Biology topic 2B (cells)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
The basic structure of all cell membranes are
the same
cell surface membranes are
partially permeable
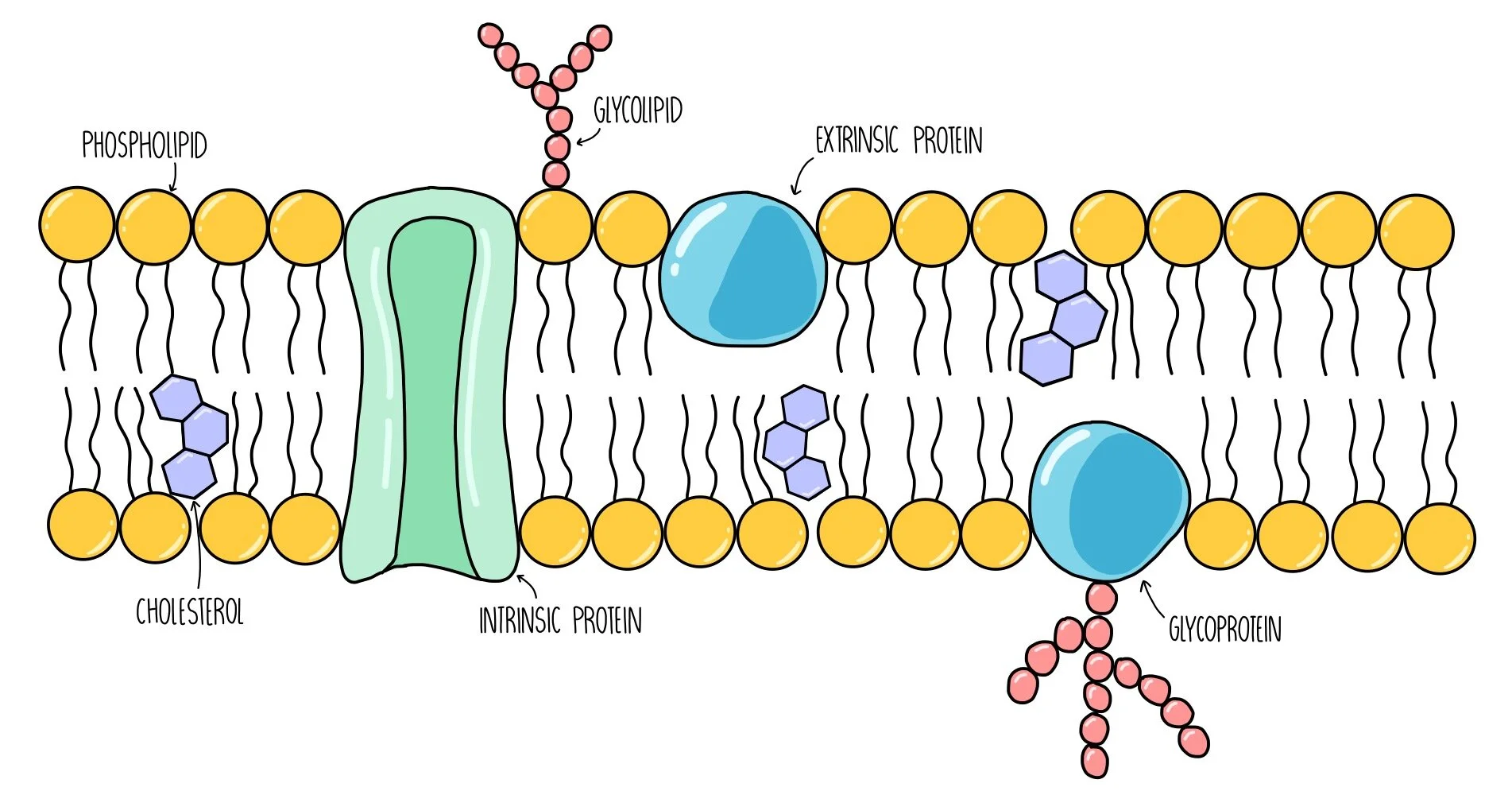
The fluid mosaic model
phospholipid molecules form a continuous bilayer, which is fluid as phospholipids are constantly moving.
proteins are scattered through the bilayer (like tiles in a mosaic) -channel and carrier proteins.
glycoproteins
proteins with a carbohydrate attached
glycolipids
lipids that have a carbohydrate attached
cell membrane structure (diagram)
role of phospholipids
forms a barrier to dissolved (water-soluble) substances
how phopholipids form a barrier
arrange themselves- heads→ hydrophilic (outside)
tails→ hydrophobic (inside)
so centre is hydrophobic so water-soluble substances cannot dissolve through
role of cholesterol
provides stability
binds to hydrophobic tails causing them to pack tightly together and restrict movement of phospholipids.
Simple diffusion
when particles diffuse directly through the cell membrane (small molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide)
is diffusion active or passive
passive
limitations imposed by phospholipid bilayer
only small molecules can pass through- can pass through spaces in the phospholipids
only non-polar molecules can pass through as they are soluble so can dissolve in the hydrophobic layer.
facilitated diffusion in a carrier protein
-large molecule attaches to carrier protein
-protein changes shape to release molecule on other side
facilitated diffusion in channel proteins
forms pores in the membrane for charged particles to diffuse down
Osmosis
diffusion of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential. This is a passive process.
water potential
likelihood of water molecules to diffuse out of or into a solution
isotonic
if two solutions have the same water potential
hypotonic
solutions with a higher water potential than in the cell
hypertonic
solutions with a lower water potential than the cell
Active transport -carrier proteins
-attaches to carrier protein
-changes shape to move molecule to other side → from low to high concentration
-requires energy from ATP (undergoes a hydrolysis reaction- splitting into ADP and an inorganic phosphate which releases energy)
co- transporters are
a type of carrier protein that bind two molecules at a time.
the concentration gradient of one molecule is used to move the other molecule against its own concentration gradient.
mammalian ileum
the concentration of glucose is too low for glucose to diffuse out into the blood
so glucose is absorbed from the lumen of the ileum by co transport
antigens
molecules that generate an immune response when detected by the body
found on the surface of cells
foreign antigens
not normally found in the body
pathogens
have antigens on surface- detected by antigens as foreign
organisms that cause disease
Toxins
immune system responds to these molecules
cells from other individuals
blood transfusion- cells will have antigens that are different from ur own
triggers an immune response
antigens enable the immune system to identify
-pathogens
-cells from other organisms of the same species
-abnormal body cells
-toxins
phagocyte
a phagocyte found in the blood or tissues responds to an immune system trigger
phagocytosis of pathogens
-phagocyte recognises foreign antigens on pathogen
-cytoplasm moves round the pathogen engulfing it
-phagocytic vacuole in the cytoplasm of a phagocyte
-lysosome fuses with the phagocytic vacuole. The lysozymes break down the pathogen
-phagocyte presents the pathogens antigens on its surface → antigen presenting cell
T cells
type of white blood cell
receptor proteins on its surface bind to complementary antigens
helper T cells
release chemical signals that activate and stimulate phagocytes