31. nocardia, actinomyces, dermatophilus
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
actinomyces/nocardia gram stain
gram positive
do actinomyces and nocardia tend to cause acute or chronic infections?
chronic, slow-developing
what are the characteristics of a mycetoma?
swelling
draining sinuses
granules (in draining fluid)
actinomyces/nocardia transmission
traumatic inoculation into skin or mucosa
actinomyces/nocardia pathogenesis
injury creates niche for bacteria → multiply as filaments, resistant to phagocytosis
swollen lesions form that may drain and contain granules (microcolonies)
actinomyces/nocardia treatment
debride or surgically reduce lesion
penicillins (actinomyces) or sulfa (nocardia) for dogs & cats; iodides for large animals
actinomyces source
commensal → oral and GI microbiota
is actinomyces aerobic or anaerobic?
facultative to strict anaerobes
what disease is actinomyces associated with primarily in cattle? what causes this infection?
“lumpy jaw” → actinomyces bovis
caused by traumatic injury within the oral cavity (ex. chewing on something sharp)
normal flora inoculate into soft tissue
anaerobic environment
chronic lumpy jaw lesions
mycetoma
actinomyces tends to invade bone
how is lumpy jaw treated?
resect or drain lesions
treat with iodides (relatively inexpensive), penicillins
may recur
try to get cow through pregnancy or lactation
treatment is difficult, expensive, and prolonged
other presentations of actinomycosis
actinomyces suis → swine; soft tissue wounds, mastitis
dogs and cats → thoracic abscesses
periodontal disease
can contribute to chronic inflammation, bone loss
nocardia sources
environmental → found in soil, water (not commensal)
is nocardia aerobic or anaerobic?
aerobic
in dogs, what type of lesion is often caused by nocardia?
soft tissue abscesses
purulent, bloody “tomato soup” exudate
can be mixed infections
nocardiosis in other species
mastitis in cattle (uncommon)
usually contamination during dry cow therapy, chronic, difficult to treat
horses → placentits
occasional pathogen of fish, shellfish
humans → skin infections following inoculation; if inhaled, can mimic tuberculosis (rare)
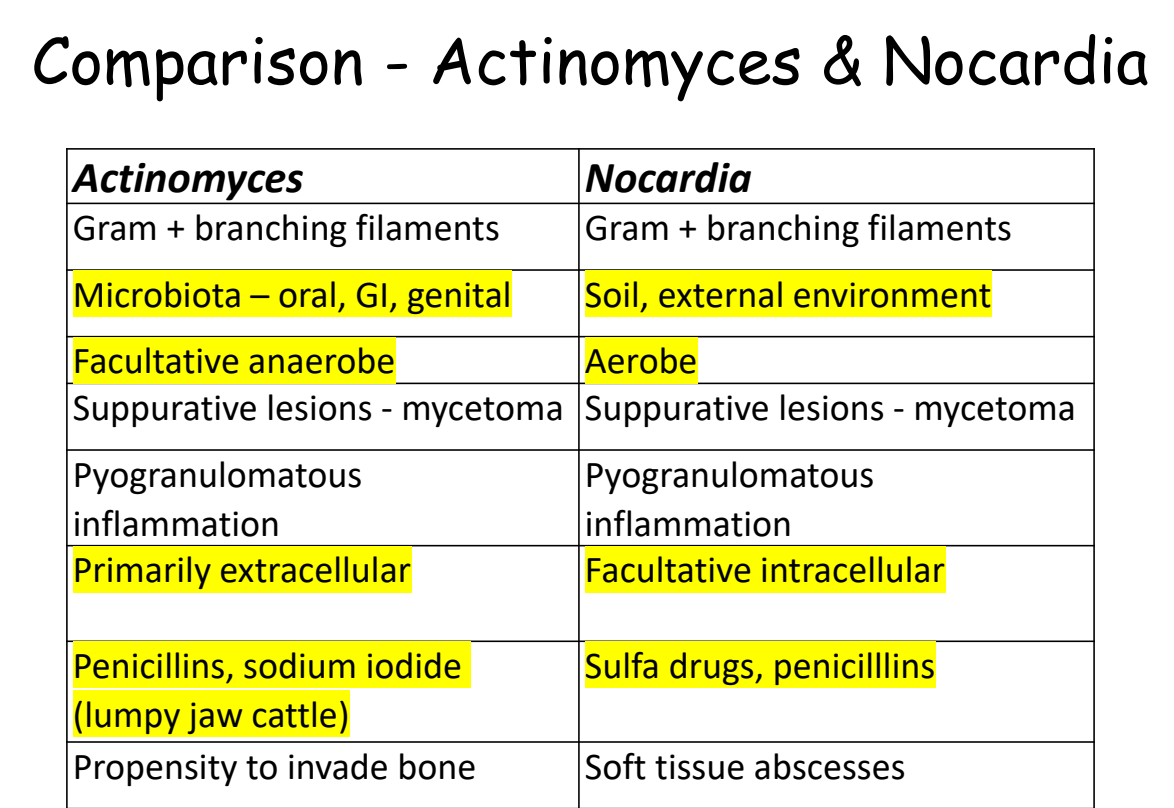
how are actinomyces and nocardia similar? how are they different?
what body site/tissue does dermatophilus infect?
invades epidermis (attracted to CO2)
dermatophilus source
skin lesions on infected animals
how is dermatophilus transmitted?
wet conditions enhance survival and transmission from animal to animal via sloughed skin
short term survival on vegetation
dermatophilus pathogenesis
motile zoospores in skin lesions swim to new sites on same or different animal
burrow into skin → form large filaments that fragment into zoospores
attract PMNs → skin sloughs → can transmit to others
what types of lesions do dermatophilus cause?
superficial crusty, scabby lesions
what diseases do dermatophilus cause?
“lumpy wool disease”
“strawberry footrot”
“rain scald”
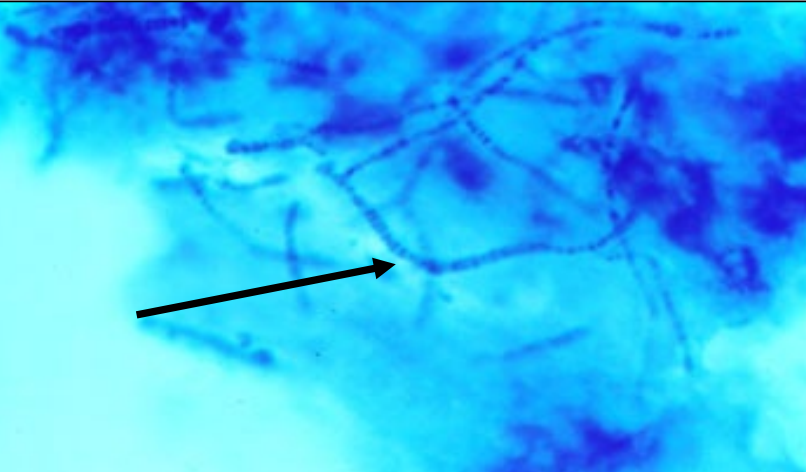
dermatophilus diagnosis
appearance of lesions
visualize organisms in scabs (Giemsa stain)
dermatophilus treatment
improve hygiene (e.g. wet conditions)
penicillin, other antibiotics
topical treatment (debride lesions)
what is the significance of ticks in dermatophilus transmission?
in the tropics, amblyoma ticks serve as a mechanical vector to transmit d. conglolensis