Lec Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
1
New cards
metabolism
the sum of all catabolic and anabolic reactions
2
New cards
anabolism
synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones together with the storage of energy
\
constructive metabolism
\
constructive metabolism
3
New cards
catabolism
breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, together with the release of energy
\
destructive metabolism
\
destructive metabolism
4
New cards
redox reactions
transfer of electrons (H) from donors to acceptors
always occur simultaneously
cells use electron carriers (H atoms) to shuttle them around
most anabolic reactions
\
Important ones
* Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
* Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+)
* Primarily used in photosynthesis
* Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
always occur simultaneously
cells use electron carriers (H atoms) to shuttle them around
most anabolic reactions
\
Important ones
* Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
* Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+)
* Primarily used in photosynthesis
* Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
5
New cards
conditions that affect enzymatic activity
* temperature
* pH
* competitive and noncompetitive inhibition
* feedback inhibition
* pH
* competitive and noncompetitive inhibition
* feedback inhibition
6
New cards
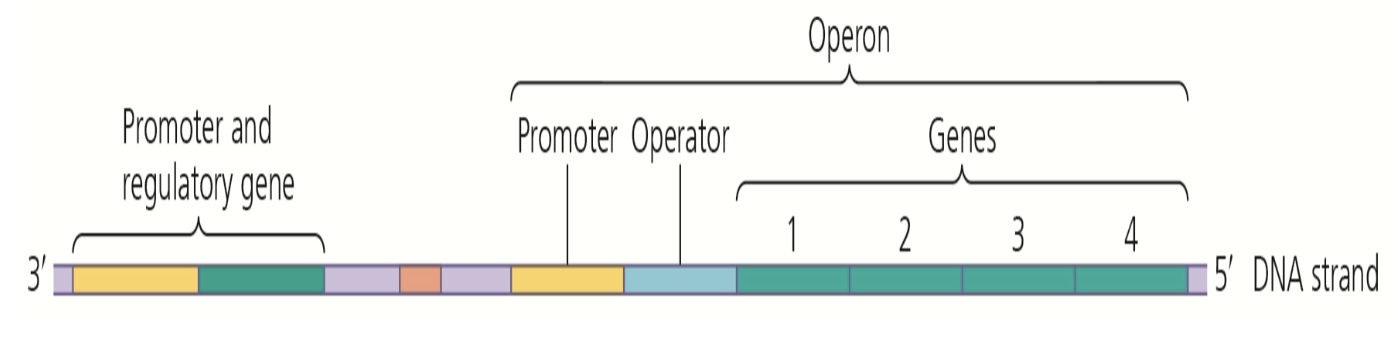
temperature
insufficient temperature for enzymes, typically increased temperatures, leads to denaturation
psychrophile – organisms that prefers to or can grow at lower temperatures
* Listeria can grow at refrigerator temperatures (outbreaks in prepackaged food – lettuce, deli meats, cheese)
* Cool temperatures can inhibit growth and reproduction of bacteria
* Do not become denatured when frozen
\
Mesophiles – organisms that prefer to grow best at or around body temperature
* Not limited to growing at this temperature
* E coli., Serratia, pseudomonas
\
Thermophiles and hyperthermophiles – organisms that prefer to grow at high temps
* Majority are archaea
psychrophile – organisms that prefers to or can grow at lower temperatures
* Listeria can grow at refrigerator temperatures (outbreaks in prepackaged food – lettuce, deli meats, cheese)
* Cool temperatures can inhibit growth and reproduction of bacteria
* Do not become denatured when frozen
\
Mesophiles – organisms that prefer to grow best at or around body temperature
* Not limited to growing at this temperature
* E coli., Serratia, pseudomonas
\
Thermophiles and hyperthermophiles – organisms that prefer to grow at high temps
* Majority are archaea
7
New cards
pH
* Most enzymes work best at a pH close to 7.35 (human pH)
* Organisms that can grow at more acidic pH acidophiles
* Lots of fungi
* Those that grow at more alkaline pH are alkaliphiles
* Extreme swings in pH can affect enzyme activity and they can denature
* Organisms that can grow at more acidic pH acidophiles
* Lots of fungi
* Those that grow at more alkaline pH are alkaliphiles
* Extreme swings in pH can affect enzyme activity and they can denature
8
New cards
inhibition
competitive
* inhibitor binds to the substrate before the enzyme blocking the enzyme from binding with the substrate
* Sulfanilamide drugs compete for the same receptors used to make folic acid (important in cell division to help make cofactors) in some bacteria
\
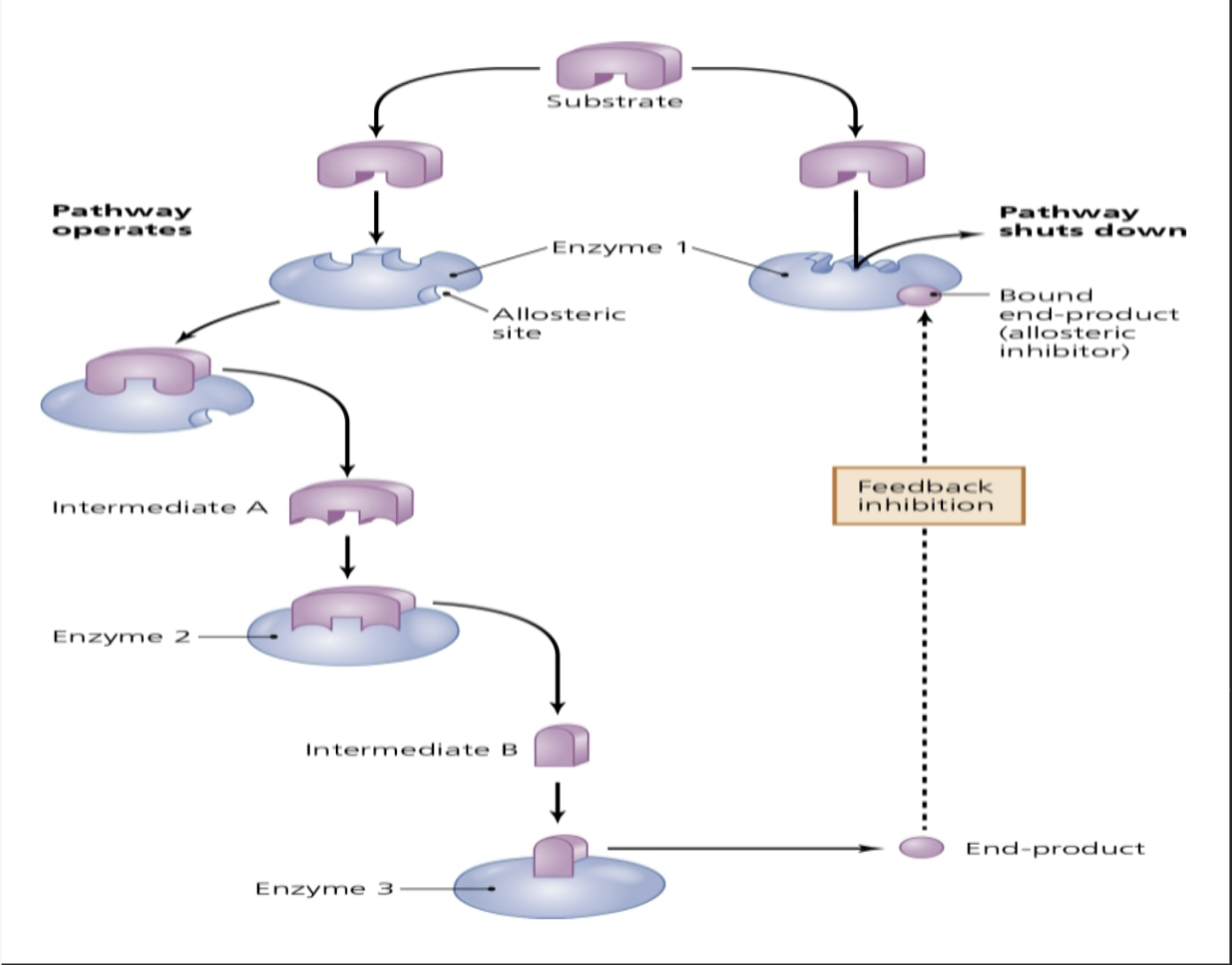
noncompetitive (allosteric)
* inhibitor binds to allosteric site of the enzyme and change the composition of the active site preventing the enzyme from binding to substrate or slow it down
* can be allosteric activators and can increase enzymatic activity for positive feedback
* inhibitor binds to the substrate before the enzyme blocking the enzyme from binding with the substrate
* Sulfanilamide drugs compete for the same receptors used to make folic acid (important in cell division to help make cofactors) in some bacteria
\
noncompetitive (allosteric)
* inhibitor binds to allosteric site of the enzyme and change the composition of the active site preventing the enzyme from binding to substrate or slow it down
* can be allosteric activators and can increase enzymatic activity for positive feedback
9
New cards
feedback inhibition
enzyme's activity is inhibited by the enzyme's end product
10
New cards
types of enzymes
* Hydrolases
* Isomerases
* Ligases or Polymerases
* Lyases
* Oxidoreductases
* Transferases
* Isomerases
* Ligases or Polymerases
* Lyases
* Oxidoreductases
* Transferases
11
New cards
hydrolases
commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond
12
New cards
isomerases
enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of a specified compound to an isomer
13
New cards
ligases/polymerases
catalyzing the reaction of joining two large molecules by establishing a new chemical bond
14
New cards
lyases
responsible for catalyzing addition and elimination reactions
15
New cards
oxidoreductases
catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions
16
New cards
transferases
catalyze the transfer of a group of atoms, such as amine, carboxyl, or phosphoryl from a donor substrate to an acceptor compound
17
New cards
enzymes
organic reactions would occur far too slowly to sustain life
* 1 mill – 10 million times slower without enzymes
\
not changed or destroyed during a reaction
\
lower the energy needed to break bonds (activation energy)
\
specific to certain sets of reactions (name often tells you)
\
made of proteins
\
activation energy is the hill that must be climbed before a catabolic reaction
* 1 mill – 10 million times slower without enzymes
\
not changed or destroyed during a reaction
\
lower the energy needed to break bonds (activation energy)
\
specific to certain sets of reactions (name often tells you)
\
made of proteins
\
activation energy is the hill that must be climbed before a catabolic reaction
18
New cards
glycolysis
occurs in the cytoplasm of most cells \n
initially requires the input of 2ATP
\
from this input 4 ATP are made for a net gain of 2ATP
\
2 NADH are also formed which are important if oxygen is present \n
final products are 2 pyruvic acid molecules, which can enter the next cycle as long as oxygen is present
initially requires the input of 2ATP
\
from this input 4 ATP are made for a net gain of 2ATP
\
2 NADH are also formed which are important if oxygen is present \n
final products are 2 pyruvic acid molecules, which can enter the next cycle as long as oxygen is present
19
New cards
aceytl coA
\n Pyruvic acids are stripped of carbon and oxygen and converted into:
* 2 Acetyl-CoA
* 2 NADH
* 2 CO2
* 2 Acetyl-CoA
* 2 NADH
* 2 CO2
20
New cards
kreb’s cycle
2 acetyl CoA’s enter this cycle and undergo a series of reactions with acid molecules (beginning \n with citric acid, hence the name) \n
overall result is the formation of:
* 2 ATP
* 6 NADH
* 2 FADH2
* 4 CO2
\
the main source of carbon dioxide that exits cells as waste to be carried by the blood stream
overall result is the formation of:
* 2 ATP
* 6 NADH
* 2 FADH2
* 4 CO2
\
the main source of carbon dioxide that exits cells as waste to be carried by the blood stream
21
New cards
electron transport chain
comprised of a series of electron transport carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane \n
electrons are transferred from FADH, NADH to the carriers and when this happens, H+ ions are \n released out of the mitochondrion. \n
last step the electrons are transferred from the carrier molecule to the Oxygen \n
H+ ions move with their concentration gradient through special membrane channels and this causes phosphates to be added to an ADP molecule to create ATP
electrons are transferred from FADH, NADH to the carriers and when this happens, H+ ions are \n released out of the mitochondrion. \n
last step the electrons are transferred from the carrier molecule to the Oxygen \n
H+ ions move with their concentration gradient through special membrane channels and this causes phosphates to be added to an ADP molecule to create ATP
22
New cards
ATP synthase
oxygen attracts hydrogens and as they move back in through ATP synthase ATP is created
\
10 NADH, 2 FADH, donate hydrogens
cytochrome C – shuttle protein
\
complex 4 electrons are starting to be transferred to FEA (final electron acceptor)
\
creates lots of O- and creates chemiosmotic gradient to draw positive H electrons through ATP synthase
\
3 turns of ATP synthase = 3 ATP
FADH only gives off enough for ATP to turn twice
\
10 NADH, 2 FADH, donate hydrogens
cytochrome C – shuttle protein
\
complex 4 electrons are starting to be transferred to FEA (final electron acceptor)
\
creates lots of O- and creates chemiosmotic gradient to draw positive H electrons through ATP synthase
\
3 turns of ATP synthase = 3 ATP
FADH only gives off enough for ATP to turn twice
23
New cards
fermentation
partial oxidation of sugar to release energy using an organic molecule from within the cell as the electron acceptor
NADH is oxidized to NAD+ using something within the cell. \n
Common end products are:
* C02
* Lactic Acid
* Alcohol
* Some industrial solvents – acetone, butanol
\
different bacteria create different end products
\
Aerobic – oxygen \n Anaerobic – hydrogen, sulfur, nitrogen containing compounds
NADH is oxidized to NAD+ using something within the cell. \n
Common end products are:
* C02
* Lactic Acid
* Alcohol
* Some industrial solvents – acetone, butanol
\
different bacteria create different end products
\
Aerobic – oxygen \n Anaerobic – hydrogen, sulfur, nitrogen containing compounds
24
New cards
fat metabolism
lipolysis - Triacylglycerols are broken down into glycerol and free fatty acids \n
glycerol - can easily be converted and go into one of the phases of glycolysis by forming pyruvic acids \n
free Fatty Acids - undergo beta-oxidation to become acetyl CoA molecules which can enter the citric acid cycle \n
processes are reversible \n
lipogenesis – occurs when ATP and glucose levels are high
glycerol - can easily be converted and go into one of the phases of glycolysis by forming pyruvic acids \n
free Fatty Acids - undergo beta-oxidation to become acetyl CoA molecules which can enter the citric acid cycle \n
processes are reversible \n
lipogenesis – occurs when ATP and glucose levels are high
25
New cards
protein metabolism
amino acids can be interconverted to allow them to enter phases of carbohydrate metabolism \n
bacteria or fungi that use protein catabolism are often related to food spoilage (i.e. the fishy smell or dead fish)
bacteria or fungi that use protein catabolism are often related to food spoilage (i.e. the fishy smell or dead fish)
26
New cards
order of use of macromolecules
1. glucose
2. glycogen
3. fats = glycerol and fatty acid
4. proteins = amino acids interconverted
27
New cards
anaerobes
* only grow where there is no oxygen
* Will not make SOD (superoxide dismutase)
\
Obligate
* Micrococcus luteus
* Pseudomonas
\
Strict
* Clostridium sporogeneses
* Do not use oxygen and its toxic to them
* Do not have SOD or catalase to detoxify oxygen
* Will not make SOD (superoxide dismutase)
\
Obligate
* Micrococcus luteus
* Pseudomonas
\
Strict
* Clostridium sporogeneses
* Do not use oxygen and its toxic to them
* Do not have SOD or catalase to detoxify oxygen
28
New cards
aerobes
grows in the presence of air or requires oxygen for growth
\
use other antioxidants to combat ROS
* Vitamins C and E
\
use other antioxidants to combat ROS
* Vitamins C and E
29
New cards
aerotolerant anaerobes
* tolerate but do not need oxygen
* Will not use it but if its present it does not kill them
* Will not use it but if its present it does not kill them
30
New cards
facultative anaerobes
* most use oxygen first
* Can switch when oxygen runs out
* *E coli.*
* Can switch when oxygen runs out
* *E coli.*
31
New cards
microaerophiles
* aka capnophiles
* Primarily grow at border between oxic and anoxic zone
* Grow best in environments with little oxygen
* *H pylori.* causes stomach ulcers
* Primarily grow at border between oxic and anoxic zone
* Grow best in environments with little oxygen
* *H pylori.* causes stomach ulcers
32
New cards
photoautotrophs
* Use photosynthesis
* Uses light and CO2 to feed itself
* Cyanobacteria – plankton
* Use water as electron source to reduce CO2 and produce energy and O2 as waste
* Uses light and CO2 to feed itself
* Cyanobacteria – plankton
* Use water as electron source to reduce CO2 and produce energy and O2 as waste
33
New cards
chemoautotrophs
* Uses chemical compounds and organic compounds to feed itself
* Hetero- = different
* Can eat wide variety of things to get C from them
* Hetero- = different
* Can eat wide variety of things to get C from them
34
New cards
singlet oxygen
(1O2)
has higher energy electrons
production of carotenoids
has higher energy electrons
production of carotenoids
35
New cards
superoxide radical
(O2-)
produced during incomplete reduction during aerobic respiration
superoxide dismutase
produced during incomplete reduction during aerobic respiration
superoxide dismutase
36
New cards
peroxide anion
(O22-)
hydrogen peroxide is sometimes formed during aerobic respiration and must be broken down
catalase or peroxidase enzymes
hydrogen peroxide is sometimes formed during aerobic respiration and must be broken down
catalase or peroxidase enzymes
37
New cards
hydroxyl radicals
(OH-)
result from radiation and incomplete breakdown of peroxides
generally low because of catalase and peroxidase
result from radiation and incomplete breakdown of peroxides
generally low because of catalase and peroxidase
38
New cards
quorum sensing
the regulation of gene expression in response to fluctuations in cell-population density
39
New cards
biofilm formation
1. free swimming microbes are vulnerable to environmental stresses
2. some microbes land on a surface and attach
3. cells begin producing and extra cellular matrix and secrete quorum-sensing molecules
4. quorum sensing triggers cells to change their biochemistry and shape
5. new cells arrive, possibly including new species, and water channels form in the biofilm
6. some microbes escape from the biofilm to resume a free-living existence and perhaps to form a new biofilm on another surface
40
New cards
temperature effect on growth
\
psychrophiles like growing in fridge temperatures
* Listeria can cause
* 10 C
* Min -> max growth temperature
* Peak is preferred temperature
\
Mesophiles – grow best at body temp 37 C
* 98.6 F
* Wide growth range – Serratia and pseudomonas
\
Thermophiles peak temp 65 C
* Extra H bonds and covalent bonds
* Help proteins maintain shape
\
Hyperthermophiles peak temp 95 C
psychrophiles like growing in fridge temperatures
* Listeria can cause
* 10 C
* Min -> max growth temperature
* Peak is preferred temperature
\
Mesophiles – grow best at body temp 37 C
* 98.6 F
* Wide growth range – Serratia and pseudomonas
\
Thermophiles peak temp 65 C
* Extra H bonds and covalent bonds
* Help proteins maintain shape
\
Hyperthermophiles peak temp 95 C
41
New cards
prokaryote and protozoa pH
preferred range 6.5-7.5
\
Acidophiles – grow better in acidic environments
* Parts of our body naturally inhibit certain microbes
\
Alkalinophiles – grow better in alkaline environments
* Vibrio cholera – grows best at pH 9
\
Acidophiles – grow better in acidic environments
* Parts of our body naturally inhibit certain microbes
\
Alkalinophiles – grow better in alkaline environments
* Vibrio cholera – grows best at pH 9
42
New cards
osmotic pressure
Hypertonic solutions – will cause cells to shrivel
\
Hypotonic solutions – will cause cells to swell or burst
\
Halophiles – can tolerate high salt environments
* Staph aureus is facultative halophile that can tolerate 20% salt
\
Hypotonic solutions – will cause cells to swell or burst
\
Halophiles – can tolerate high salt environments
* Staph aureus is facultative halophile that can tolerate 20% salt
43
New cards
selective media
* Selects for or inhibits growth of organisms
* Use salt to select for staph
\
e.g.,
* Use salt to select for staph
\
e.g.,
44
New cards
differential media
* Cause color change
* PH change
* Does not stop anything from growing
* Blood
* Homolysis – bacteria digesting RBCs
* PH change
* Does not stop anything from growing
* Blood
* Homolysis – bacteria digesting RBCs
45
New cards
binary fission
Asexual reproduction
\
Steps
* Replicates chromosomes
* Cell elongates and growth between attachments sites pushes the chromosomes apart
* Cells form new membranes and wall across midline
* Septum is complete and daughter cells may or may not separate
\
Steps
* Replicates chromosomes
* Cell elongates and growth between attachments sites pushes the chromosomes apart
* Cells form new membranes and wall across midline
* Septum is complete and daughter cells may or may not separate
46
New cards
generation time
how long it takes for a bacterial cell to grow and divide
\
average generation for E coli. Is 18 minutes
* E coli is one of the fastest
\
staph aureus are around 20-25 minutes
\
many bacteria have generation times of 1 hour-2 hours
\
Mycobacteria
* Cause TB
* Between 7-10 days
* Very slow generation time
\
average generation for E coli. Is 18 minutes
* E coli is one of the fastest
\
staph aureus are around 20-25 minutes
\
many bacteria have generation times of 1 hour-2 hours
\
Mycobacteria
* Cause TB
* Between 7-10 days
* Very slow generation time
47
New cards
growth phases
Lag phase can last a few days
* Adjusting to environment
\
Log phase
* Exponential growth
* Target for antimicrobials
* Work best when bacteria are very active
\
Stationary phase
* Nutrients begin to deplete
* Equal numbers of dead and living bacterial cells
* Bacteria is still susceptible to antimicrobial
\
Decline phase
* More nutrients run out
* Begins to die off
* Endospore formation
* Extremely difficult to destroy
* Adjusting to environment
\
Log phase
* Exponential growth
* Target for antimicrobials
* Work best when bacteria are very active
\
Stationary phase
* Nutrients begin to deplete
* Equal numbers of dead and living bacterial cells
* Bacteria is still susceptible to antimicrobial
\
Decline phase
* More nutrients run out
* Begins to die off
* Endospore formation
* Extremely difficult to destroy
48
New cards
logarithmic growth
exponential growth
49
New cards
persister cells
\
* Different from endospores
* Random variation
* The ones who survive the longest in poor conditions
* Different from endospores
* Random variation
* The ones who survive the longest in poor conditions
50
New cards
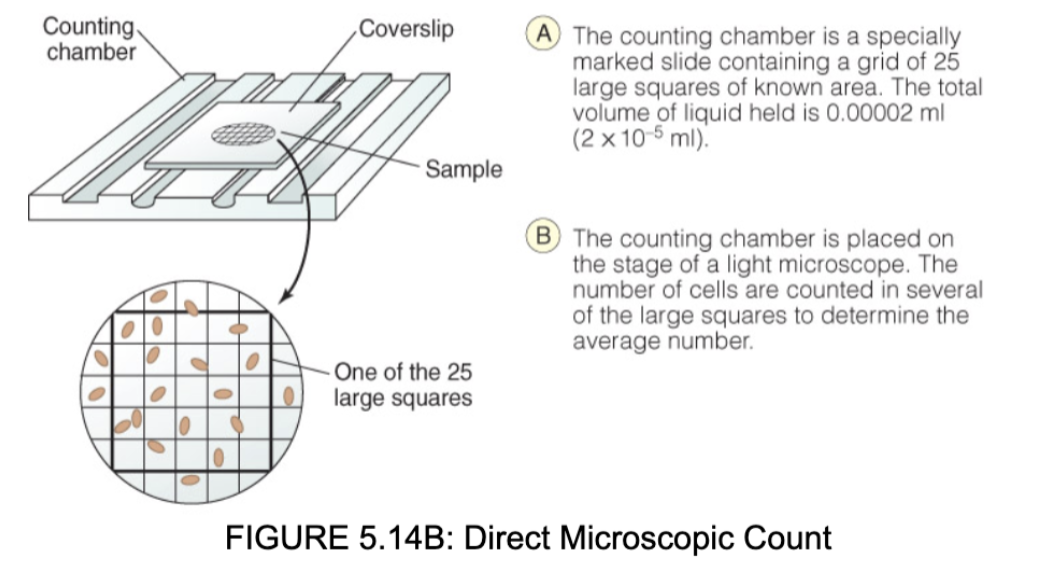
direct measuring of bacterial population
* Direct microscopic count using live cells
* More accurate than dilution
* More accurate than dilution
51
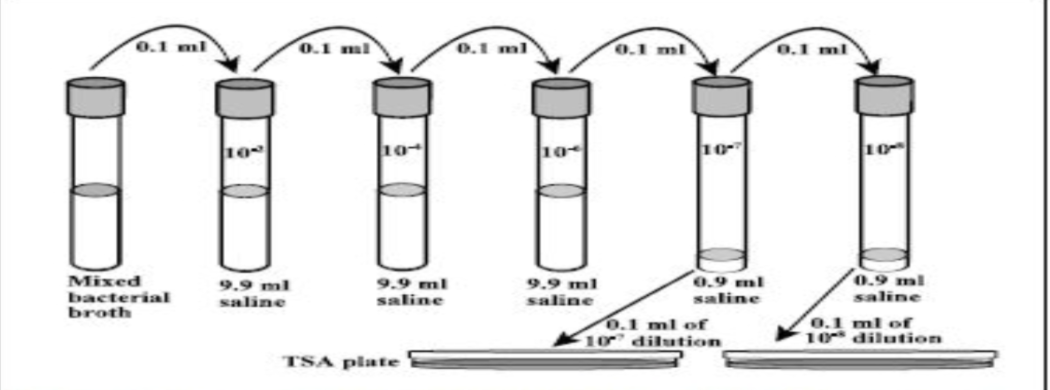
New cards
indirect measuring of bacterial population
* serial dilution
* estimation
* estimation
52
New cards
other ways of measuring bacterial population
* Turbidity of a sample can be measured with a spectrophotometer
* Dry weights can be taken of the cell population
* Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide consumption can be measured
* Genetic Methods are becoming increasingly common
* Dry weights can be taken of the cell population
* Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide consumption can be measured
* Genetic Methods are becoming increasingly common
53
New cards
DNA
* The same across all organisms
\
Principal of complementarity
* Thymine -> Adenine
* Guanine -> Cytosine
\
* Deoxyribose backbone
* Highly coiled to save space
* Protects it from being degraded
* Essential function – to code for proteins
\
Principal of complementarity
* Thymine -> Adenine
* Guanine -> Cytosine
\
* Deoxyribose backbone
* Highly coiled to save space
* Protects it from being degraded
* Essential function – to code for proteins
54
New cards
prokaryote genome
bacteria
* single copies (haploid) of one or more chromosomes
* plasmids present in some
* circular or linear DNA
* DNA in nucleoid of cytoplasm and plasmids
* no histones
\
archaea
* one (haploid)
* plasmids present in some
* circular DNA
* DNA in nucleoid of cytoplasm and plasmids
* histones present
* single copies (haploid) of one or more chromosomes
* plasmids present in some
* circular or linear DNA
* DNA in nucleoid of cytoplasm and plasmids
* no histones
\
archaea
* one (haploid)
* plasmids present in some
* circular DNA
* DNA in nucleoid of cytoplasm and plasmids
* histones present
55
New cards
eukaryote genome
* diploid chromosomes
* plasmids present in some algae, protozoa, and fungi
* linear DNA in nucleus and chloroplasts
* nonlinear DNA in plasmids and mitochondria
* histone in nuclear chromosomes not non nuclear
* plasmids present in some algae, protozoa, and fungi
* linear DNA in nucleus and chloroplasts
* nonlinear DNA in plasmids and mitochondria
* histone in nuclear chromosomes not non nuclear
56
New cards
plasmids
* DNA that can be transferred between bacteria
\
F plasmid
* Fertility plasmids, carry information for conjugation
\
R plasmids
* Resistance plasmids, carry genes for resistance to other bacteria
\
Bacteriocin plasmids
* kills bacteria of the same species or similar species to eliminate competitors
\
Virulence plasmids
* carry genes that code for enzymes or toxins that make them pathogenic
* Especially gram positive is through production of exotoxins
* Can be exchanged between bacteria
\
F plasmid
* Fertility plasmids, carry information for conjugation
\
R plasmids
* Resistance plasmids, carry genes for resistance to other bacteria
\
Bacteriocin plasmids
* kills bacteria of the same species or similar species to eliminate competitors
\
Virulence plasmids
* carry genes that code for enzymes or toxins that make them pathogenic
* Especially gram positive is through production of exotoxins
* Can be exchanged between bacteria
57
New cards
leading strand
* replicated continuously
* does not require DNA ligase
* 5’-3’
* only single RNA primer is required
* does not require DNA ligase
* 5’-3’
* only single RNA primer is required
58
New cards
lagging strand
* discontinuous growth
* formed in fragments - Okasaki fragments
* ligase is required to glue together fragments
* starting of each fragment requires RNA primer
* slower to replicate than leading
* formed in fragments - Okasaki fragments
* ligase is required to glue together fragments
* starting of each fragment requires RNA primer
* slower to replicate than leading
59
New cards
bacterial DNA replication
* replication much faster than eukaryotic bc of generation time
* bi-directionality
\
methylated as created
* helps to control bacterial gene expression, initiate DNA replication, differentiate own DNA from viral DNA
* bi-directionality
\
methylated as created
* helps to control bacterial gene expression, initiate DNA replication, differentiate own DNA from viral DNA
60
New cards
topoisomerase
winds DNA back up
61
New cards
helicase
unwinds DNA
62
New cards
polymerase
binds the strands of DNA
63
New cards
genotype
genetic sequence that codes for characteristics
64
New cards
phenotype
physical expression of gene
65
New cards
inducible operon
* lac operon
* Usually turned off and must be activated by inducers
* Produces genes that make enzyme to digest lactose
* Usually turned off and must be activated by inducers
* Produces genes that make enzyme to digest lactose
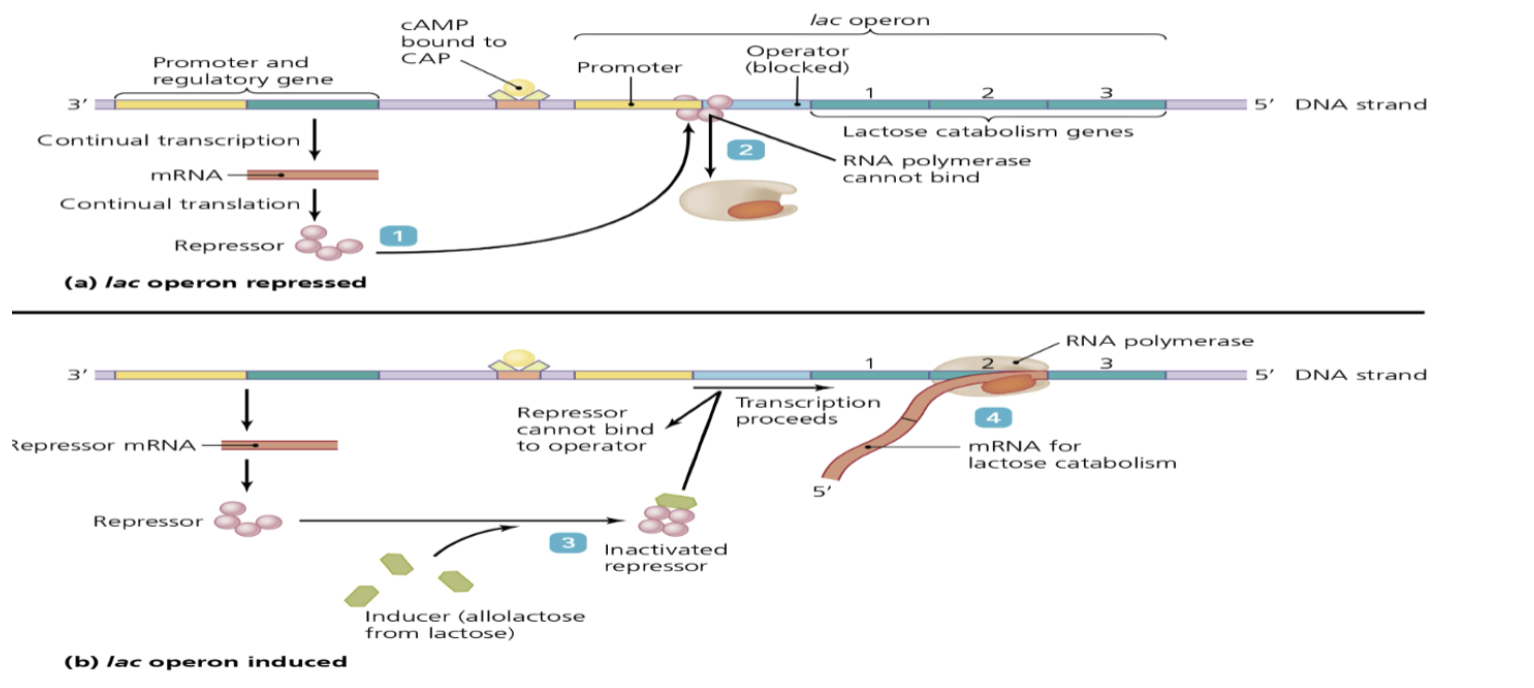
66
New cards
repressible operon
* trp operon
* Usually turned on and must be inhibited by repressors
* produces tryptophan
* Usually turned on and must be inhibited by repressors
* produces tryptophan
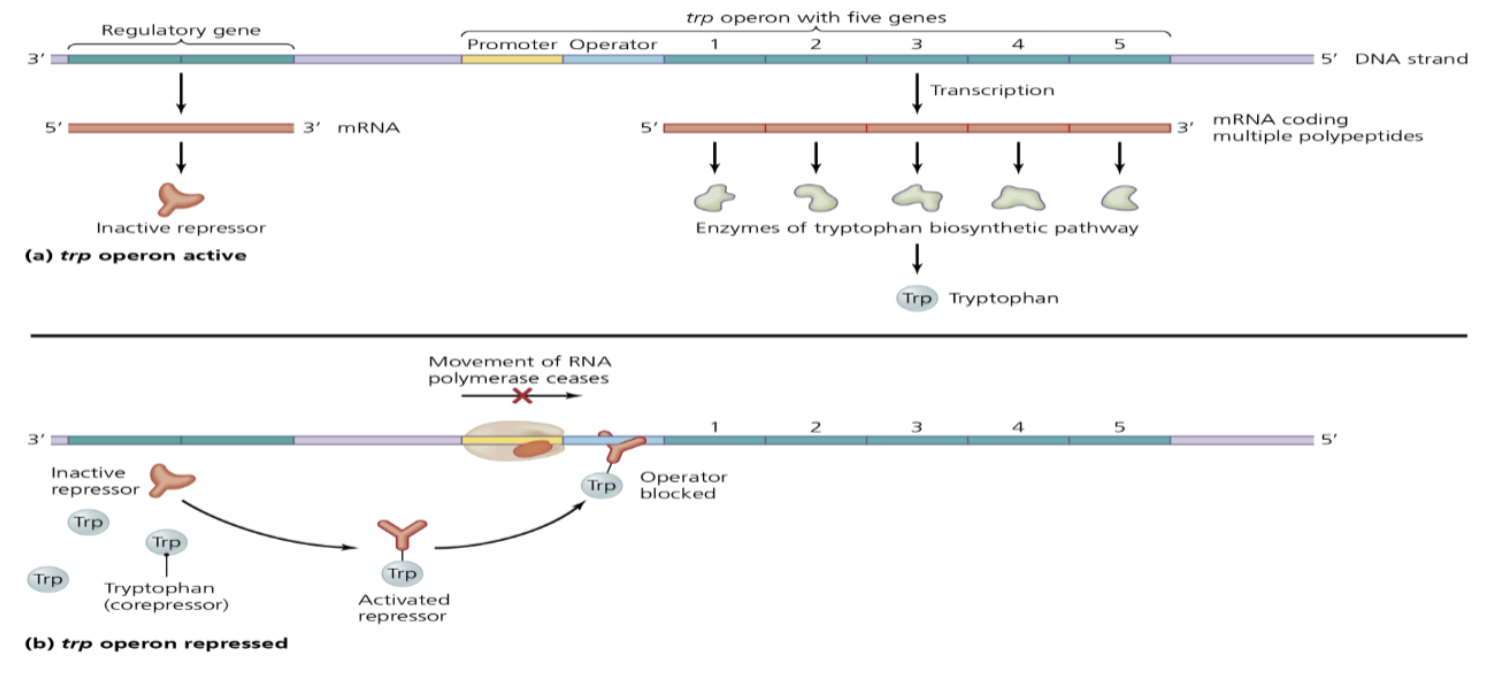
67
New cards
protein synthesis
* DNA uncoils for transcription
* mRNA is produced in the nucleus
* mRNA moves to the ribosome
* Ribosome moves along the mRNA
* tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome
* Polypeptide is produced
\
bacteria
* One maybe two proteins made from translation
\
eukarya
* must cut out introns to form mRNA
* mRNA is produced in the nucleus
* mRNA moves to the ribosome
* Ribosome moves along the mRNA
* tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome
* Polypeptide is produced
\
bacteria
* One maybe two proteins made from translation
\
eukarya
* must cut out introns to form mRNA
68
New cards
triplet
3 base sequence on DNA
69
New cards
codon
3 base sequence on mRNA
70
New cards
anticodon
3 base sequence on transfer RNA
71
New cards
operons
* contains promoter, operator, and genes that code for end product
* has promoter and regulatory gene out front
* has promoter and regulatory gene out front