Unit 3- part D- Enzymes in action
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
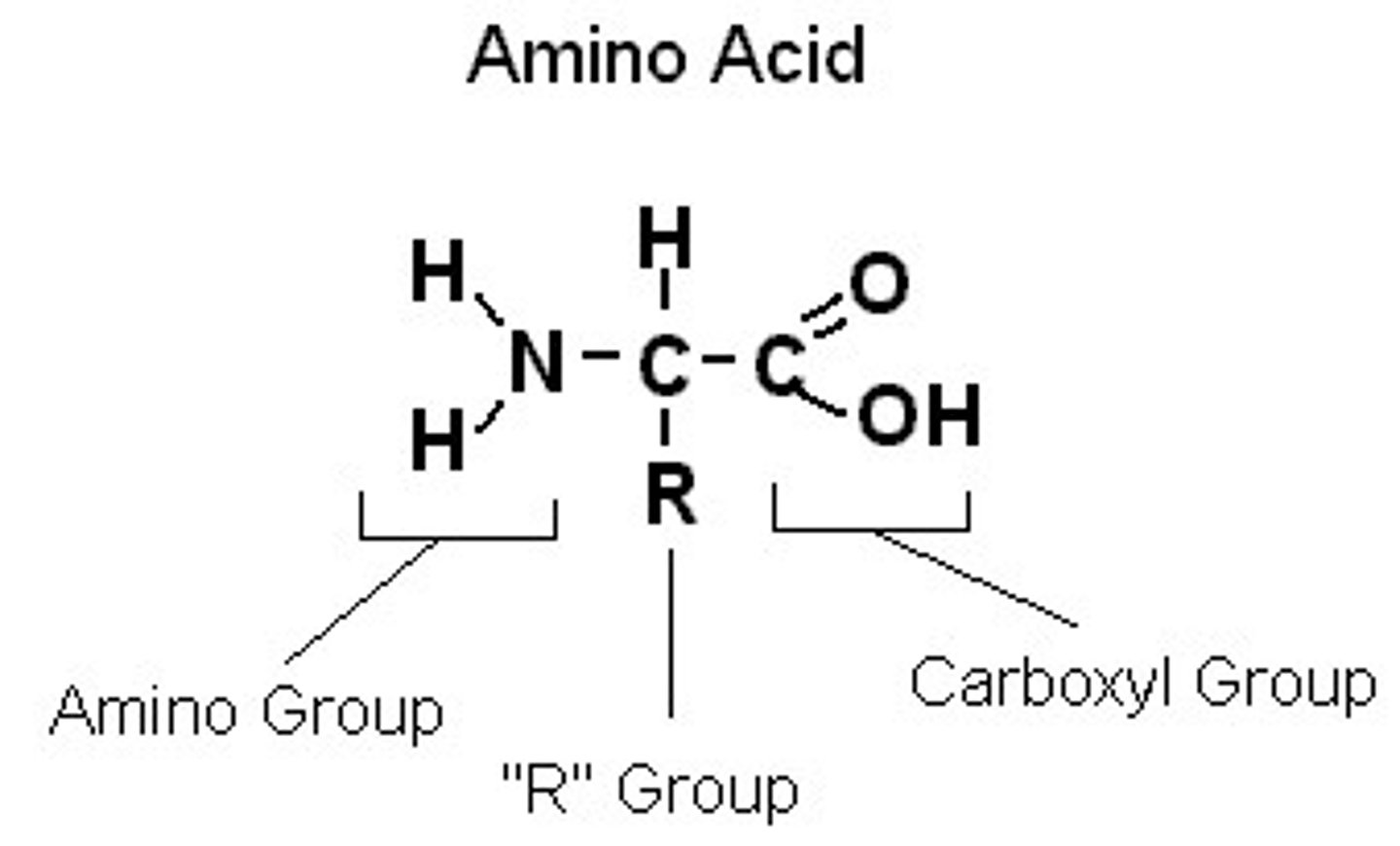
What are amino acids made out of?
an amine group, carbon atom, R group and carboxylic acid group
What are proteins made out of?
residues of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds
What is the structure of an amino acid?
amino group, R group, and carboxyl group
How many types of amino acids are there?
20
What is different in each of these types of amino acids?
the R group
What happens when two amino acids join together?
hydrogen of an amine group and the hydroxyl group (-OH) meet. A peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids.
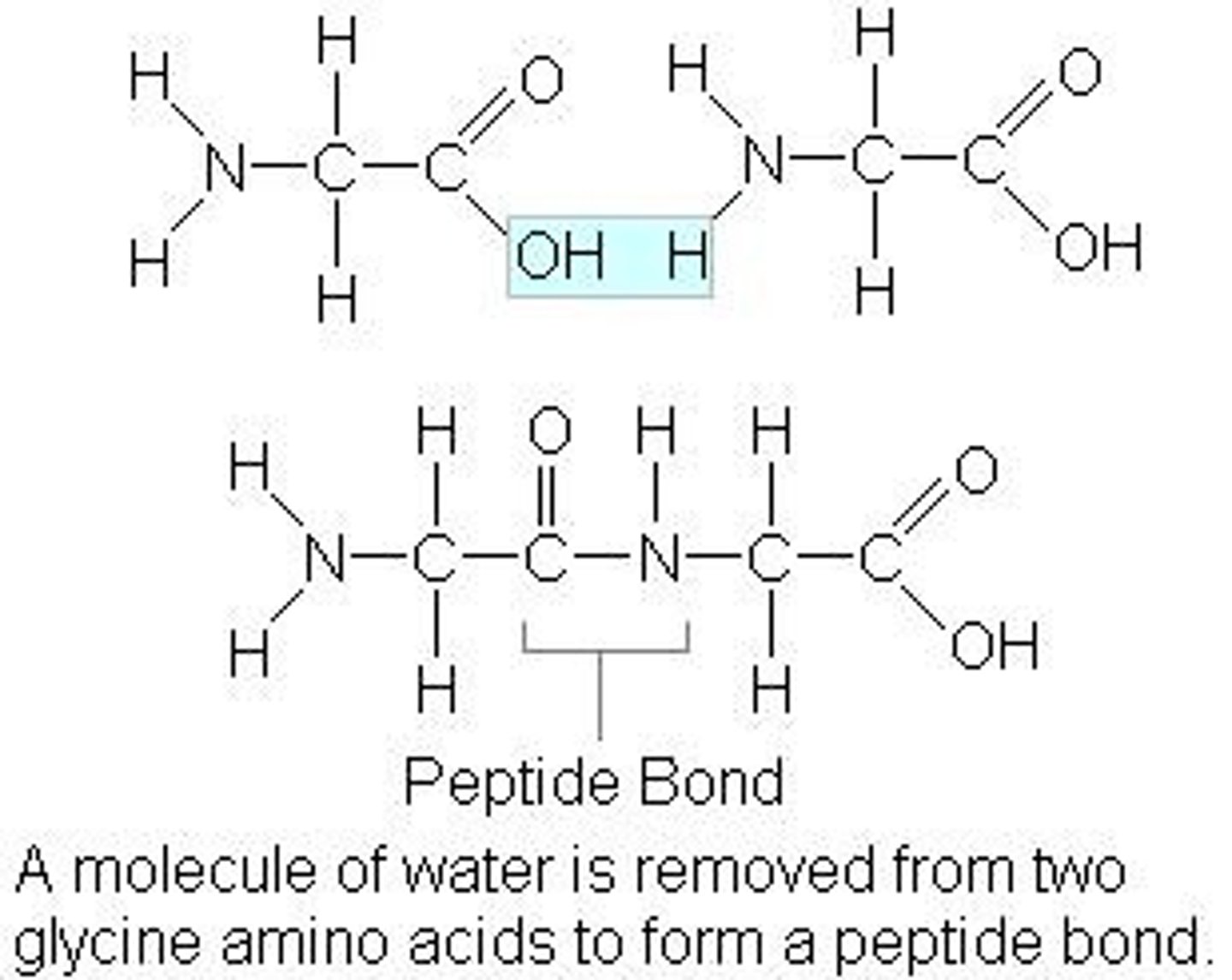
What is the name of this reaction between 2 amino acids?
Condensation reaction
What product is formed in this reaction?
water
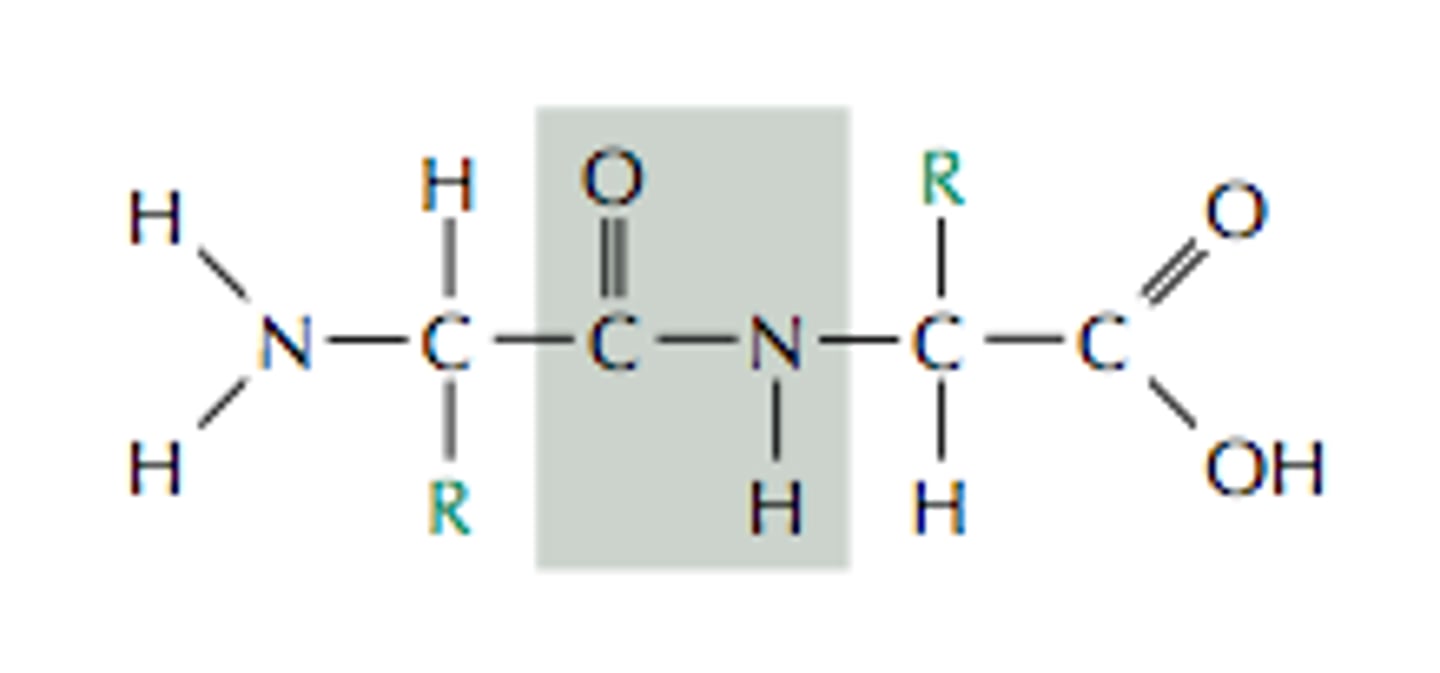
What is the name when 2 amino acids join together by peptide bonds?
Dipeptide bond
What is it called when many amino acids join together?
a polypeptide
What is the primary structure?
the order in which the amino acids are present in the protein molecule
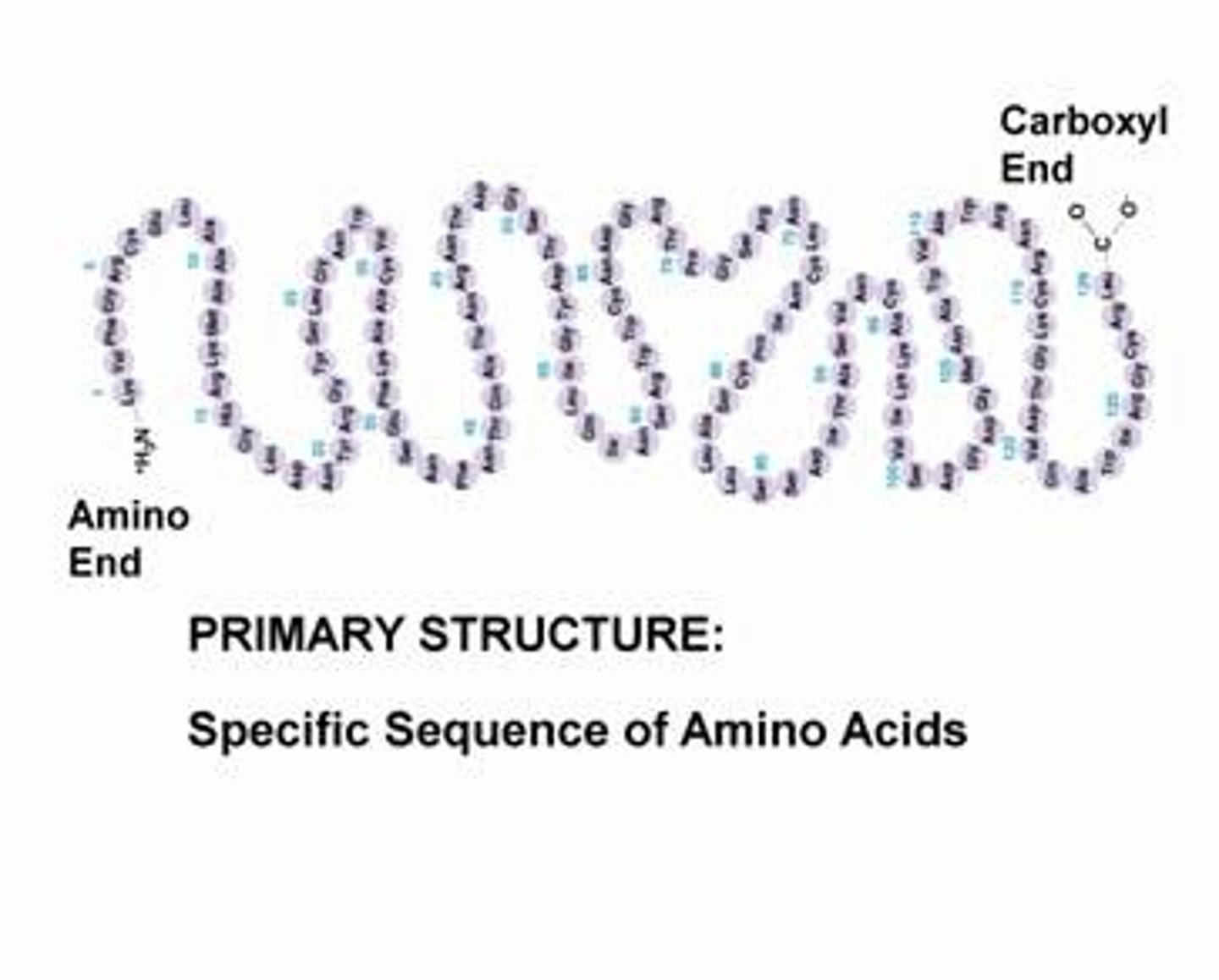
What is the secondary structure?
alpha helix or beta pleated sheet in certain areas of polypeptide chain are repeated or folded
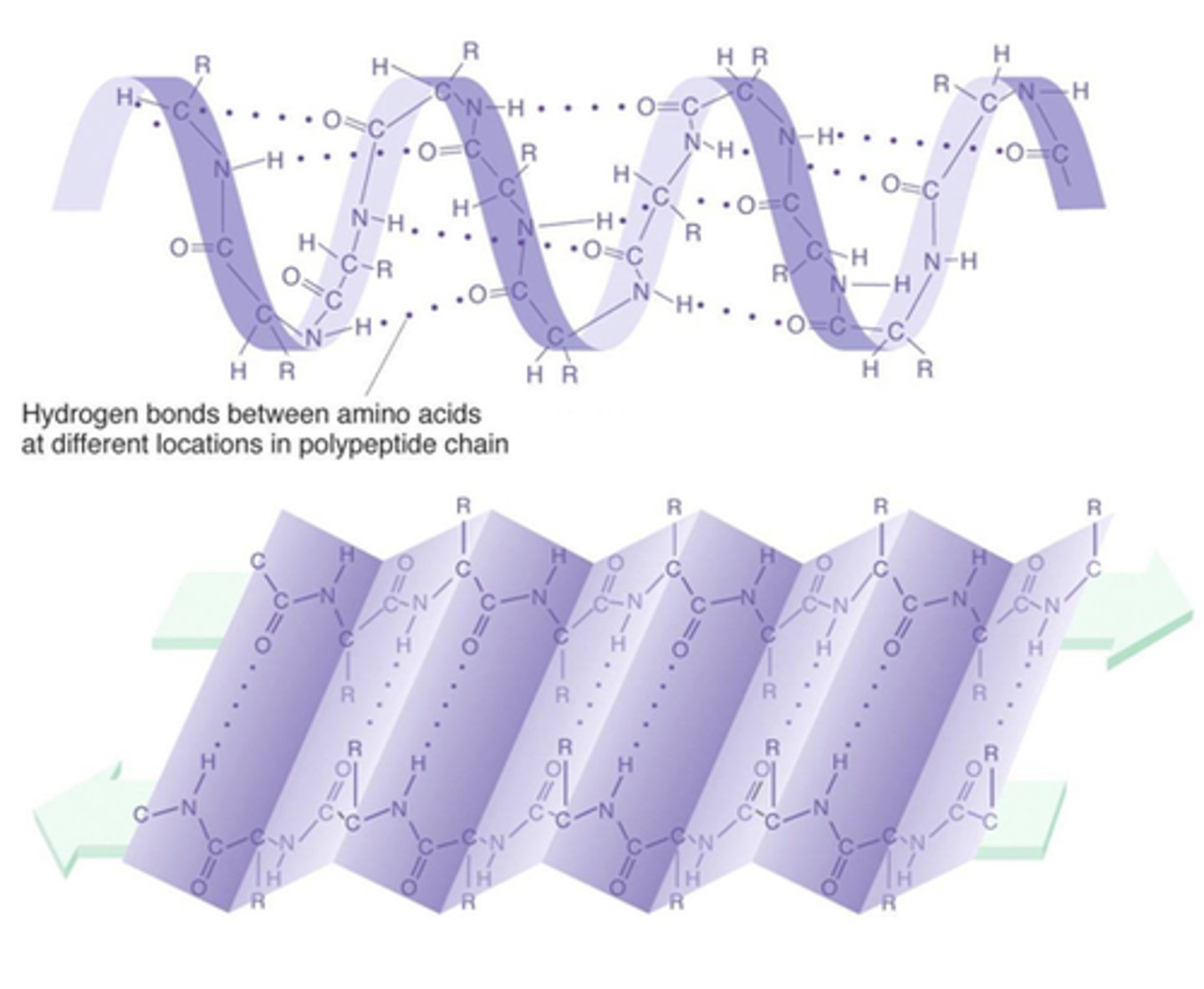
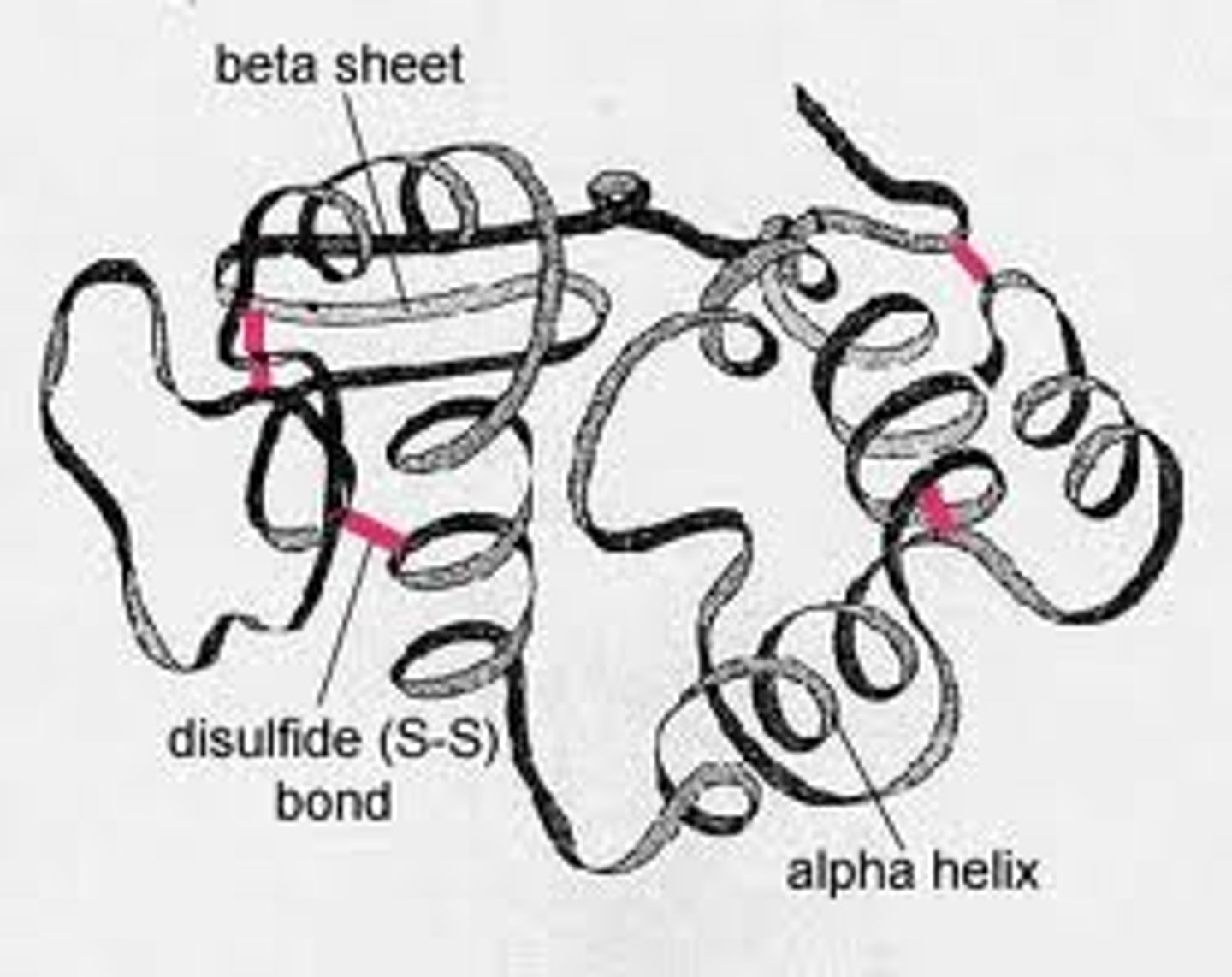
What is the tertiary structure?
The way in which the secondary structures fold themselves into a three-dimensional shape
What is the meaning of hydrophobic?
repels water
What is the meaning of hydrophilic?
Attracted to water
What is the active site?
the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds
What is the substrate?
the substance on which an enzyme acts
What does it mean when an enzyme denatures?
The active site has changed shape so the substrate can no longer fit in
What are enzymes?
biological catalysts that speedup a reaction without being used up
What is the activation energy?
the minimum amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
How can you increase the rate of reaction?
-increase the concentration of the reactants
-increase the surface area
-increase the temperature
- add a catalyst
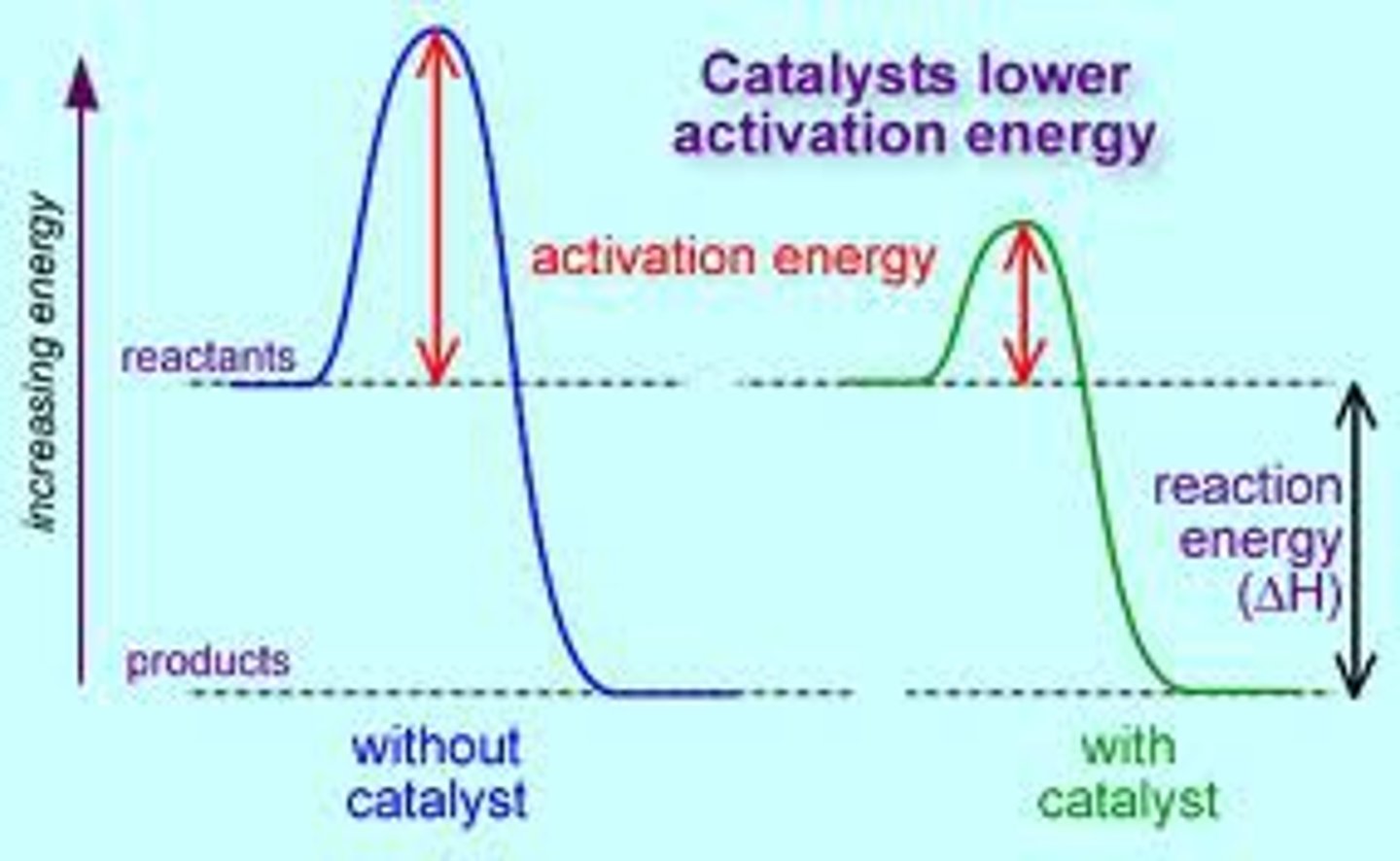
What does adding a catalyst do to a chemical reaction?
lowers the activation energy for the reaction so more collisions will have enough energy so more successful collisions
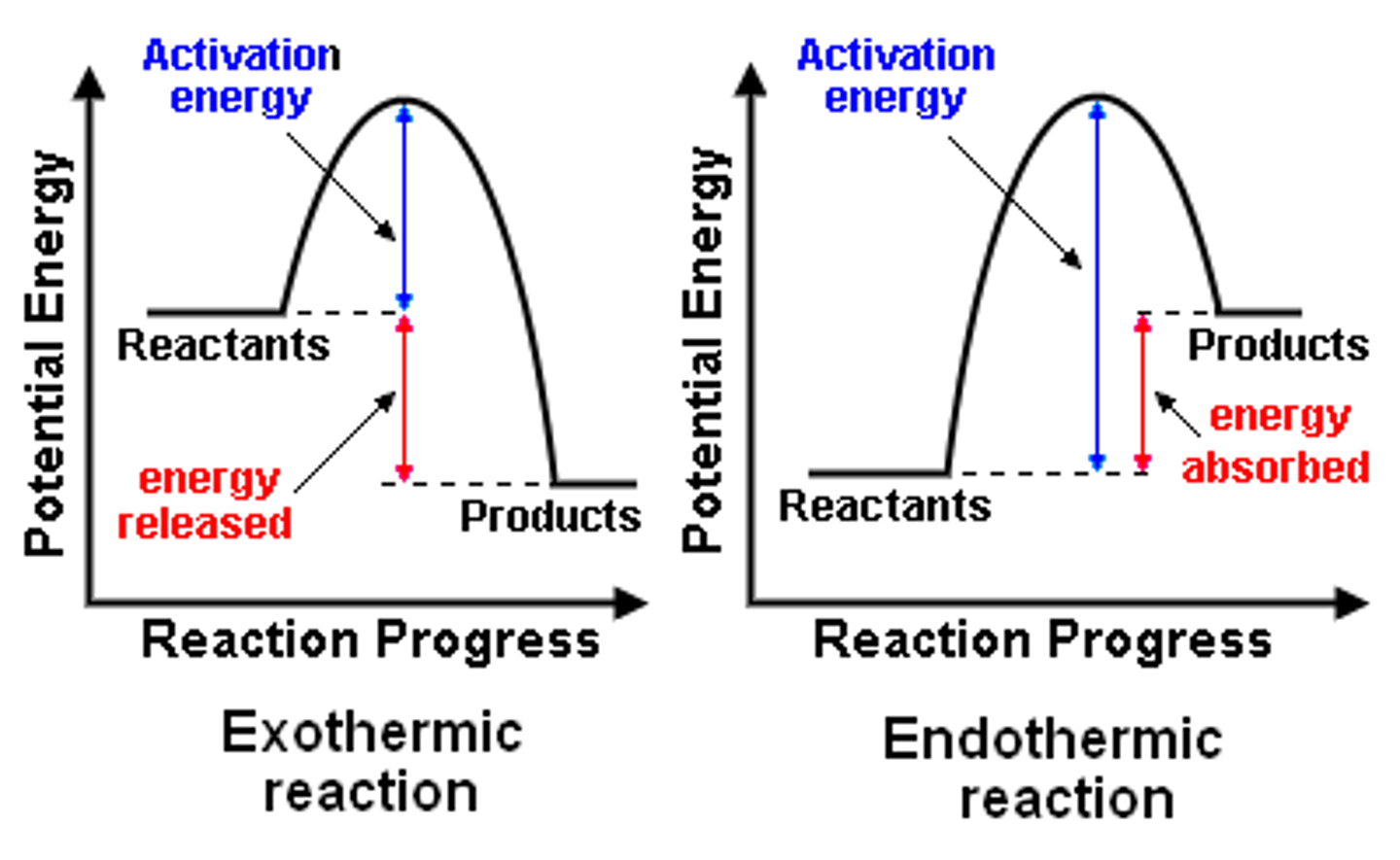
How do you show how a reaction is endothermic or exothermic?
A reaction profile
When the active site bind with the substrate, what is this called?
enzyme substrate complex
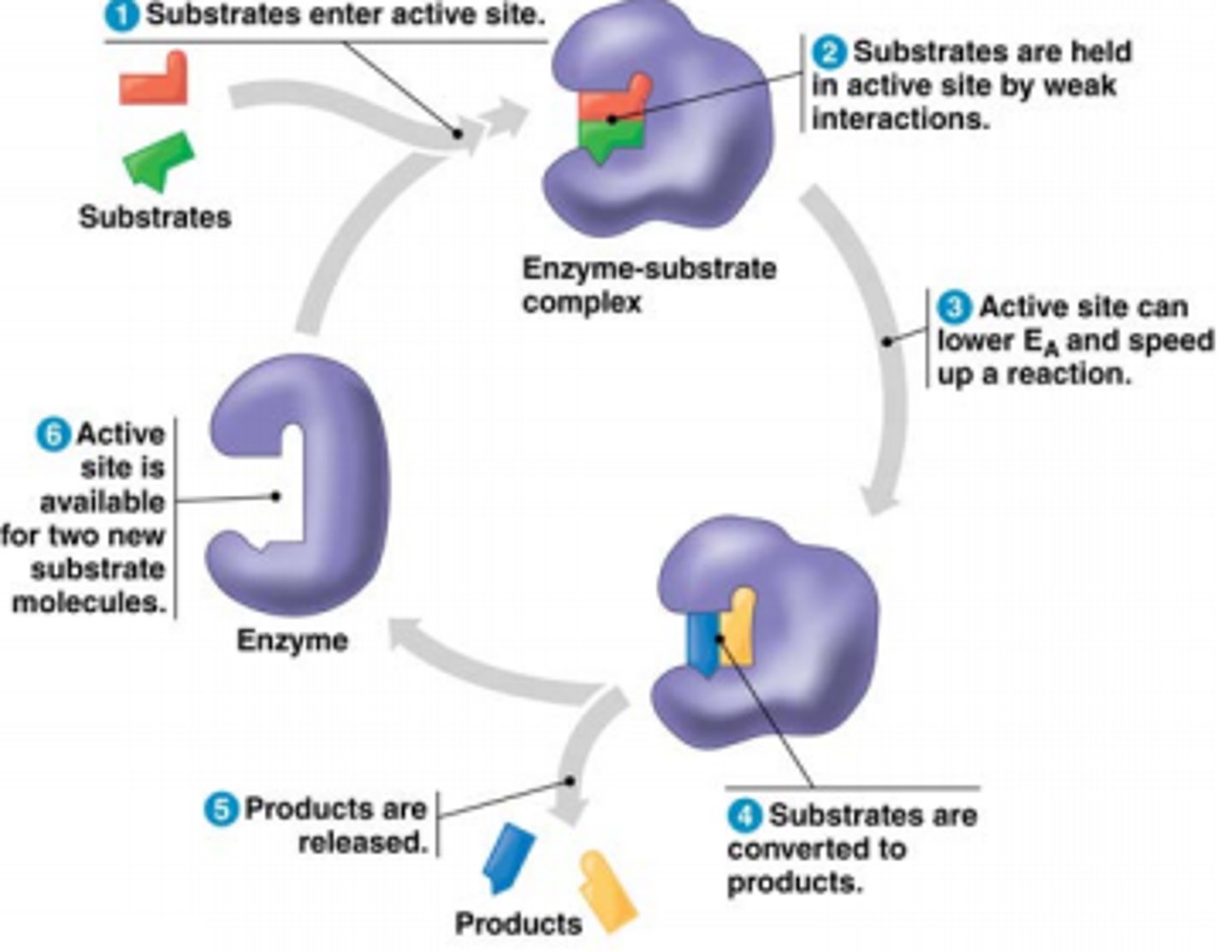
What does it mean when an enzyme has specificity?
The structure of an enzyme is such that it will only catalyse one particular chemical reaction with one particular substrate.
What does a substrate have?
a specific shape which fits exactly into the active site on the enzyme molecule
What is the meaning of induced fit?
an enzyme changes shape slightly when it binds its substrate to create the most effect fit for the enzyme
How can temperature affect the enzyme?
A higher temperature generally makes for higher rates of reaction, enzyme-catalysed or otherwise. However, either increasing or decreasing the temperature outside of a tolerable range can affect chemical bonds in the active site
How can pH effect enzymes?
For most enzyme-catalysed reactions, if the pH is either very low (strongly acidic) or very high (strongly alkaline), the enzyme can become denatured.
How can increasing the substrate or enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity?
Increasing either the substrate or enzyme concentration will mean that there will be more particles in a given volume of solution. The particles will therefore be closer together and so will collide more often. This means more substrate molecules will bind with the enzyme molecules in a given time.
Why is it important to measure the initial reaction rates?
This is because as a reaction proceeds, reactants are being used up and products are being formed.
What is fermentation?
the process by which glucose is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide in the presence of yeast.
When does fermentation take place?
absence of oxygen
What are the conditions of fermentation?
a temperature of 35 °C