Cattle housing
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
• Understand the relative importance of environmental factors on animal physiology. • • Understand the relative importance of environmental factors on disease risk and pathogen survival including moisture, air quality, air speed, temperature or mechanical impact. • • Be able to decide which design aspect of a building or system is contributing to failure to manage the key environmental variables. • Be able to identify important reference values for housing designs and layout details. • Understand the principles of building design and use systems of physical and animal measures as key performance indicators . • Be able to compile a housing farm audit questionnaire
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
what categories of housed cattle do we have?
dairy calves
fattening cattle
adult dairy cattle
adult beef suckler cows
why are growing adult cattle housed in the colder wetter months?
Housing up to 6 months of the year due to: • Poor quality and growth of grass in winter – need for supplementary feeding • Damage to pastures (poaching) in winter
the 5 freedoms in relation to housed animals
1. Freedom from hunger and thirst
2. Freedom from discomfort
3. Freedom from pain, injury and disease
4. Freedom to express normal behaviours
5. Freedom from fear and distress
Consider:
Animal signs which may indicate poor/good housing design
Physical measures in housing design
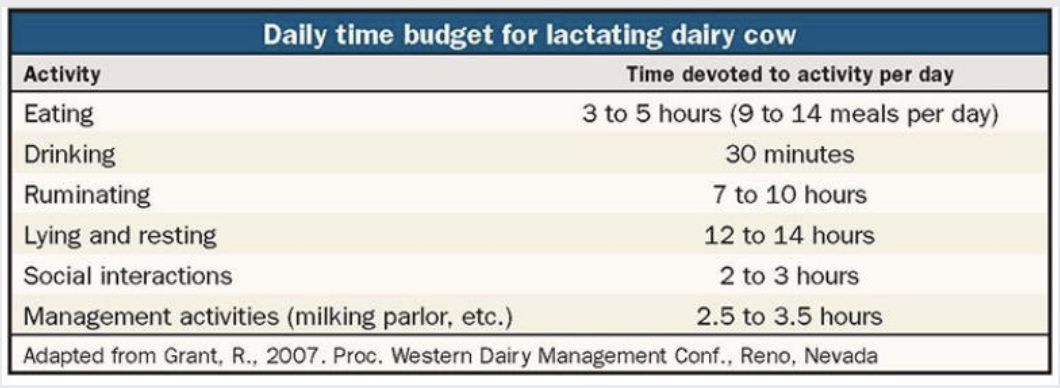
what are the dairy cow time budgets?
housing design
Consider:
• Airspace – cubic metres of air/animal
• Stocking density – square metres /animal
• Ventilation – exchanges of air/hour
• Feeding – access to deliver and to eat
• Water – access and quality
• Bedding – amount and type
• Flooring – type and maintenance
• Drainage – slopes and drains
• Ability to clean and disinfect – hygiene and dirty cows
• Fittings – type and condition
• Movement and restraint of housed animals – access and design
• Waste production/disposal – slurry removal and disposal
e.g. Adult dairy cow
Urine production – 50mL/kg/day (600kg cow = 30L/day)
Faeces - Dairy cow 30-50Kg/day
legislations and codes of welfare


audits
checklists and are used to check for good/bad housing design in commercial assurance schemes

ventilation - replacement of air in a given a given space
Appropriate ventilation rates results in:
Removal of heat
Reduction in humidity
Removal and reduction of carbon dioxide, ammonia concentrations
Removal/reduction of airborne organisms (reduction of atmospheric load)
Common mistake is to reduce ventilation rates in cold weather to retain heat.
Ventilation rates must be maintained for the reasons above.
ventilation - clearance of organisms and atmospheric load
Stocking density determines 90% of bacterial and viral load.
Atmospheric bacterial and viral load are reduced by:
Sedimentation (Gravitates to the ground)
Ventilation (very important)
Death of organism (low levels of humidity)
Space allowance more important than ventilation in decreasing airborne bacterial/viral
density.
A tenfold increase in ventilation rate is only 2/3 as effective as doubling the airspace.
relative humidity
Keep below 80% if possible (not always possible in UK winter) as:
1. high humidity increases pathogen/bacterial survival ( e.g. increasing from 60% to 90% increases atmospheric load x10)
2. nasal turbinate's less effective in high humidity at clearance of small particles in upper airways
what does poor ventilation result in
an increased susceptibility and incidence of respiratory disease (pneumonia) with welfare implications and loss of financial return due to poor growth rates

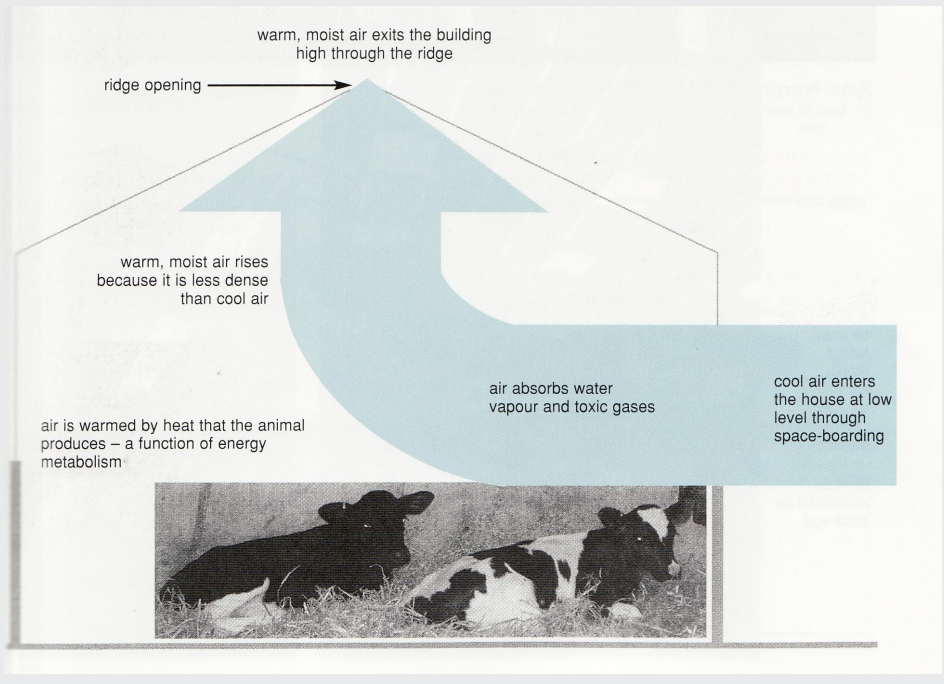
what are the patterns of air flow through a well-designed building?
Hot air rises and fresh air is drawn into the building
Note the open ridge and the gaps under the eaves of the roof
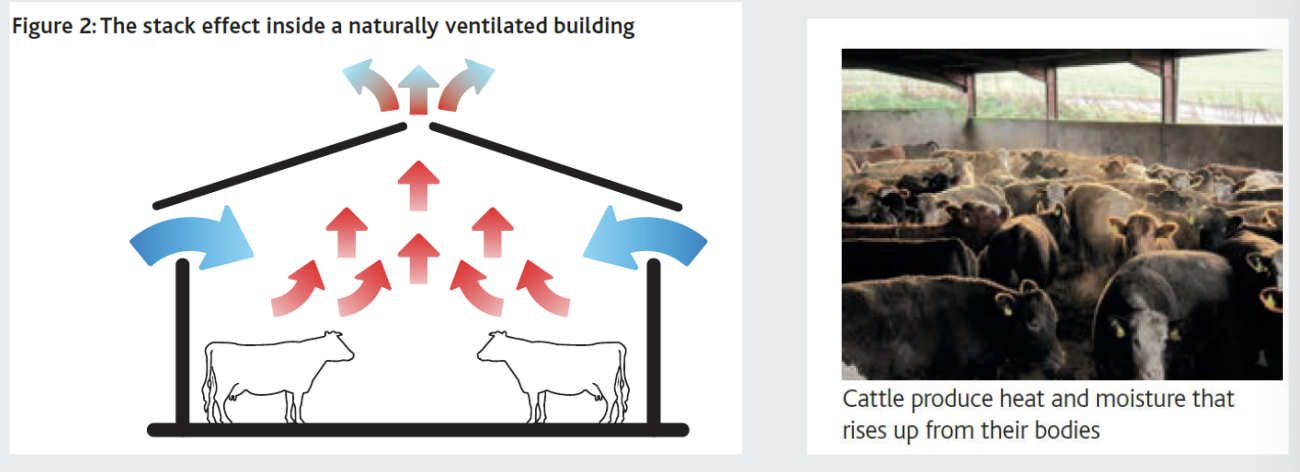
typical guidelines for airspace in cubic metres and the ridge opening

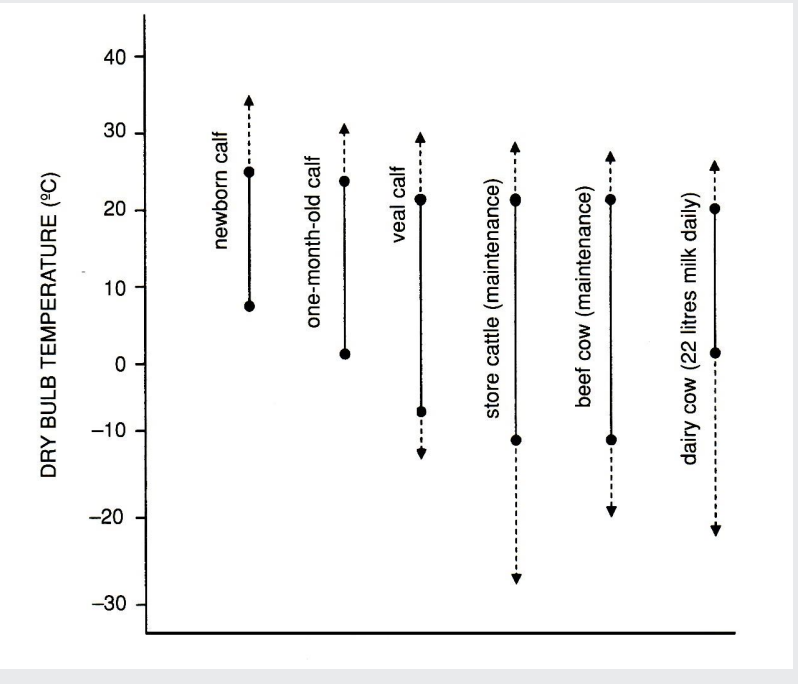
what is the range of thermal comfort of different classes of cattle
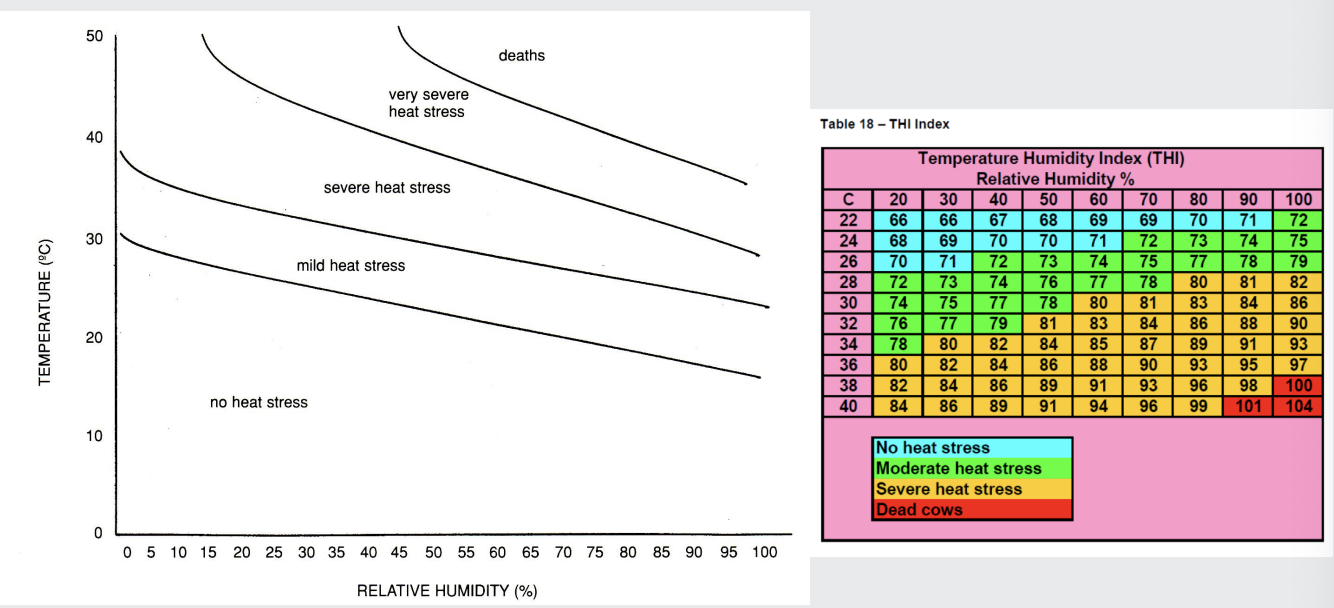
what is the relationship between temperature and humidity and heat stress in cattle
measuring stocking density, ventilation and humidity
Airflow and ventilation – smoke bomb
Stocking density and airspace -tape measure or laser pointer
Relative humidity - Dry/wet thermometer
what is calf housing like
Sometimes farms use adapted unused building to house calves
Ventilation and drainage are often sub-optimal
Calves may be kept singly or in groups

individual pens v groups
Individual –
Must be within sight, sound and can touch other calves and under 8 weeks old
Hutches (outside)
Individual pens (inside)
Advantages
Can monitor food and water intake
Minimise spread of diseases
Disadvantages
Ability to express normal behaviours limited
Grouped calves –
Converse of the above

typical design of a calf house (double pitched)
Open ridge (ventilation)
Slatted boards (Ventilation)
Perspex skylight for increasing light
Straw bales kennels for insulation
1/20 fall for drainage
Feed passage for access between the rows
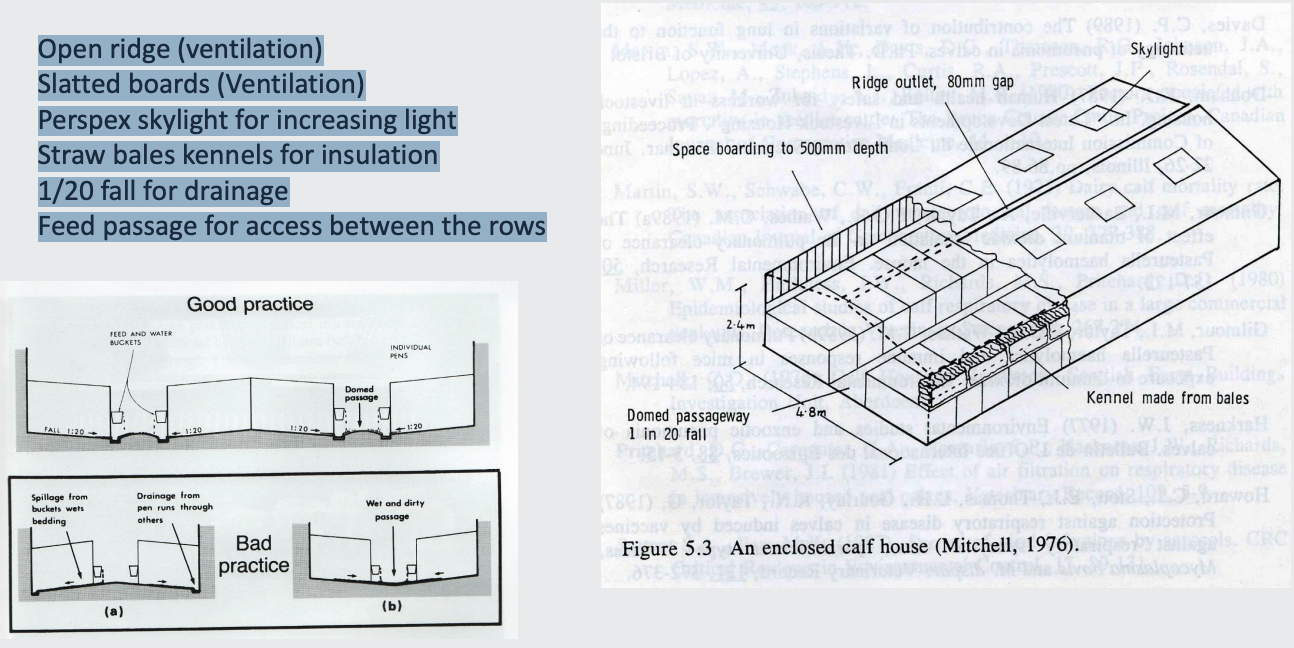
how does double pitched building illustrating air flow in a calf house
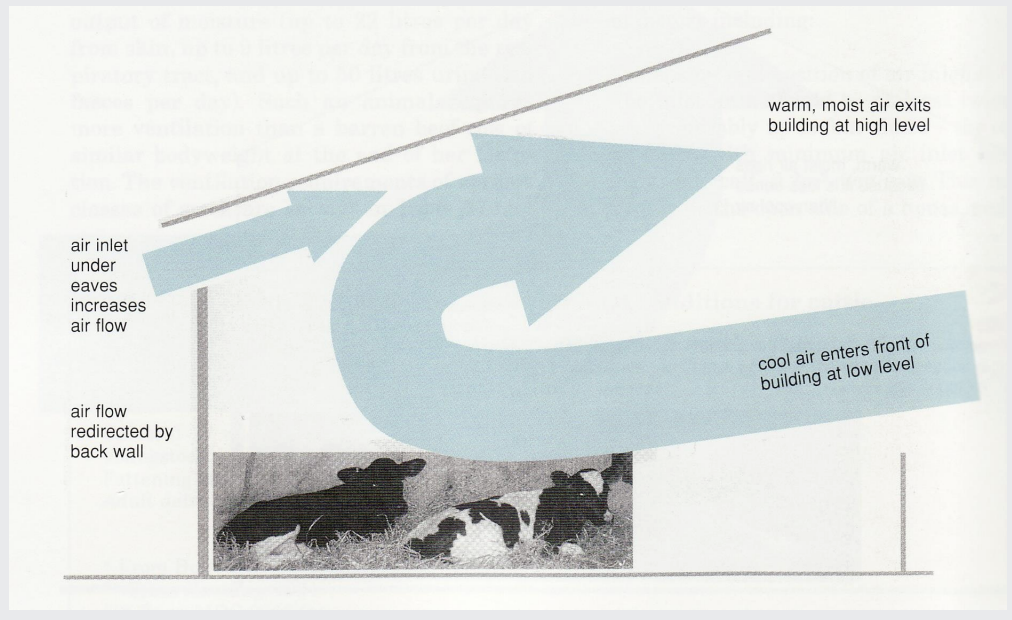
how does mono-pitch building distributes airflow
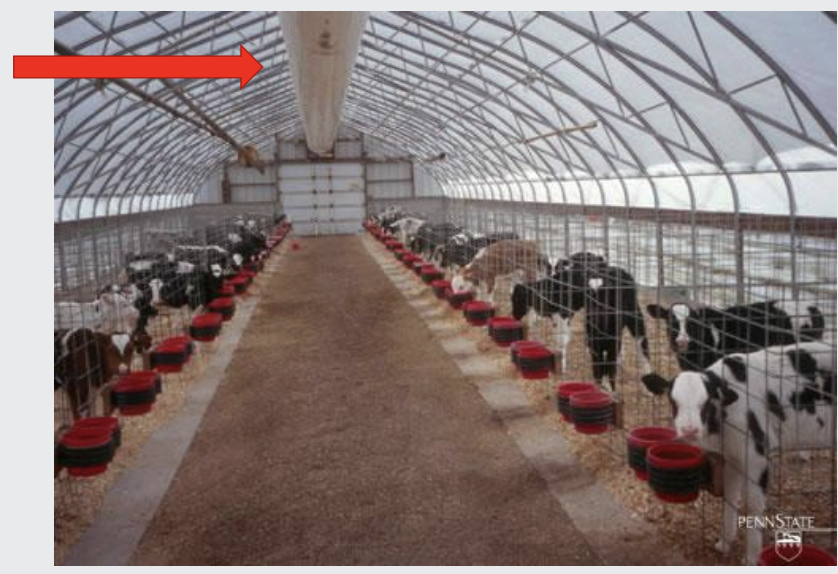
what is this?
poly-tunnel calf house with ventilation fans blowing air down the pipe in the centre to provide ventilation

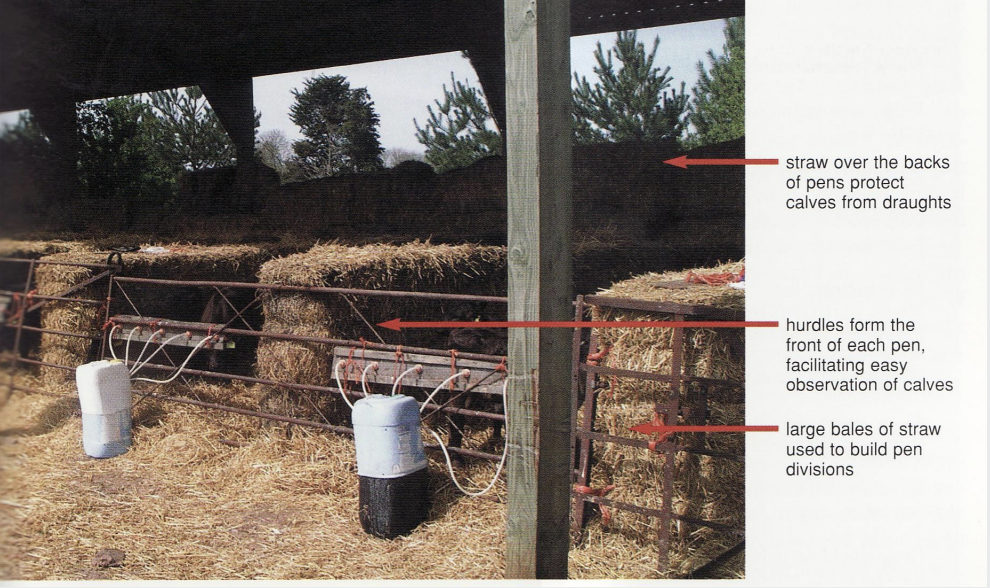
some horrible diagram on calf housing

home-made pens for calves

what are straw yards used for?
• Dairy cattle
Winter housing
• Fattening cattle
Winter housing or intensive rearing
• Suckler cows
Winter housing
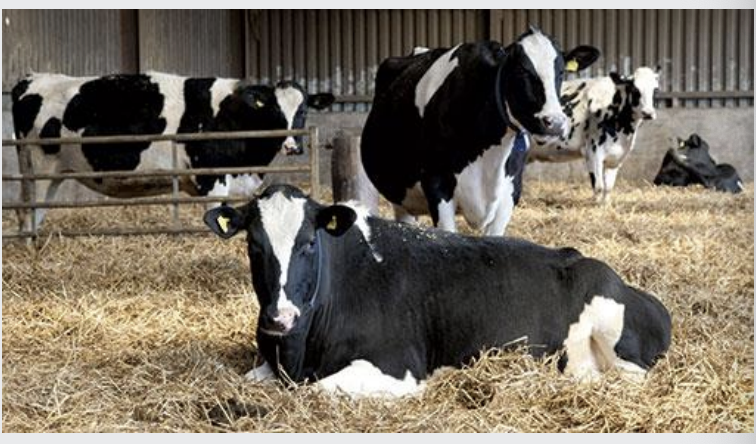

strawed area + loafing area + feeding area
• Appropriate stocking density
• Sufficient air space
• Good ventilation
• Good feed access
• Appropriate water supply
• Appropriate bedding
• Appropriate flooring
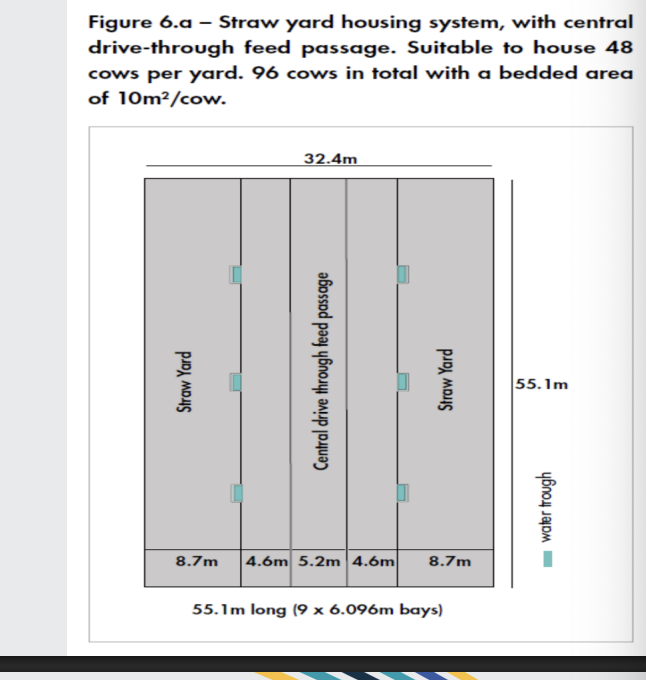
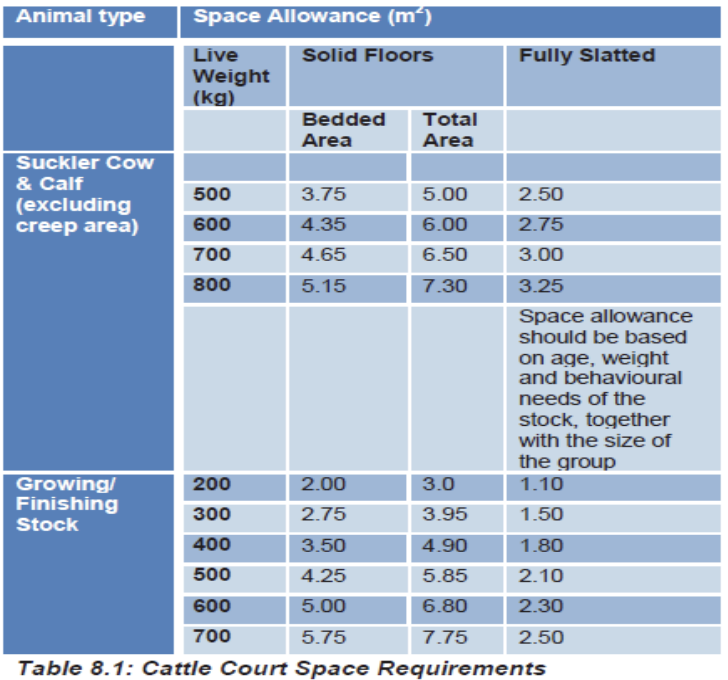
what is this
examples of stocking density reference tables for different weights and different classes of cattle
what is this showing
guidelines for bedding straw requirements (based on 25 week bedding period, except where stated otherwise)

what are feeding fences?
found in feeding fences
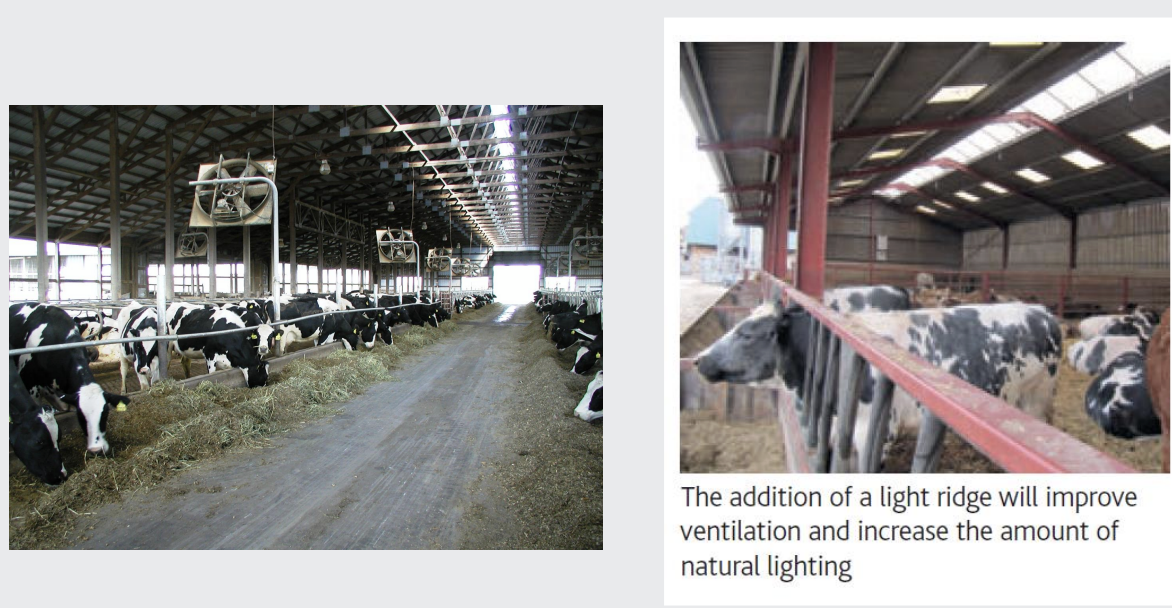

feeding fences with barriers
dairy free stall layouts- cubicles
some barriers enable the cow to be ‘locked’ in place with self locking yokes as the cow can the restrained

how do we ensure good feed access
• Feed barriers to allow animals to eat unhindered by other cattle.
• Also prevents food tossing which may put the feed beyond reach.
• All cattle to need to be able to access the feed barrier at the same time.
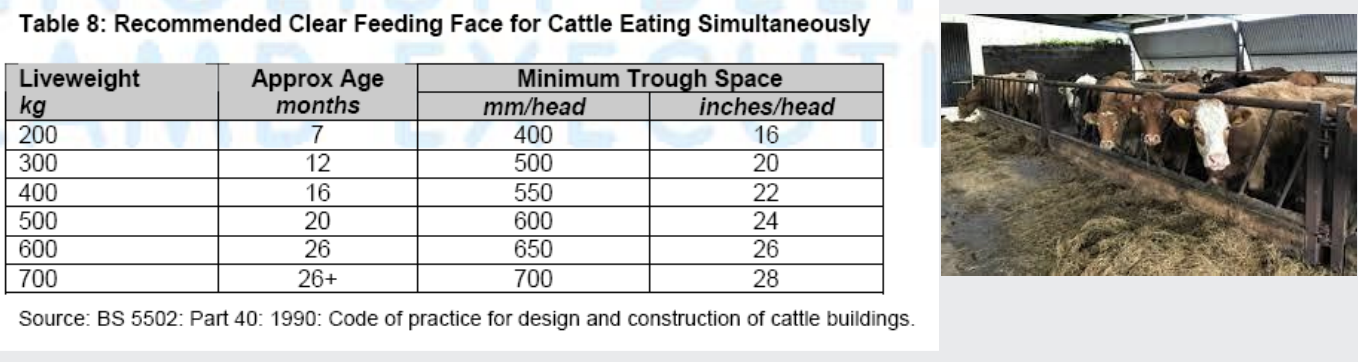
what are the water requirements
must be met and there are standards regarding the supply and trough space e.g. dairy cows require 70cm of water trough spare per cow

slats
Some growing cattle can be kept on slats with underground waste disposal systems
This is a large saving as no bedding is used

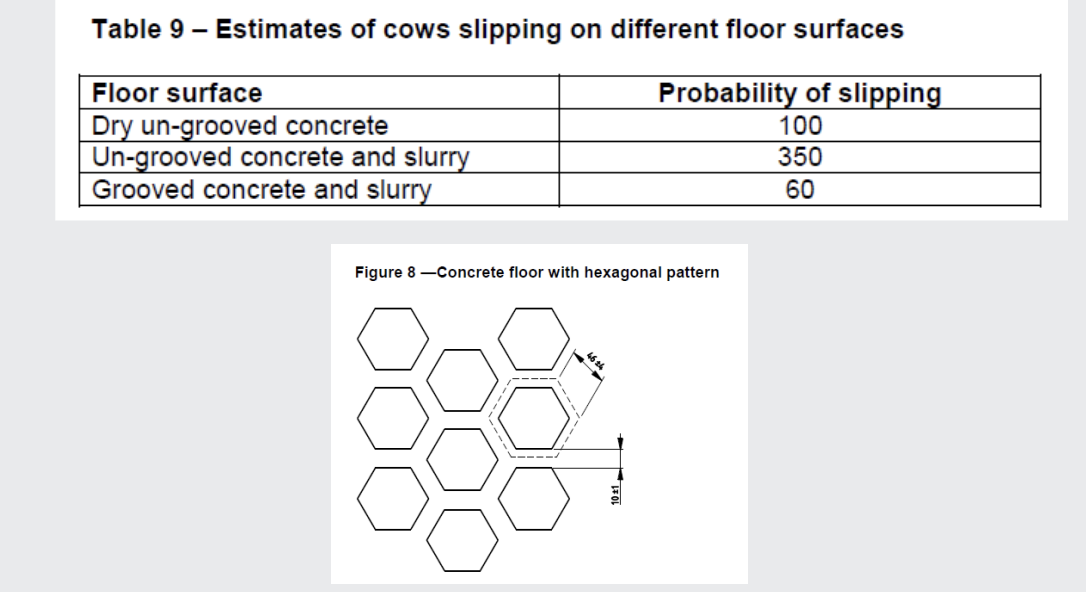
design of concrete floors important - slipping risk
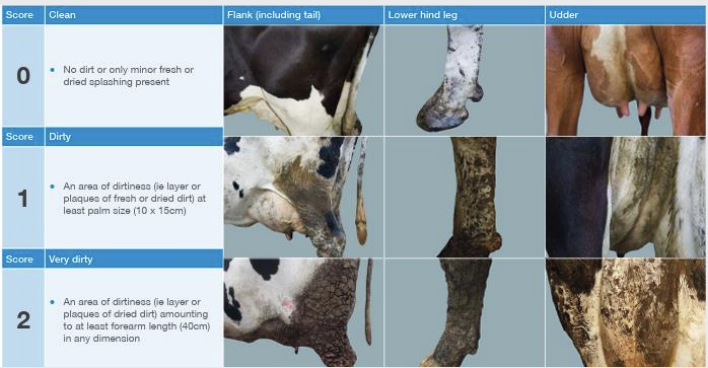
clean cattle - dirty cattle are a sign of poor bedding and poor bedding management
Straw bedding needs regularly topping up with fresh bedding
Abattoirs may reject dirty cows
Clean cows reduce the risk of meat contaminated with diseases such as:
• E.coli O157,
• Campylobacter
• Salmonella
Clean cows reduce the risk of getting mastitis.
what is the cleanliness scorecard in an audit
what are dairy cow cubicle systems
• Cubical systems are commonly used for housing adult dairy cattle specially in areas where straw is expensive and in short supply.
• A cubicle is an independent protected space for an individual.
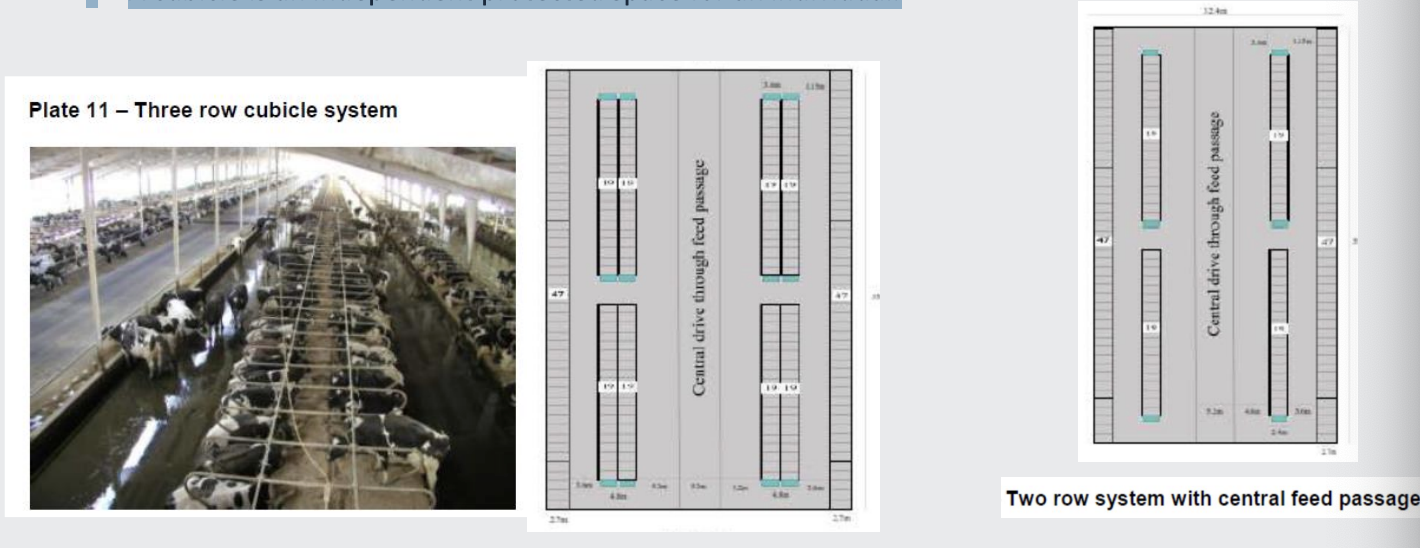
what are the important factors to consider in cubicles
• Cubicle design and bedding (Straw, saw dust, rubber mats)
• Cubicle numbers
• Lay out of the cubicles and escape routes
• Flooring – none slip
• Passage way - slurry management
Scrappers-manual/automatic

what good cubicle features?
Cubicles should be as comfortable as possible to encourage lying time.
Size 600kg cow 2.2m long, 1,2m wide
Provide enough lunge space

cubicles - design features
• Provide individual space – without cross-lying
• Be able to get in and out easily without injury
• Comfort-increase lying times
• Clean and dry
• Maximise the use of expensive housing

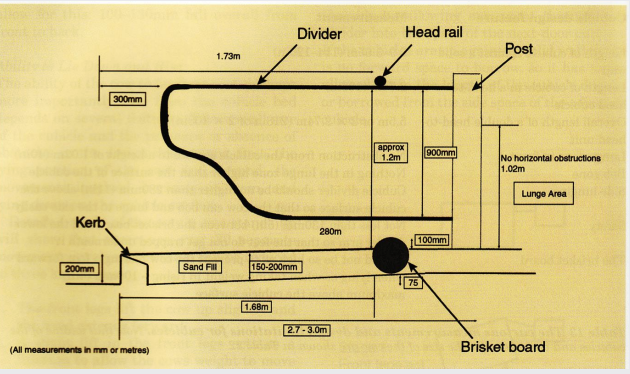
what is this image showing
cubicles design features
Partitions
providing maximum space with minimal interference
Lunge spaces
to front (and side?)
Head rail
pushes cow back so defaecate/urinate in passageway
Slope
cows like to lie uphill (slope10-13cm front to rear)
Brisket board
avoids cow getting too close to wall (preserves lunge space)
Kerb
Not too high, cows do not like backing off a high kerb
Surface
Comfortable, avoids injury (sand, mattress plus bedding)
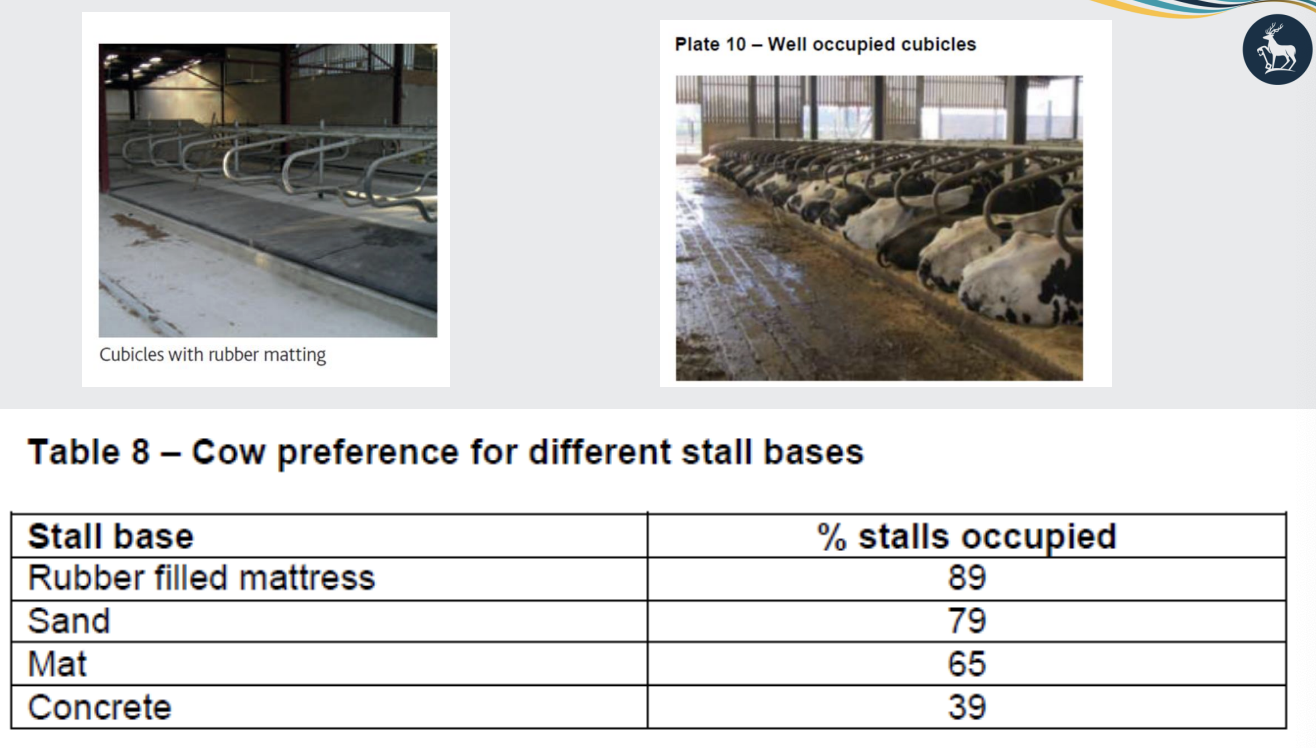
what are the lying times and cubicle beds
did you know there is a higher incidence of lameness in animals housed in cubicles than in straw yards
Lying times and cubicle beds
Ideally cows should lie down for 12 - 14 hours daily
Type of cubicle bed Daily lying time (Hours)
Bare concrete 7.2
Chopped straw on concrete 14.1
Cow cushion 14.4
what is the most preferred stall base for cows?
rubber
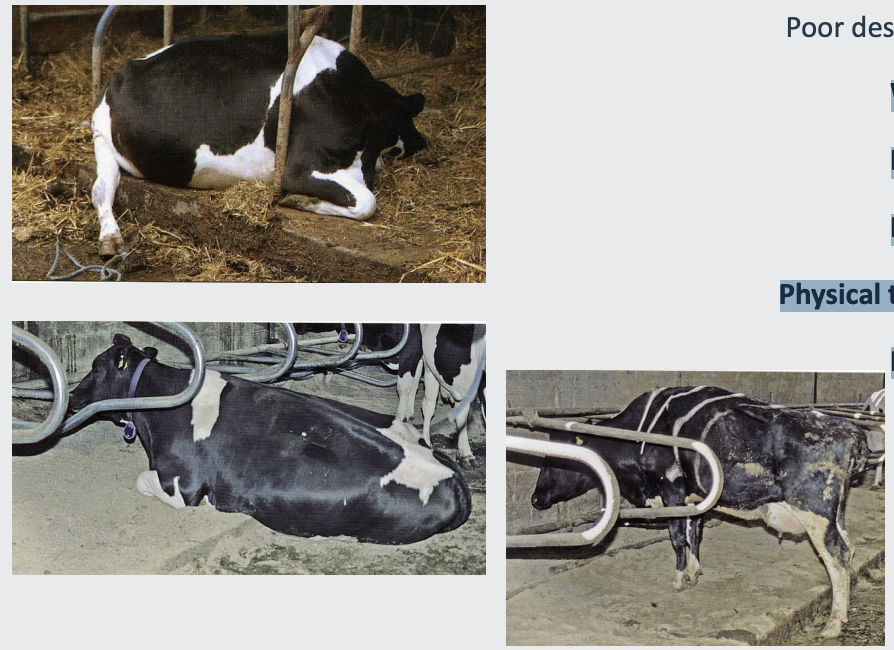
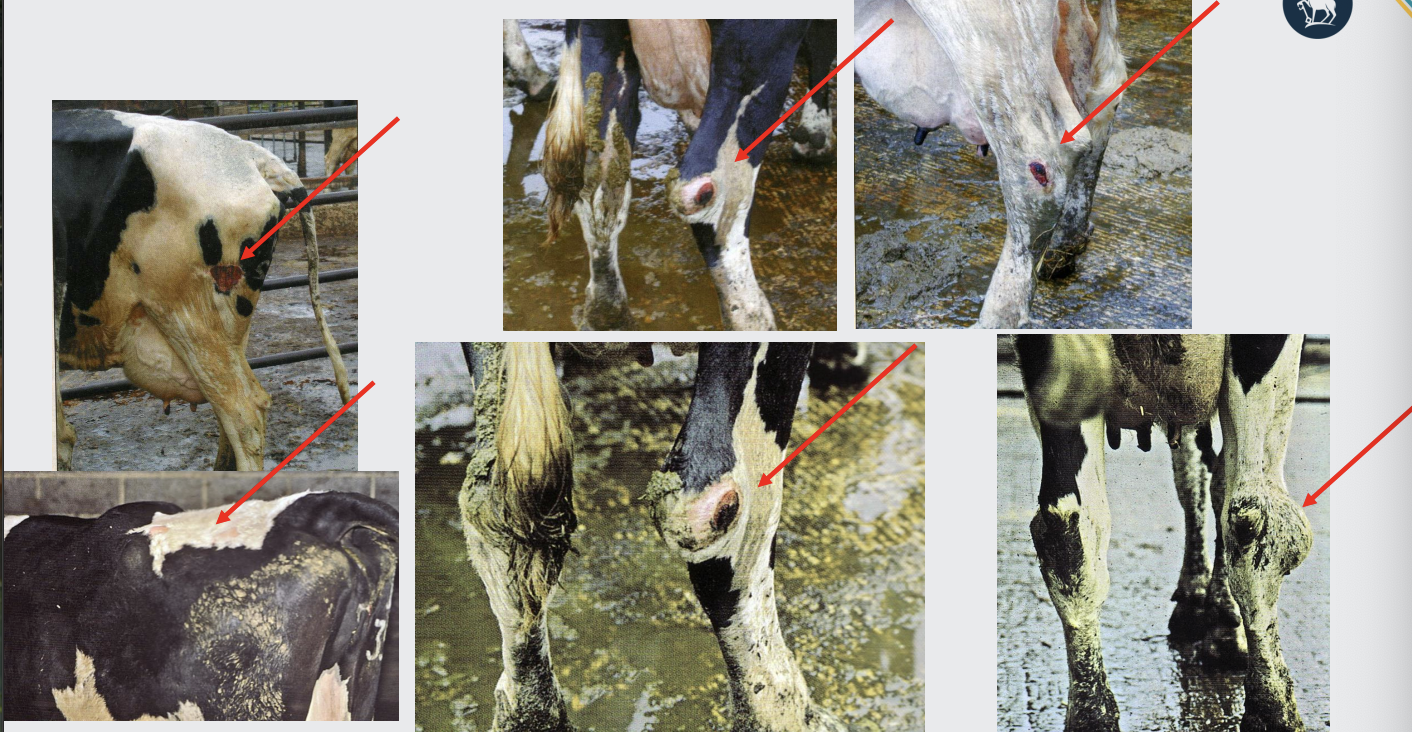
what is poor cubicle design?
Walking and standing in slurry
softens the horn of the hoof
Less time spent lying down
reduced rumination
More time standing
Foot anoxia – blood flow slow
Physical trauma
damaged hocks and carpi.
Physical damage and impact forces feet
Narrow passage ways
sharp turns
what are cow comfort indicators
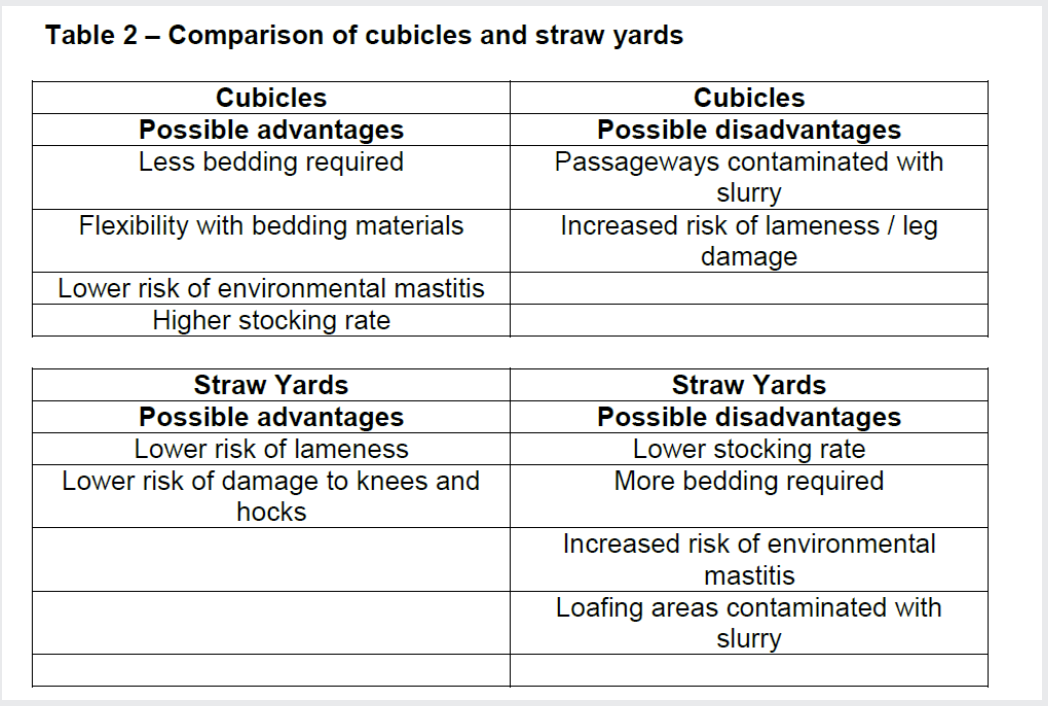
how do cubicles and straw yards compare?
lighting and ventilation dairy cattle housing

what is also considered?
keeping vermin out
birds, rodents, badgers

questions to test your understanding of cattle housing design
1. What type of winter housing are used for adult cattle?
2. What are the main environmental requirements?
3. How can housing design facilitate the 5 freedoms in cattle?
4. Indicate the key design features of cattle cubicles and the purpose of each component?
5. What can cow signs indicate about the housing design?
6. Compare and contrast straw yards and cubicles
7. What are the key housing design features when housing calves prior to weaning?
8. Explain what is meant by stocking density and air space
9. Why is slurry management important?
10. What do you understand by cow comfort and why is it important?