ANATOMY OF SENSES: EYES
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
photoreceptors
used by eyes to detect light
III, IV, VI
which cranial nerves stimulate the rectus and oblique muscles to move the eye?
sclera, urea, and retina
layers of the wall of the eye
Orbital Region
region of the eye that is protected by surrounding bones, supported by connective tissues, and cushioned by fatty tissues behind the eyes
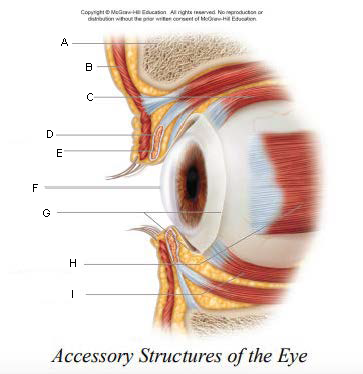
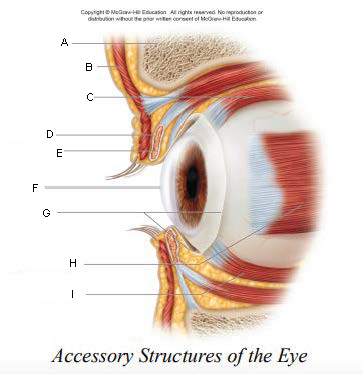
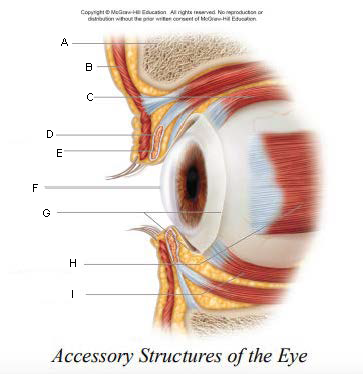
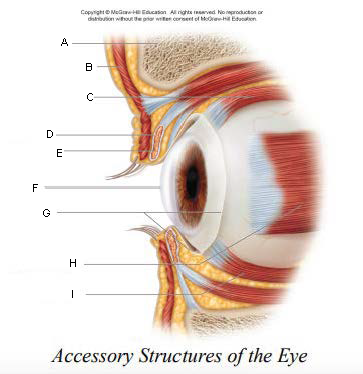
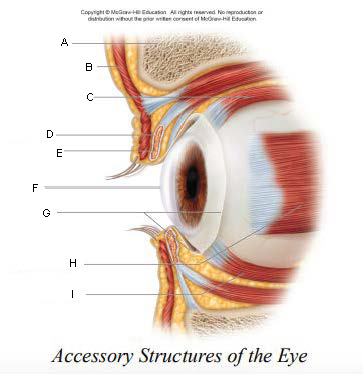
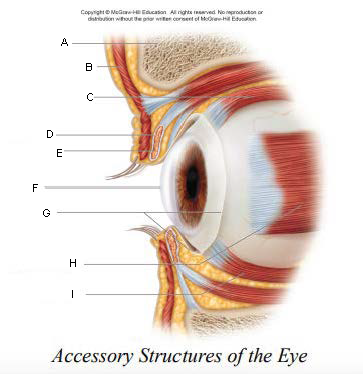
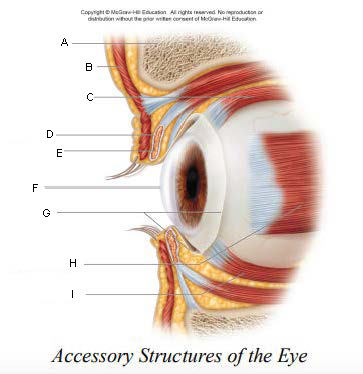
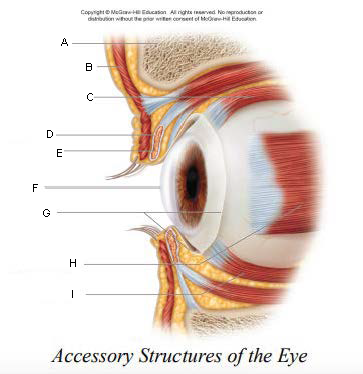
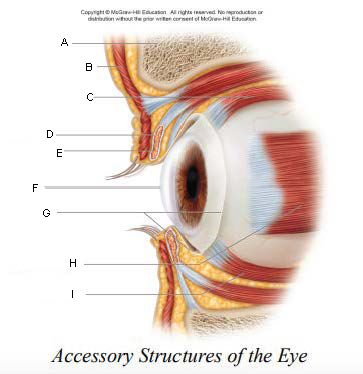
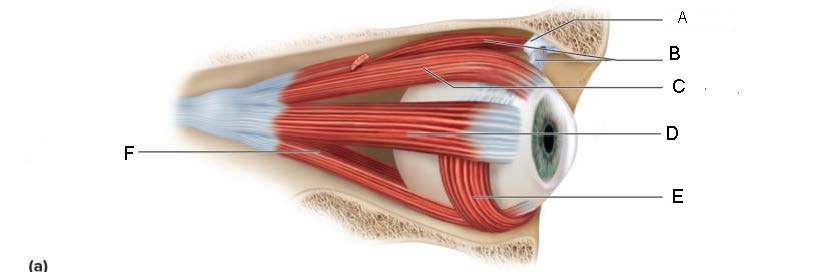
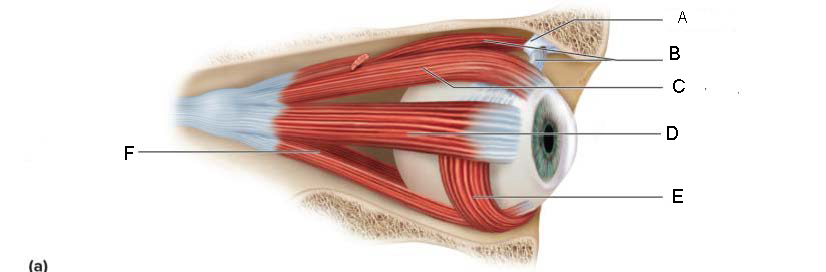
Pupil
A.
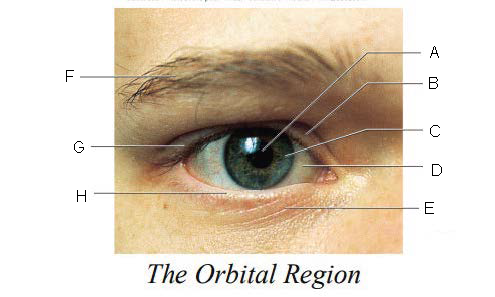
Upper Eyelid
B.
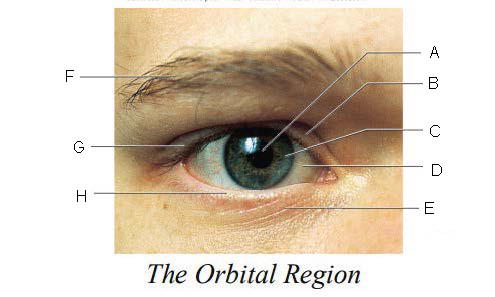
Iris
C.
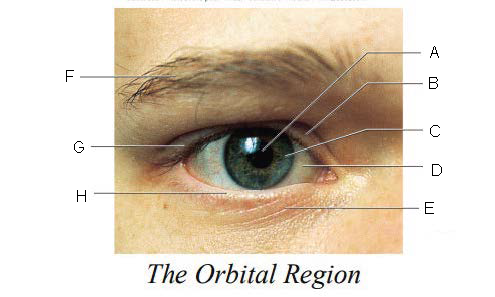
Sclera
D.
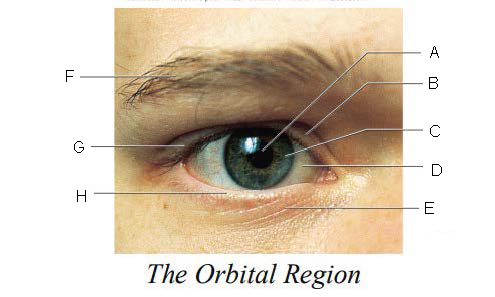
Lower Eyelid
E.
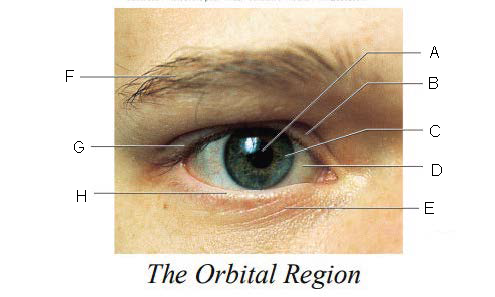
Eyebrow
F.
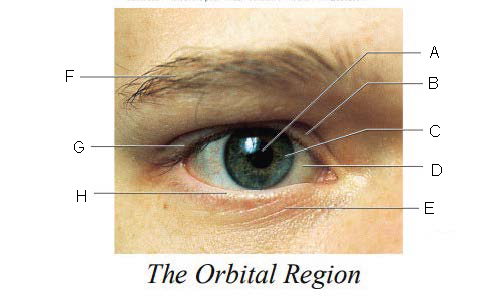
Eyelashes
G.
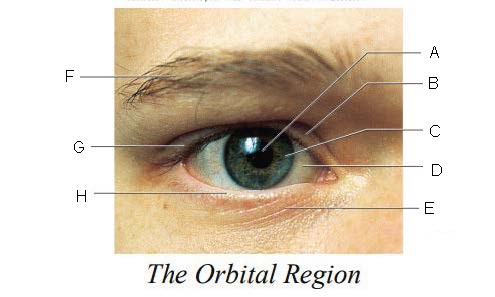
Tarsal Plate
H.
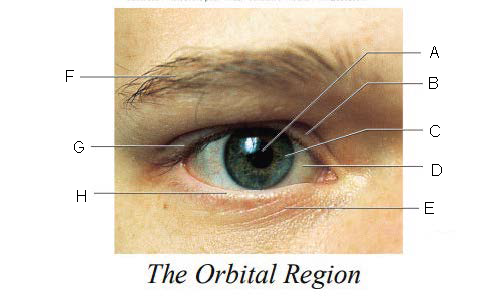
Eyelid
keep the eyes moist by spreading tears and mucus; lubricates when blinking
Eyelashes
keep out airborne particles and protect from excessive light
Eyebrows
shield eyes from overhead light and sweat
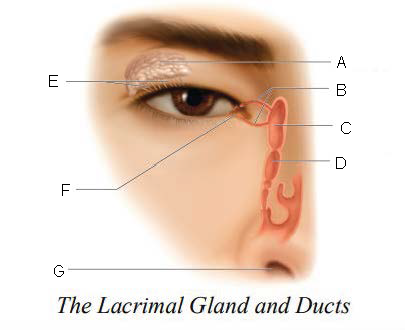
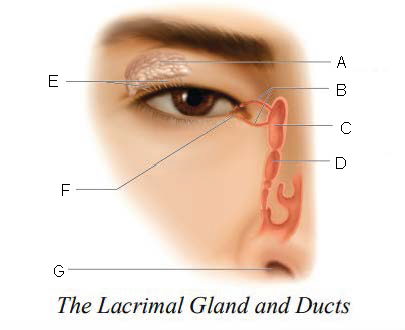
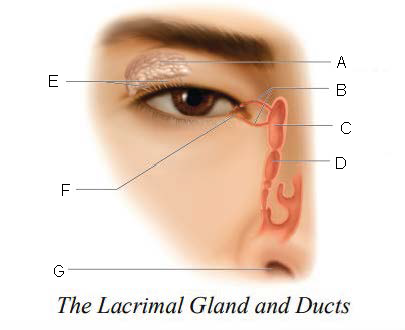
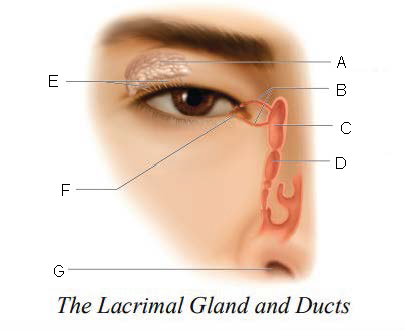
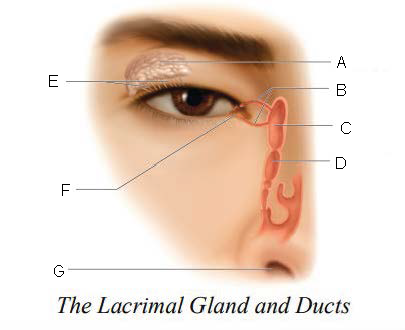
Lacrimal gland and ducts
organs responsible for tear production
Lacrimal Gland
organs that produces tears
Lacrimal Ducts
organs that carry tears to eye surface
moist
TEAR FUNCTIONS:
Keep eyes __________.
Wash away _________.
Contain __________ to reduce infection chances.
1 = ?
foreign particles
TEAR FUNCTIONS:
Keep eyes __________.
Wash away _________.
Contain __________ to reduce infection chances.
2 = ?
lysozyme
TEAR FUNCTIONS:
Keep eyes __________.
Wash away _________.
Contain __________ to reduce infection chances.
3 = ?
Lacrimal Gland
A.
Lacrimal Canals
B.
Lacrimal Sac
C.
Nasolacrimal duct
D.
Ducts
E.
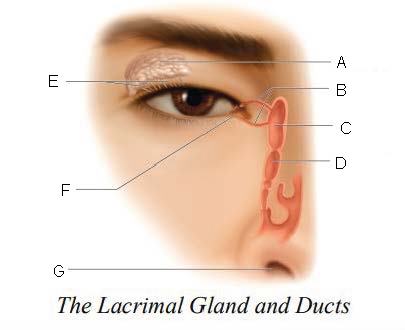
Lacrimal punctum
F.
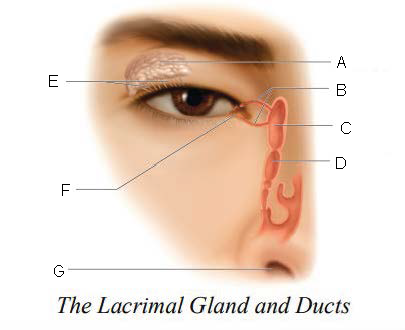
Nostril
G.
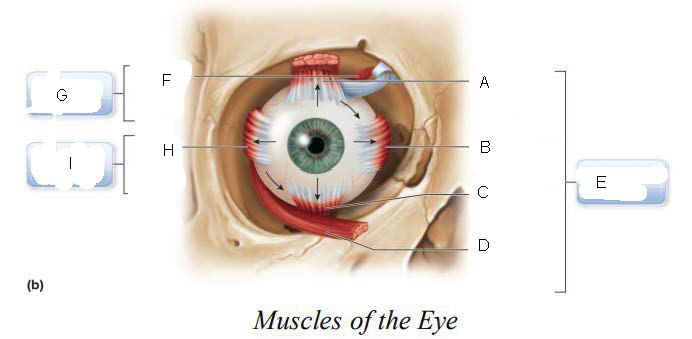
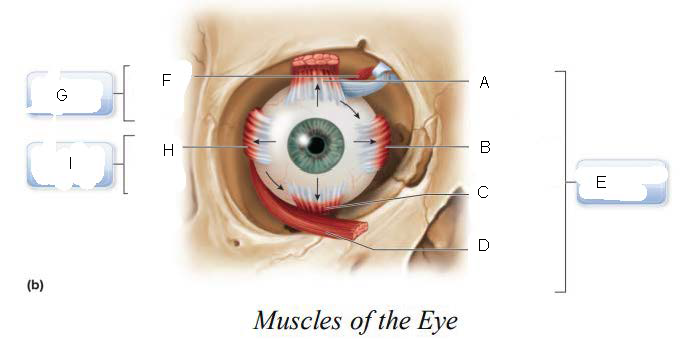
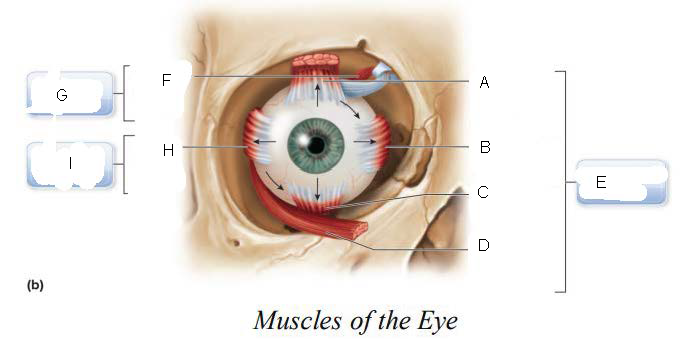
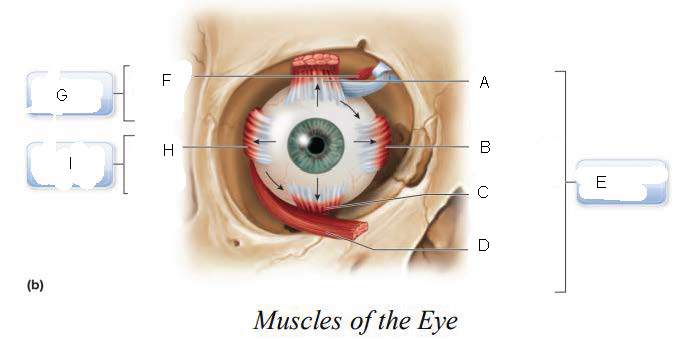
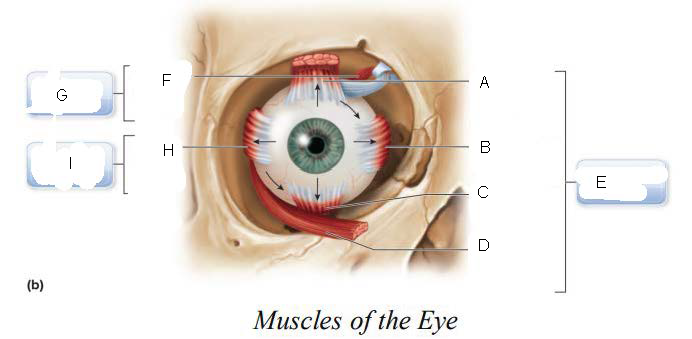
six
____________ muscles that originate on the back of the eye orbit and insert on the eyeball which function as a coordinated group to enable eye movement.
frontal bone
A.
Orbicularis oculi muscle
B.
superior rectus muscle
C.
tarsal plate
D.
Tarsal glands
E.
cornea
F.
conjunctiva
G.
lateral rectus muscle
H.
Inferior Rectus Muscle
I.
trochlea
A.
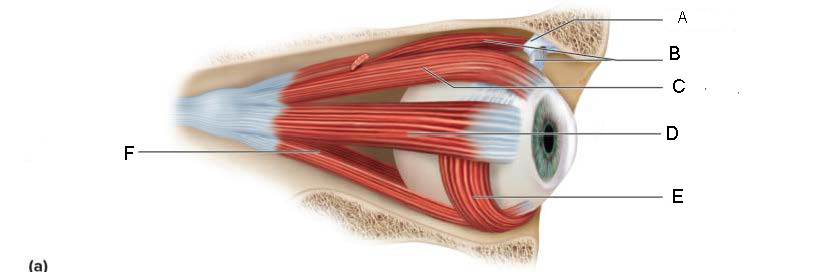
Superior oblique
B.
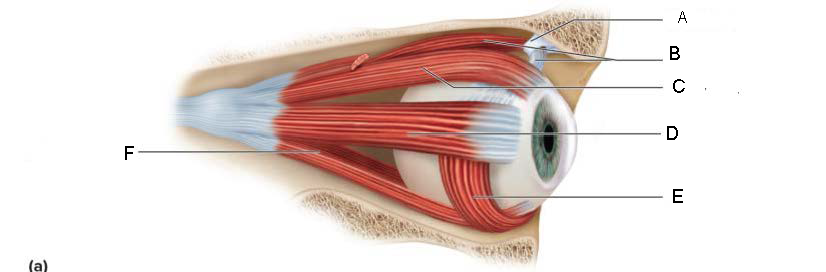
Superior rectus
C.
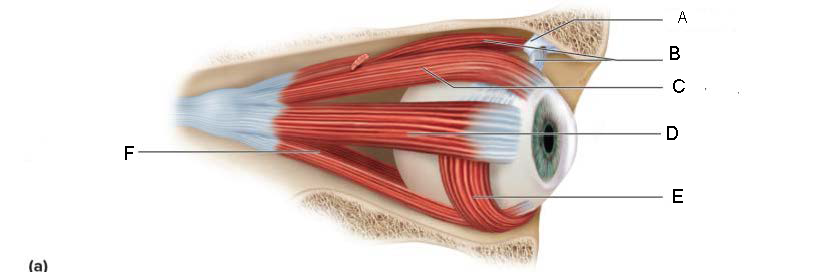
Lateral rectus
D.
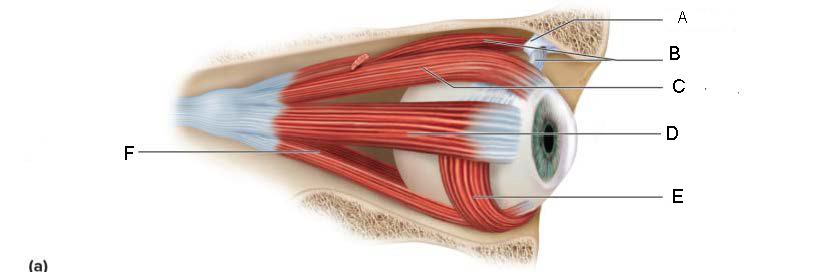
inferior oblique
E.
Inferior rectus
F.
Superior Rectus Muscle
A.
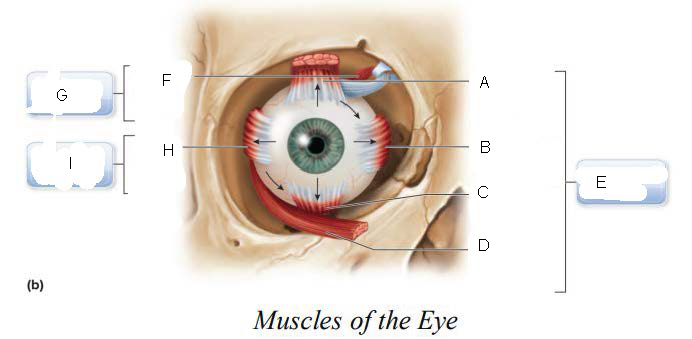
Medial Rectus Muscle
B.
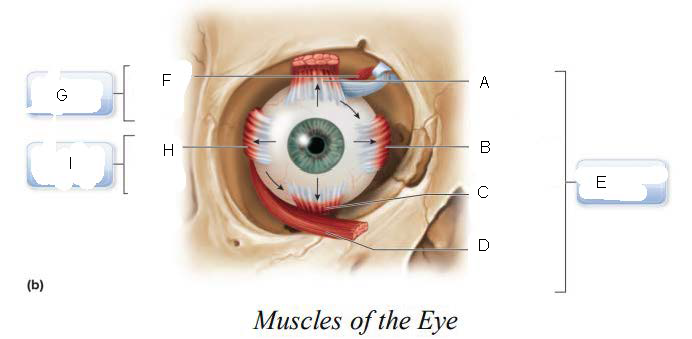
Inferior Rectus Muscle
C.
Inferior Oblique Muscle
D.
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
E.
superior oblique muscle
F.
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
G.
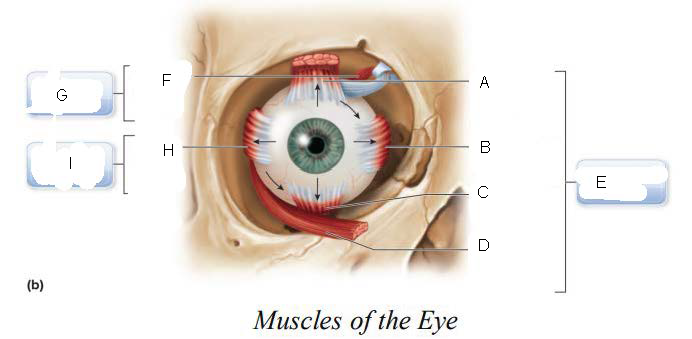
Lateral Rectus Muscle
H.
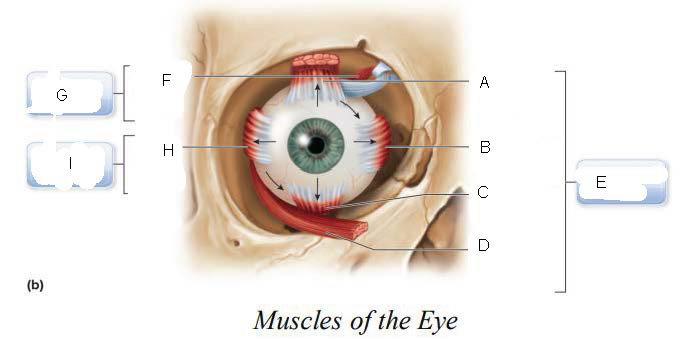
Abducens Nerve (VI)
I.
2.5 cm
The eyeball is hollow and spherical, roughly __________ in diameter.
Aqueous Humor and Vitreous Body
interior spaces of the eyeball are filled with fluids known as ______________________ to support and maintain eye shape.
anterior and posterior chamber
interior spaces that are filled with aqueous humor
vitreous chamber
interior spaces that are filled with vitreous humor/body
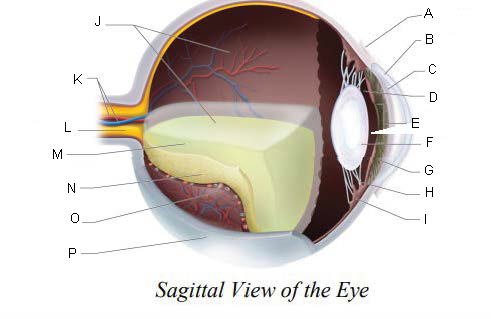
Conjunctiva
A.
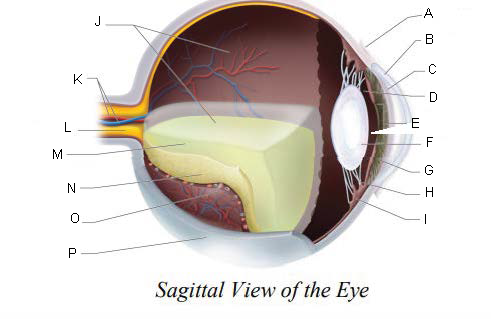
Cornea
B.
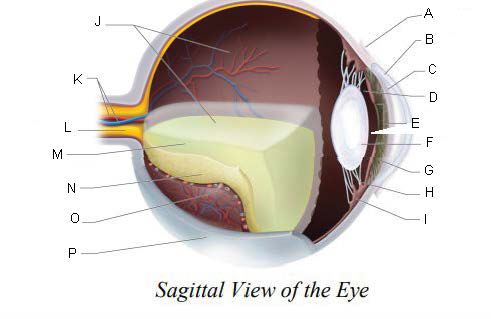
Anterior Chamber
C.
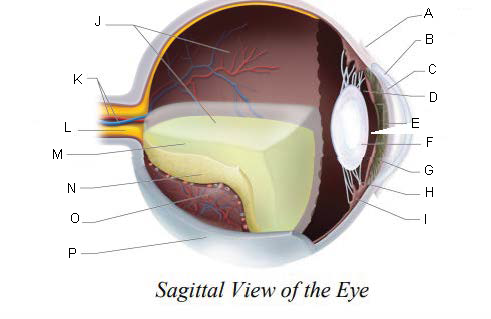
Posterior Chamber
D.
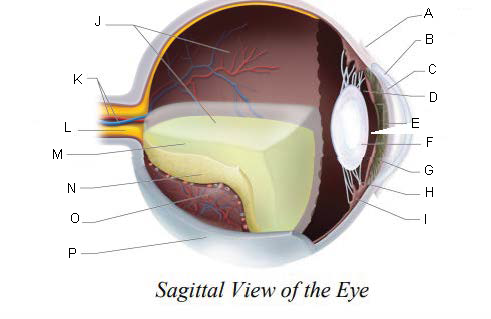
Pupil
E.
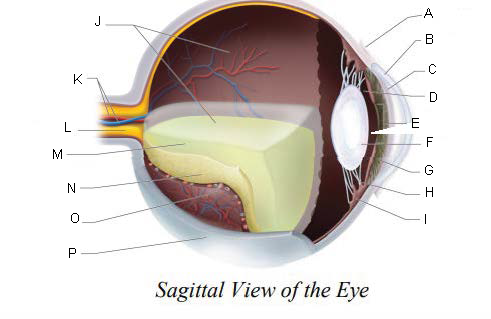
Lens
F.
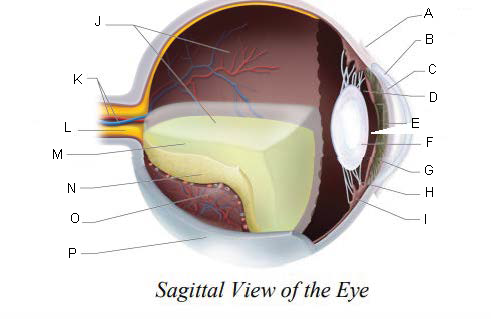
Iris
G.
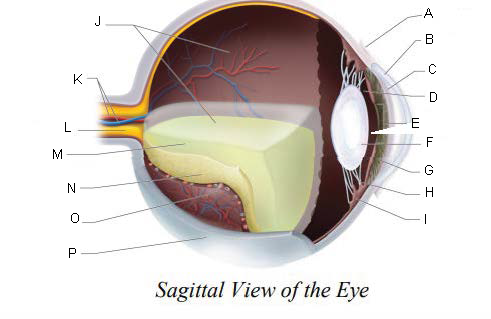
Suspensory ligaments
H.
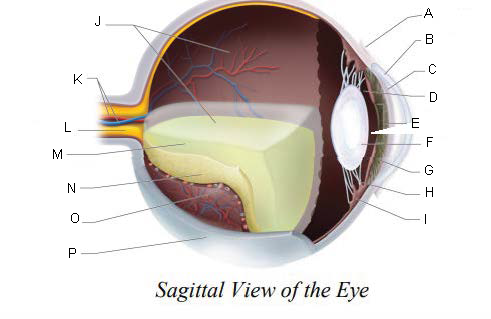
ciliary body
I.
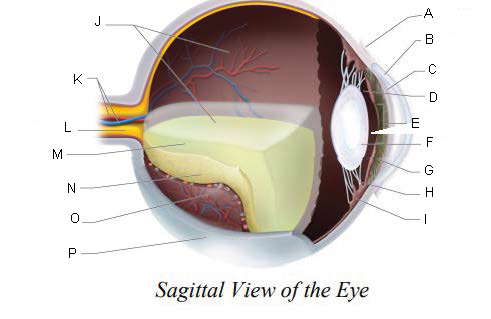
Vitreous Chamber
J.
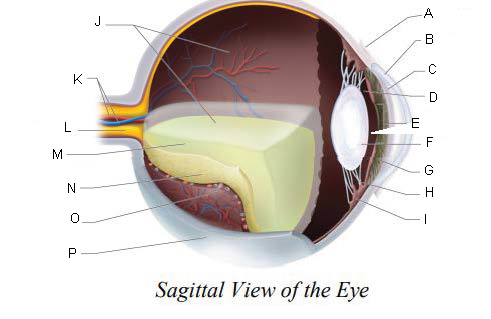
Central Retinal Artery and Vein
K.
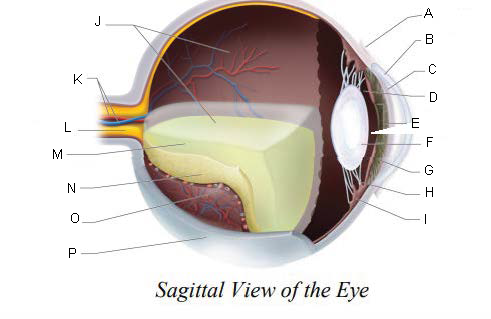
Optic Nerve
L.
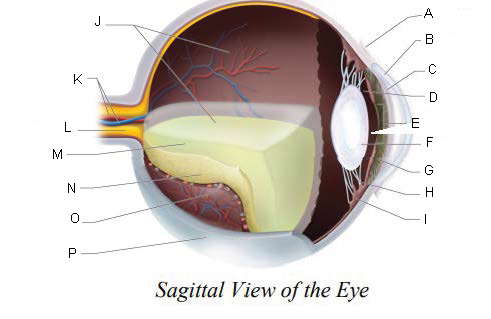
Vitreous Humor
M.
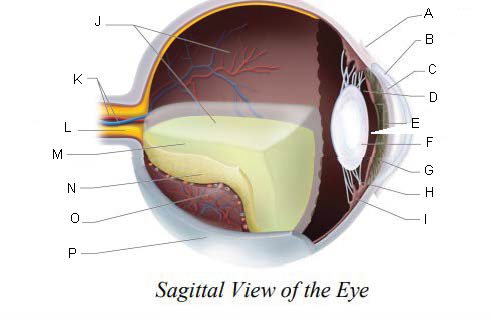
Retina
N.
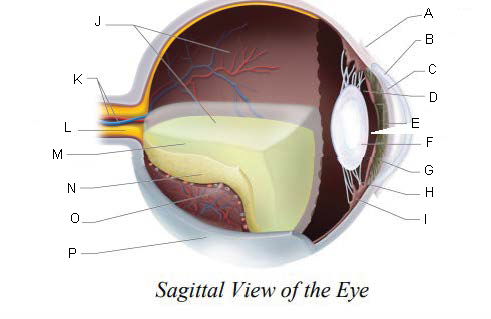
Choroid Layer
O.
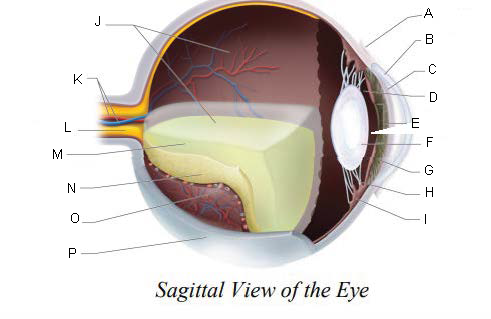
Sclera
P.
Sclera
tough, fibrous, opaque, white portion of the eye that provides protection for delicate internal portions of eye and optic nerve
Cornea
anterior, convex, clear window of the eye which bends light rays as they pass through it
Choroid Coat
PART OF THE UVEA:
has large blood vessels to nourish the eye
has melanin to prevent backscattering of light
Ciliary Body
PART OF THE UVEA:
has ciliary muscles that surround the lens
can change shape of lens
Suspensory Ligaments
PART OF THE UVEA:
found between the ciliary body and lens which hold the lens in place
Iris
PART OF THE UVEA:
colored portion of the eye
controls the amount of light entering the eye by controlling the size of the pupil
Pupil
PART OF THE UVEA:
opening in the center of the iris that allows light to pass into the eye
constricted = bright light
dilated = dim light
Retina
lines the interior of the eye posterior to the ciliary body
Rods
located at the retina for black and white vision
sensitive only to presence of light
least concentrated at the fovea centralis
density increases with distance from fovea
Cones
located at the retina for color vision
requires bright light to function
most concentrated at the fovea centralis
density decreases with distance from the fovea
Macula lutea
A.
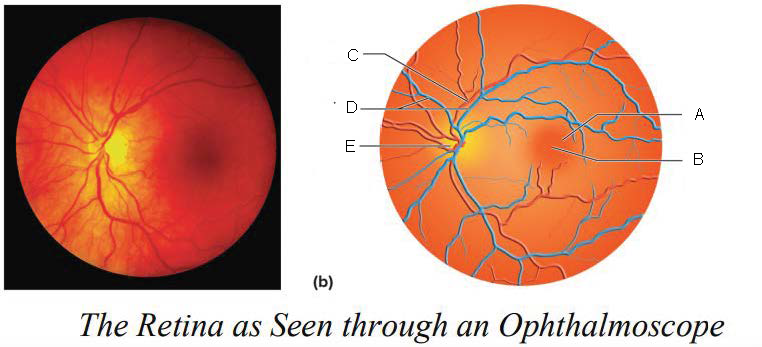
Fovea centralis
B.
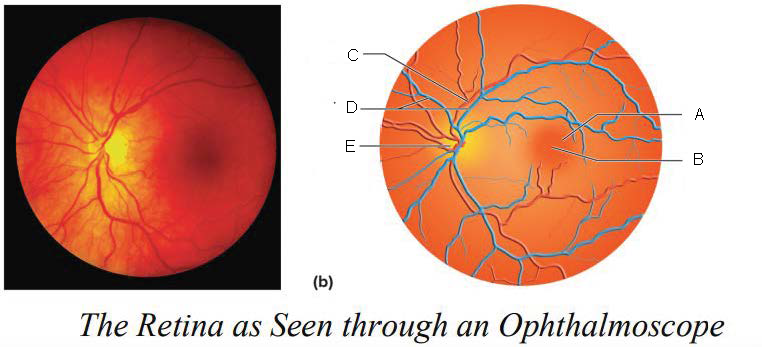
Artery
C.
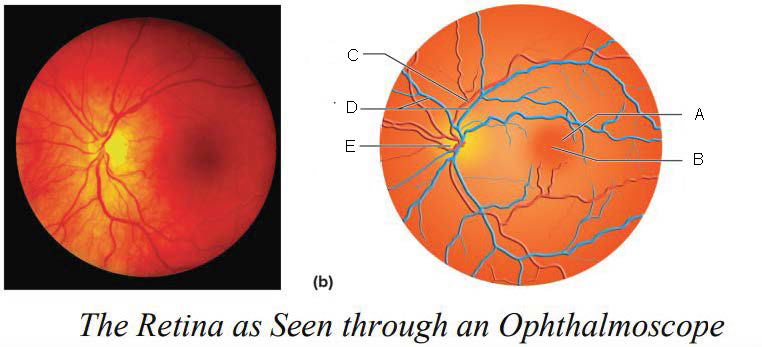
Veins
D.
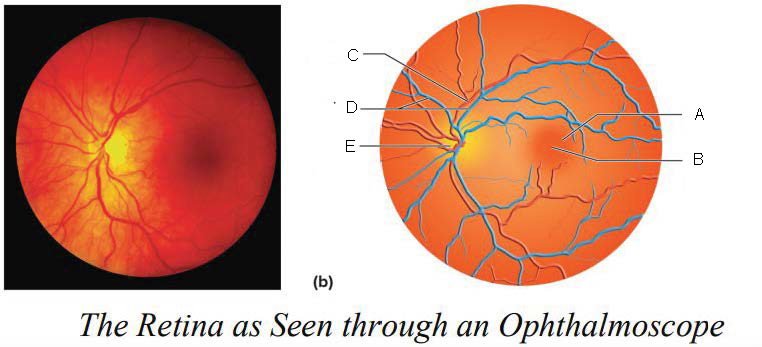
Optic disk
E.
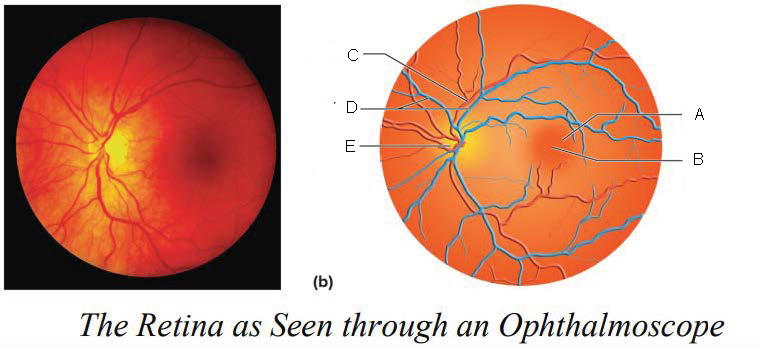
Optic Disc
blood vessels enter and exit the eye
axons exit the eye
no receptor cells = blind spot
Macula Lutea
yellowish disc on the retina
contains fovea centralis (contains only cones, area of sharpest vision)