MY LAB Chapter 12 Productive and Allocative Efficiency
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
if the marginal cost of producing the last unit of a product is the same for all firms in an industry, we can say that the industry is achieving _____ efficiency, but we do not know enough to say that the industry is achieving _____ efficiency.
productive - allocative
the market structure that leads to both productive and allocative efficiency is
perfect competition
a monopolistic industry may be productively efficient but will not be allocatively efficient because
P>MC
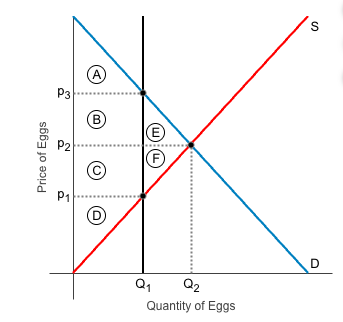
a the free market equilibrium P2 and Q2 what areas represent consumer surplus?
A B and E
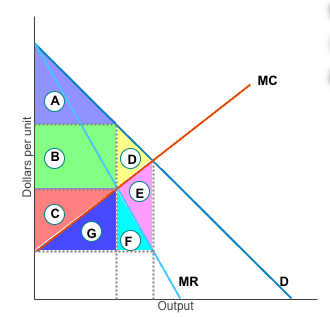
if monopolist charges its single profit maximizing price what area is consumer surplus?
A
allocative efficiency is
about getting the quantities right, specifically getting the quantities such the marginal cost (to society) of each good equals the marginal benefit to society of each good
which market structure leads to productive and allocative efficiency?
perfect cmpetition and monopolistic competition lead to productive efficiency and perfect competition leads to allocative efficiency
natural monopoly refers to an industry in which only a single firm can operate at its
minimum efficient scale
a regulated natural monopoly that is subject to average-cost pricing and operating on the downward-sloping portion of its LRAC curve will earn ____, since price _____ MC, this outcome will not be _____
zero profits, exceeds, allocatively efficient
average cost pricing for a falling cost natural monopoly results in
zero profits with allocative inefficiency
if a falling cost natural monopoly is regulated to charge a price equal to MR the resulting level of output is
allocatively efficient and profits are negative
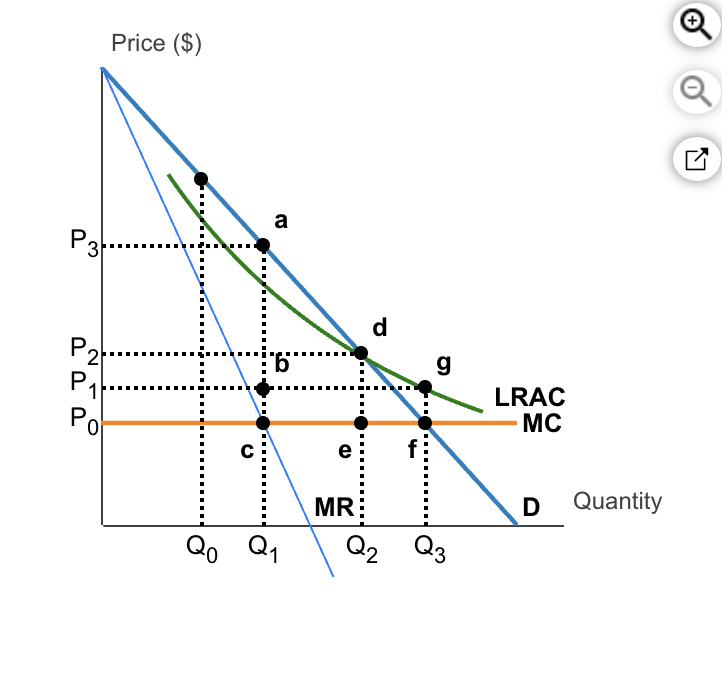
natural monopoly, its deadweigt loss is equal to area____ if the monopolist is not regulated and is equal to _____ if the monopolist is regulated and average-cost pricing is used.
acf, def
the objective of canadian competition policy is
to prevent unecessary mergers and collusive practives
in reviewing a proposed merger the main issue that the competition bureay should consider is the
possible cost reductions versus potential reduction in competition
a major aim of canadian competition policy is to
restrict mergers and trade practices that unduly lessen competition