Vesicular transport
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
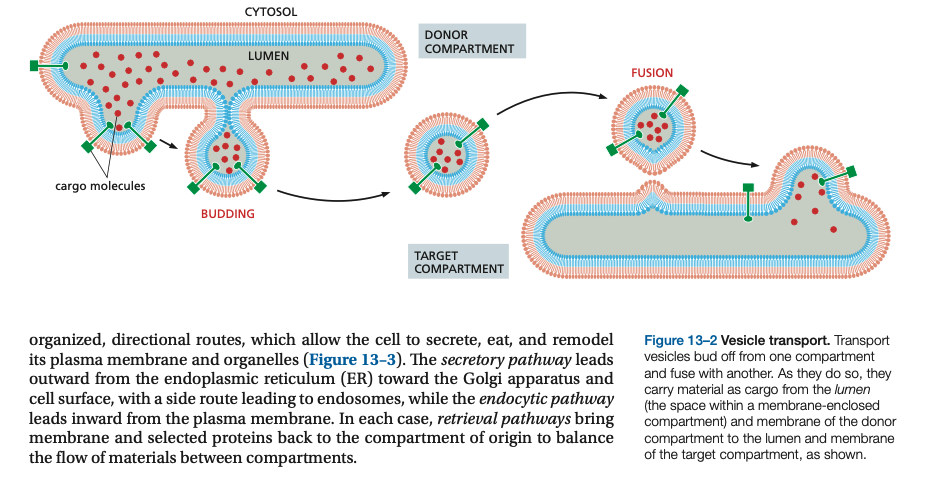
Transport vesicles bud off from one compartment and ___ with another. As they do so, they carry material as ___ from the lumen (the space within a membrane-enclosed compartment) and membrane of the donor compartment to the lumen and membrane of the _____ compartment
Transport vesicles bud off from one compartment and fuse with another. As they do so, they carry material as cargo from the lumen (the space within a membrane-enclosed compartment) and membrane of the donor compartment to the lumen and membrane of the target compartment
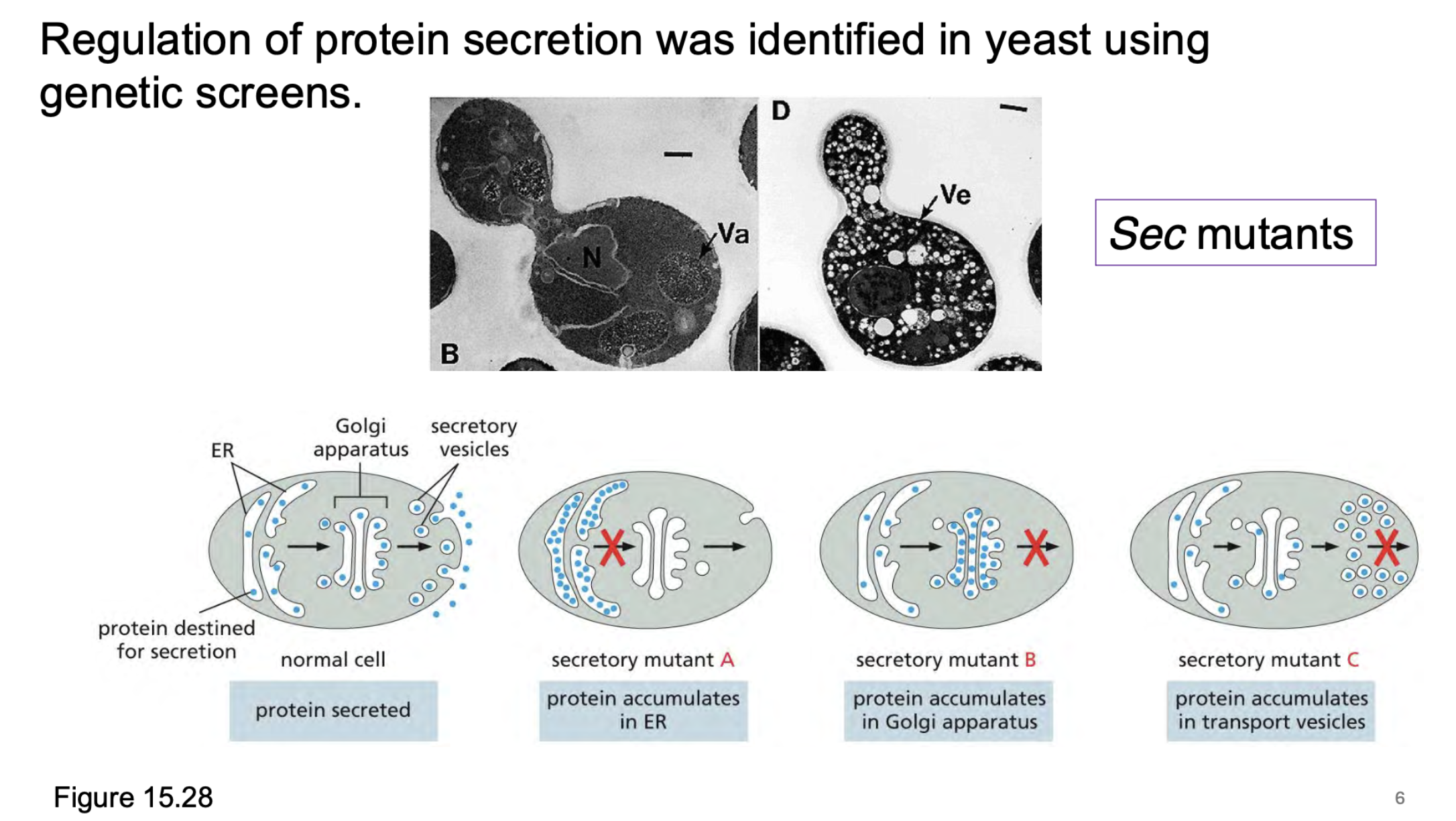
The regulation of protein secretion in yeast was identified through genetic screens by isolating temperature-sensitive (ts) secretion (_____) mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Mutants were grown at a permissive temperature (e.g., 25°C) and then shifted to a restrictive temperature (e.g., 37°C) to identify those that ________ secretory proteins due to ______ secretion pathways.
The regulation of protein secretion in yeast was identified through genetic screens by isolating temperature-sensitive (ts) secretion (sec) mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Mutants were grown at a permissive temperature (e.g., 25°C) and then shifted to a restrictive temperature (e.g., 37°C) to identify those that accumulated secretory proteins due to defective secretion pathways.
Clathrin mediates _____ and _____-to-______ transport. It forms a triskelion structure that assembles into a lattice to drive vesicle budding. Adaptor proteins (AP complexes) help recruit specific cargo.
Clathrin mediates endocytosis and Golgi-to-endosome transport. It forms a triskelion structure that assembles into a lattice to drive vesicle budding. Adaptor proteins (AP complexes) help recruit specific cargo.
COPI vesicles mediate ______ transport (_____ → _____ and intra-Golgi transport). They maintain Golgi structure and recycle ER-resident proteins (via KDEL receptors) back to the ER.
COPI vesicles mediate retrograde transport (Golgi → ER and intra-Golgi transport). They maintain Golgi structure and recycle ER-resident proteins (via KDEL receptors) back to the ER.
COPII vesicles handle ______ transport (____ → ____). The coat assembles via Sar1 GTPase, recruiting Sec23/24 (cargo selection) and Sec13/31 (scaffolding) to drive vesicle formation
COPII vesicles handle anterograde transport (ER → Golgi). The coat assembles via Sar1 GTPase, recruiting Sec23/24 (cargo selection) and Sec13/31 (scaffolding) to drive vesicle formation
retromer is not a classic coat protein but a _____ _____ that mediates cargo retrieval from ______ back to the Golgi or plasma membrane (e.g., recycling mannose-6-phosphate receptors for lysosomal targeting). It includes Vps35, Vps26, and Vps29 with sorting nexins (SNXs) for membrane binding.
retromer is not a classic coat protein but a recycling complex that mediates cargo retrieval from endosomes back to the Golgi or plasma membrane (e.g., recycling mannose-6-phosphate receptors for lysosomal targeting). It includes Vps35, Vps26, and Vps29 with sorting nexins (SNXs) for membrane binding.
Clathrin is composed of a large subunit (the _____ chain) and a small subunit (the ____ chain). _____ heavy chains and _____ light chains assemble into a three-legged structure called a ____
Clathrin is composed of a large subunit (the heavy chain) and a small subunit (the light chain). Three heavy chains and three light chains assemble into a three-legged structure called a triskelion

Clathrin proteins form a _____ ___ structure around the forming vesicle.
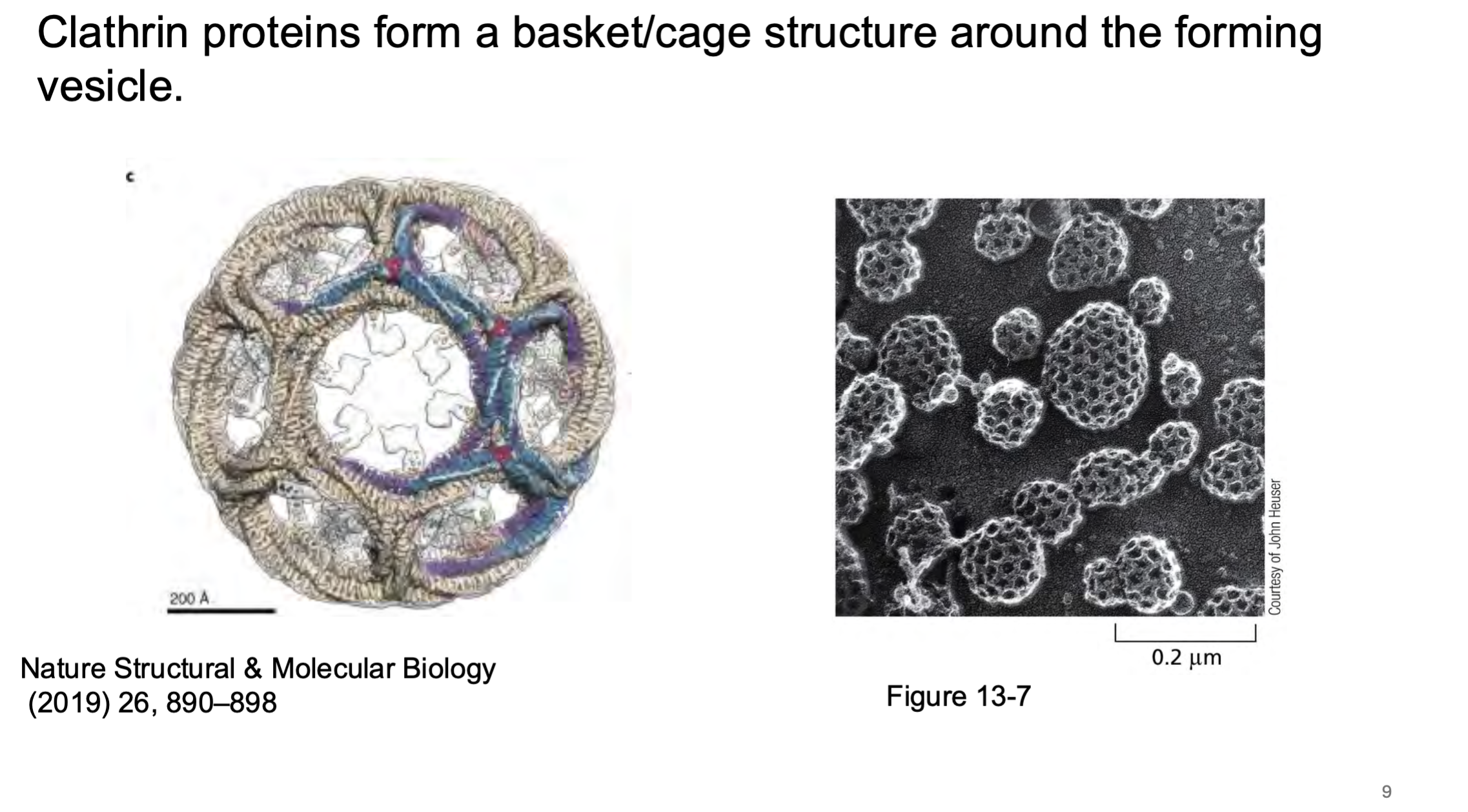
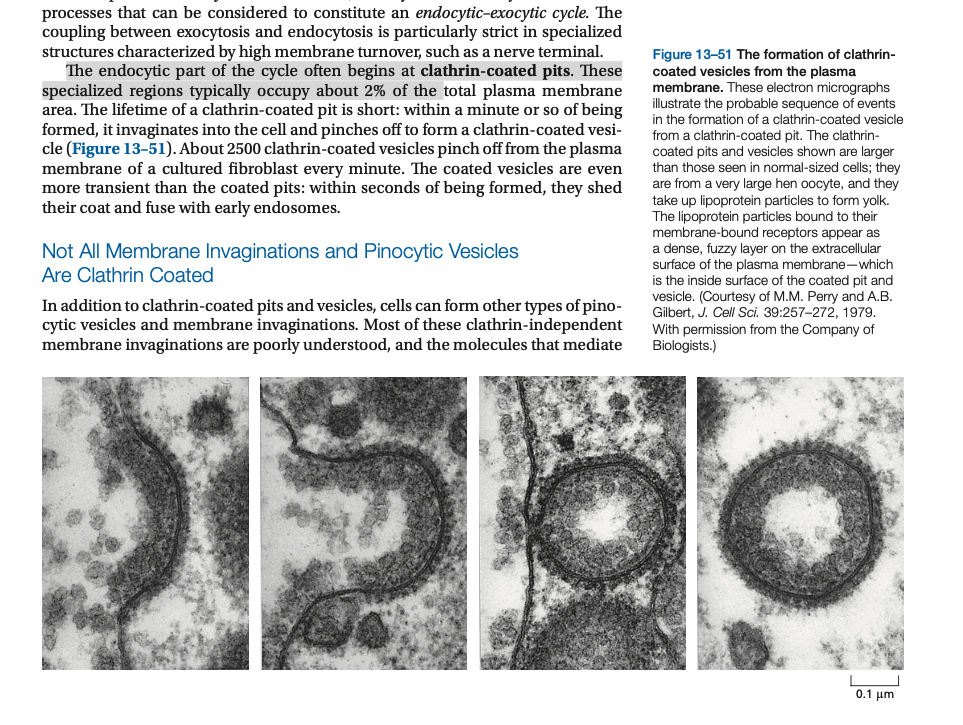
Specificity of what gets incorporated into the vesicle ____ _____ determined by the clathrin coat.
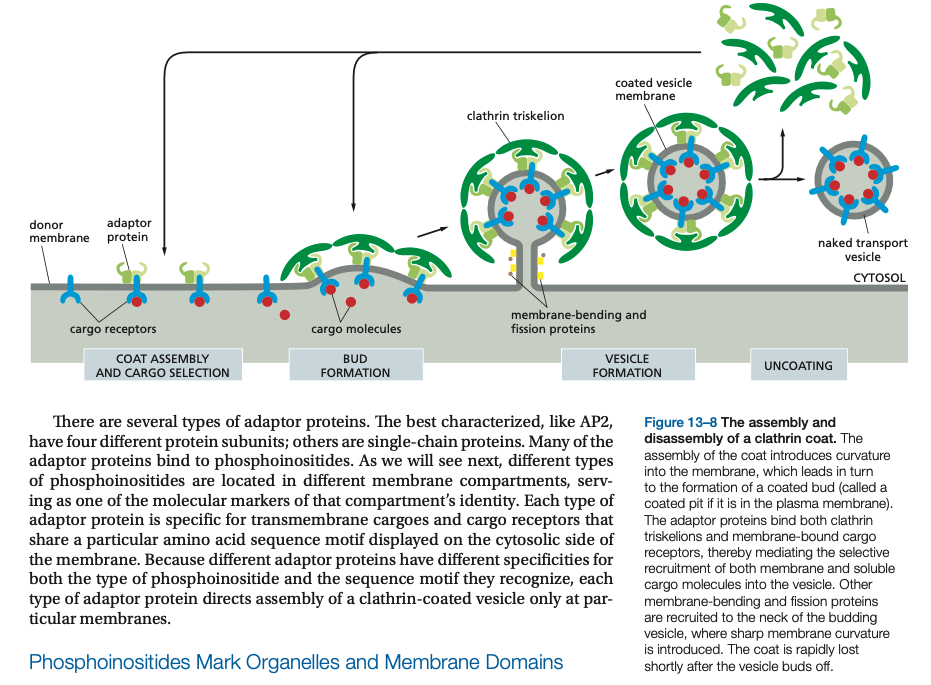
The assembly of the coat introduces ______ into the membrane, which leads in turn to the formation of a coated bud (called a coated pit if it is in the plasma membrane).
The ____ ____ bind both clathrin triskelions and membrane-bound cargo receptors, thereby mediating the selective recruitment of both membrane and soluble cargo molecules into the vesicle.
Other membrane-bending and fission proteins are recruited to the neck of the budding vesicle, where sharp membrane curvature is introduced. The ____ is rapidly lost shortly after the vesicle buds off.
Specificity of what gets incorporated into the vesicle IS NOT determined by the clathrin coat.
The assembly of the coat introduces curvature into the membrane, which leads in turn to the formation of a coated bud (called a coated pit if it is in the plasma membrane).
The adaptor proteins bind both clathrin triskelions and membrane-bound cargo receptors, thereby mediating the selective recruitment of both membrane and soluble cargo molecules into the vesicle.
Other membrane-bending and fission proteins are recruited to the neck of the budding vesicle, where sharp membrane curvature is introduced. The coat is rapidly lost shortly after the vesicle buds off.
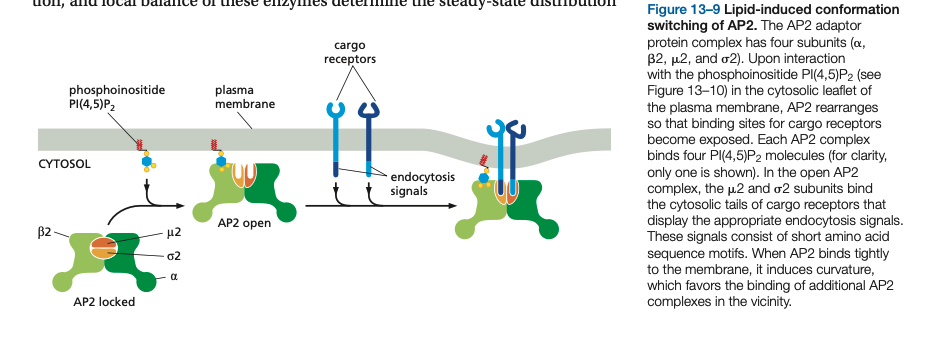
Specificity is defined by the _____ ____ that bind to the cargo ____.
The AP2 adaptor protein complex has four subunits (α, β2, μ2, and σ2). Upon interaction with the _______ PI(4,5)P2 (see Figure 13–10) in the cytosolic leaflet of the plasma membrane, AP2 rearranges so that binding sites for _____ receptors become exposed.
Each AP2 complex binds ____ PI(4,5)P2 molecules (for clarity, only one is shown). In the open AP2 complex, the μ2 and σ2 subunits bind the cytosolic tails of ____ receptors that display the appropriate endocytosis signals. These signals consist of short amino acid sequence motifs. When AP2 binds tightly to the membrane, it induces curvature, which favors the binding of additional AP2 complexes in the vicinity.
Specificity is defined by the adaptor proteins that bind to the cargo receptors.
he AP2 adaptor protein complex has four subunits (α, β2, μ2, and σ2).
Upon interaction with the phosphoinositide PI(4,5)P2 (see Figure 13–10) in the cytosolic leaflet of the plasma membrane, AP2 rearranges so that binding sites for cargo receptors become exposed.
Each AP2 complex binds four PI(4,5)P2 molecules (for clarity, only one is shown). In the open AP2 complex, the μ2 and σ2 subunits bind the cytosolic tails of cargo receptors that display the appropriate endocytosis signals. These signals consist of short amino acid sequence motifs. When AP2 binds tightly to the membrane, it induces curvature, which favors the binding of additional AP2 complexes in the vicinity.
Phosphoinositol lipids regulate which _____ recruit which ____ _____ to form the coated vesicle. Phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphoinositides (phosphatidylinositol phosphates, or PIPs).
Phosphoinositol lipids regulate which membranes recruit which adaptor proteins to form the coated vesicle. Phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphoinositides (phosphatidylinositol phosphates, or PIPs).
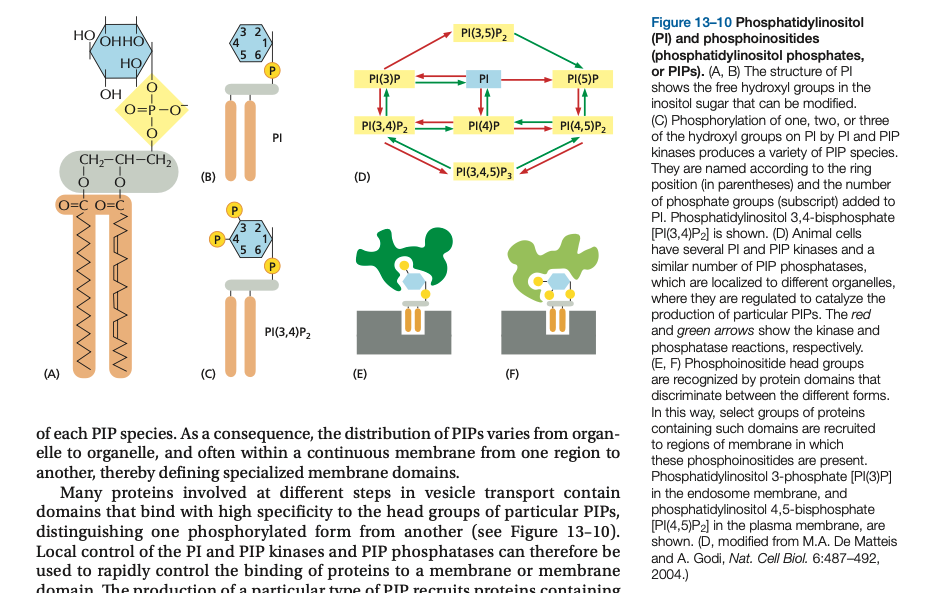
Different types of PIPs are located in different membranes and membrane domains, where they are often associated with specific vesicle _____ events, and where vesicle ____ can assemble.
Different types of PIPs are located in different membranes and membrane domains, where they are often associated with specific vesicle transport events, and where vesicle coats can assemble.
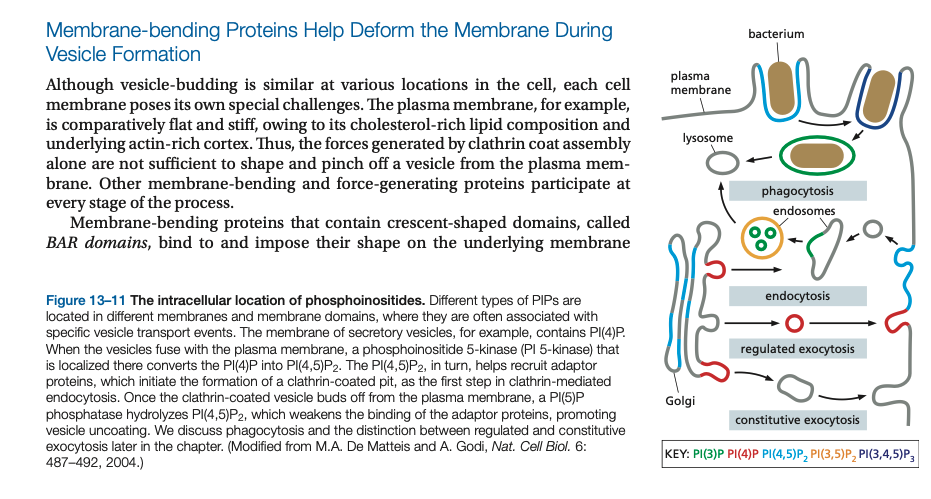
Monomeric GTPases can control ___ assembly...
The coat-recruitment GTPases control the assembly of ___ and __ __ coated vesicles.
Two classes of proteins regulate the toggling: guanine nucleotide exchange factors (______) activate the proteins by catalyzing the exchange of GDP for GTP, and (____) inactivate the proteins by triggering the hydrolysis of the bound GTP to GDP
____ GTPases → COP I (___)
____ protein → COP II (ER)
___ → retromer (____)
Monomeric GTPases can control coat assembly...
The coat-recruitment GTPases control the assembly of COP I and COP II coated vesicles.
Two classes of proteins regulate the toggling: guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) activate the proteins by catalyzing the exchange of GDP for GTP, and GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) inactivate the proteins by triggering the hydrolysis of the bound GTP to GDP
Arf GTPases → COP I (Golgi)
Sar1 → COP II (ER)
Rab7 → retromer (endosomes)
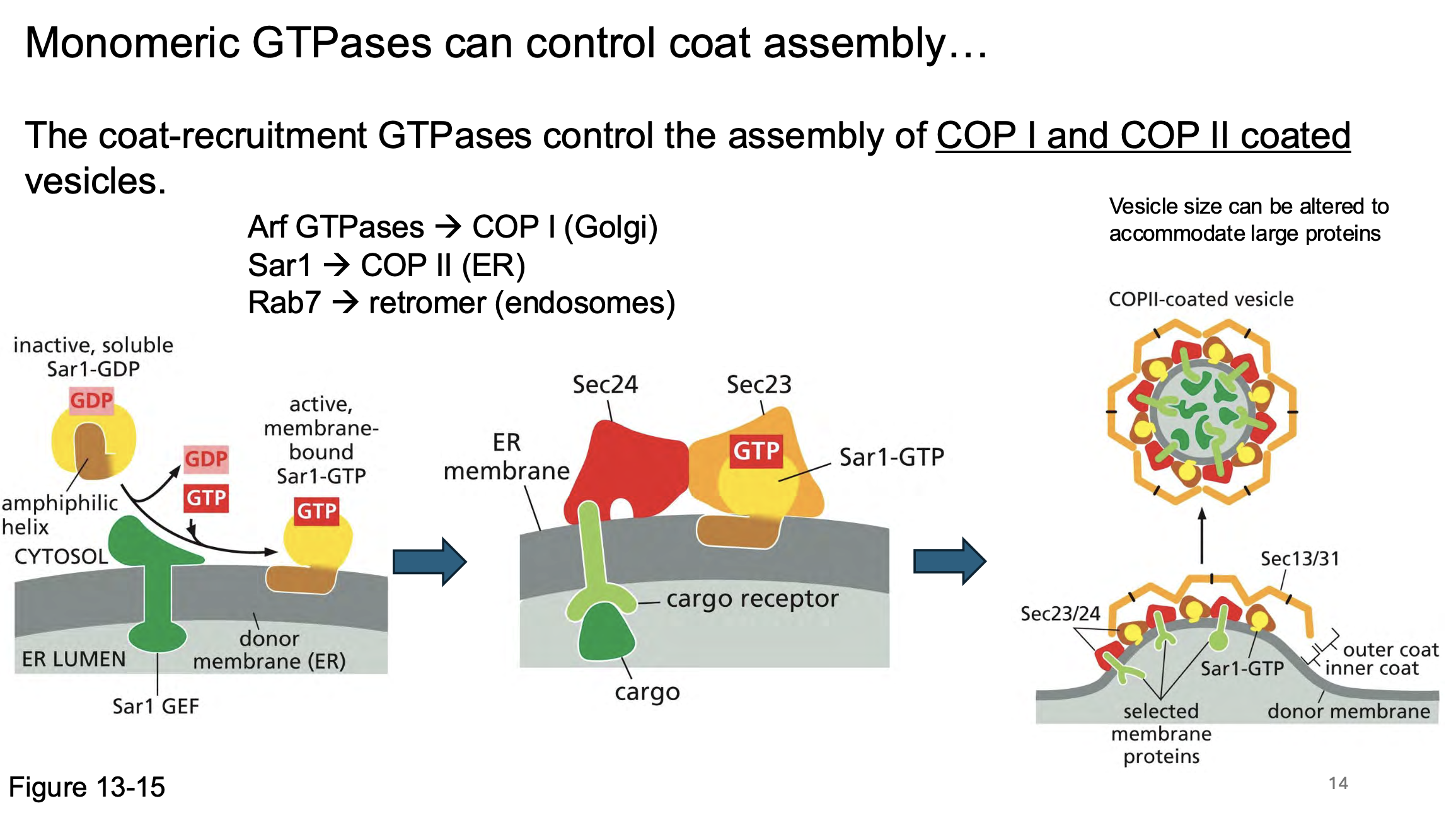
Mutations in ______ and _____ can cause defects in formation of the early CNS.
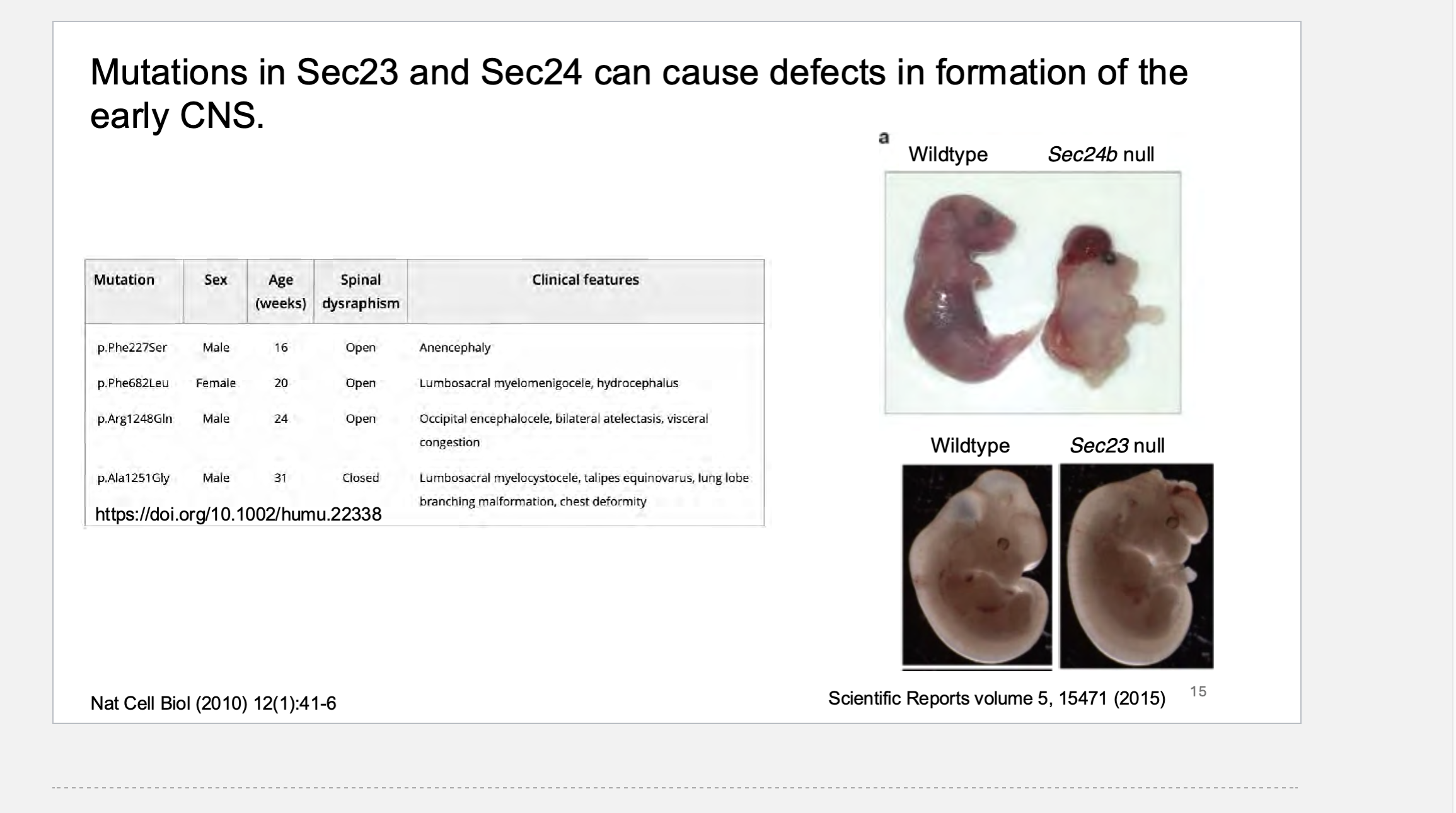
_____ _____ also directs the vesicle to the correct target membrane. The Rab GTPases: over 60 different Rab proteins encoded by the mammalian genome.
Found on both the vesicles and the target membranes.
_____ ____ can regulate the “identity” of both the vesicle and the target membrane.
Monomeric GTPases also directs the vesicle to the correct target membrane. The Rab GTPases: over 60 different Rab proteins encoded by the mammalian genome. Found on both the vesicles and the target membranes. Rab GTPase can regulate the “identity” of both the vesicle and the target membrane.
Two types of markers act sequentially to ensure the specificity of vesicle targeting. First, _____ proteins direct the vesicle to specific spots on the correct target membrane. Second, _____ proteins enable the fusion of the lipid bilayers.
Two types of markers act sequentially to ensure the specificity of vesicle targeting. First, Rab proteins direct the vesicle to specific spots on the correct tar- get membrane. Second, SNARE proteins enable the fusion of the lipid bilayers.
Rab proteins cycle between a membrane and the cytosol and regulate the reversible assembly of protein complexes on the membrane. In their GDP-bound state, they are inactive and bound to another protein (GDP dissociation ____, or GDI) that keeps them soluble in the ____. Membrane-bound Rab _____ activate Rab proteins by catalyzing the exchange of GDP for GTP. Once in the GTP-bound state, the Rab protein’s lipid anchor inserts into the membrane where the Rab binds to a diverse set of proteins called Rab _____
Rab proteins cycle between a membrane and the cytosol and regulate the reversible assembly of protein complexes on the membrane. In their GDP-bound state, they are inactive and bound to another protein (GDP dissociation inhibi- tor, or GDI) that keeps them soluble in the cytosol. Membrane-bound Rab GEFs activate Rab proteins by catalyzing the exchange of GDP for GTP. Once in the GTP-bound state, the Rab protein’s lipid anchor inserts into the membrane where the Rab binds to a diverse set of proteins called Rab effectors
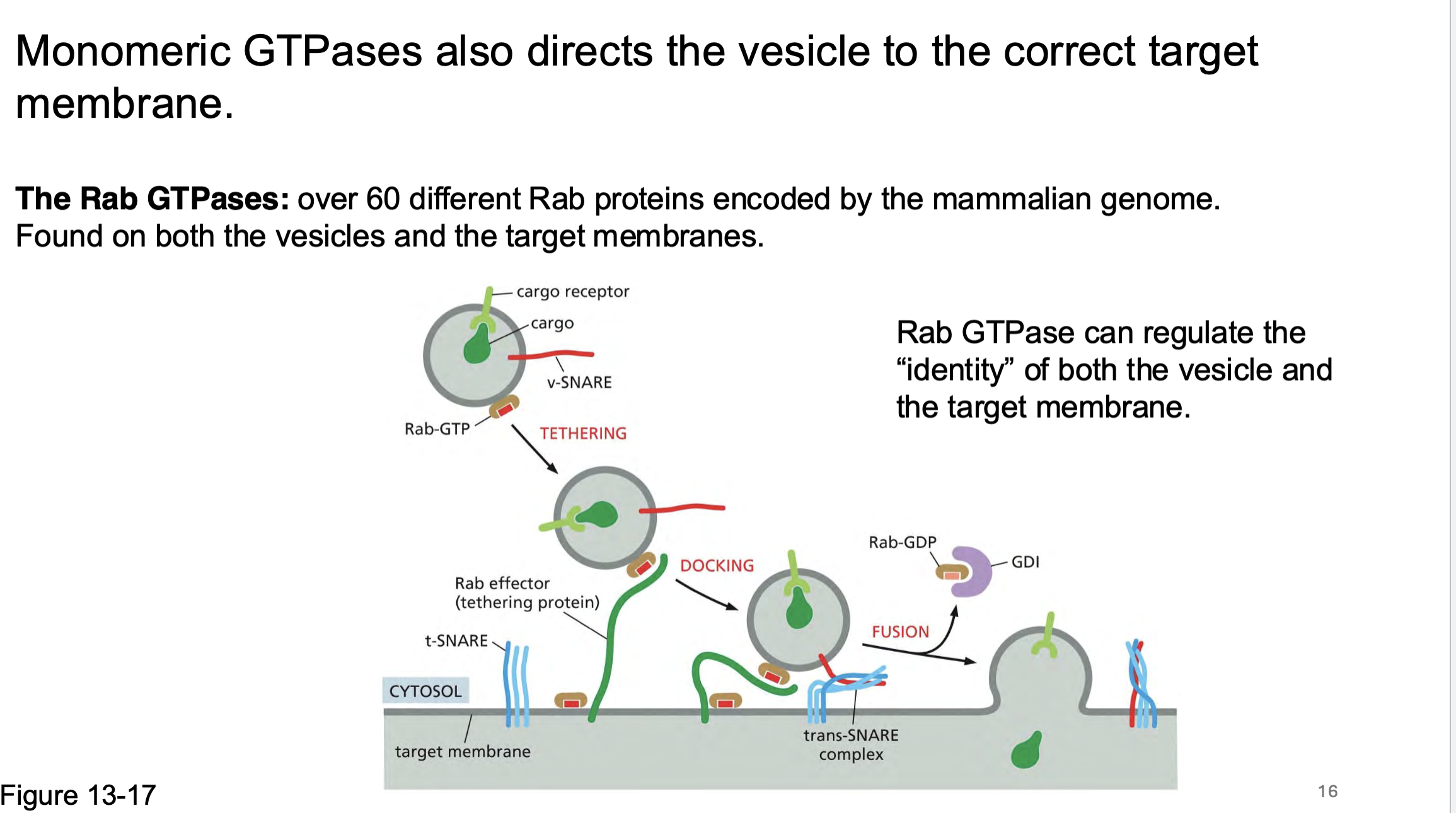
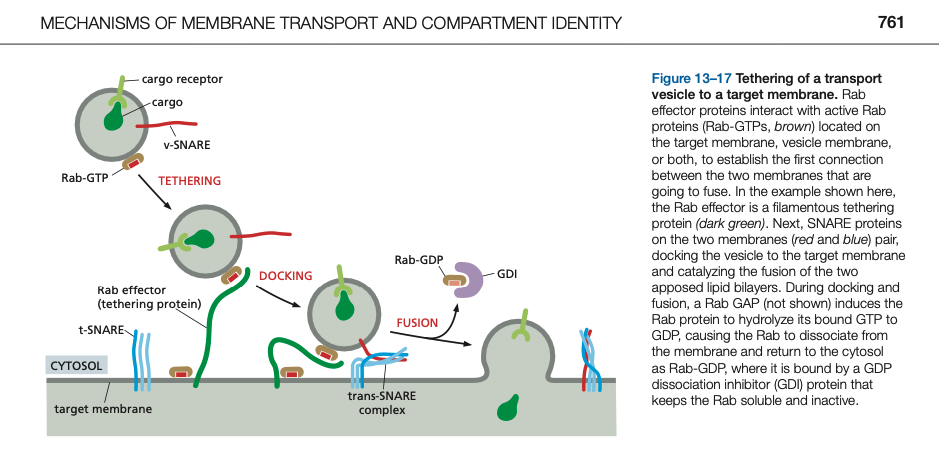
_______ proteins determine membrane targeting and membrane fusion.
After SNARE proteins have participated in membrane fusion, the highly stable trans-SNARE complexes have to disassemble before the SNAREs can mediate new rounds of transport. A crucial protein called ___ cycles between membranes and the cytosol and catalyzes the disassembly process.
SNARE proteins determine membrane targeting and membrane fusion.
After SNARE proteins have participated in membrane fusion, the highly stable trans-SNARE complexes have to disassemble before the SNAREs can mediate new rounds of transport. A crucial protein called NSF cycles between mem- branes and the cytosol and catalyzes the disassembly process.
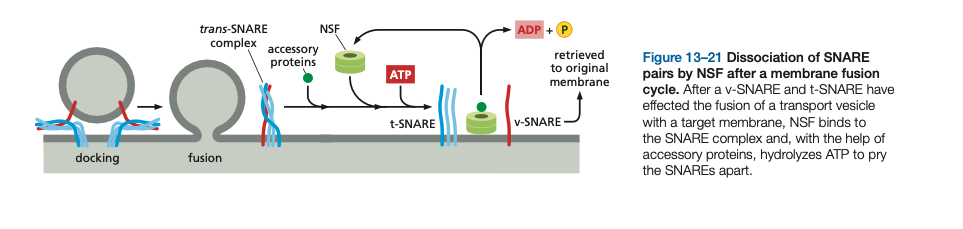
v-SNAREs (Vesicle-SNAREs) – Located on _____, they guide the vesicle to the correct target membrane. Example: Synaptobrevin/VAMP in synaptic vesicles.
t-SNAREs (Target-SNAREs) – Located on the _____ _____, they interact with v-SNAREs to drive membrane fusion. Examples: Syntaxin and SNAP-25 at the plasma membrane.
v-SNAREs (Vesicle-SNAREs) – Located on vesicles, they guide the vesicle to the correct target membrane. Example: Synaptobrevin/VAMP in synaptic vesicles.
t-SNAREs (Target-SNAREs) – Located on the target membrane, they interact with v-SNAREs to drive membrane fusion. Examples: Syntaxin and SNAP-25 at the plasma membrane.
Transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus occurs via _____ tubular clusters.
ransport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus occurs via vesicular tubular clusters.
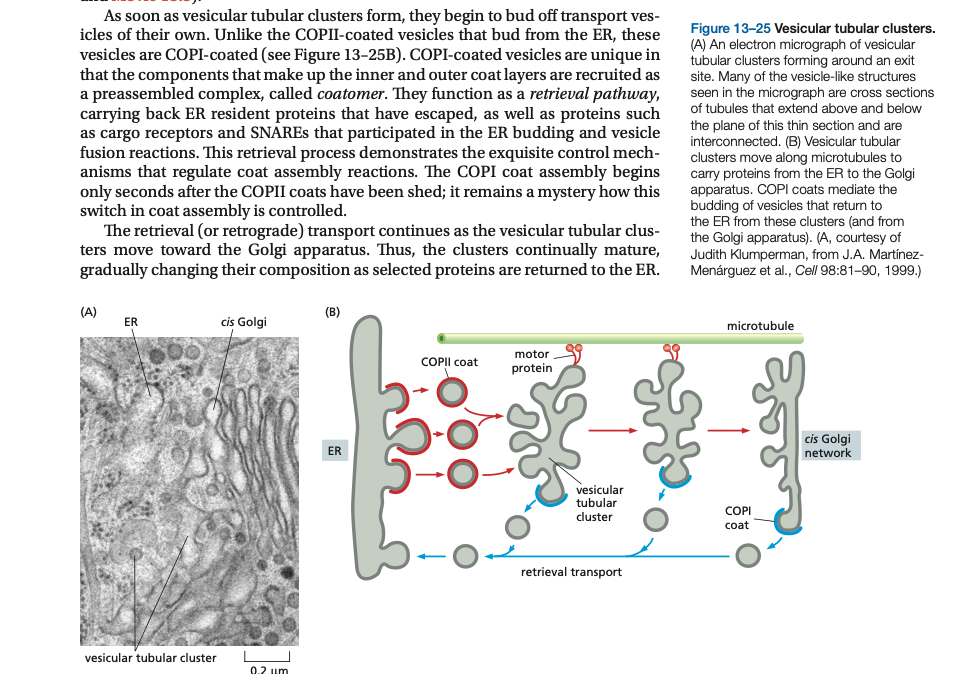
the cis Golgi network (CGN) and the trans Golgi network (TGN), respectively. The CGN is a collection of fused ___ _____ clusters arriving from the ER. Proteins and lipids ____ the cis Golgi network and _____ from the trans Golgi network, bound for the cell surface or another compartment.
the cis Golgi network (CGN) and the trans Golgi network (TGN), respectively. The CGN is a collection of fused vesicular tubular clusters arriving from the ER. Proteins and lipids enter the cis Golgi network and exit from the trans Golgi network, bound for the cell sur- face or another compartment.
After arrival in the CGN (Cis-Golgi Network), proteins enter the first of the Golgi processing compartments (the _____ Golgi cisterna). They then move to the next compartment (the ____ cisterna) and finally to the _____ cisterna, where _____ is completed. The lumen of the ____ cisterna is thought to be continuous with the TGN, the place where proteins are segregated into different transport packages and dispatched to their next destinations.
After arrival in the CGN, proteins enter the first of the Golgi processing compartments (the cis Golgi cisterna). They then move to the next compartment (the medial cisterna) and finally to the trans cisterna, where glycosylation is completed. The lumen of the trans cisterna is thought to be continuous with the TGN, the place where proteins are segregated into different transport packages and dispatched to their next destinations.
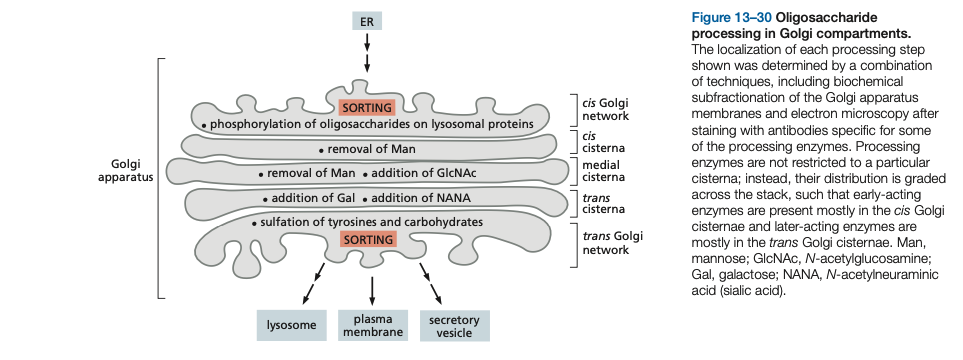
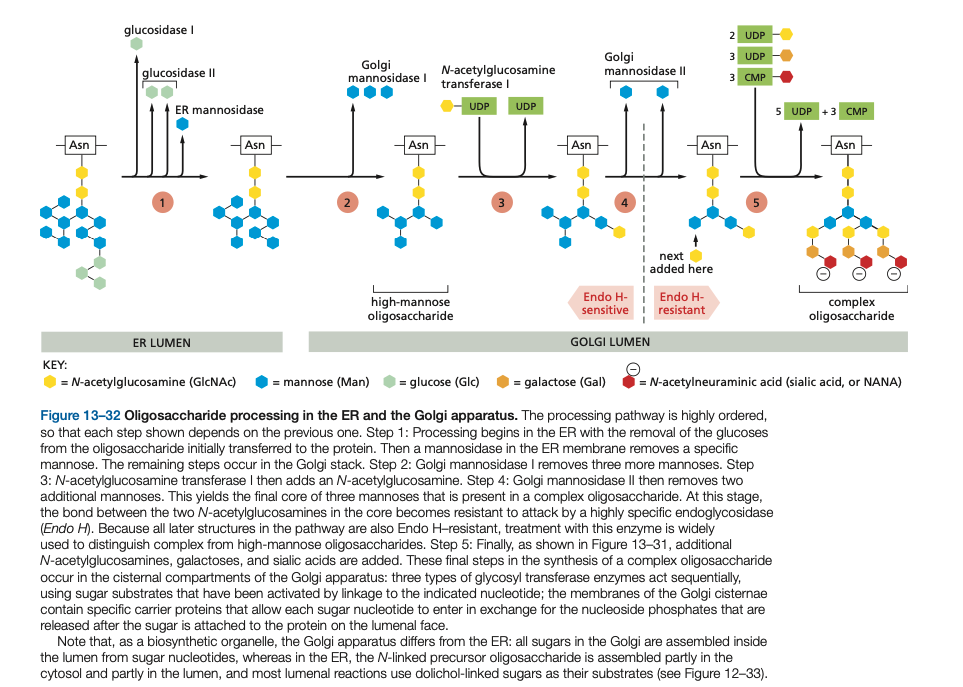
Oligosaccharide processing starts in the ___ and is completed in the ____.
Oligosaccharide processing starts in the ER and is completed in the golgi.
Proteins and lipids move from the ___ to other destinations
Proteins and lipids move from the golgi to other destinations
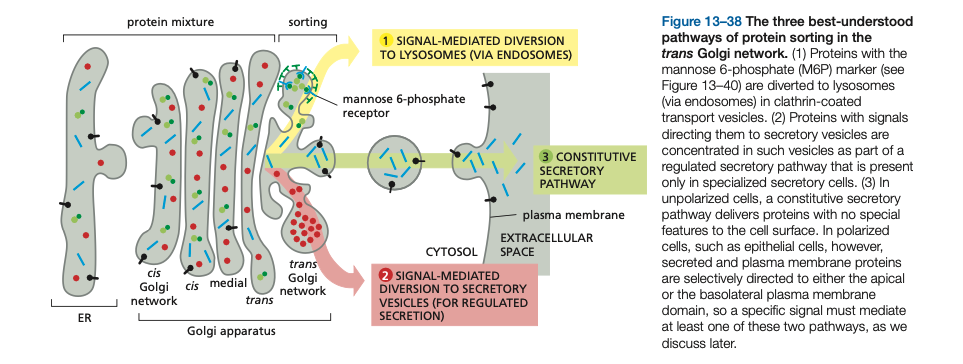
Polarized cells direct proteins from the _____ Golgi Network to the appropriate domain of the plasma membrane.
Polarized cells direct proteins from the Trans Golgi Network to the appropriate domain of the plasma membrane.
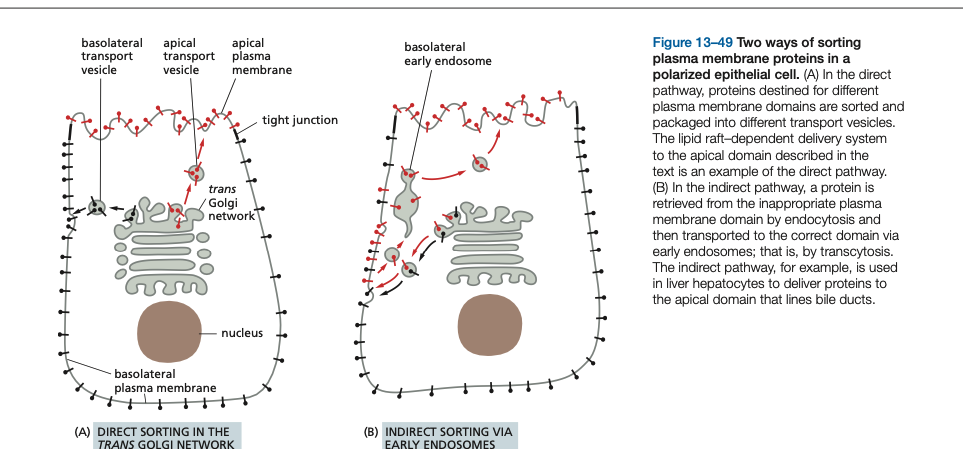
____ ____ vesicles internalize materials from the plasma membrane.
Clathrin-coated vesicles internalize materials from the plasma membrane.
In the early ______, the LDL receptor dissociates from its ligand, LDL, and is recycled back to the ____ membrane for reuse, leaving the discharged LDL to be carried to lysosomes
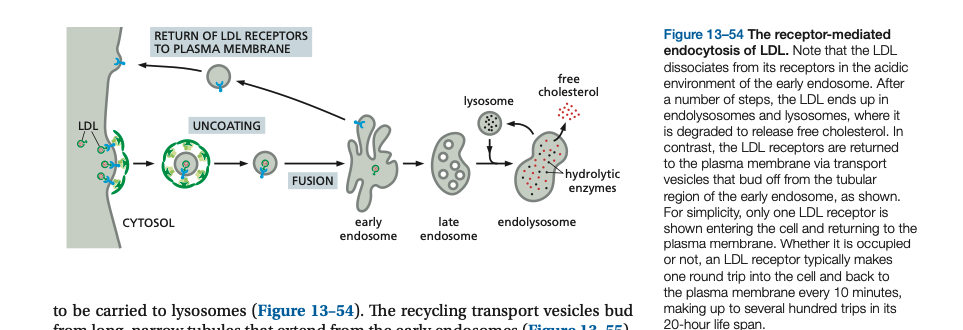
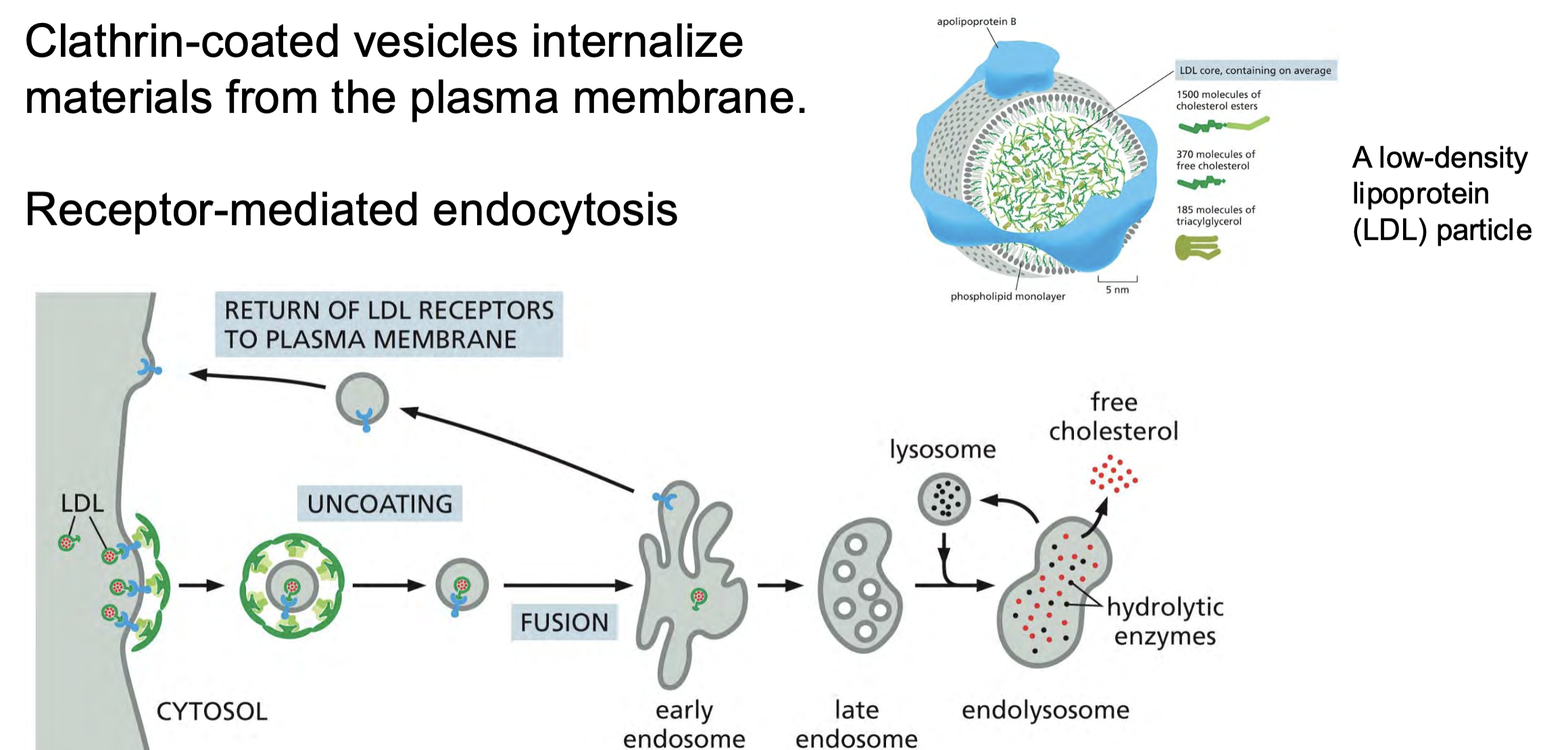
In the early endosome, the LDL receptor dissociates from its ligand, LDL, and is recycled back to the plasma membrane for reuse, leaving the discharged LDL to be carried to lysosomes
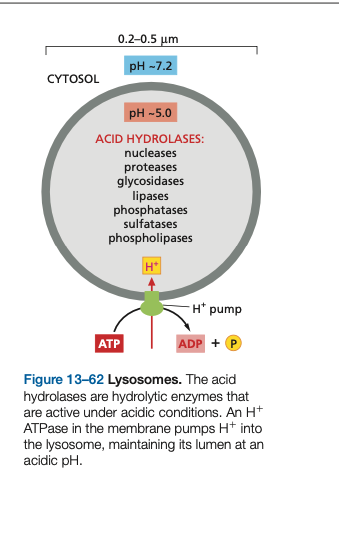
Internalized materials are broken down by ______.
Internalized materials are broken down by lysosomes.
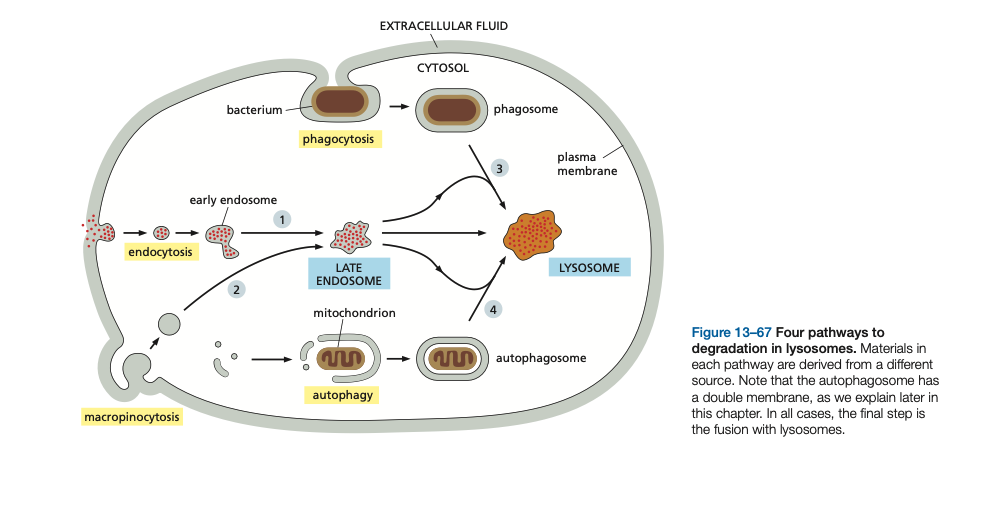
Phagocytosis is used to engulf ____ materials.
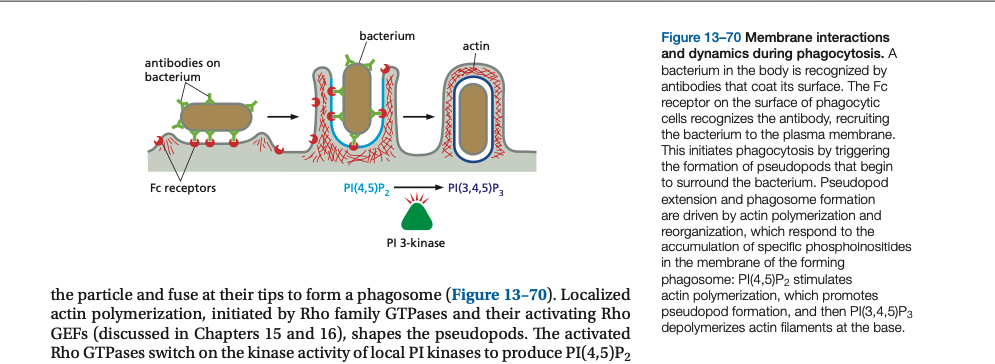
Phagocytosis is used to engulf large materials.
Autophagy ____ and ____ unwanted proteins and organelles.
During autophagy, a portion of the cytoplasm is engulfed into a membrane structure called the _____ that subsequently fuses with the ____ where the autophagosome’s contents are degraded
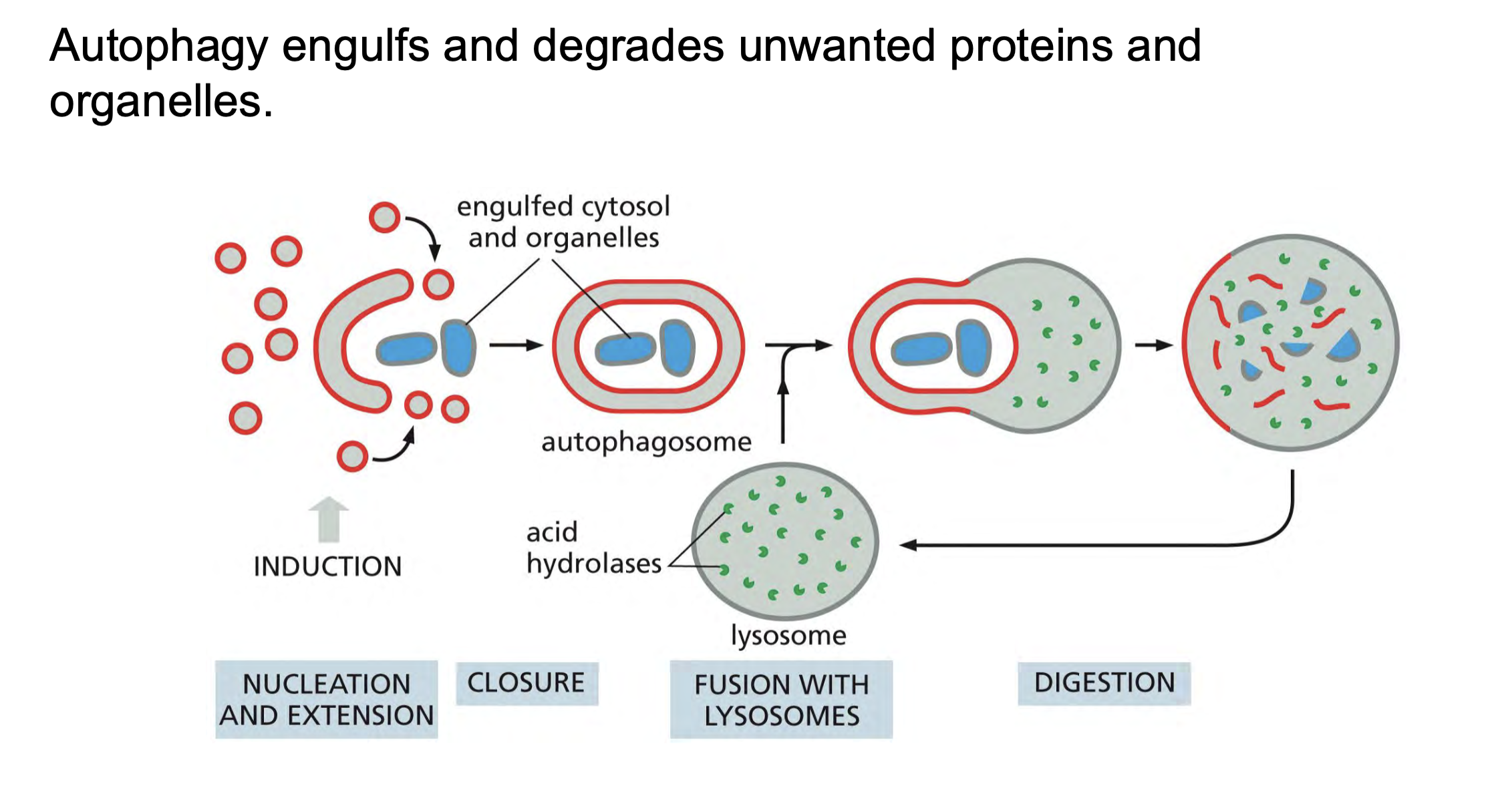
Dur- ing autophagy, a portion of the cytoplasm is engulfed into a membrane structure called the autophagosome that subsequently fuses with the lysosome where the autophagosome’s contents are degraded
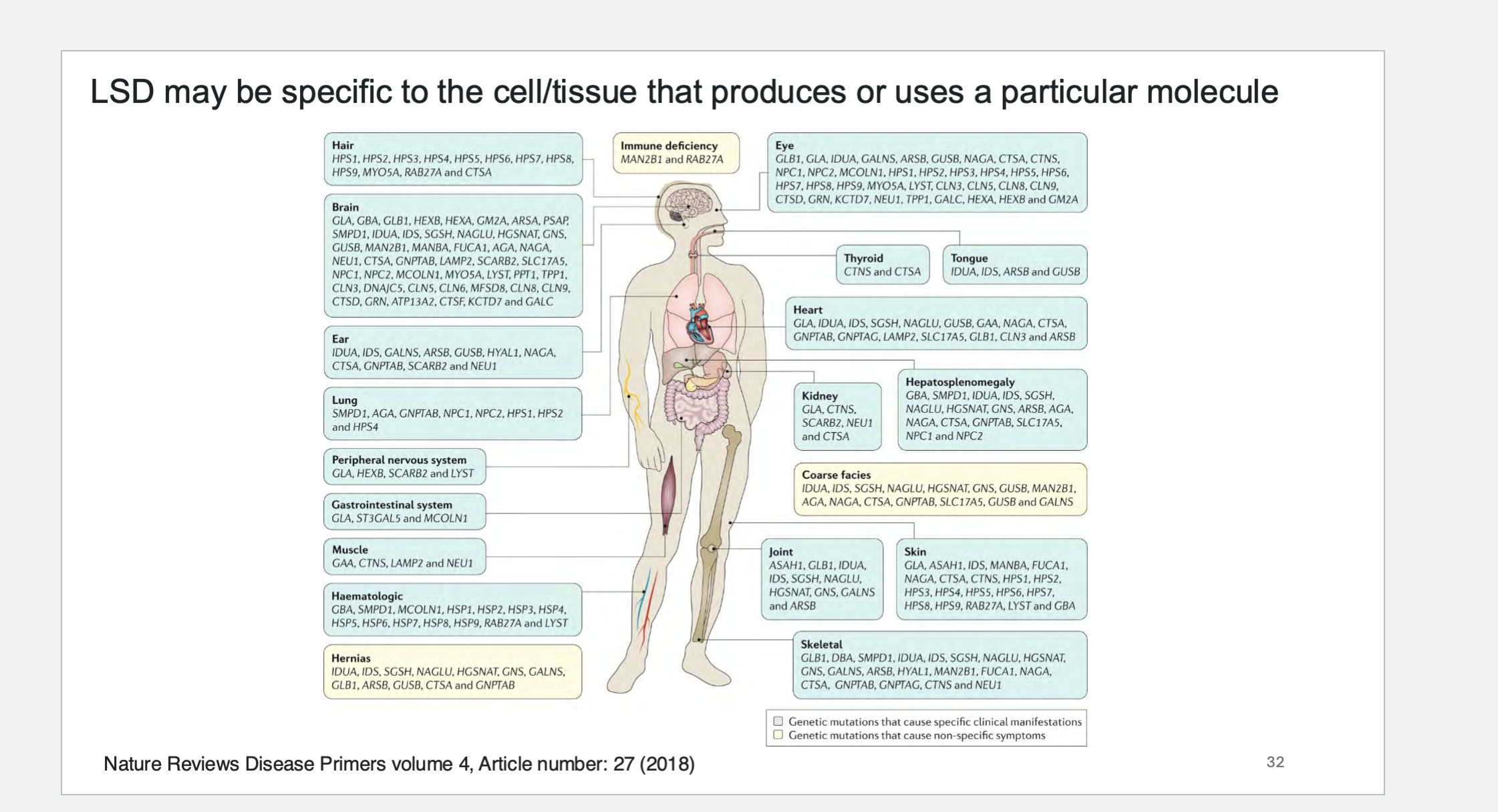
Errors in _____ cause toxic buildup of materials. The build-up causes damage to other cells and organs. The damage from _____ _____ disorders can affect many parts of your body, including: Brain and central nervous system. Heart. Skeletal system. Skin.
Errors in lysosomes cause toxic buildup of materials. The build-up causes damage to other cells and organs. The damage from lysosomal storage disorders can affect many parts of your body, including: Brain and central nervous system. Heart. Skeletal system. Skin.
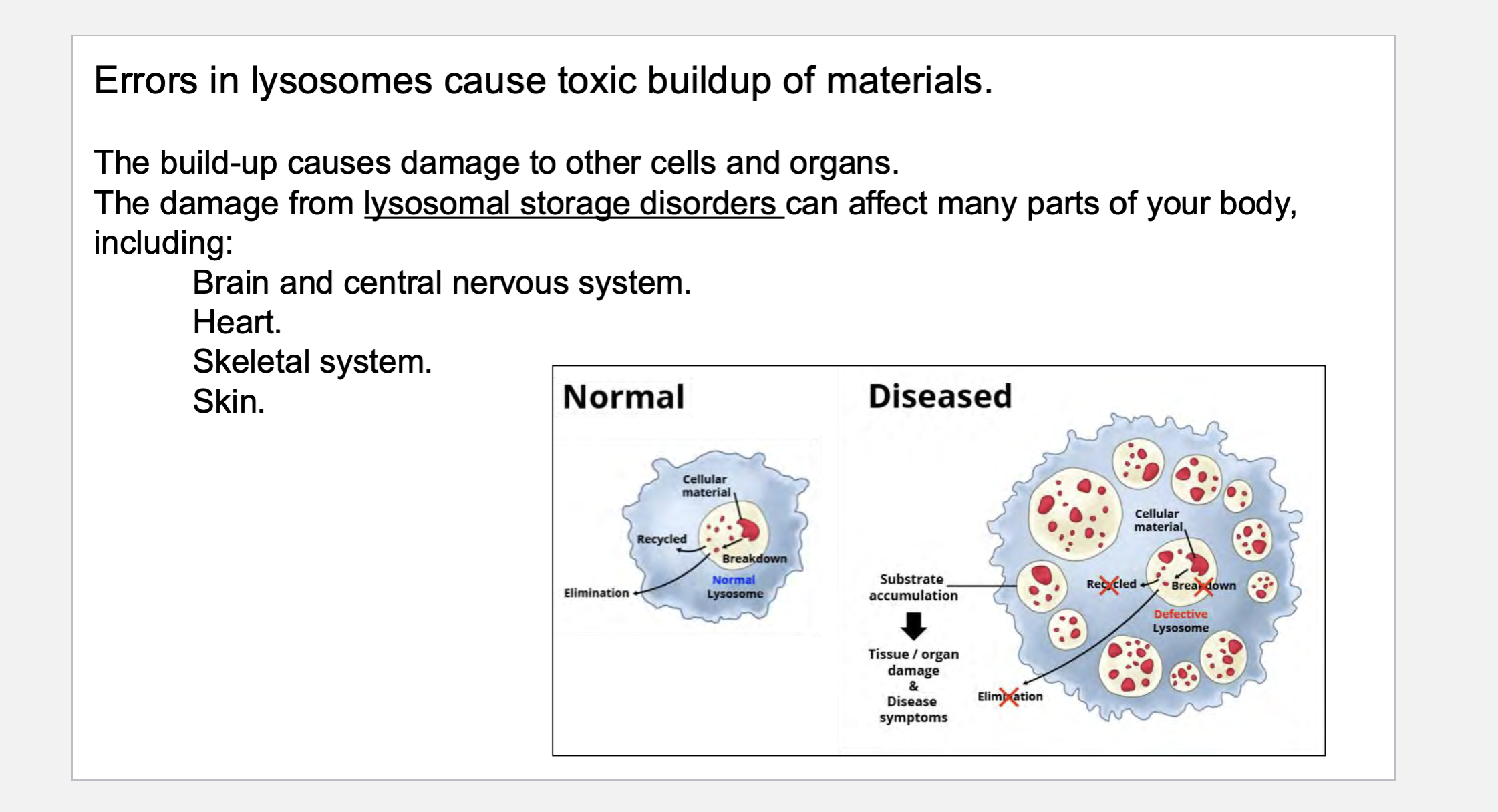
LSD (lysosome storage diseases) may be _____ to the cell/tissue that produces or uses a particular molecule
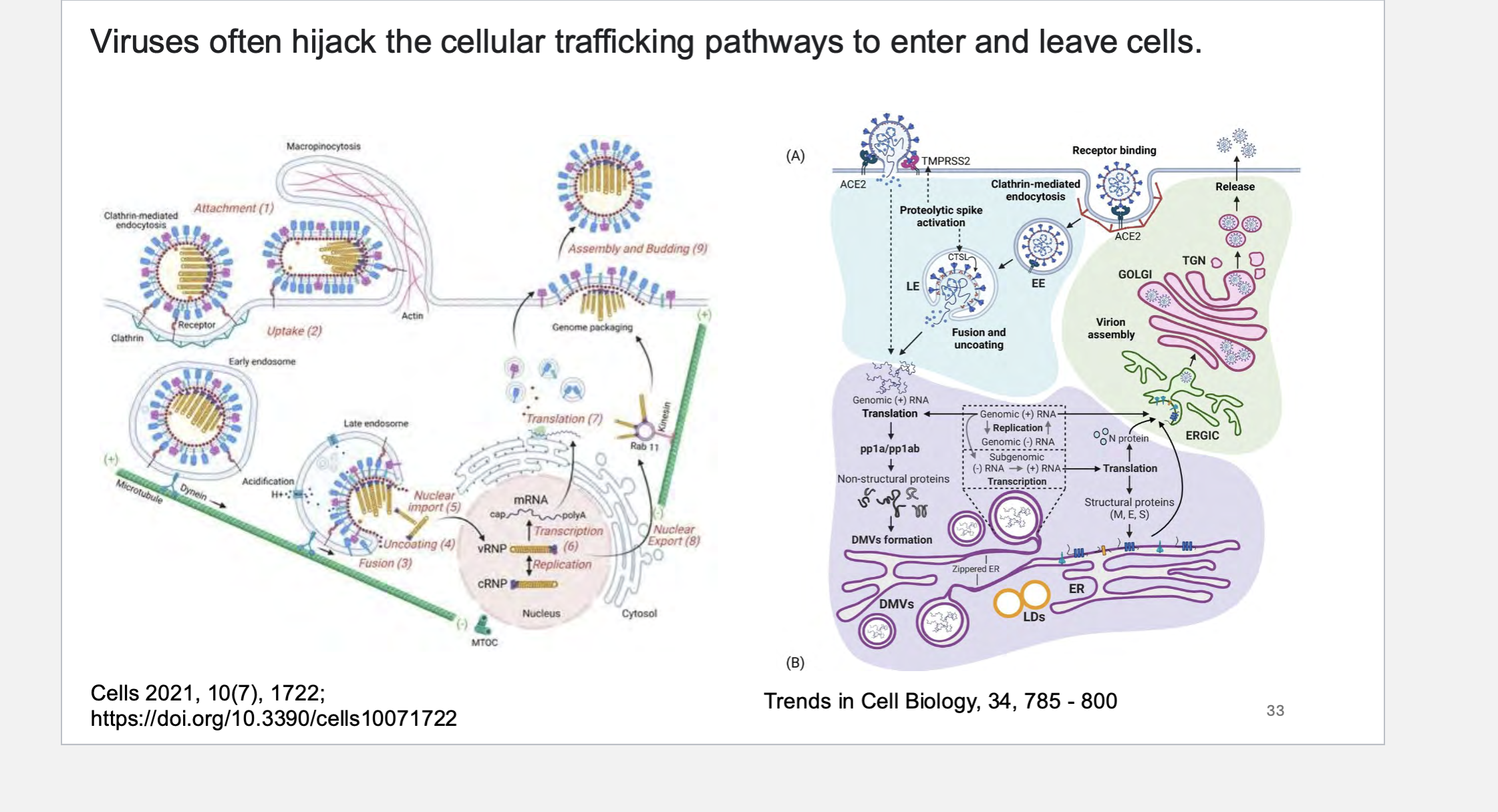
Viruses often ____ the cellular trafficking pathways to enter and leave cells.
LSD may be specific to the cell/tissue that produces or uses a particular molecule
Viruses often hijack the cellular trafficking pathways to enter and leave cells.