UNIT 1 AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY - THINKING GEOGRAPHICALLY
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Spatial Perspective
where something is and why it is there
Map Distortion
a change in the shape, size or position of a place when it is shown on a map
Pattern
How things are arranged on a particular space
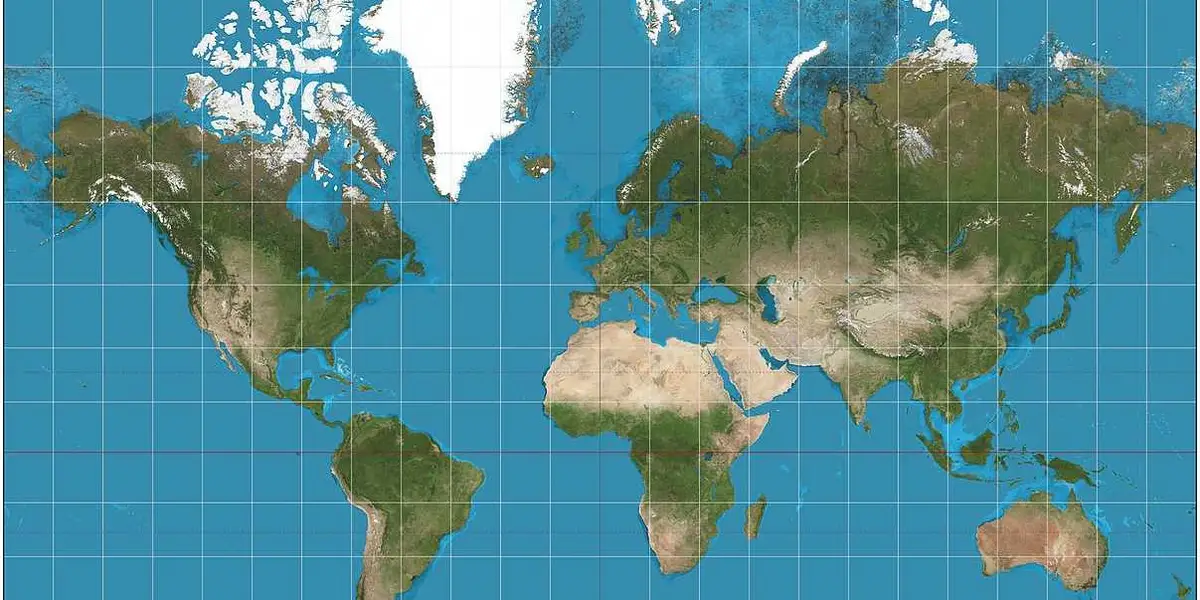
Mercator Map Projection
Accurately shown the shape and direction, but distorts the distance and size of land masses
Region
Area of the Earth’s surface with certain characteristics that make it distinct from other areas
World Systems Theory
Theory developed by Immanuel Wallerstein that explains the emergence of a core, periphery and semiperiphery in terms of economic and political connections
Human Geography
The study of events and processes that have shaped how humans understand, use, and alter Earth
Absolute Location
The exact position that something occupies on Earth’s surface (ex. Coordinates)
Absolute Distance
The distance that can be measured with a standard unit of length such as mile or kilometer
Relative Distance
Distance measured in terms such as cost or time
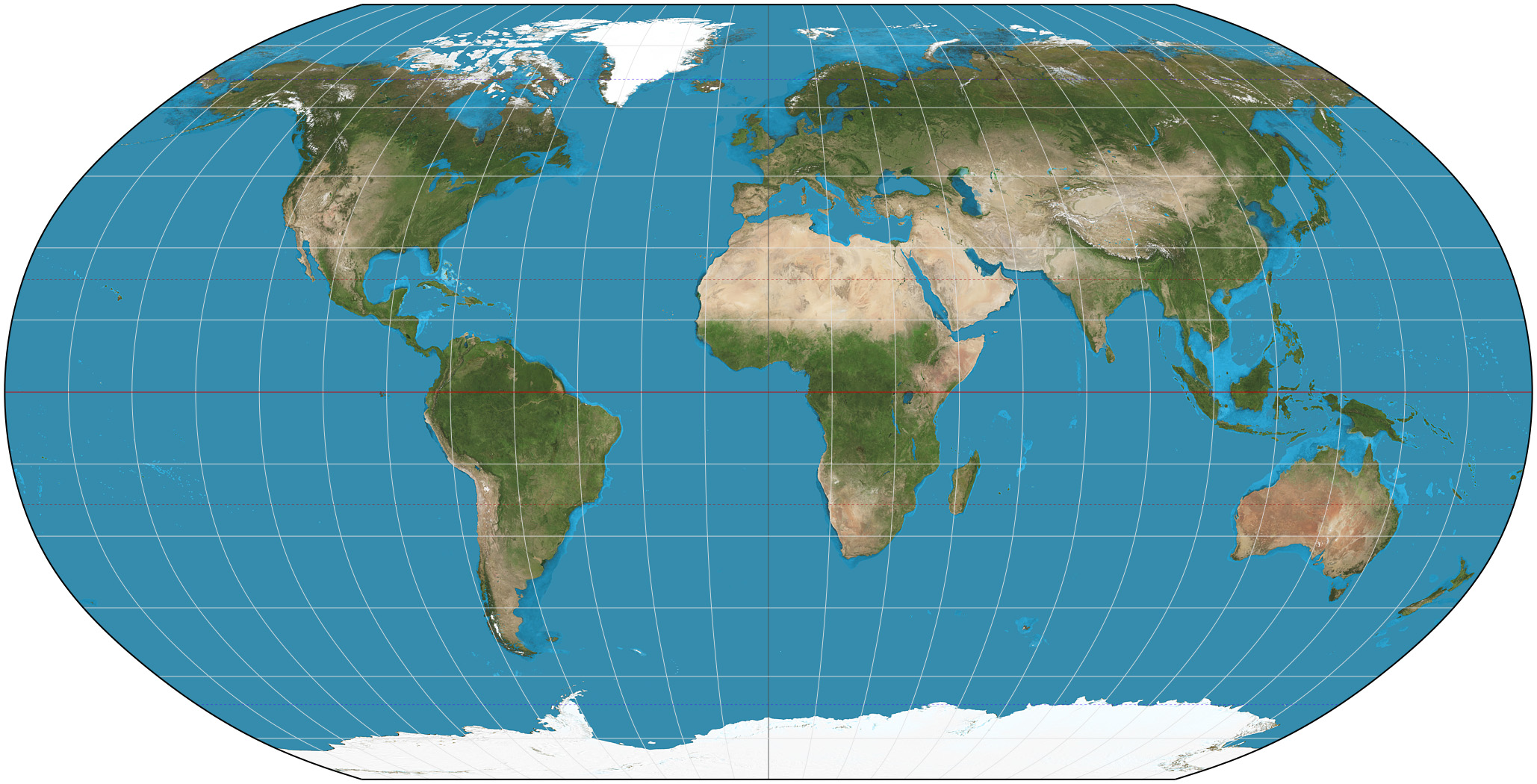
Robinson Map Projection
A map projection that does not distort the area of water to land masses as much, but whose direction does not hold true
Distance Decay
The effects of distance on interaction generally the greater the distance the less interaction
Time Space Compression
The rapid innovation of communication and transportation technologies associated with globalization that transforms the way people think about space and time and allowed time distance between places to decrease.
Core Country
Countries that are highly interconnected with good transportation and communication networks and infrastructure that supports economic activity they often provide manufactured goods for trade.
Periphery Country
Countries that have less stable government and poorer services such as mental health care, They often provide the raw materials to the core countries.
Absolute Direction
A compass direction such as north or south
Place
A location on Earth’s surface that is distinguished by physical and huma characteristics
Relative Location
A description of where a place is located in relation to other places or features.
Site
A place’s absolute location, as well its physical features such as landforms, climate and resources.
Sustainable Development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Qualitative Data
Interpretations of data sources such as field observations, media reports, travel narratives, policy documents, etc.
Relative Direction
Directions such as left, right, forward, backward, up and down based on peoples perception of places.
Natural Resources
Materials or Substances such as minerals, forests, water and fertile land that occur in nature and can be use for economic gain
Land Use
Various ways humans use the land such as agricultural, industrial, and residential or recreational.
Formal Region
Area that has one or more shared traits, can be physical, cultural or combination
Perceptual/Vernacular Region
A region that reflects peoples feels and attitudes about a place.
Map Scale
The relationship between the size of an object on a map and the size of the actual feature on Earth’s surface.
Reference Map
A map type tat shows reference information for a particular space, making it useful for finding landmarks and for navigation
Thematic Map
A type of map that displays one or more variables such as population, or income level within a specific area.
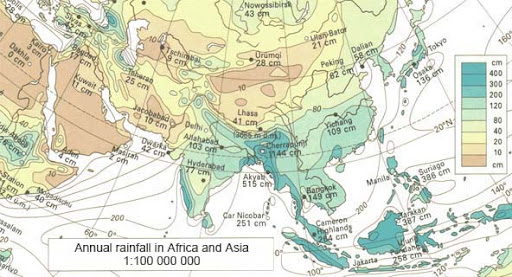
Isoline Map
Map displaying lines that connect points of equal value, for example, a map showing elevation levels.
Graduated Symbol Map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.

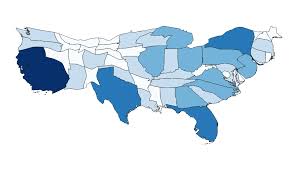
Cartogram Map
A special kind of map that distorts the shapes and sizes of countries or other political regions to represent economic or other kinds of data for comparison
Globalization
The expansion of economic, political and cultural processes to the point that they become global in scale and impact
Quantitative Data
information measured in numbers
Census
The official count of the # of people in a defined area
Topography
The shape and features of land
Situation
A place’s location in relation to other places or its surrounding features.
Space
The area between two or more things on Earth’s Surface
Density
Number of things such as animals people, objects in a specific area
Semi - Periphery Country
Countries that are in the process of industrializing
Dot Distribution Map
A map where dots are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena.
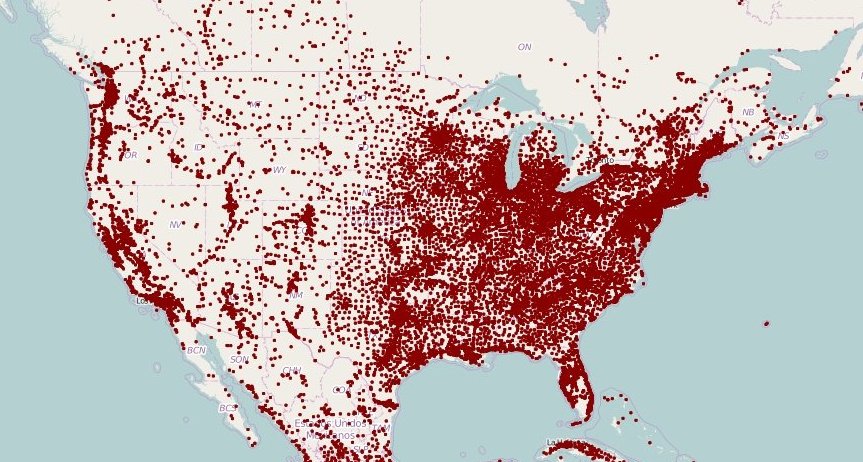
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes and displays geographic data
Global Posting System
An integrated network of at least 31 satellites in the U.S. System that orbit Earth and transmit location data to handheld readers.
Remote Sensing
The scanning of the Earth by Satellite or high-flying aircraft in order to obtain information about it
Choropleth Map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors or tones to represent spatial data as average values per unit area
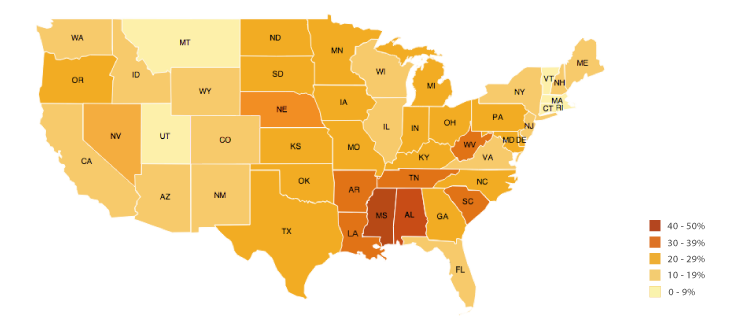
Political Map
A map showing units such as countries, provinces, districts, etc.
Clustering
Gathering; forming in a group
Azimuthal Map Projection
A map projection in which a region of the earth is projected onto a plane tangential to the surface, usually at a pole or the equator

Gall - Peters Projection
Equal area projection that distorts the shape of land masses (looks stretched out)
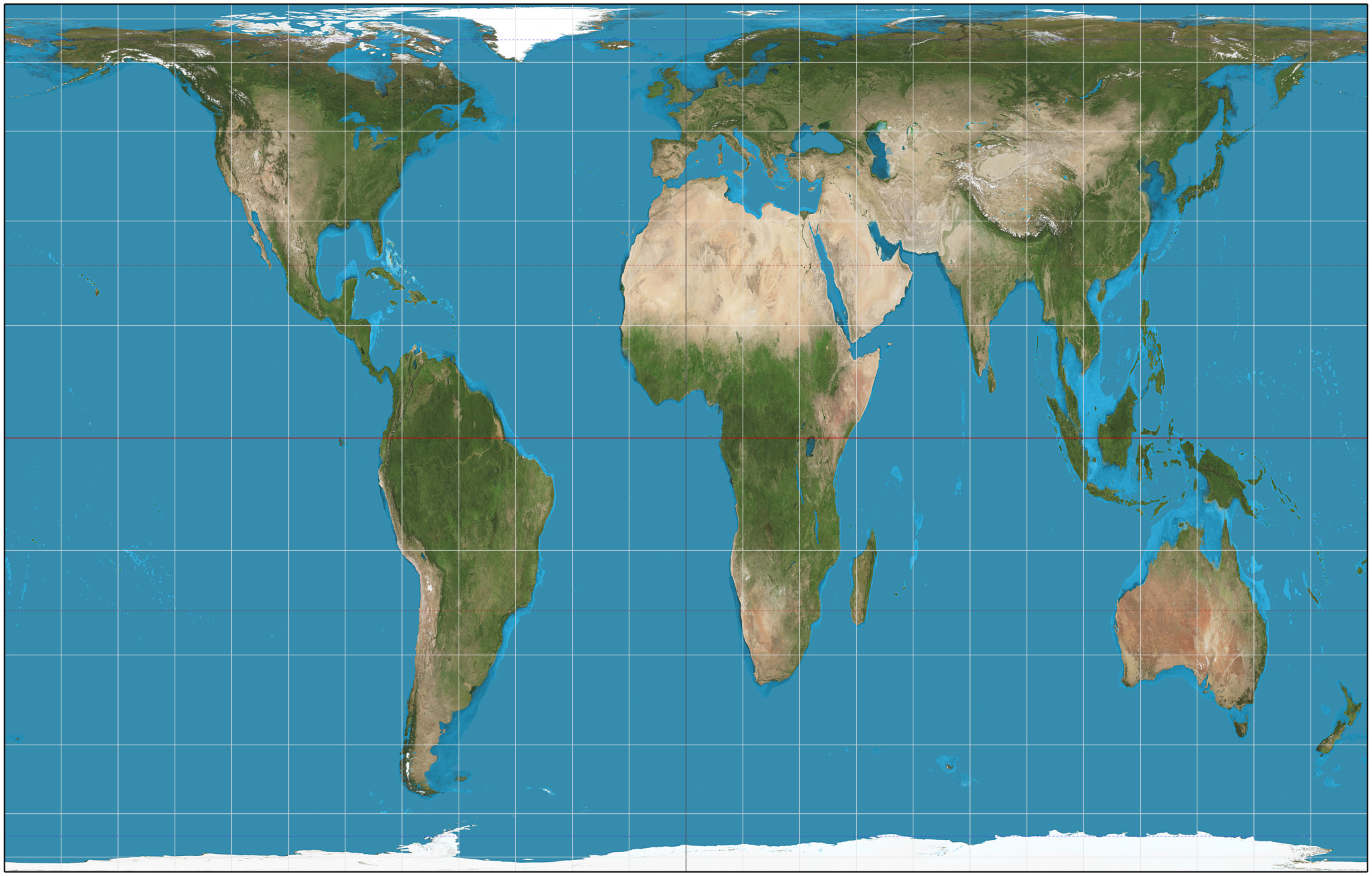
Flow
Movement of people, goods, information that has economic, social, political, or cultural effects on societies.
Environmental Determinism
Human behaviors is controlled by the physical environment
Possibilism
A theory that argues that humans have more urgency, or ability to produce a result, than environmental determinism would suggest
Functional Region
An area organized around a node or focal point
Sustainability
The use of Earth’s land and natural resources in a way that is ensured they will continue to be available in the future
Scale
The area of the world being studied
Dispersal
the distribution of individuals within geographic population boundaries.
Elevation
heigh above sea level
Node
The focus on a region