit scores to assess the creditworthiness of individuals. They affect loan approvals, interest rates, and credit limits.

What goes into a credit score:

Payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, new credit, and credit mix.

Benefits of good credit:

Lower interest rates on loans and credit cards, better terms for borrowing, higher credit limits, easier approval for renting apartments or buying homes, and potential employment opportunities.

Keys to saving/financial success:

Budgeting, Emergency fund, Investing, Debt management, Financial planning

Stocks
Securities that represent ownership in a corporation and entitle the shareholder to a part of the company's profits and assets.

Stock types

Common Stocks, Preferred Stocks, Growth Stocks, Value Stocks, Dividend Stocks
Common stocks
These represent a share of ownership in a company and come with voting rights.

Preferred stocks
These stocks provide no voting rights but offer fixed dividends and priority over common stocks in asset distribution during liquidation.

Growth stocks
Stocks from companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market.

Value stocks
These stocks are considered undervalued in price and are trading for less than their intrinsic value.

Dividend Stocks:

Stocks that regularly pay dividends to shareholders.
Stocks features
Dividend yield, price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, earnings per share (EPS), market capitalization.
Stock table
Provides information about a company's stock, including its symbol, price, change, volume, and other financial data.

Dividends
Payments made by a corporation to its shareholders, usually in the form of cash or additional shares of stock.

Growth stocks:

Companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to others.
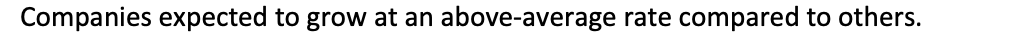
Value stocks
Companies that appear to be undervalued in price.

Annual reports (four financial reports)

Balance sheet, Income statement, Cash flow statement, Statement of shareholders' equity

Balance sheet
Shows the company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity.

Income statement
Shows the company's revenue, expenses, and profit or loss.
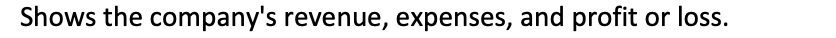
Cash flow statement

Shows the company's cash inflows and outflows.

Statement of shareholders' equity:

Shows changes in the ownership interest of the company's shareholders.

Bull market
A period of rising stock prices.

Bear market
A period of falling stock prices.

Stock exchange platforms
stocks and other securities are bought and sold. Examples include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ.
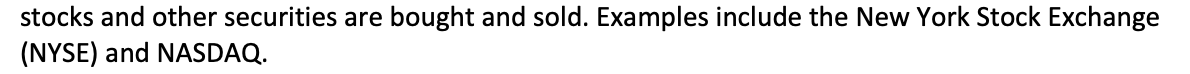
Stock Indexes (what are they):

Benchmarks that track the performance of a group of stocks. Examples include the S&P 500 and the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
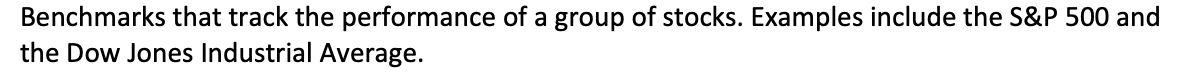
Bonds
Fixed-income securities that represent a loan made by an investor to a borrower, typically corporate or governmental.

Bond types
Corporate bonds, Municipal bonds, Treasury bonds, Convertible bonds.

Corporate bonds:

Issued by companies.

Municipal bonds
Issued by local governments.

Treasury bonds
Issued by the federal government.
Convertible bonds:

Can be converted into a set number of shares of the issuing company's stock.

Bond features
Interest rate (coupon), maturity date, face value, and credit quality.
Bond Taxation
Interest earned on bonds may be subject to federal, state, and local taxes, depending on the type of bond.
Bond rating agencies
Organizations like Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch Ratings that assess the creditworthiness of bond issuers.

Bonds (Vs stocks)
Fixed income, lower risk, priority in case of bankruptcy.

Stocks (Vs bonds)
Variable income, higher risk, potential for higher returns.
