PR - Module 01
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Qualitative, Quantitative, Mixed-methods research
What are the types of formal research?
Formal Research
It is conducted using a systematic and scientific approach. Usually, it contains abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and method, results and analysis, conclusion, and bibliography.
Qualitative Research
It is an approach for exploring and understanding the meaning of individuals or groups ascribe to a social or human problem. The process of research involves emerging questions and procedure, data typically collected in the participant’s setting, data analysis inductively building from specific to general themes, and the researcher making interpretations of the meaning of the data.
Quantitative Research
It is an approach for testing objective theories by examining the relationship among variables. These variables can be measured, typically on instruments, so that numbered data can be analyzed using statistical procedures. The final written report has a set structure consisting of introduction, literature and theory, methods, results, and discussion.
Mixed-methods Research
It is an approach to inquiry involving collecting both quantitative and qualitative data, integrating the two forms of data, and using distinct designs that may involve philosophical assumptions and theoretical frameworks. The core assumption of this form of inquiry is that the integration of qualitative and quantitative data yields additional insight beyond the information provided by either the quantitative or qualitative data alone.
Survey, descriptive, correlational, experimental research.
What are the types of quantitative research?
Survey Research
It provides a quantitative or numeric description of trends, attitudes, or opinions of a population by studying a sample of that population. It includes cross-sectional and longitudinal studies using questionnaires for data collection — with the intent of generalizing from a sample to a population.
Descriptive Research
It is a method which identifies the characteristics of observed phenomenon and collects more information. In simple words, it is all about describing the phenomenon, observing it, and drawing conclusions from it.
Correlational Research
It is conducted to establish a relationship between two closely-knit entities and how one impacts the other and what are the changes that are eventually observed. This research method is carried out to give value to naturally occurring relationships, and a minimum of two different groups are required to conduct this quantitative research method successfully.
Experimental Research
It seeks to determine if a specific treatment influences an outcome. The researcher assesses this by providing a specific treatment to one group and withholding it from another and then determining how both groups scored on an outcome.
Survey Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Student Preferences in Science Education
Experimental Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Effect of Soil pH on Germination Rates of Common Crop Seeds
Experimental Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Testing the Impact of Various Light Wavelengths on Photosynthetic Efficiency in Algae
Correlational Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Connection Between Physical Activity and Cognitive Function
Correlational Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Link Between Exposure to Pesticides and Incidence of Respiratory Diseases in Agricultural Workers
Survey Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Surveying Attitudes Toward Vaccination Among College Biology Majors
Descriptive Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Documenting the Migration Patterns of Monarch Butterflies in North America
Experimental Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Effects of Different Fertilization Techniques on Plant Growth in Controlled Environments
Descriptive Research
Identify the correct type of quantitative research:
Patterns of Energy Consumption in Urban Areas
Variable
It refers to a “characteristics that has two or more mutually exclusive values or properties”
Quantitative variable & qualitative variable
What are the classifications of variables?
Qualitative variable
They are variables that have distinct categories according to some characteristic or attribute.
Quantitative variable
They are variables that can be counted or measured.
Qualitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Color of the eyes
Quantitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Income of the DOST employees
Qualitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Marital status of the architects
Qualitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Ethnicity of the ICT students
Quantitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Height of the trees in a forest park
Quantitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Temperature of a freshwater sample
Quantitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Days needed for incubation
Qualitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
Gender of the university physicists
Quantitative variable
Classify whether the following given variables are QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE variables:
pH level of various chemical solutions
Discrete variable & continuous variable
What are the types of quantitative variables?
Discrete variable
This type of quantitative variable assume values that can be counted. They are obtained by counting. These variables can only assume any whole value within the limits of the given variables.
Continuous variable
This type of quantitative variable can assume an infinite number of values between any two specific values. They are obtained by measuring. They often include fractions and decimals.
Discrete variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Number of STEM students
Continuous variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Average grade of nursing students
Discrete variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Page number of a science journal
Continuous variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Velocity of a falling object
Continuous variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Volume of a water sample
Continuous variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Length of white canes with sensor
Discrete variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Days needed for incubation
Continuous variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Age of the qualified applicants in DOST (expressed in range)
Continuous variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Body mass index of mathematics teachers
Discrete variable
Classify whether the following quantitative variables are DISCRETE or CONTINUOUS.
Age of the microbiologists (counted in years)
Scales of measurement
This refers to the way in which variables are defined and categorized. It has certain properties which in turn determines the appropriateness for use of certain statistical analyses.
Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
What are the four scales of measurement?
Nominal level
It classifies data into mutually exclusive (nonoverlapping) categories in which no order or ranking can be imposed on the data. It includes labeled and named variables.
Ordinal level
It classifies data into categories that can be ordered, or ranked; however, precise differences between the orders and ranks do not exist.
Interval level
It ranks data, and precise differences between units of measure do exist; however, there is no meaningful and true zero.
Ratio level
It possesses all the characteristics of interval measurement, and there exists a true zero. In addition, true ratios exist when the same variable is measured on two different members of the population.
True
Identify whether the following statements is
TRUE or FALSE about the levels of measurement.
The religious preference of the Filipino scientists is an example of nominal level.
False
Identify whether the following statements is
TRUE or FALSE about the levels of measurement.
The Paris 2024 Olympic medals for the athletes is an example of interval level.
True
Identify whether the following statements is
TRUE or FALSE about the levels of measurement.
An example of interval level is the temperature of water expressed in degrees Celsius.
False
Identify whether the following statements is
TRUE or FALSE about the levels of measurement.
The income of the government employees in DOE can be considered as ordinal level only.
True
Identify whether the following statements is
TRUE or FALSE about the levels of measurement.
The volume of Benedict’s solution is considered as ratio level.
Independent, dependent, control, intervening variable
What are the kinds of variable?
Dependent variable
This is the response or effect variable that is observed or measured to determine the effect of the independent variable. It changes when the independent variable varies. For example, a researcher wishes to study the effects of reciprocal peer tutoring in the learning motivation of Grade 11 STEM students.
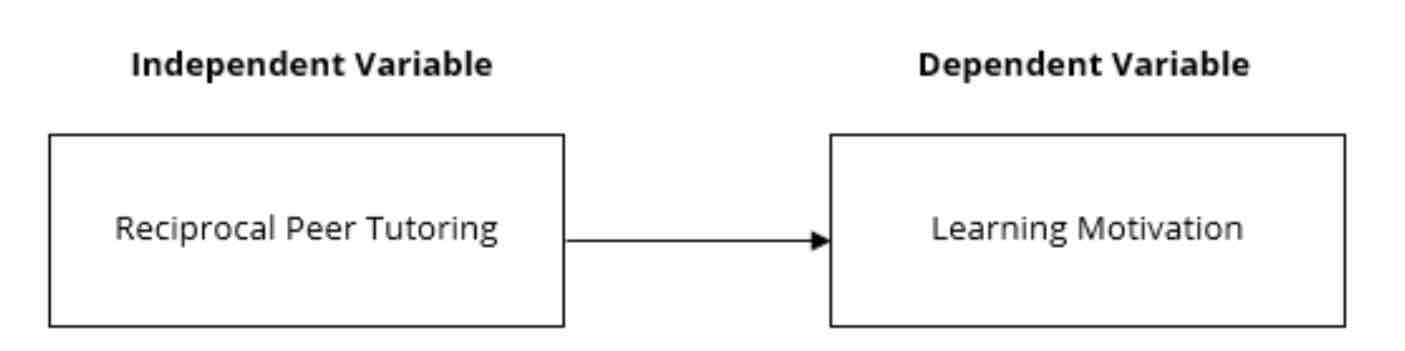
Control variable
This is a variable controlled by the researcher in which the effects can be neutralized by eliminating and removing the variable. For instance, a researcher wants to determine the effects of independent variable A on dependent variable B. The researcher may control D as control variable. In other words, the researcher may remove or eliminate D to neutralize the effects.
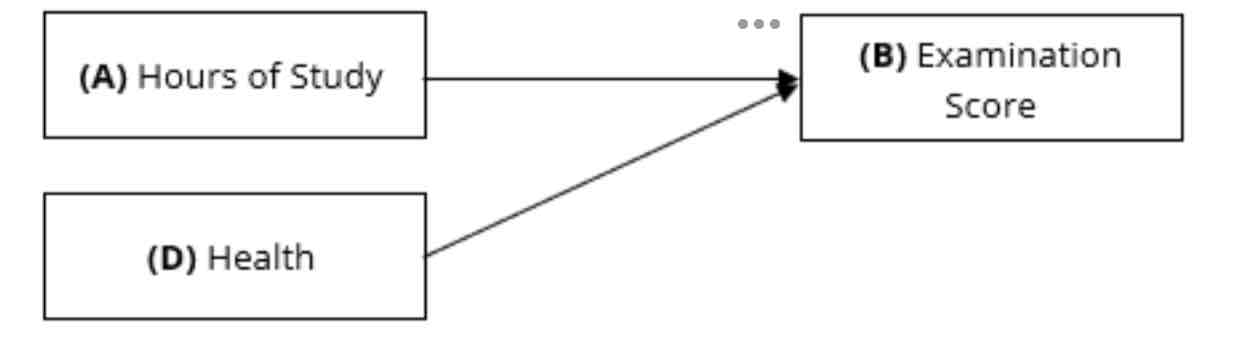
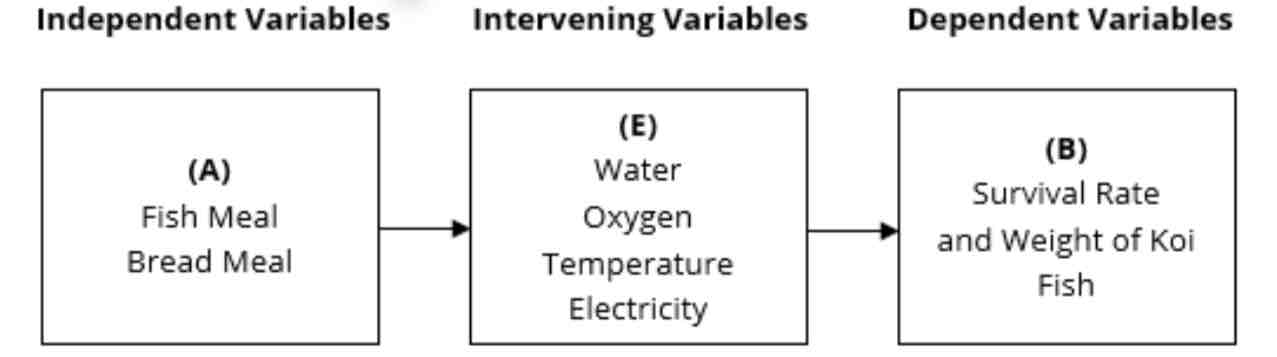
Intervening variable
This is a variable which interferes and hinders the independent and dependent variables, but the effects can either strengthen or weaken the said variables. For example, the researcher wishes to determine how independent variable A will affect the dependent variable B. It is possible that intervening variable E might have an effect on dependent variable B.
Independent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
Temperature
Independent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
Amount of fertilizer
Independent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
Study time
Independent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
Type of diet
Dependent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
Exam scores
Dependent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
Plant height
Independent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
In a sleep study, the amount of exposure to natural light during the day can be a/an ________ to investigate its influence on sleep patterns.
Independent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
In a nutrition study, the type of diet (e.g., Mediterranean, low-carb) can be manipulated as a/an ________ to analyze its effects on health.
Dependent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
In a physiology study, a person’s heart rate in response to exercise can be a/an _______ to assess cardiovascular health.
Dependent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
In health research, BMI can be a/an _______ to understand the impact of diet and exercise on an individual's weight.
Independent variable
Identify whether the following statements is
DEPENDENT or INDEPENDENT VARIABLE.
In an environmental study, the level of noise pollution can be a/an ________ to examine its effects on human health.