Literary Genres of Philippine Literature: Prose, Fiction, and Non-Fiction
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Genre
A category of artistic work that has a specific form or characteristics.
Prose
Known to be a conversational language presented orally or in writing, composed of sentences and paragraphs instead of lines and stanzas.
Fiction
A genre that represents real-life experiences in imaginary narratives, yet its essence can be based on factual and verifiable events.
Novel
A long narrative in written form that has a very complicated plot, usually divided into chapters that are crucial to the story's main plot, and should have at least 50,000 words.
Novella
A work of fiction intermediate in length and complexity between a short story and a novel.
Short Story
Shorter than a novella and has a simpler plot.
Legend
More often secular than sacred, and their principal characters are human. These stories tell of migrations, wars and victories, deeds of past heroes, chiefs and kings, and successful in ruling dynasties.
Myth
A story that explains the origin of the world, humanity, death or natural phenomena, and deals with Gods and folkloric creatures.
Fable
A story about animals that can behave like humans, containing morals that apply to humanity.
Parable
A story found in the sacred scriptures that contains symbols that, when interpreted, can teach a life lesson in accordance with Christian faith and teaching.
Characters
The actors in the story, usually embodying a trait or human attribute that the author intends to include in the narrative.
Protagonist
The story's main character, whose presence is crucial because it propels the plot forward.
Antagonist
An opponent who challenges the protagonist and obstructs the protagonist's success.
Round characters
Characters that undergo a certain change and have complex personalities that are strategically unraveled throughout the story.
Flat characters
Characters that remain constant or do not change throughout the story.
Setting
The time and place/environment of the story.
Plot
The chain of connected events that make up a narrative; the sequence of events in the story.
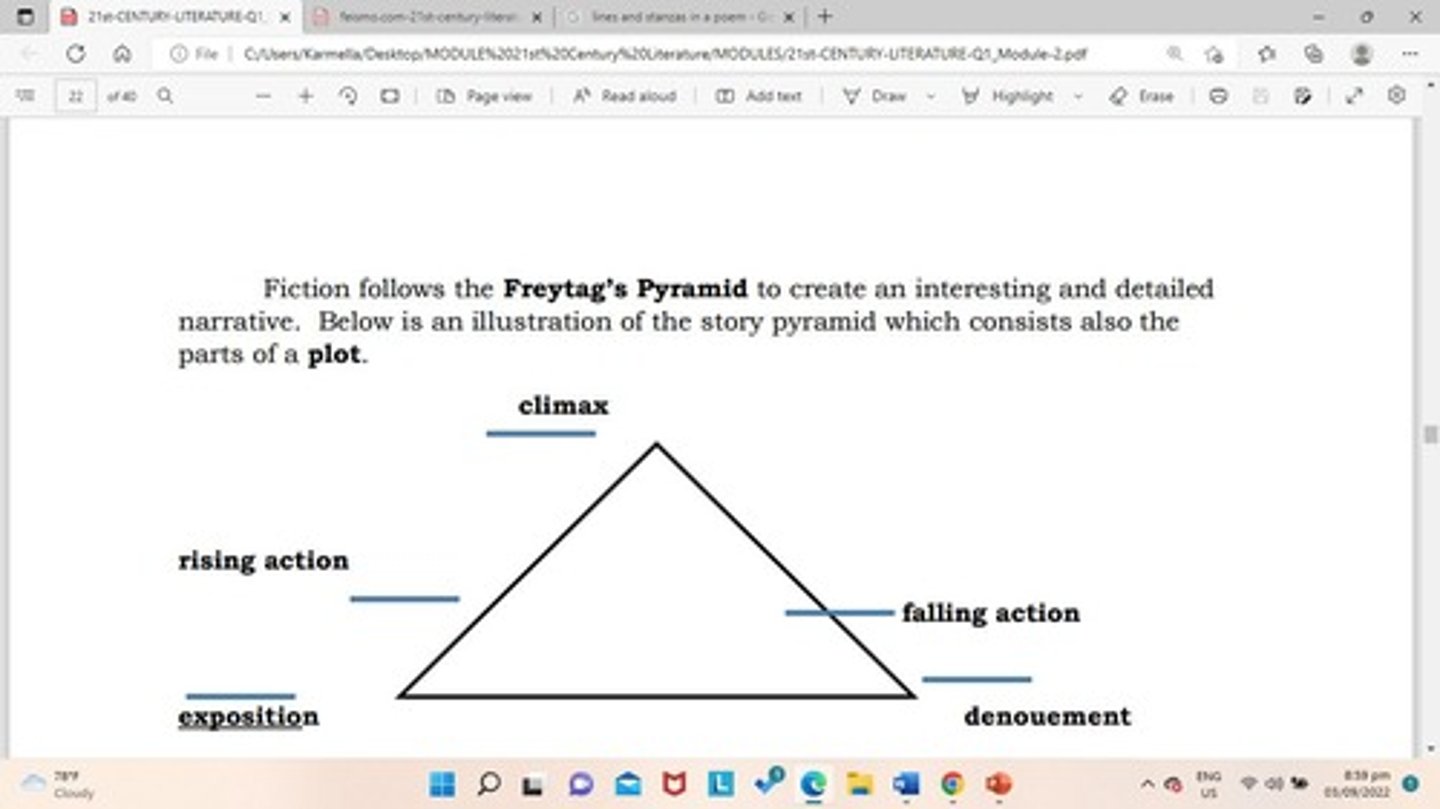
Exposition
Tells about the background of the story, including the setting, characters' back stories, or historical contexts.
Rising action
Part of the story after the characters and setting are introduced, where events begin to reveal probable conflicts that the protagonist must resolve.
Climax
The highest point of tension in the story, usually the most interesting part.
Falling action
The part of a story after the climax and before the very end.
Resolution/denouement
The final outcome of the story where other secrets are revealed, if there are any.
Theme
The central binding thought or topic of the story.
Non-fiction
A literary genre that tells about stories that actually happen in real life, dealing with real people, places, and events.
Autobiography
A self-written biography where the author writes about all or a portion of their own life.
Memoir
A narrative of an episode in one's life which usually contains a certain memorable experience.
Biography
The story of a person's life told by another person, including all pertinent details from the subject's life, typically arranged in chronological order.
Essay
A piece of writing that centers on one topic or subject matter, with the purpose to inform, describe, entertain, or persuade the readers.
Diary
A personal record of a person's daily activities.
Journal
Logs of events that happen to a person or group.