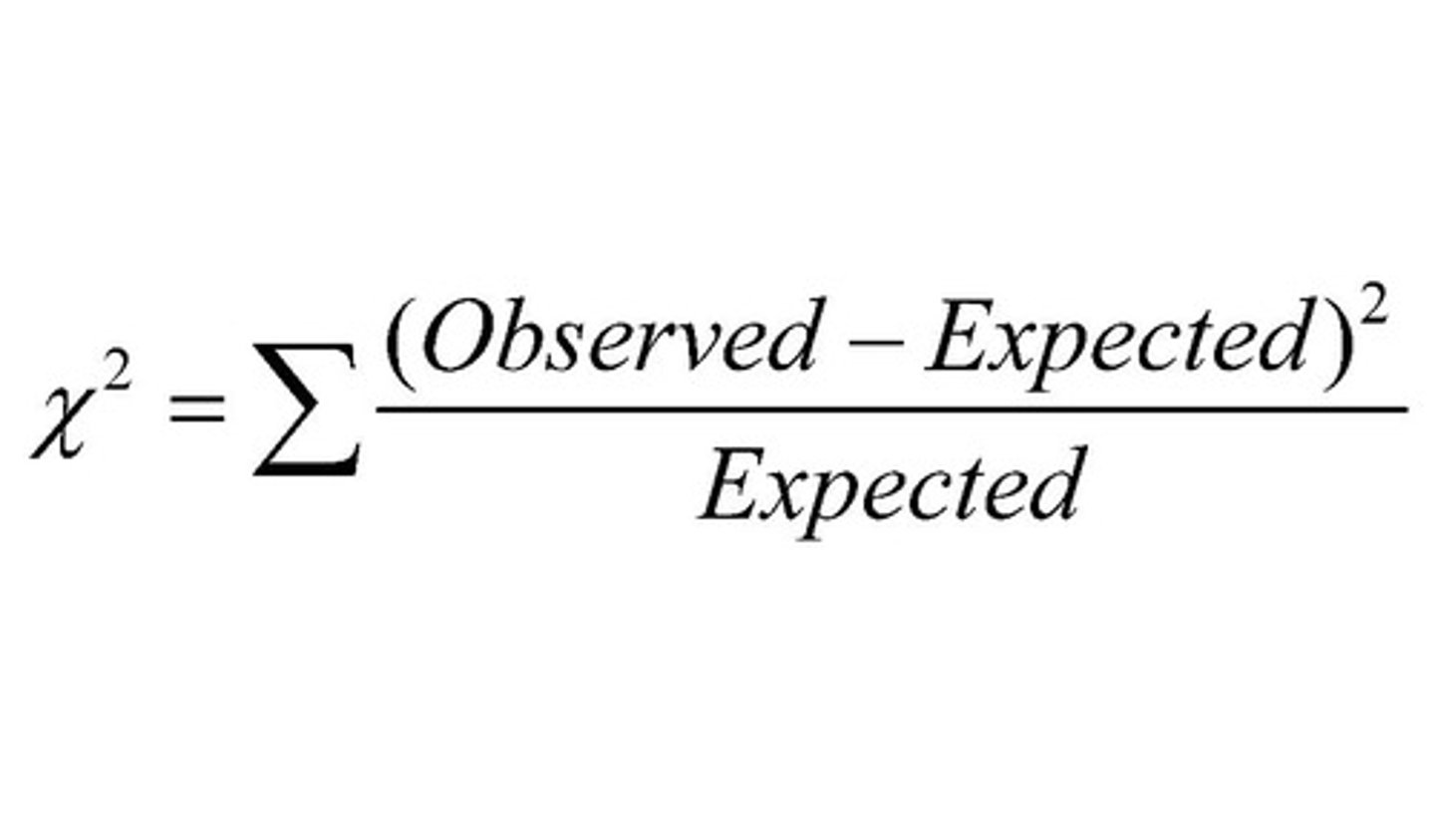AP Bio 7A Vocab
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
LaMarck
French naturalist who proposed that evolution resulted from the inheritance of acquired characteristics (1744-1829)

acquired characteristics
traits altered by an individual organism during its life

Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)

Galapagos Islands
Chain of islands near South America where Darwin developed his theory of natural selection by studying the unique life there.
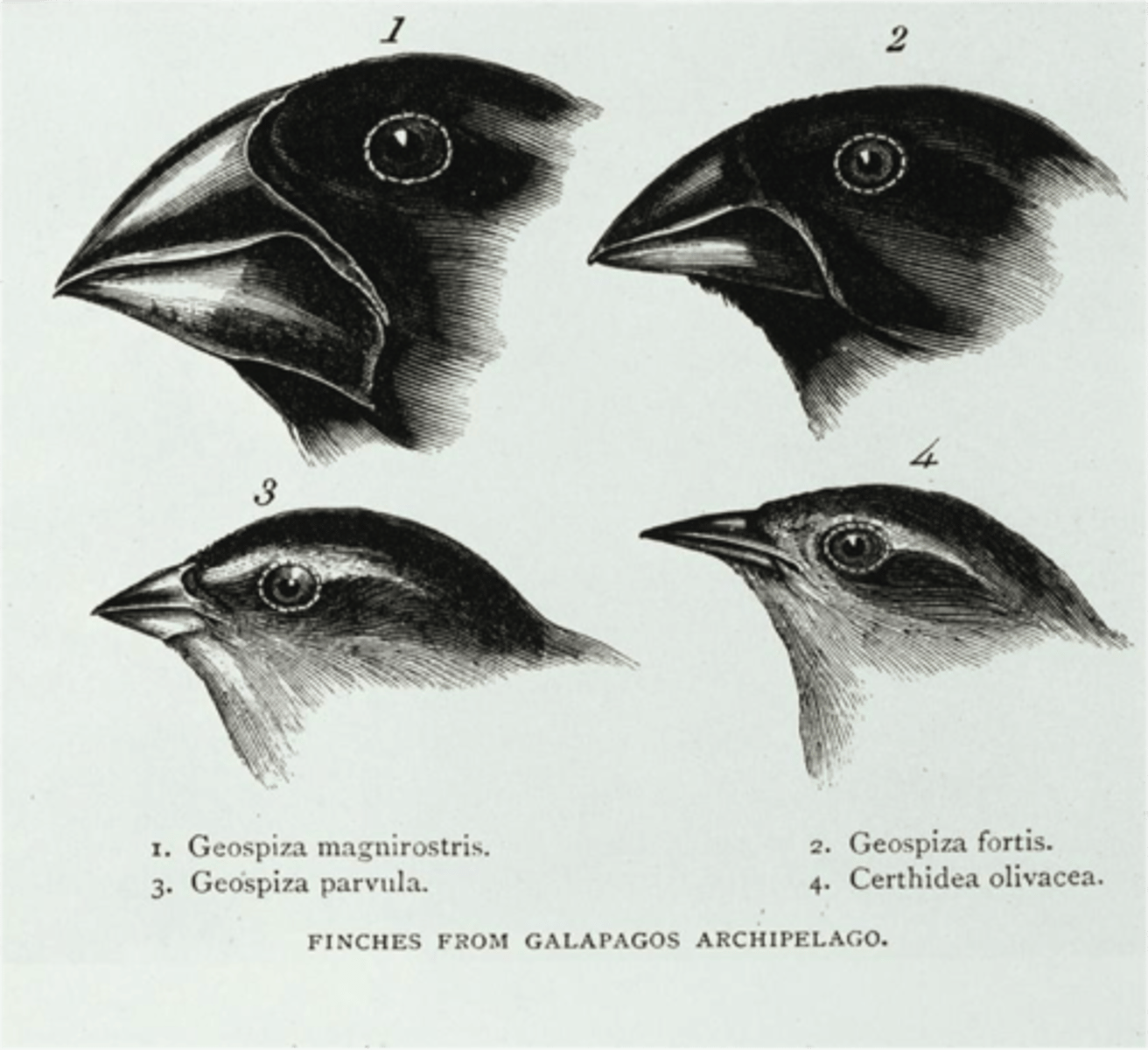
Galapagos Finches
beak shape is determined by the availability of food
variation
Any difference between individuals of the same species.
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
adaptations
traits that improve an individual's ability to survive and reproduce
survival of the fittest
A natural process resulting in the evolution of organisms best adapted to the environment.
peppered moth
example of natural selection caused by pollution
disruptive selection
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
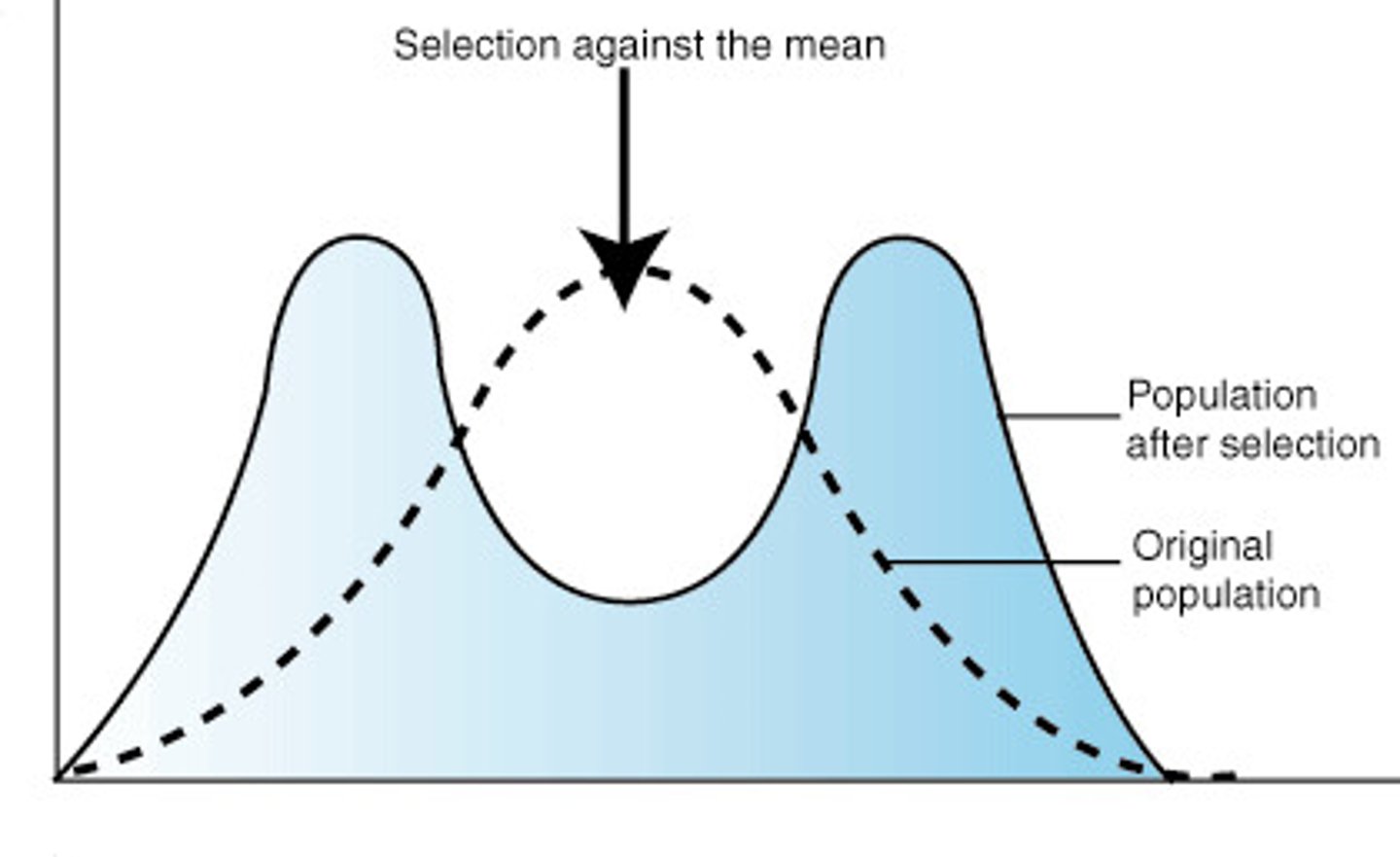
stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants (center) by acting against extreme phenotypes
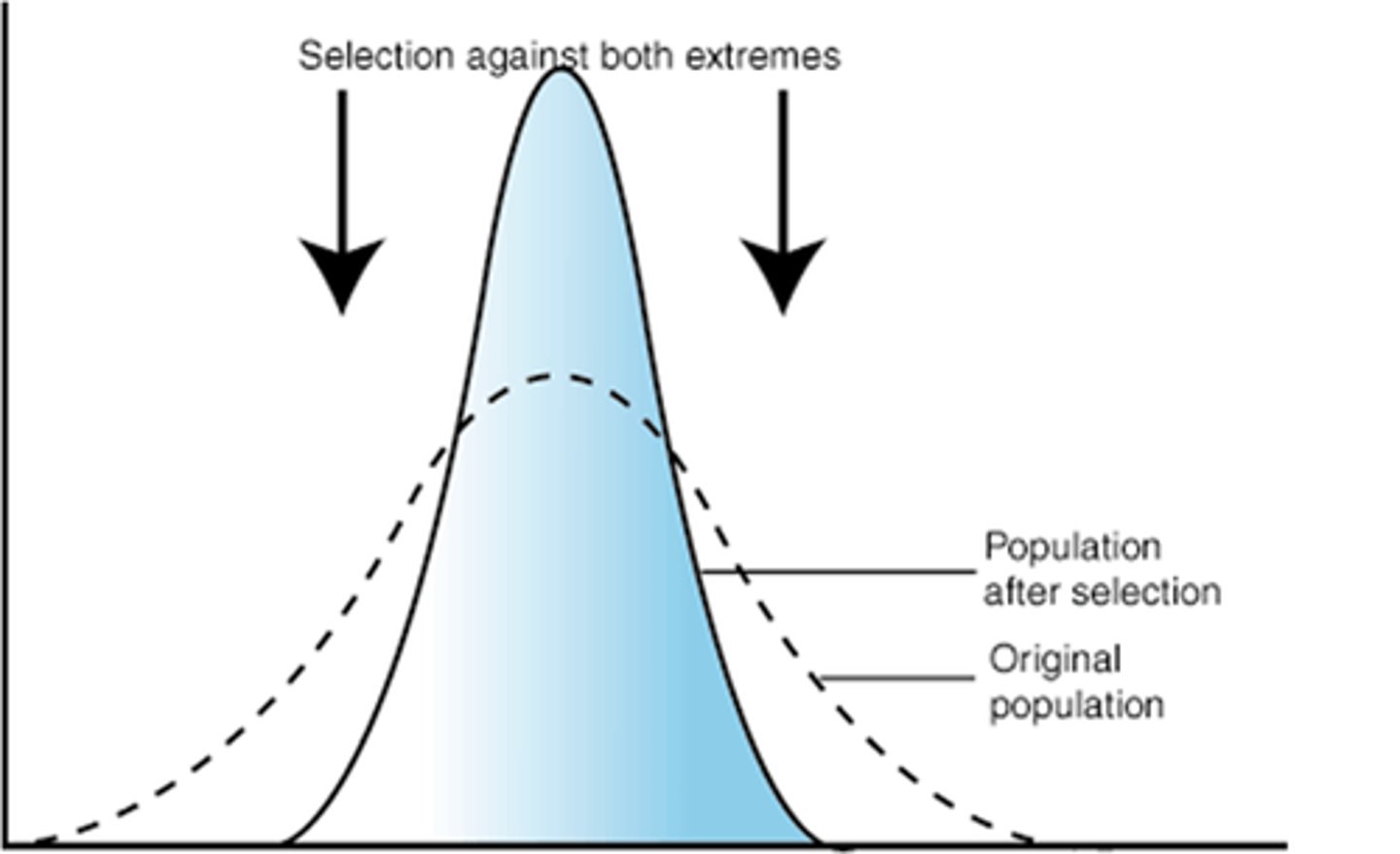
directional selection
occurs when natural selection favors one of the extreme variations of a trait
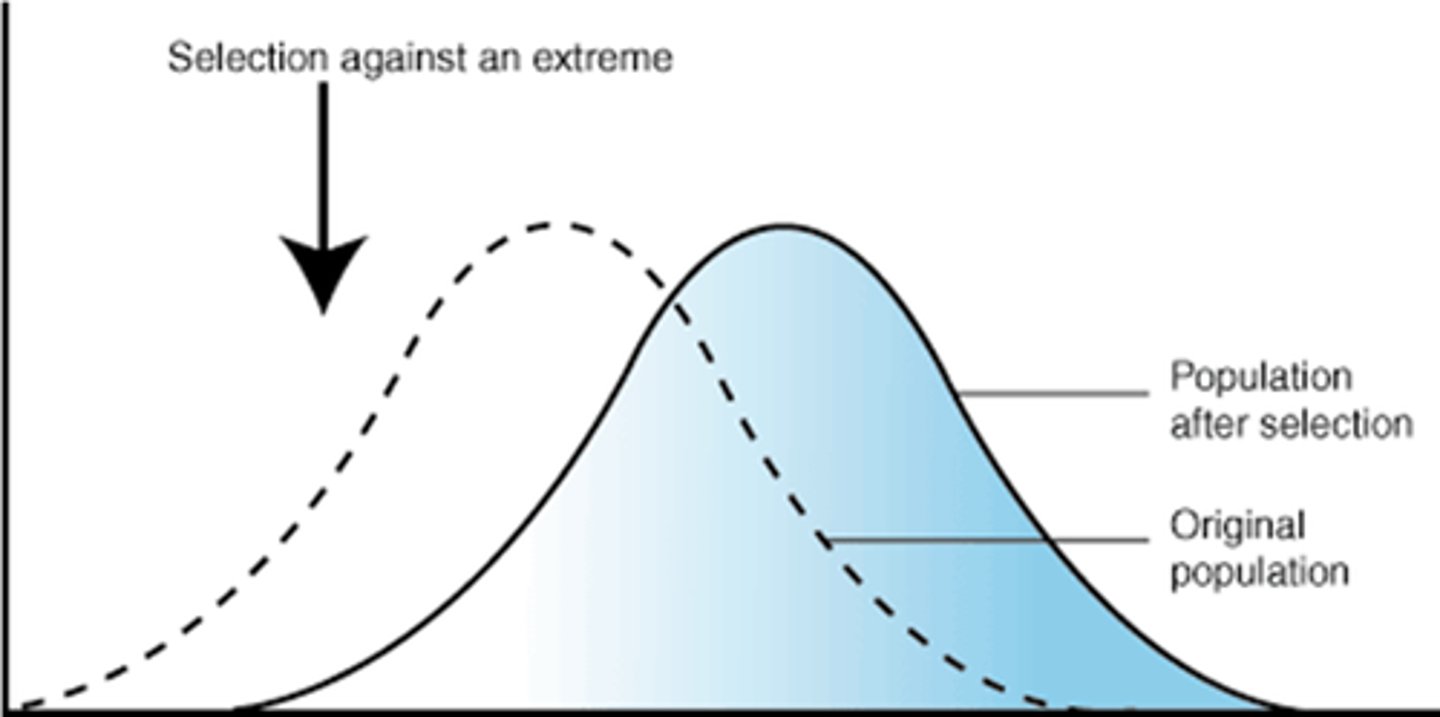
artificial selection
selective breeding of plants and animals to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in offspring
microevolution
evolutionary change within a species or small group of organisms, especially over a short period.
gene pool
All the genes, including all the different alleles for each gene, that are present in a population at any one time
alleles
different versions of a gene
gene flow
movement of individuals and alleles in and out of population; increases variation in the population
genetic drift
random change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations; decreases variation in the population
mutations
create variation in a population by changing the DNA sequence
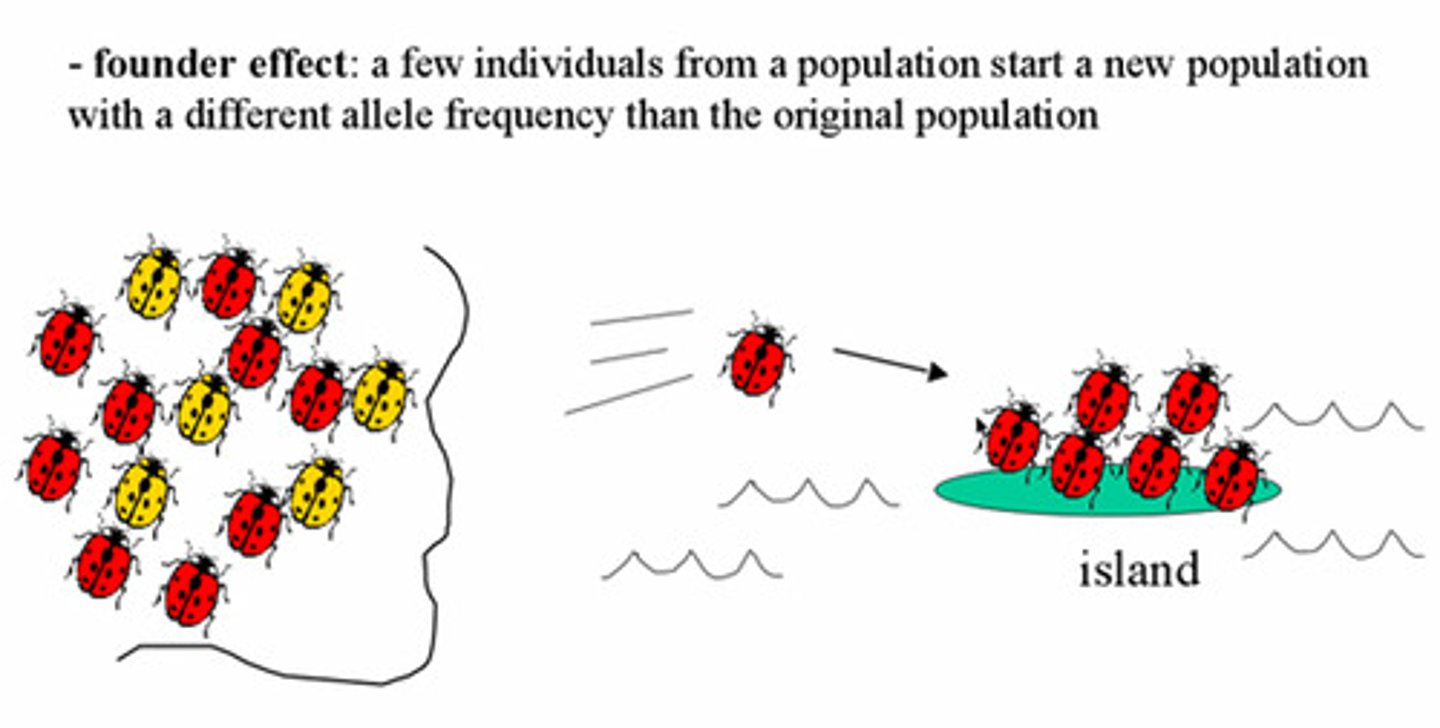
founder effect
genetic drift that occurs after a small number of individuals colonize a new area
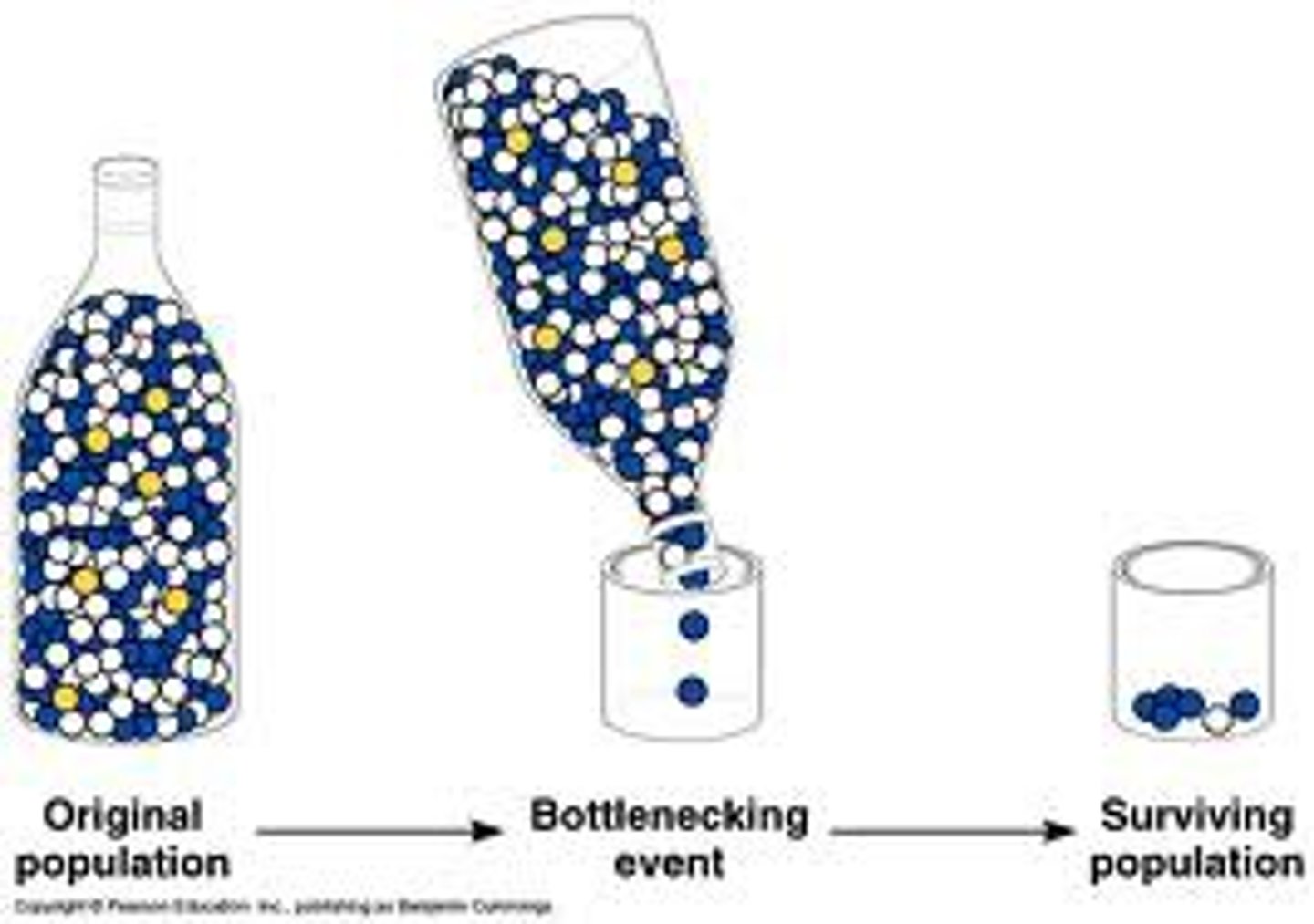
bottleneck effect
Genetic drift resulting from the reduction of a population, typically by a natural disaster, such that the surviving population is no longer genetically representative of the original population.
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
condition that occurs when the frequency of alleles in a particular gene pool remain constant over time
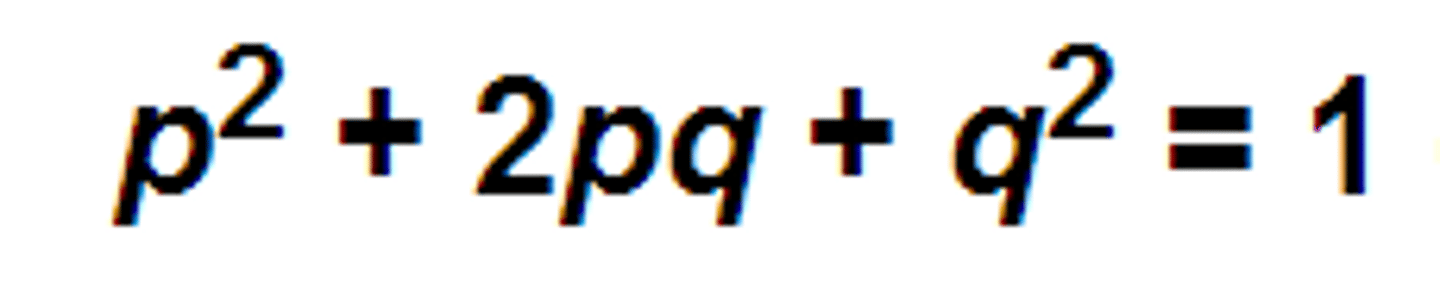
chi squared formula
sum of (observed-expected)^2/expected