Government Accounting Pinnacle
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on Government Accounting
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Government Accounting
Encompasses the processes of analyzing, recording, classifying, summarizing, and communicating all transactions involving the receipt and disposition of government funds and property, and interpreting the results thereof.
Charged with government accounting Responsibility
Commission on Audit (COA)
Department of Budget and Management (DBM)
Bureau of Treasury (BTr)
Other government agencies.
Commission on Audit (COA)
Has the exclusive authority to promulgate accounting and auditing rules and regulations.
Keeps the general accounts of the government, supporting vouchers, and other documents.
Submits financial reports to the president and congress.
Department of Budget and Management (DBM)
Responsible for the formulation and implementation of the national budget with the goal of attaining the nation’s socio-economic objectives.
Bureau of Treasury (BTr)
Acts as cash custodian of the government.
Authorized to receive and keep national funds and manage and control the disbursements thereof
Maintains accounts of financial transactions of all national government offices, agencies and instrumentalities.
Government Agencies
Refers to any department, bureau or office of the national government, or any of its branches and instrumentalities, or any political subdivision, as well as any government owned or controlled corporation (GOCC), including its subsidiaries, or other self-government board or commission of the government.
National Budget
The government’s estimate of the sources and uses of government funds within a fiscal year.
The Budget Cycle
Budget Preparation
Budget Legislation
Budget Execution
Budget Accountability.
Budget call
The budget preparation starts when the Department of Budget and Management (DBM) issues this to all government agencies.
It contains, among other things, the next fiscal year’s targets, the agency’s budget ceiling and other guidelines in the completion and submission of agency budget proposals.
Budget hearing
The DBM deliberates on the budget proposals, makes recommendations, and consolidates the deliberated proposals into the National Expenditure Program (NEP) and Budget of Expenditures and Sources of Financing (BESF). The DBM then submits the proposed budget to the President
Preparation to the Office of the President
After the President approves the proposed budget, the DBM finalizes the budget documents to be submitted to the Congress. At this point, the proposed budget is referred to as the President’s Budget.
House Deliberations
The house of representatives conducts hearings to scrutinize the various agencies’ respective proposed programs and expenditures. Thereafter, the HOR will prepare General Appropriation Bill (GAB).
Senate Deliberation
The senate conducts its own deliberations on the GAB
Bicameral deliberations
This is formed to harmonize any conflicts between the representatives and senate versions of GAB. Thereafter, final GAB is submitted to the President for enactment.
President’s enactment
The president enacts the GAB and will now known as General Appropriations Act (GAA). The president, however, may exercise his veto power before his enactment of the bill.
Release guidelines and BEDs
The DBM issues guidelines on the release and utilization of funds while the various agencies submit their Budget Execution Documents (BEDs).
Allotment
Authorization issued by the DBM to government agencies to incur obligations for specified amounts contained in a legislative appropriation in the form of budget release documents.
Posted in the Registry of Appropriations and Allotments (RAPAL) and Registries of Allotments, Obligations, and Disbursements (RAOD).
Incurrence of obligations
Government agencies incur obligations which will be paid by the government.
Recorded in the Obligation Request and Status (ORS) documents and Registries of Allotments, Obligations, and Disbursements (RAOD)
Appropriation
Authorization by a legislative body to allocate funds for specified purposes.
Posted in the Registry of Appropriations and Allotments (RAPAL).
Obligation
Amount contracted by an authorized officer for which the government is held liable.
Disbursement
Actual amount paid out of the budgeted amount.
Budget accountability reports
It is required by the government agencies to submit.
Performance reviews
The DBM and COA perform periodic reviews of the agencies’ performance and budget accountability and report to the president.
Audit
The COA audits the agencies
Budget Registries
Registries of revenue and other receipts (RROR)
Registries of appropriations and allotment (RAPAL)
Registries of allotments, obligations and disbursements (RAOD)
Registries of budget, utilization, and disbursements (RBUD)
Registries of revenue and other receipts (RROR)
Used to monitor the budgeted amounts, actual collections and remittances of revenue and other receipts.
Registries of appropriations and allotments (RAPAL)
Used to monitor appropriations and allotments. This is to ensure that allotments will not exceed appropriations.
Registries of allotments, obligations and disbursements (RAOD)
Used to monitor the allotments received, obligations incurred against the corresponding allotment, and the actual disbursements made.
Personnel Services (PS)
Pertain to all types of employee benefits.
Maintenance and other operating expenses (MOOE)
Pertain to various operating expenses other than employee benefits and financial expenses.
Financial Expenses (FE)
Pertain to finance costs.
Capital Outlays (CO)
Pertain to capitalizable expenditures.
Registries of budget, utilization, and disbursement (RBUD)
Used to record the approved special budget and the corresponding utilizations and disbursements charged to retained income.
Budget Preparation
Budget Call
Budget Hearing
Preparation to the Office of the President
Budget Legislation
House Deliberations
Senate Deliberation
Bicameral Deliberations
President’s enactment
Budget Execution
Release guidelines and BEDs
Allotment
Incurrence of obligations
Disbursement authority
Disbursement authority
Appropriation
Allotment
Obligation
Disbursement
Budget Accountability
Budget accountability reports
Performance reviews
Audit
Journals
General journal
Cash receipts journal
Cash disbursements journal
Check disbursement journal
Ledgers
General ledgers
Subsidiary ledgers
Object of Expenditures
Personnel Services (PS)
Maintenance and other operating expenses (MOOE)
Financial Expenses (FE)
Capital Outlays (CO)
The Government Accounting Cycle
Appropriation
Allotment
Incurrence of obligation
Disbursement authority – Notice of cash allocation (NCA)
Disbursements
Billings, collections & remittances
Unadjusted trial balance
Adjusting entries
Closing entries
Preparation of financial statements
BOOKS OF ACCOUNTS AND REGISTRIES
Journals
Ledgers
Registries
Journal entry for Disbursement authority – NCA
Dr. Cash – Modified Disbursement System, Regular
Cr. Subsidy from National Government

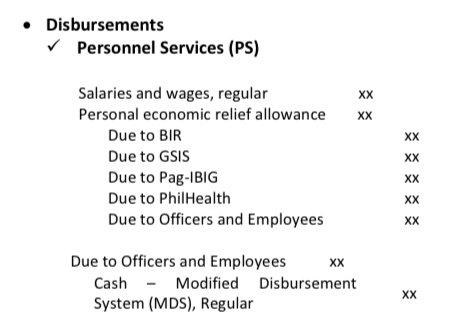
Journal entry for Disbursement - Personnel Services
Dr. Salaries and wages, regular
Dr. Personal economic relief allowance
Cr. Due to BIR
Cr. Due to GSIS
Cr. Due to Pag-IBIG
Cr. Due to PhilHealth
Cr. Due to officers and employees
Dr. Due to officers and employees
Cr. Cash - Modified Disbursement System, Regular
Journal entry for Disbursement - Maintenance and other Operating Expenses
Dr. Water Expenses
Dr. Electricity Expenses
Dr. Telephone Expenses
Dr. Janitorial Expenses
Dr. Security Expenses
Cr. Due to BIR
Cr. Cash - Modified Disbursement System, Regular

Journal entry for Disbursement - Capital outlays
Dr. Office Equipment
Cr. Accounts payable

Journal entry for Disbursement - Remittances of amounts withheld
Dr. Cash-tax remittance advice
Cr. Subsidy from National Government
Dr. Due to BIR
Cr. Cash-tax remittance advice
Dr. Due to GSIS
Dr. Due to Pag-IBIG
Dr. Due to PhilHealth
Cr. Cash-modified disbursement system, regular

Journal entry for Billings, Collections & Remittance
Dr. Accounts receivable
Cr. Service fees
Dr. Cash-collecting officers
Cr. Accounts receivable
Dr. Cash-treasury/agency deposit, regular
Cr. Cash-collecting officers

Adjusting entries to recognize the reversion of unused NCA
Dr. Subsidy from national government
Cr. Cash - modified disbursement system, regular

Journal entry for the closing entries in the government accounting cycle
Dr. Subsidy from national government
Cr. Revenue and expense summary
