Introduction to Microbiology: Bacteria, Viruses, and Diagnostic Techniques
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the primary goal of clinical microbiology?
To culture organisms from patient specimens, characterize and identify them, and predict antimicrobial susceptibility patterns.
What are the main types of microorganisms studied in microbiology?
Bacteria, parasites (including unicellular protozoa and multicellular tapeworms), fungi (yeast and mold), and viruses (DNA or RNA, ds or ss).
What is the equivalent of a human 'clan' in microbial taxonomy?
Family.
How is the genus in microbial taxonomy analogous to human naming conventions?
It is equivalent to a human last name.
What is the correct way to write the species name Staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus or S. aureus, with the genus capitalized and the species name in lowercase.
What are the three kingdoms of cellular type in classification?
Eubacteria, Eukarya, and Archaea.
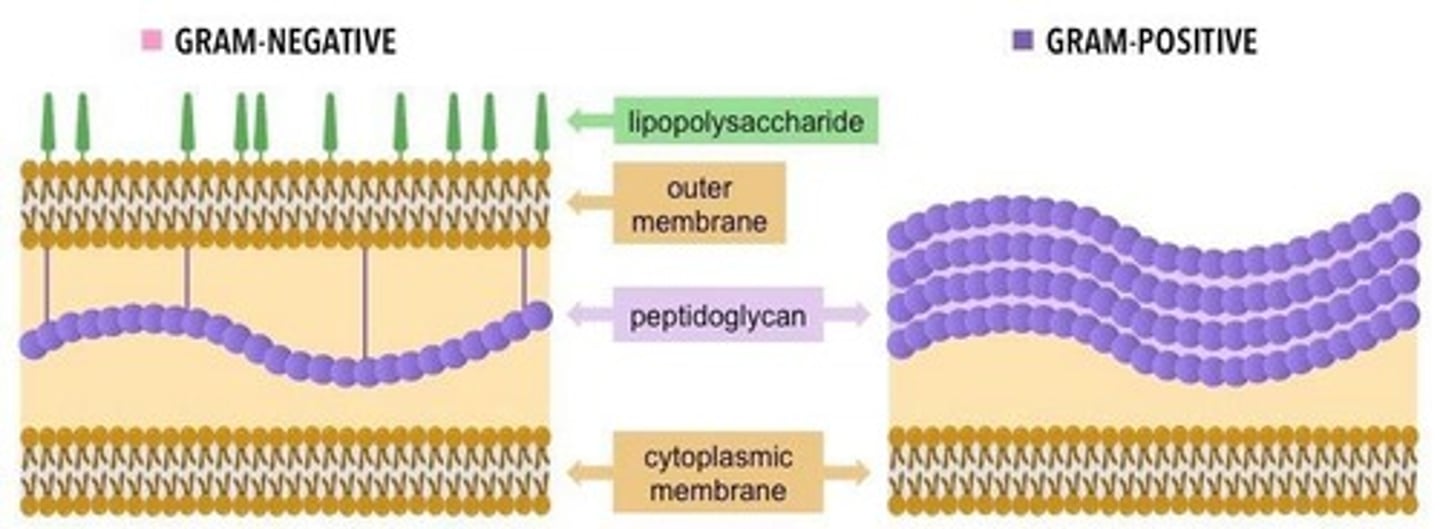
What distinguishes Gram-positive bacteria from Gram-negative bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer, while Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane.
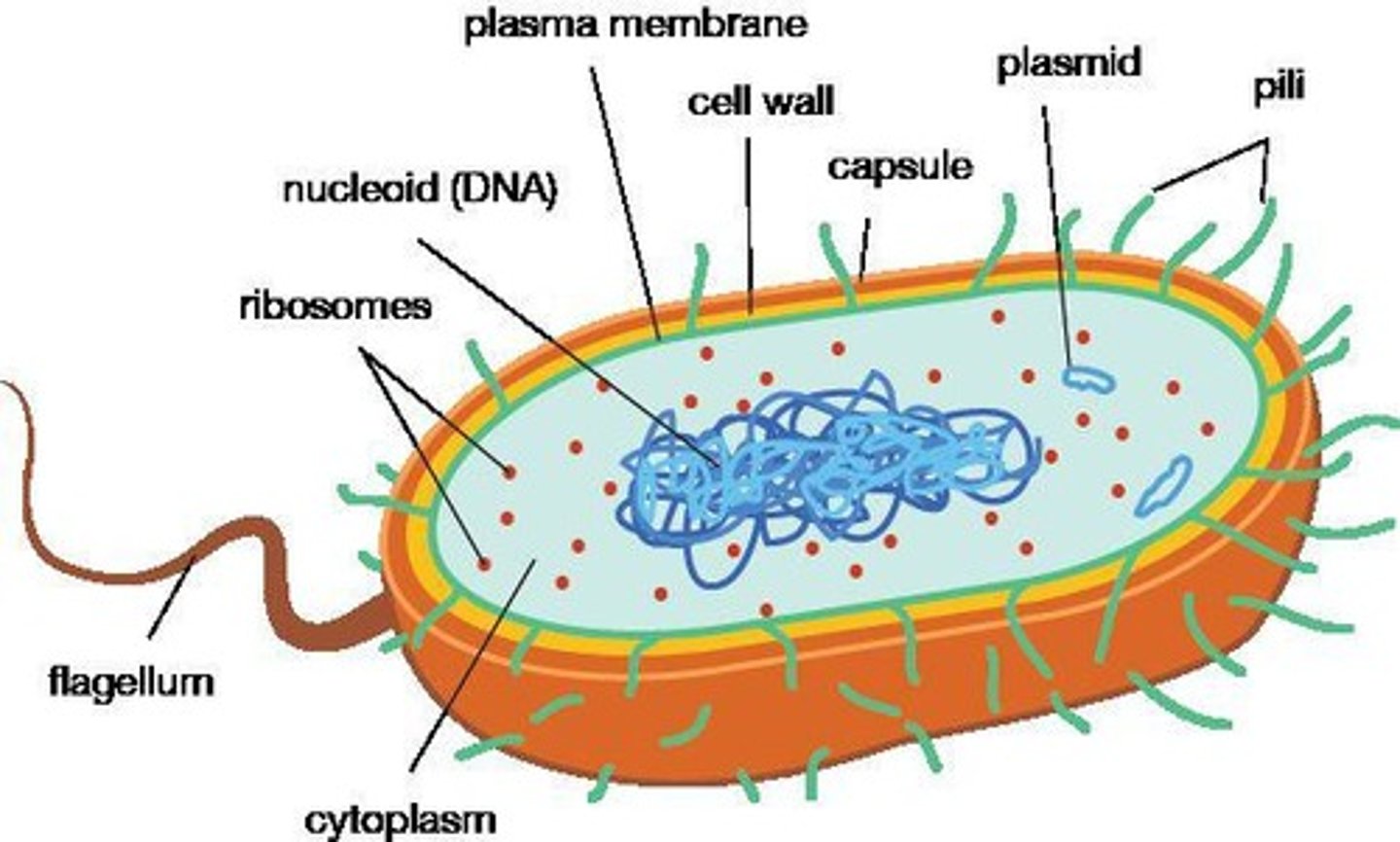
What are the main cellular structures found in prokaryotic cells?
Nuclear body, ribosomes, cytoplasmic granules, spores, plasma membrane, and cell wall.
What is the function of the capsule in bacteria?
It serves as a surface polymer that can protect the bacteria and aid in adherence.
What are the motility organelles found in eukaryotic cells?
Cilia and flagella.
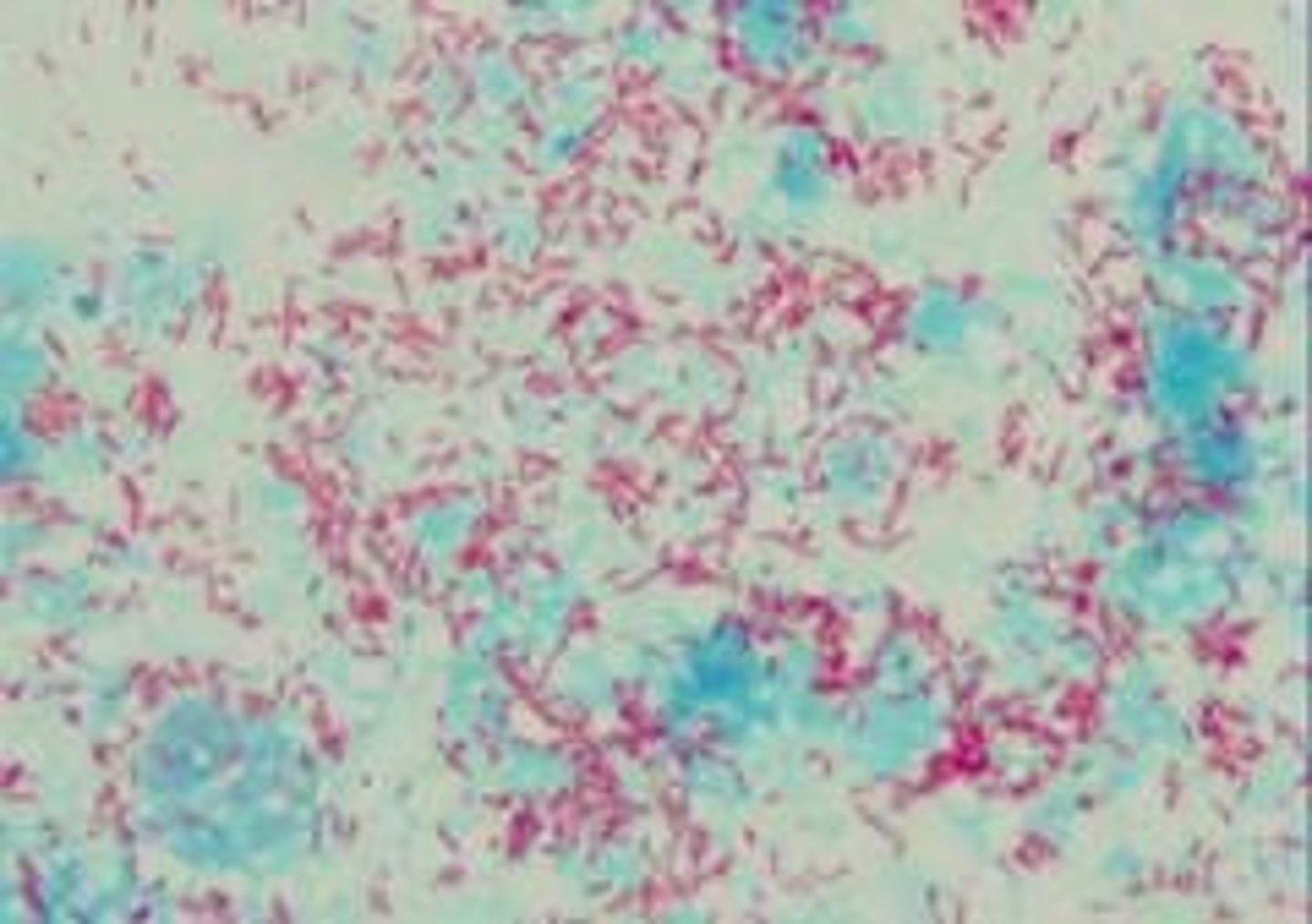
What is the purpose of a Gram stain in microbiology?
To differentiate between Gram-positive (purple/blue) and Gram-negative (pink) bacteria.
What is the purpose of selective media in microbiology?
To inhibit the growth of some bacteria while allowing others to grow.
What type of bacteria require oxygen for growth?
Obligate aerobes.
What is the growth curve phase where bacteria prepare to divide?
Lag phase.
What are the mechanisms of gene transfer in bacteria?
Transformation, transduction, and conjugation.
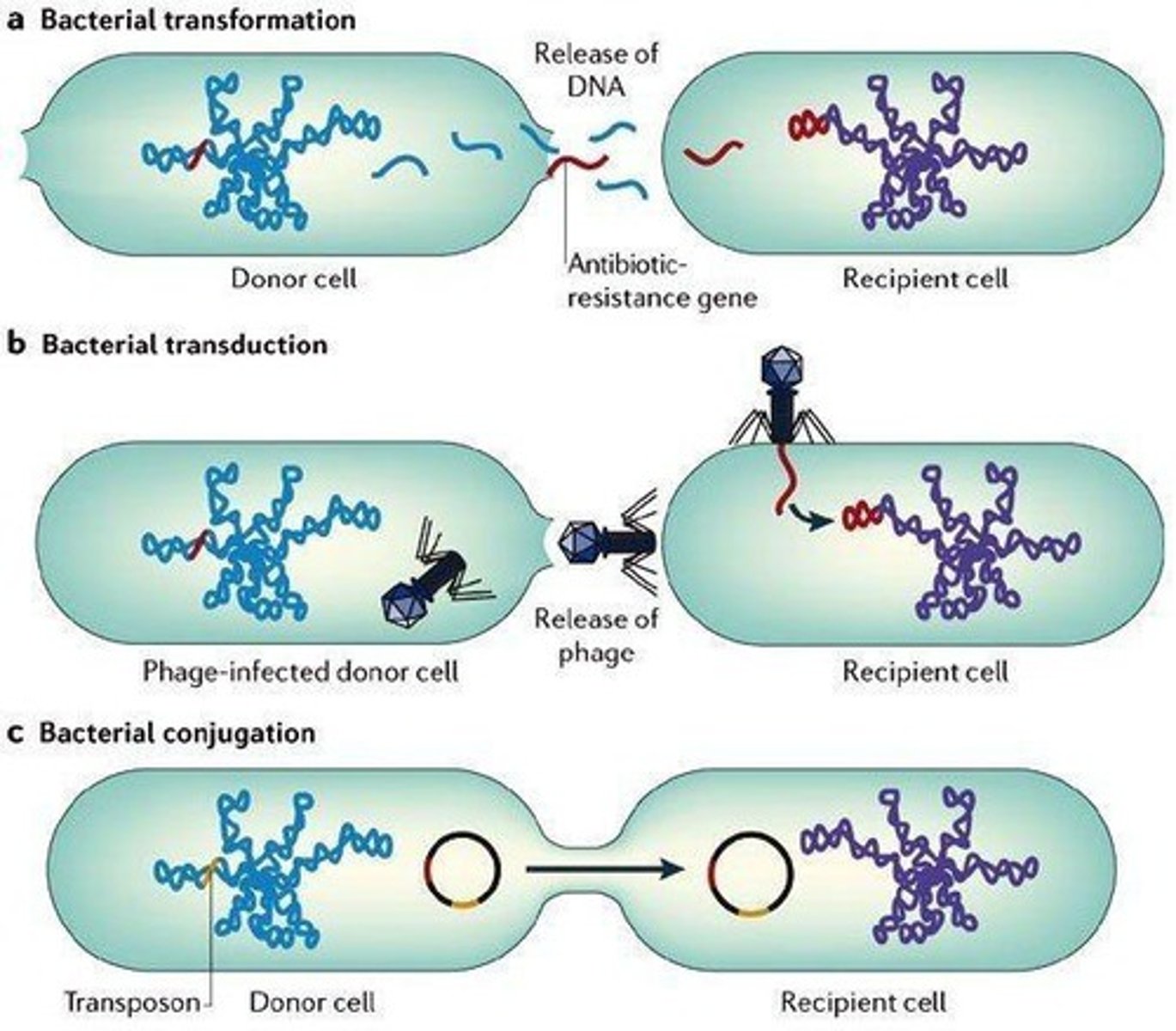
What is transformation in the context of bacterial genetics?
The uptake of 'naked' DNA from the environment and incorporation into the host genome.
What is transduction in bacterial genetics?
The transfer of bacterial DNA fragments by a bacteriophage during infection.
What is conjugation in bacterial genetics?
The direct transfer of chromosomal material between two bacterial cells during close contact.
What role do restriction enzymes play in bacterial defense?
They cleave foreign DNA that does not share the same methylation pattern as 'self' DNA.
What is the significance of plasmids in bacteria?
They can carry genes that confer new characteristics, such as toxin production and antimicrobial resistance.
What is the purpose of differential media in microbiology?
To allow visualization of metabolic differences among bacteria.
What is the basic structure of a bacterial cell wall?
It is rigid and maintains structure, with variations such as Gram-positive and Gram-negative types.
What is the function of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells?
It contains cholesterol and provides structural integrity.
What is the significance of the growth media in microbiology?
It provides necessary nutrients and conditions for the growth of microorganisms.
What is the role of atmospheric conditions in bacterial growth?
Different bacteria have specific oxygen and carbon dioxide requirements for optimal growth.
What is the generation time for bacterial growth?
It can range from 20 minutes to over 24 hours, depending on the species.
What is the stationary phase in the bacterial growth curve?
A phase where nutrient levels become limited and the number of viable bacteria remains constant.