Comprehensive Review of Kidney Disorders: AKI, CKD, and Urological Conditions
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
250 Terms
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
8-20 mg/dL; Amount of Urea Nitrogen in the blood.
Creatinine
0.6-1.2 mg/dL; Product of muscle creatine catabolism (energy production in muscles).
Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR)
90-120 /min/1.73 mL/m2; How much blood your kidneys filter per minute.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
A sudden episode of kidney damage/failure that happens within a few hours or a few days.
Mortality rate of AKI
15-60%; Indicates the risk of death associated with acute kidney injury.
Azotemia
Nitrogen in blood (nitrogenous products- blood urea nitrogen- BUN, creatinine and secondary waste products).
Oliguria
Too little urine leaving the body.
Prerenal dysfunction
Caused by decreased blood flow and perfusion to the kidney.
Common causes of Prerenal dysfunction
Severe blood loss, low blood pressure, severe dehydration, and third spacing.
Intrarenal dysfunction
Caused by damage to structures within kidney.
Examples of Intrarenal dysfunction
Acute tubular necrosis, Acute Glomerulonephritis, Malignant HTN, Bilateral acute pyelonephritis.
Postrenal dysfunction
Caused by obstruction of urinary tract below level of kidneys.
Examples of Postrenal dysfunction
Renal calculi, blood clots, tumors, enlarged prostate (BPH), bladder that doesn't empty properly.
Rhabdomyolysis
Muscles breakdown and release myoglobin and Creatine Kinase-CK.
Hallmark of Rhabdomyolysis
Coca-cola colored urine.
Symptoms of AKI
Swelling in legs, ankles, and around the eyes; fatigue; shortness of breath; confusion; nausea; seizures; chest pain.
Impaired fluid and electrolyte balance
A condition that may occur due to acute kidney injury.
Decrease in GFR
A common finding in acute kidney injury.
Common population affected by AKI
Hospitalized patients (ICU) and older adults.
Treatment of AKI
AKI may be reversed if treated quickly and successfully.
Acute Oliguria
Often reversible with treatment.
Onset Phase of AKI
Lasts hours to days: time from precipitating event that causes the AKI to when symptoms begin.
Oliguric Phase of AKI
Lasts 8-14 days.
Uremia
A constellation of signs and symptoms of renal failure due to failure of excretion of waste products (fluids, electrolytes, waste products).
GFR
Glomerular Filtration Rate; decreases during the oliguric phase.
Fluid Retention
Causes edema, water intoxication, and pulmonary congestion.
Hypertension (HTN)
A possible manifestation during the oliguric phase of AKI.
Neurological Manifestations
Includes seizures, coma, and death during the oliguric phase.
Hyperkalemia
May cause cardiac dysrhythmias.
Diuretic Phase of AKI
Lasts 1-3 weeks; kidneys try to heal and urine output increases.
Osmotic Diuresis
Can occur up to 5L per day.
Recovery Phase of AKI
Lasts several months to 1 year; tubular edema resolves and renal function improves.
Renal Replacement Therapy
Includes dialysis or transplant needed when GFR <15.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Defined as either kidney damage or a GFR less than 60ml/min/1.73m2 for 3 months or longer.
Permanent Loss of Nephrons
Usually occurs gradually in CKD.
Risk Factors for Kidney Disease
Includes age >60 years, diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, family history, and racial tendency.
eGFR
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate; <60 indicates CKD.
Normal GFR
120 to 130 mL/min/1.73 mL/m2.
Creatinine Clearance
Can be directly measured with a 24-hour urine test.
Albuminuria
Key marker of kidney damage; protein leaks into the urine.
Screening for Albuminuria
Screen in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) and hypertension (HTN).
Urine Sediment
Presence of red blood cells (RBC) and white blood cells (WBC) in urine.
Abnormal Imaging Studies
Imaging studies that show irregularities indicating kidney issues.
Cystin C
Amino acid biomarker used as a predictor of kidney function.
Platelet Function in CKD
Platelets are normal but their function is impaired, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Hypertension (HTN) in CKD
Early manifestation of chronic kidney disease (CKD) characterized by increased volume and peripheral vascular resistance (PVR).
Heart Disease in CKD
Fluid overload, anemia, hypertension, and increased heart workload lead to heart disease; late stages may result in congestive heart failure (CHF) and pulmonary edema.
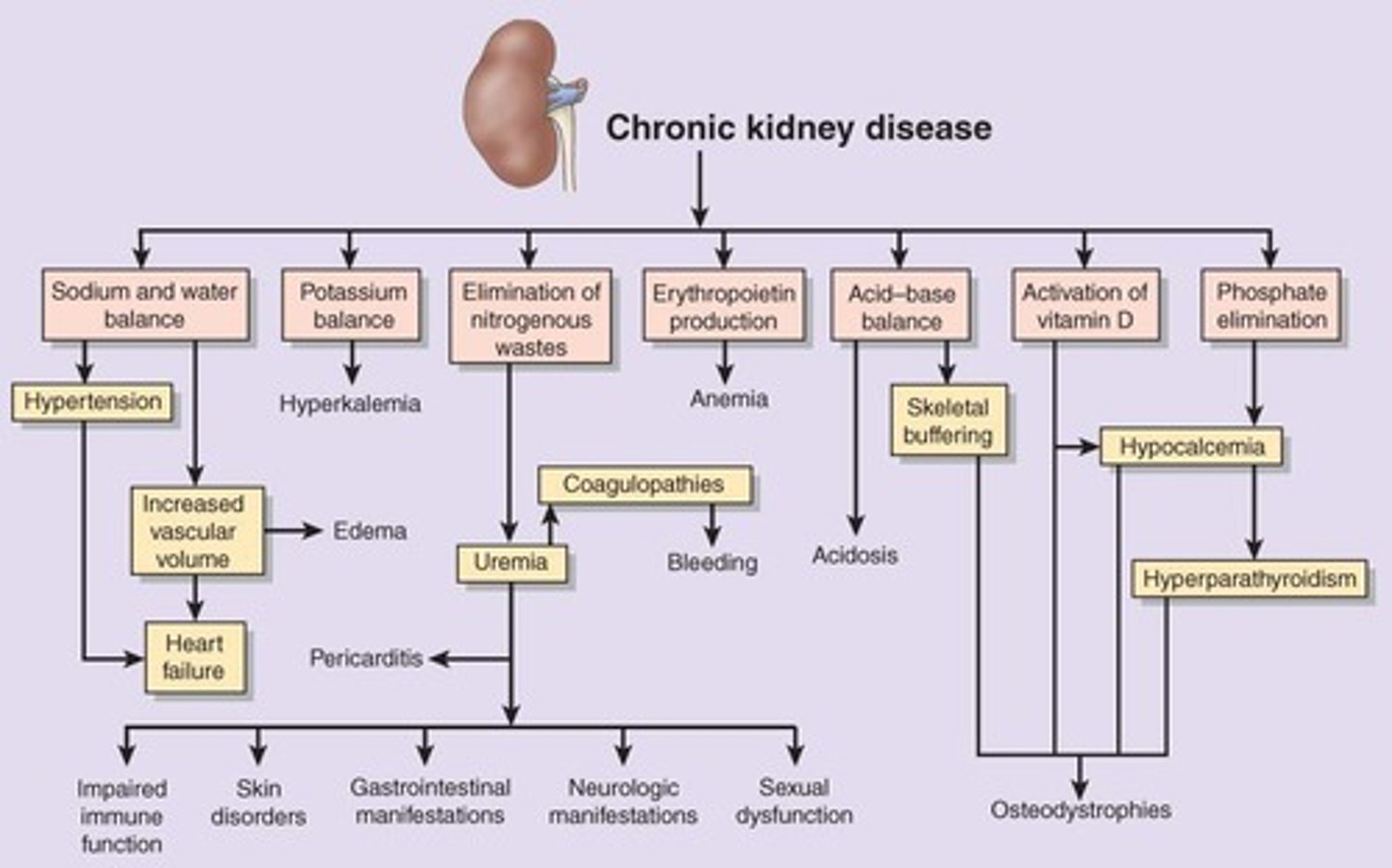
Pericarditis in CKD
Occurs in Stage 5 CKD due to uremia.
Gastrointestinal Manifestations of CKD
Anorexia, nausea/vomiting (N/V), metallic taste, bleeding from GI mucosa, ulcerations, and hiccups.
Neuromuscular Symptoms in CKD
Peripheral neuropathy primarily in lower limbs, with symptoms like creeping, prickling, itching, and burning sensations.
Uremic Encephalopathy
Clinical manifestations from uremia, including reduced alertness, memory loss, delirium, coma, and seizures.
Skin Integrity in CKD
Pale, sallow skin with dryness and pruritus; nails become thin and brittle.
Drug Metabolism in CKD
Impaired drug metabolism through the kidneys.
Normal BUN Levels
Normal BUN is about 8-20 mg/dL, may rise up to 800 mg/dL.
Creatinine Levels in CKD
Decreased urinary clearance and gradual serum accumulation; normal range is 0.6-1.2 mg/dL, may rise to 15-30 mg/dL.
Uremia Definition
Describes clinical manifestations of kidney failure when 2/3 of nephrons are destroyed.
Signs of Uremia
Weakness, fatigue, nausea, and apathy progressing to severe symptoms like vomiting and confusion.
Fluid, Electrolyte, Acid Base Disorders
Kidneys regulate extracellular fluid volume; dehydration or fluid overload is possible.
Hyperkalemia in CKD
Develops when kidney function is severely compromised, leading to elevated potassium levels.
Metabolic Acidosis in CKD
Loss of ability to eliminate hydrogen ions or regenerate bicarbonate.
Bone Disease in CKD
Characterized by increased calcium (↑Ca++) and decreased phosphate (↓Phos) levels.
Phosphate Excretion in CKD
Impaired phosphate excretion leads to elevated serum phosphate levels.
Calcium and Phosphate Relationship
Calcium levels drop as they are inversely related to phosphate levels.
Osteodystrophy
Lead to Skeletal Disorders.
High bone turnover
Results in low bone density and porous bones (WEAK).
Low bone turnover
Characterized by a slow rate of bone formation and defects in bone mineralization.
Symptoms of both high and low turnover
Bone tenderness, muscle weakness, and bone fractures.
Chronic anemia
Occurs due to low erythropoietin, chronic blood loss, bone marrow suppression from uremic factors, and iron deficiency.
Erythropoietin
A hormone produced primarily by the kidneys that controls RBC production by bone marrow.
Anemia Symptoms
Weakness, fatigue, decreased cognitive function, elevated heart rate, and limited oxygen supply leading to angina.
Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO)
Used since 1989 to help increase hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
Peritoneal Dialysis
A process where the patient's peritoneum is filled with a dialysis solution that pulls wastes and extra fluid from the blood.
Dialysate
The dialysis solution that contains certain electrolytes causing diffusion of solutes and ultrafiltration of fluid.
Dwell time
The period the dialysis solution sits in the peritoneal cavity, approximately 4 hours.
Exchanges in Peritoneal Dialysis
A typical schedule requires approximately four exchanges a day, each with a dwell time of 4 to 6 hours.
Hemodialysis
A treatment where the patient's blood is drawn out of the body at a rate of 200 to 400 mL/minute and passed through a dialyzer.
Arteriovenous fistula
A connection created in the arm to facilitate blood flow for hemodialysis.
Dialyzer
A device that removes excess solutes and fluid from the blood during hemodialysis.
Blood volume circulation in Hemodialysis
The patient's entire blood volume (about 5,000 mL) circulates through the machine every 15 minutes.
Dialysis frequency
The procedure is usually required at least three times a week, with each session lasting 4 to 6 hours.
Kidney Transplantation
Can be from cadavers, living related donors (siblings, parents), or living-unrelated donors (spouse) if compatible.
Dietary Management for Kidney Patients
Restrict protein to reduce nitrogenous wastes, lower BUN, and obtain calories from fats and carbs.
Sodium and fluid restrictions
May be necessary based on kidney function.
Potassium restriction
Necessary if GFR is extremely low; avoid salt substitutes as they contain potassium.
Detrusor muscle
The major muscle of the bladder, innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
Sympathetic nerves
Nerves that relax the detrusor muscle but tighten the internal sphincter of the bladder neck, allowing filling.
Parasympathetic nerves
Nerves that contract the detrusor muscle and relax the internal sphincter as the bladder fills.
Urethral sphincter
Controlled both voluntarily and autonomically.
Bladder capacity
The bladder holds 300-400 ml of urine.
Urge to urinate
Begins when 25% of bladder capacity is reached.
Cerebral cortex
Can override the micturition reflex, allowing conscious control of urination.
Urinary Incontinence
Involuntary loss of urine, a symptom with many possible causes.
Stress Incontinence
Most common type of incontinence characterized by involuntary urinary leakage due to relaxed pelvic floor muscles and increased abdominal pressure.
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
Characterized by urgency, frequency, dysuria, and may or may not have incontinence.
Detrusor overactivity
Involuntary bladder contractions during filling, causing urgency and frequency.
Neurogenic mechanism
Involves CNS and neural control of bladder sensation and emptying, leading to uncontrolled voided reflexes.
Myogenic mechanism
Involves smooth muscle of the bladder, where bladder outlet obstruction partially destroys nerve endings controlling bladder excitability.
Overflow Incontinence
Occurs due to chronic overdistension and urinary retention in the bladder, leading to involuntary urine loss.
BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, a frequent cause of overflow incontinence in men.
Fecal impaction
Can cause overflow incontinence by pushing against the urethra and blocking urine flow.