NP11 Motor Control: Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
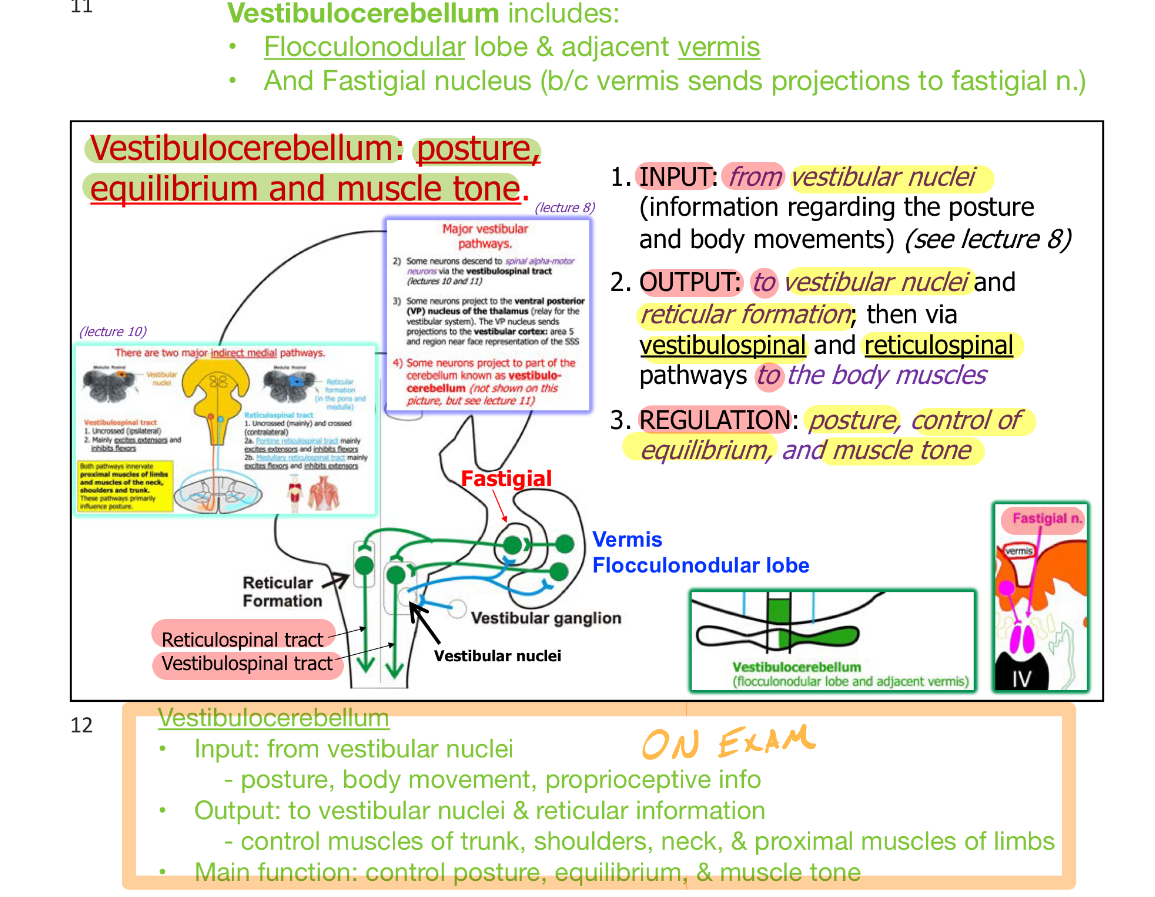
Vestibulocerebellum - Input:
From vestibular nuclei
posture, body movement, proprioceptive info
Vestibulocerebellum - Output:
To vestibular nuclei & reticular information
control muscles of trunk, shoulders, neck, & proximal muscles of limbs
Vestibulocerebellum - Regulation (Main function):
Control posture, equilibrium, and muscle tone
Vestibulocerebellum includes:
Flucculonodular lobe & adjacent vermis
And Fastigial nucleus (b/c vermis sends projections projections to fastigial nucleus)
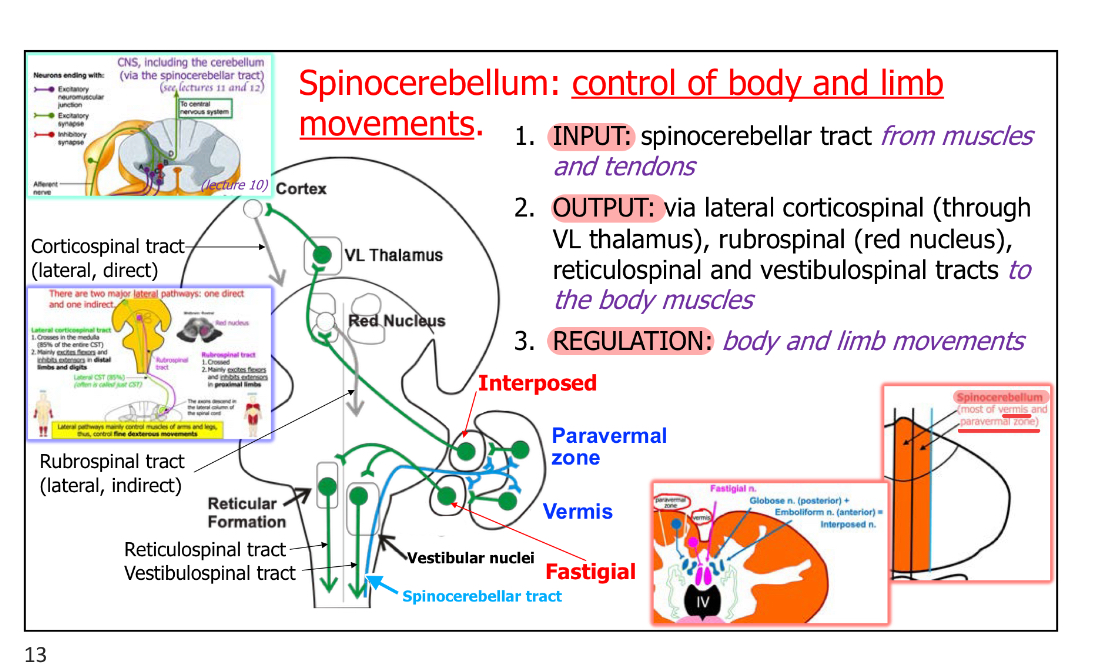
Spinocerebellum - Input:
Spinocerebellar tract from muscles & tendons
Info about status of muscle contraction, muscle force, proprioceptive info
Axons from muscle spindle circuits & Golgi tendon organ circuits descend to CNS, and some travel to spinocerebellum
Spinocerebellum - Output:
Via lateral corticospinal (through VL thalamus), rubrospinal (red nucleus), Reticulospinal, & Vestibulospinal tracts to the body muscles
Spinocerebellum - Regulation (Main function):
Body & limb movements
Spinocerebelllum includes:
most of vermis & paravermal zone
2 nuclei are part of this circuitry
Fastigial nucleus (Vermis → Fastigial n.)
Interposed nucleus (Paravermal zone → Interposed n.)
How many groups of deep cerebellar nuclei?
Vermis → Fastigial nucleus
Paravermal zone → Interposed nucleus
Lateral zone → Dentate nucleus
Fastigial nucleus
Receives projections from the Vermis
*Vermis → Fastigial n.
Interposed nucleus
Receives projections from the Paravermal zone
*Paravermal zone → Interposed n.
Interposed n. = Globose n. (Posterior) + Emboliform n. (Anterior)
Dentate Nucleus
Receives projections from Lateral zone
*Lateral zone → Dentate n.
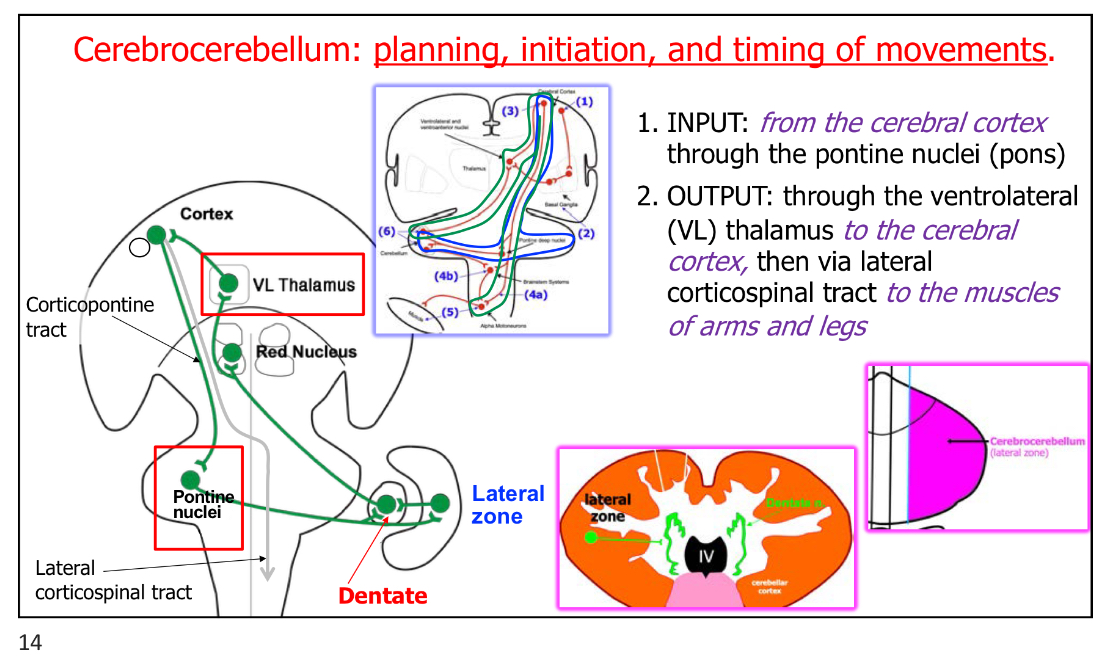
Cerebrocerebellum - Input:
From cerebral cortex through the Pontine Nuclei (pons)
Cerebrocerebellum - Output:
Through the VL of thalamus to the cerebral cortex
Then via lateral corticospinal tracts to the muscles of arms & legs
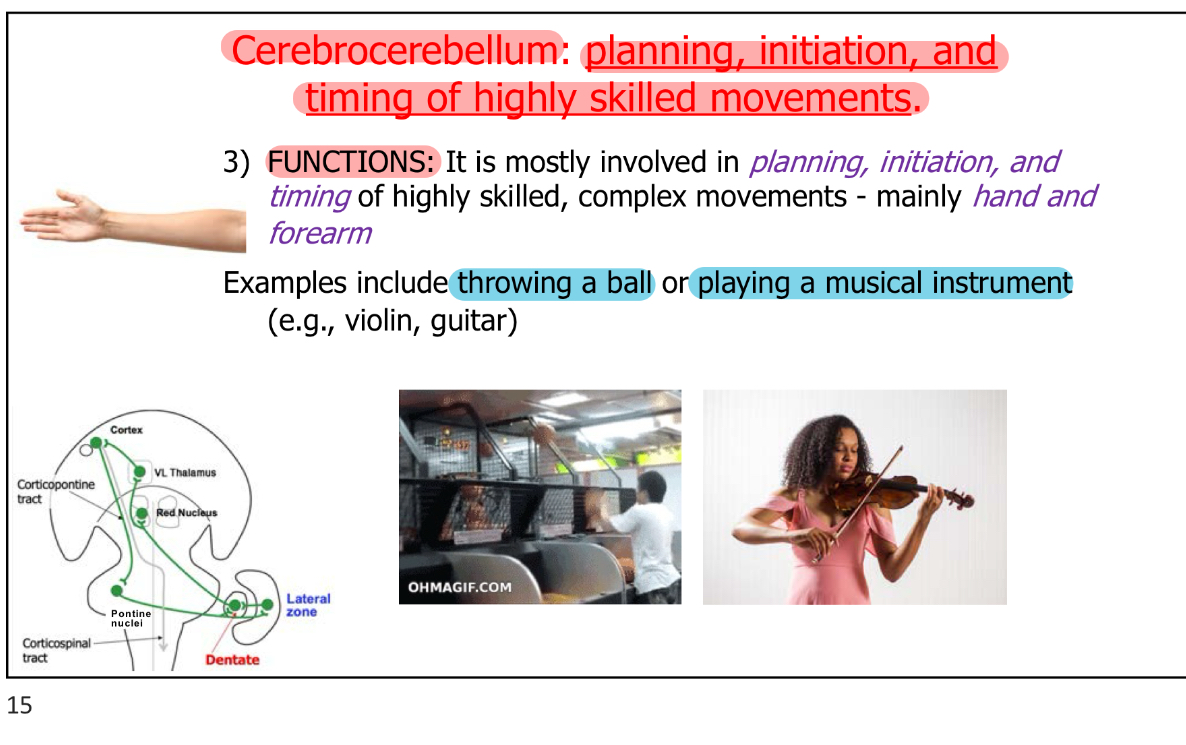
Cerebrocerebellum - Regulation (Main function):
Planning, initiation, & timing of highly skilled movements, complex movements
Mainly hand & forearm
Ex:
throwing a ball
Playing musical instrument (like violin & guitar)
Cerebrocerebellum includes:
Dentate nucleus & projections from the lateral zone
*Lateral zone → Dentate n.