HSM (HUMAN MOVEMENT STUDIES) NOTES
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Notes to remember for class so you don't fall and look stupid :) you'er welcome.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
acclimatisation
The process of the body adjusting to changes in its environment.
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
a high-energy compound that stores and transfers energy to body cells, allowing them to perform their specialised functions, such as muscle contraction.
anaemia
a medical term to describe a low red blood cell count
angina
chest pain that occurs when the heart has an insufficient supply of oxygenated blood
arteries
blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
atherosclerosis
the build-up of fatty and/or fibrous material on the interior walls of arteries
capillaries
the smallest of all blood vessels; they function to exchange oxygen and nutrients for waste involuntary muscle responsible for keeping the heart beating
circulatory or cardiovascular system
a network that carries blood with oxygen and nutrients to the body and collects waste products. It includes the heart, arteries, veins, and blood itself.
digestive tract
the organs that food and liquids travel through when they are swallowed, digested and absorbed, until they leave the body as faeces.
expiration
air movement from the lungs to the atmosphere; breathing out.
fast-twitch muscle fibres & slow-twitch fibers
They contract quickly and are used for fast, explosive activities. They are called "white" because they have less blood supply
"Red fibres," are muscles that are great for endurance. They contract slowly but can work for long periods without getting tired. They have lots of mitochondria and blood vessels, helping them use oxygen well to produce energy.
freely movable or synovial joint
a joint that allows maximum movement. Most joints in the body are synovial joints; for example, the hip joint.
glucose
It is broken down from stored glycogen in the muscles and liver, then transported through the blood to provide energy for muscles during exercise.
haemoglobin
oxygen-carrying component of the blood
homeostasis
It is the body's ability to maintain a stable in internal environment and balancing things like temperature, pH, and other factors to keep everything functioning properly.
hormone
are chemical substances produced in the body that help regulate the activity of specific cells or organs.
immovable or fibrous joint
a joint in which no movement is possible. Examples include the bones of the cranium, which are fused in lines called sutures.
inspiration
air movement from the atmosphere into the lungs; breathing in
iron deficiency
a lack of iron in the body reducing haemoglobin production in the blood
isometric contraction
occurs when muscle fibres are activated and develop force but muscle length does not change; that is, movement does not occur
isotonic concentric contraction
the most common type of muscular contraction; the muscle shortens, causing movement at the joint
isotonic eccentric contraction
occurs when the muscle lengthens while under tension; often happens with the assistance of gravity
antagoist
the muscle that relaxes to help the agonist to work it also help with control.
agonist
the prime mover of the muscle cautioning major movments
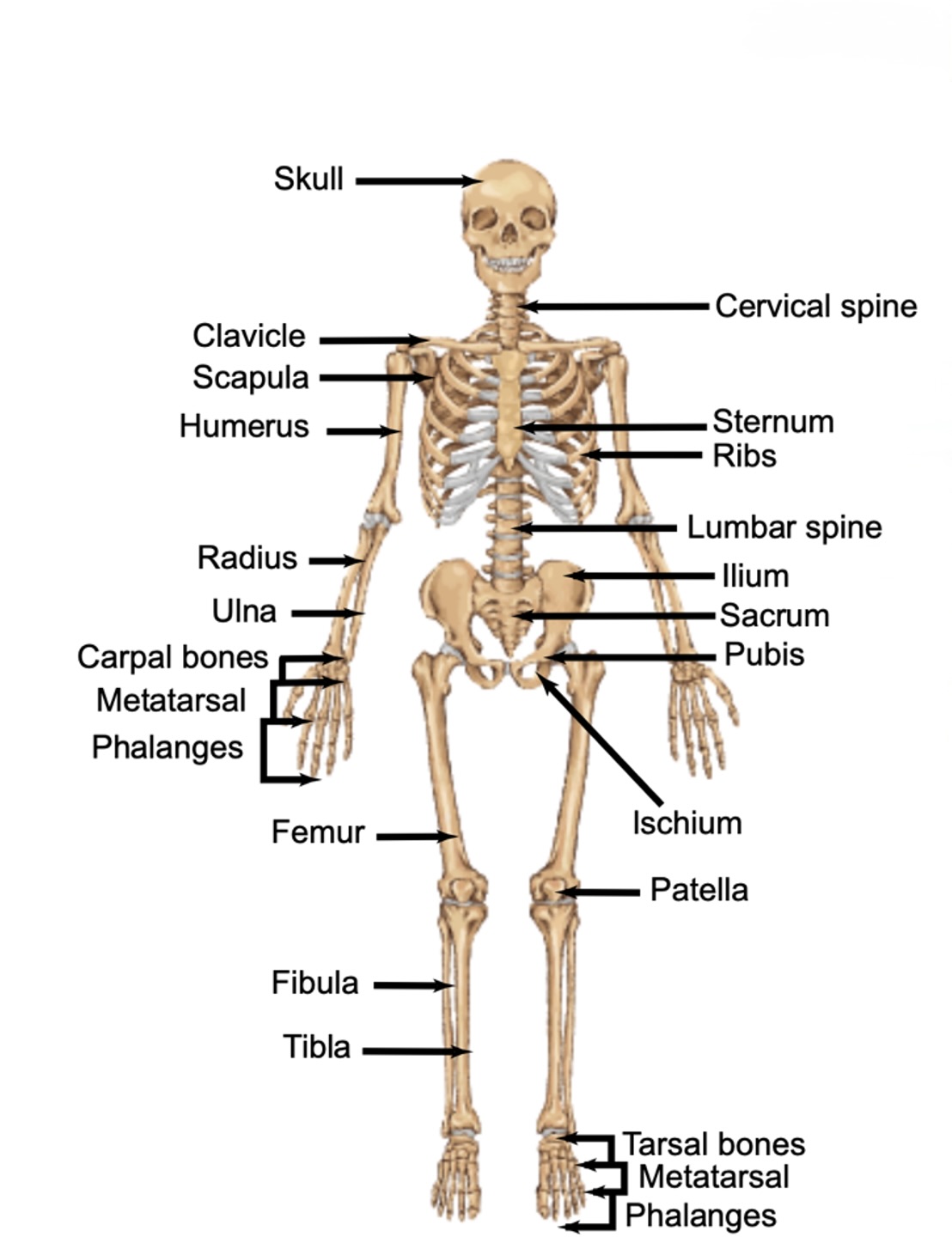
Front bones
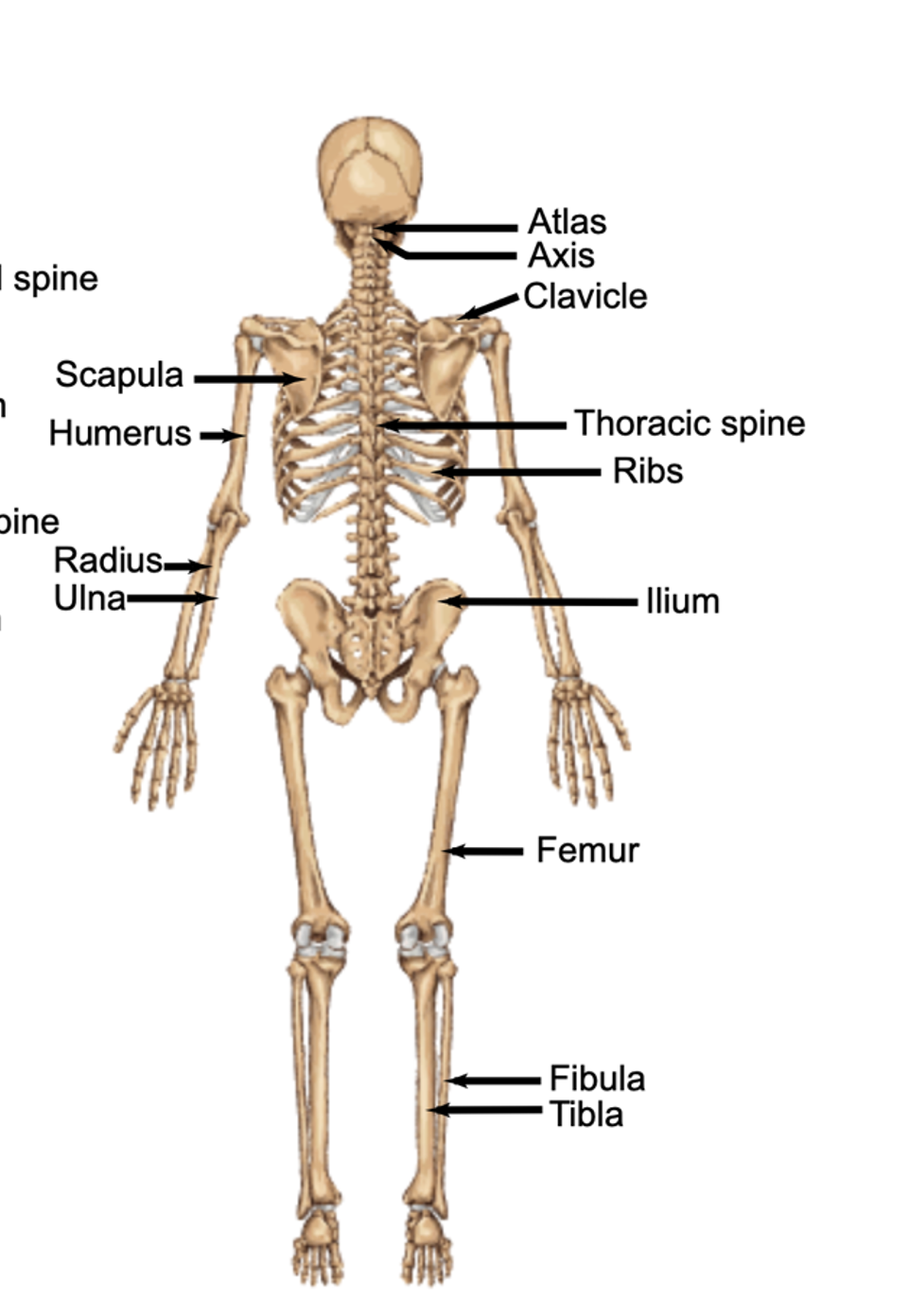
Back bones
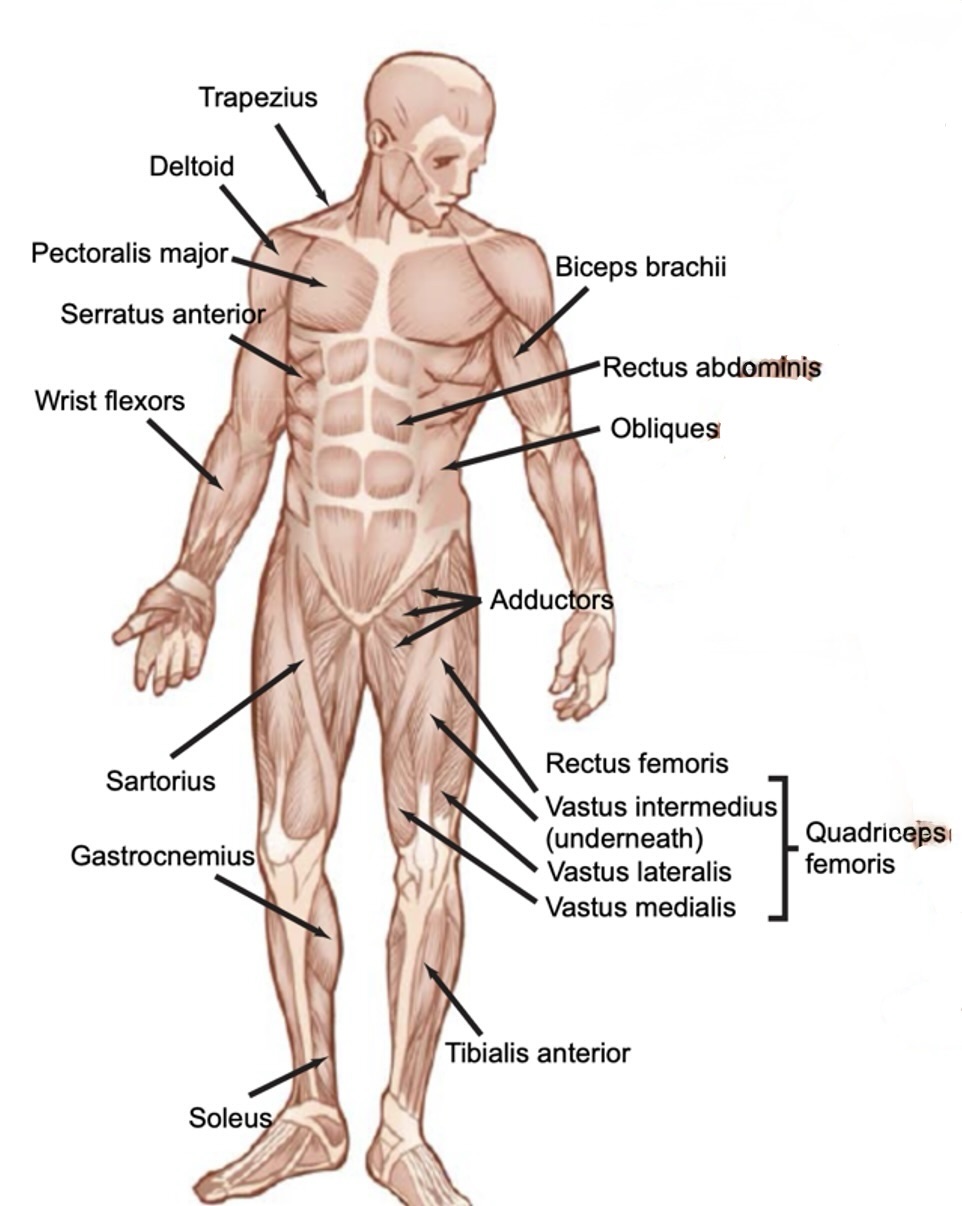
Front muscles
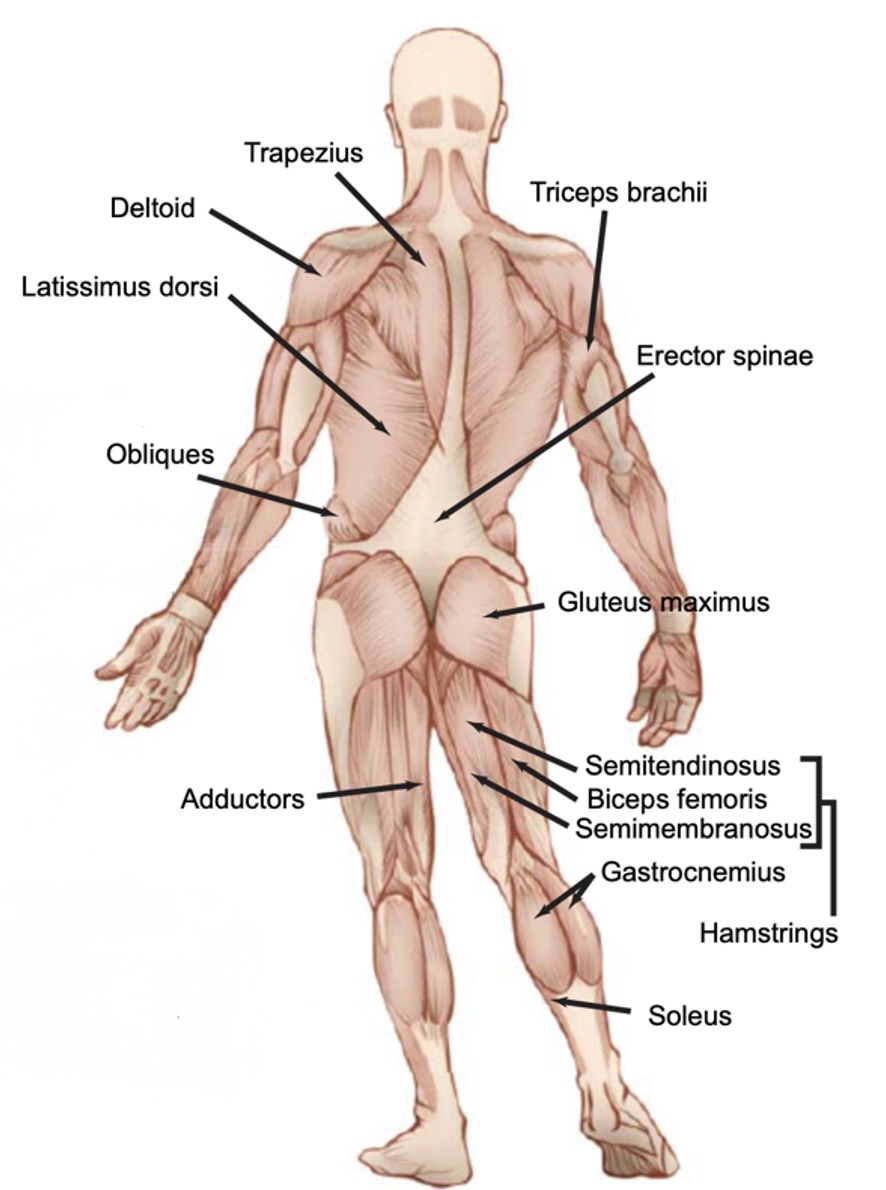
Back muscles
Joints #SECTION2
ball&socket joint
freely moveable joints around the hip
hinge joint
can move one way but not the other around the knee and elbow
gliding joint
movement against each other, where the wrist rotates
pivot joint
movement movment of the head as a rotation
condyloid joint
flexion and extension around the wrist rotations
saddle joint
flexion and extension where the hand is with no rotation
macronutrients
the main nutrients needed by the human body; these include carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
micronutrients
one of the major groups of nutrients needed by the body for energy production
plasma
a straw-coloured liquid component of blood, consisting mainly of water (about 90 per cent)
platelets
are small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding.
pulmonary circulation
the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
respiration
the process by which the body takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
slightly movable or cartilaginous joint
a joint that permits limited movement.