
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
what is a parametric test?
a test where the assumption is that the distribution of population from which the sample was taken is normally distributed
What is a non-parametric test?
a test where the assumption is that the distribution of population from which the sample was taken does not follow a specific distribution
How do we know that a piece of data is not normally distributed?
By testing for normality
What is a quantile-quantile (q-q) plot?
a graphical technique for determining if two data sets come from populations with a common distribution—a test for normality
What is the rule of thumb when it comes to q-q plots?
if data are normally distributed, the Q-Q plot will show points that mostly fall on the diagonal line
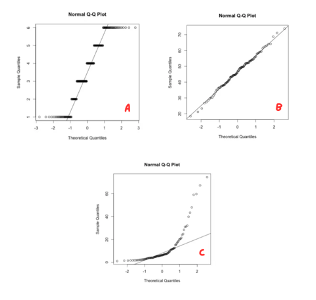
On this q-q plot which one/s is normally distributed?
B
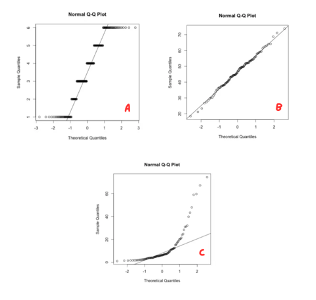
On this q-q plot which one/s is NOT normally distributed?
A & C
What is a shapiro-wilk test?
a goodness-of-fit test; it examines how close the sample data fit to a normal distribution via p value—remember anything lower/at than .05 is significant
What is the main advantage of using a non-parametric test?
make fewer assumptions and can therefore be used in more situations than parametric statistics
What is the main disadvantage of using a non-parametric test?
have generally less statistical power than their parametric counterparts—parametric tests are more likely to detect an effect when the null hypothesis is false
why would we have two types of tests for statistics?
not all data will lead to one circumstance and or assumption; on this basis—distribution
What is the spearman correlation analysis?
It functions the same way as the Pearson correlation analysis—but it measures the strength and direction of association between two ranked variables
What is the coefficient for spearman?
restricted between -1 and 1, and can be interpreted similarly to the Pearson coefficient—the greek letter — ρ
How does the spearman separate itself from the Pearson?
should be used when the variables are ranked and when there is a monotonic relationship between them
What are the assumptions affiliated with the spearman correlation?
X and Y are NOT approximately normally distributed
X and Y are NOT measured on an interval or ratio scale
there ARE outliers
the association between X and Y IS NOT linear
How is the spearman ranked?
the lowest value of a variable is assigned rank 1, the second lowest is assigned rank 2, etc—equal values receive the same rank
What are the assumptions spearman correlation follows? (FLAGGED FOR WORDING)
both variables are measured on an ordinal, interval, or ratio scale
the relationship between the two variables is monotonic
In relevance to the spearman correlation: what does it mean by a monotonic relation?
as one variable goes up, the other variable also goes up, OR as one variable goes up, the other variable goes down
What Is the Wilcoxon signed-rank test?
It functions the same way as the one-sample t-test and paired-sample t-test
How does the Wilcoxon signed-rank test function?
used to compare two sets of related data, like before-and-after measurements on the same group, to see if there's a significant difference in their median values
What are the assumptions for a Wilcoxon signed-rank test to be used when a one-sample t-test is the equivalent?
you have data from a single sample that are measured on an interval or ratio scale, and
your research question involves comparing the median of your data to some reference value
your data is not normally distributed
What are the assumptions for a Wilcoxon signed-rank test to be used when a paired-sample t-test is the equivalent?
you have data from a single sample that is measured twice, and both measurements are made on an interval or ratio scale
your research question involves comparing the median of one measurement to the median of the other measurement
What would be some research questions that would be necessary for a Wilcoxon signed-rank test?
Anything that involves comparing the median of one measurement to the median of the other measurement
Wilcoxon rank-sum test has an equivalent parametric counterpart: what is it?
a.k.a mann-whitney u test—is the non-parametric equivalent of an independent-samples t-test
How does the Wilcoxon rank-sum test function?
the comparison of two groups of nonparametric (interval or not normally distributed) data
What are the assumptions that a Wilcoxon rank-sum test follows?
you have data from two different samples, and your measurements are made on an ordinal, interval or ratio scale
your research question involves comparing the median of one sample to the median of the other sample
You’re currently using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test and find that the null hypothesis is true, what happens now?
We combine the rank data from two samples
THUS—the sum of the ranks from sample 1 should be approximately the same as the sum of the ranks from sample 2
using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, how do we know if the null hypothesis is not true?
if there are very large differences in the summed-ranks, then the null hypothesis can’t be true
What would be some research questions that would be necessary for a Wilcoxon rank-sum test?
Anything that involves comparing the median of one sample to the median of the other sample