7.1 hypothesis testing, 7.2 finding critical values, 7.3 one-tailed test, 7.4 two-tailed test
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is a hypothesis?
A statement made about the value of a population parameter
How can you test a hypothesis about a population?
By carrying out an experiment or taking a sample from the population
What is the test statistic?
The result of the experiment or the statistic that is calculated from the sample
In order to carry out the test, you need to form two hypotheses
What are the two hypotheses?
The null hypothesis, H0, is the hypothesis that you assume to be correct
The alternative hypothesis, H1, tells you about the parameter if your assumption is shown to be wrong
In this chapter, what should you always give H0 and H1 in terms of ?
p (the population parameter)

Example 1

What are one-tailed tests?
Hypothesis tests with alternative hypotheses in the form H1: p>… and H: p<…
What are two-tailed tests?
Hypothesis tests with an alternative hypothesis in the form H1: p≠….


Example 2
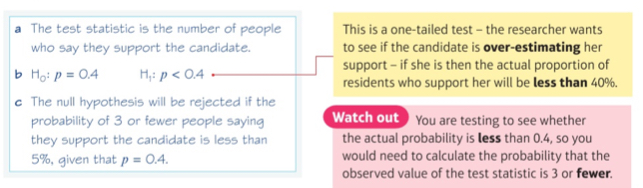
If a dice is biased towards 6, what is the probability of landing on a 6?
Greater than 1/6
In this chapter, what distribution do we assume the test statistic can be modelled by?
A binomial distribution
What is a critical region?
A region of the probability distribution which, if the test statistic falls within it, would cause you to reject the null hypothesis
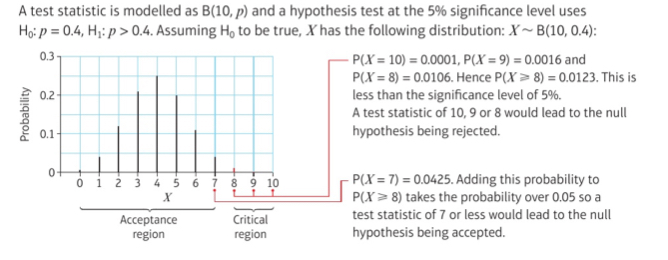
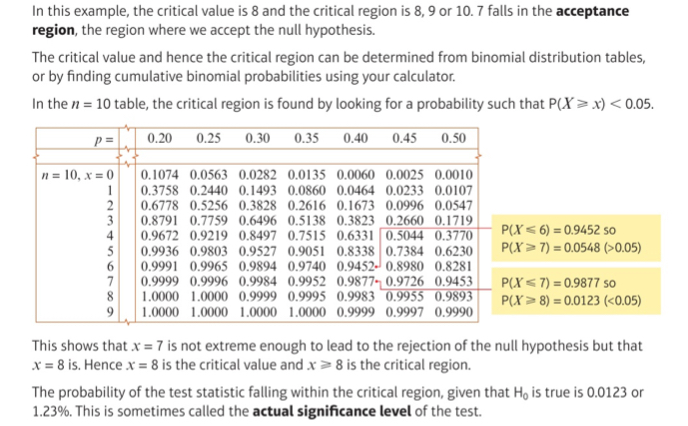
What is the critical value?
The first value to fall inside of the critical region
What is the actual significance level of a hypothesis test?
The probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis

Example 3a
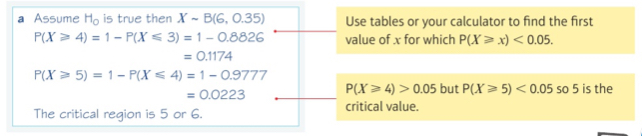

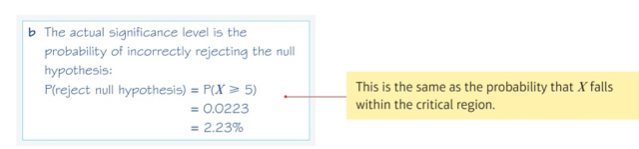
Example 3b
For a two-tailed test, what is the critical region made up of?
Two parts- one at each end of the distribution

Example 4
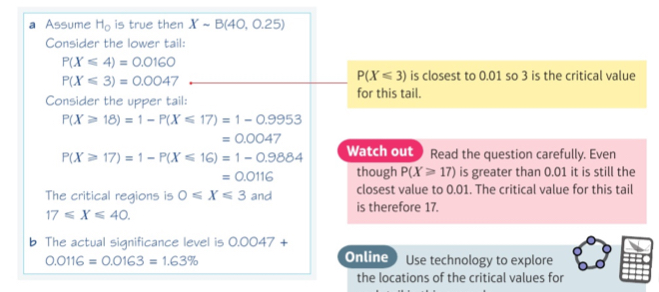
If you have to carry out a one-tailed hypothesis test, what do you need to do?
formulate a model for the test statistic
Identify suitable null and alternative hypotheses
Calculate the probability of the test statistic taking the observed value (or higher/lower), assuming the null hypothesis is true
Compare this to the significance level
Write a conclusion in the context of the question
alternatively, you can find the critical region and see whether the unserved value of the test statistic lies inside it
What is the p-value?
The probability is known as the p-value for that observation

Example 5: method 1 - using significance level
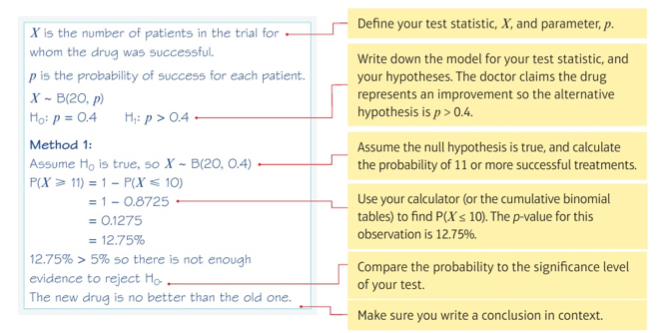

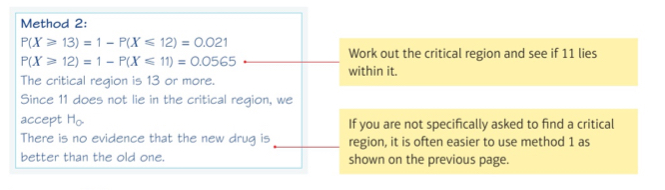
Example 5: method 2- using critical region
When is a two-tailed test used?
When it is thought that the probability has changed in either direction
How can you carry out a two-tailed test?
You can either:
Halve the significance level of the test to give a probability associated with one tail, then compare this with your calculated probability
Double your calculated probability to obtain the p-value, and compare this with the significance level of the test