Biology Khanacademy Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
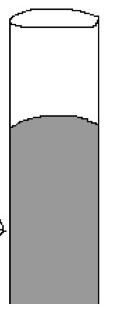
Cohesion
The attraction of molecules to other molecules of the same kind. An example of a concave down meniscus created due to _____ is shown in the picture.
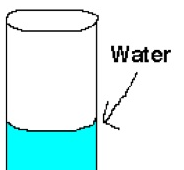
Adhesion
The attraction of molecules of one kind to molecules of a different kind. An example of a concave up meniscus created due to _____ is shown in the picture.
Meniscus
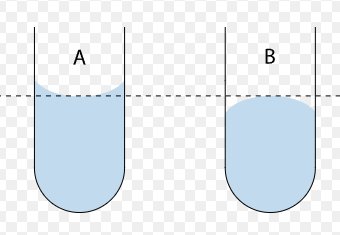
The shape made by a liquid substance at the top of it’s surface.
An adhesive liquid will make a concave up ______ whereas a cohesive liquid will make a concave down/convex ______.
Hydrophilic
A charged or polar substance that interacts with and dissolves in water
Hydrophobic
A nonpolar neutral substance that does not interact well with water. Seperates from it unlike hydrophilic substances.
Evaporative Cooling
The notion that, due to convection and cooler molecules being pushed to the bottom as well as hotter molecules being pushed to the top, water molecules with higher KE evaporate first and as they do so the surface from which they escape cools i.e. its average KE goes down.
Polar molecule
A neutral, or uncharged molecule that has an asymmetric internal distribution of charge, leading to partially positive and partially negative regions.
Organic Molecule
Any molecule that has carbon in it. (Some exceptions such as CO2 and CO exist)
Hydrocarbon
Any molecule that has exclusively hydrogen and carbon atoms.
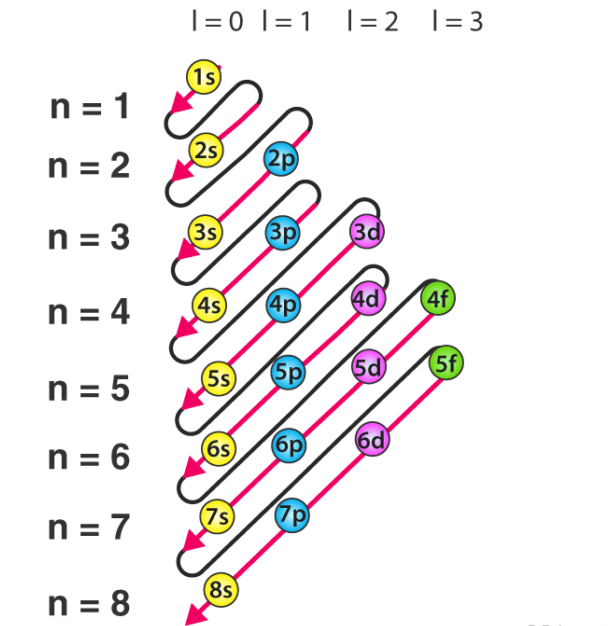
The Aufbau Principle
The principle that states electrons first fill subshells of the lowest available energy. This principle is the reason for atoms having 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s filled and then beginning to fill 3d. (3d has higher available energy and 4s has a lower energy level)
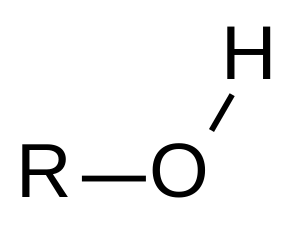
Hydroxyl Functional Group
Follows the form R-O-H
Polar with partial negative on oxygen atom and partial positive on hydrogen.
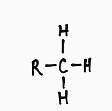
Methyl Functional Group
Follows the form R-C^-H_-H-H
Non polar and hydrophobic
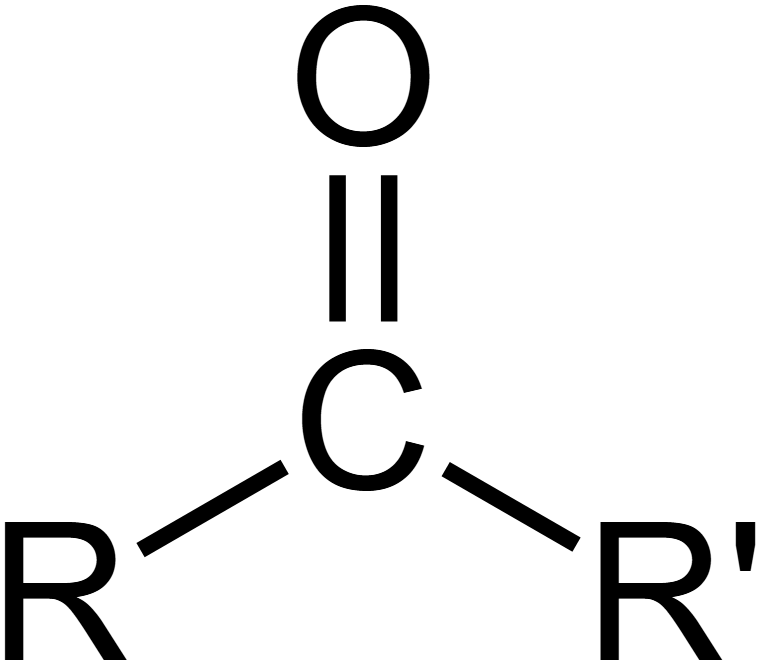
Carbonyl Functional Group
Follows the form C=O
Polar with partial negative charge on oxygen atom and partial positive on carbon
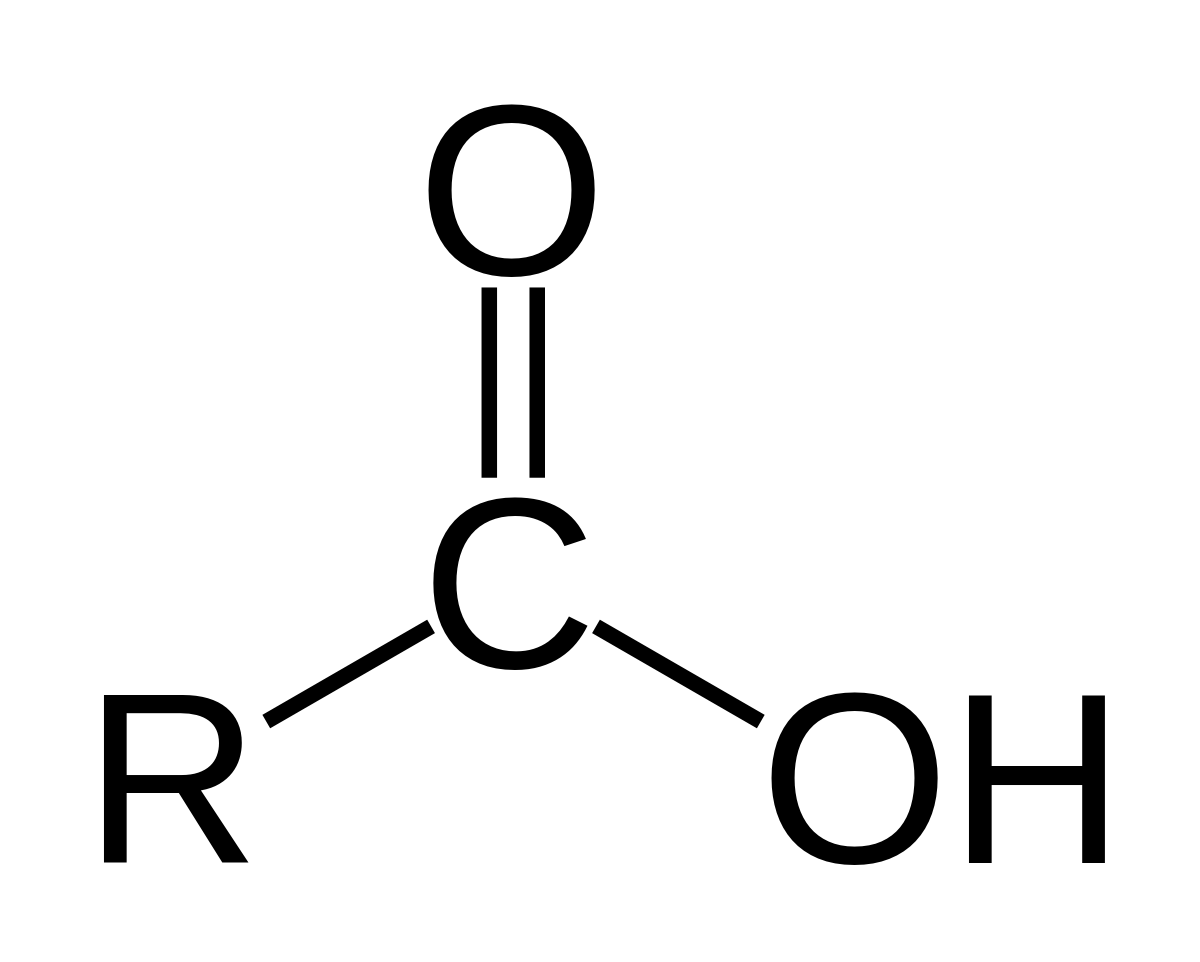
Carboxyl Functional Group
Follows the form R-C^=O_-(O-H)
Polar with partial positive on H and C atoms and partial negative on O atoms. Additionally due to the high polarity the oxygen can hog electrons and release an H+ cation => this functional group is acidic.
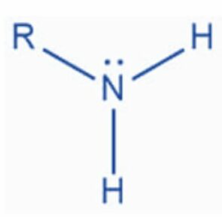
Amino Functional Group
Follows the form R-N^-H_-H
Polar/Charged. Has one lone pair of electrons => Works well as a base as it is likely to attract H+ cations and thus to neutralise acids.
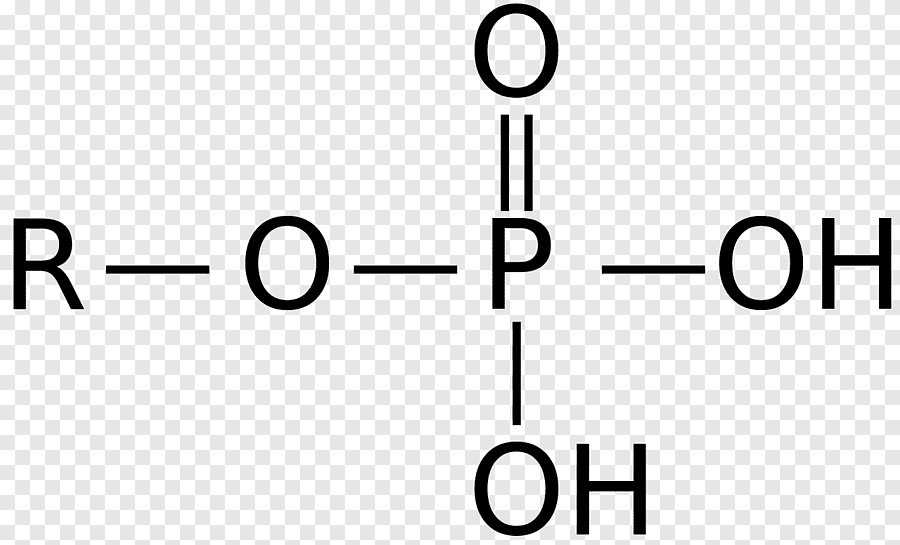
Phosphate Functional Group
Follows the form R-O-P^=O-O-H_-(O-H)
Charged/Polar. Due to the electronegativity of Oxygen it can hog the electrons and thus this functional group can act as an acid by releasing H+ cations into a substance. Note that this functional group can also be drawn as already having lost its H+ ions due to it being so acidic. Additionally it can further be drawn as its O anion having already bonded to other molecules after it has lost its H+ ion. It is drawn like this in DNA.
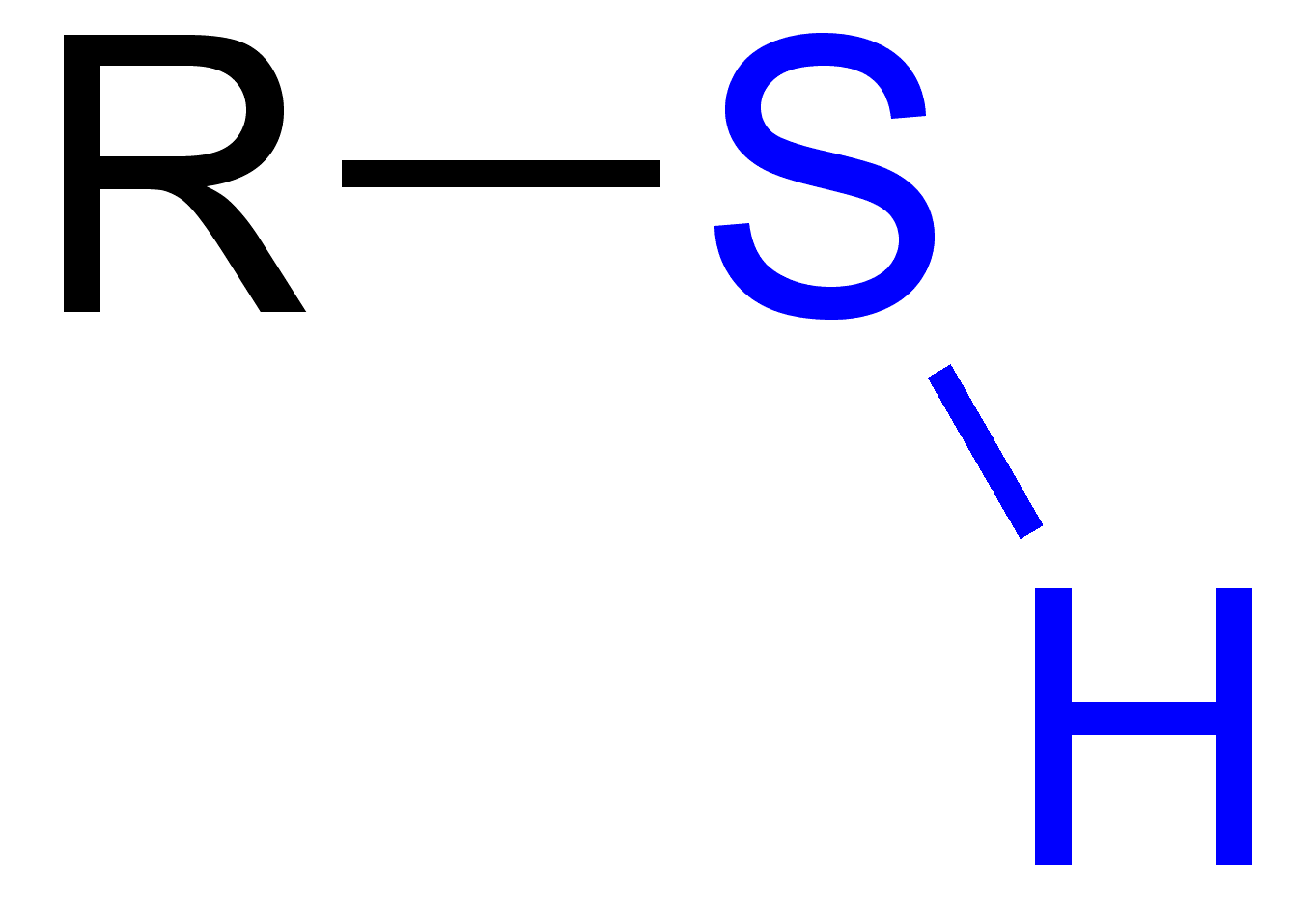
Sulfhydryl/Thiol Functional Group
Follows the form R-S-H
Polar because sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen but less polar than hydroxyl due to sulfur being less electronegative than oxygen.
Ionic bonds
Bonds created by the donation or receiving of electrons thus creating oppositely charged ions that bond to each other. These bonds occur when the difference in electronegativity between two molecules is so large that one molecule actually takes electrons.
Covalent bonds
Bonds created by the sharing of one or more electrons between 2 atoms
Cations
Positive ions formed by losing electrons.
Anions
Negative ions formed by gaining electrons.
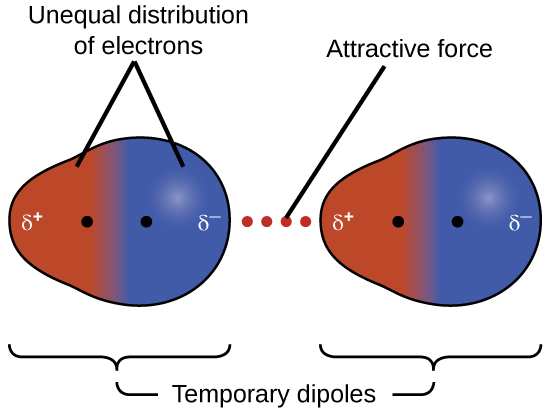
London dispersion force
A force that occurs as a result of the random constant motion of electrons. This force occurs in a special moment within which the electrons of a molecule are all in a certain region resulting in a partially positive charge in the opposite region and a partially negative charge in the region containing the electrons.
This partial charge in both region can then induce an opposing partial charge in nearby molecules by pushing electrons away or attracting them and thus attracting the whole molecule resulting in a temporary bond.
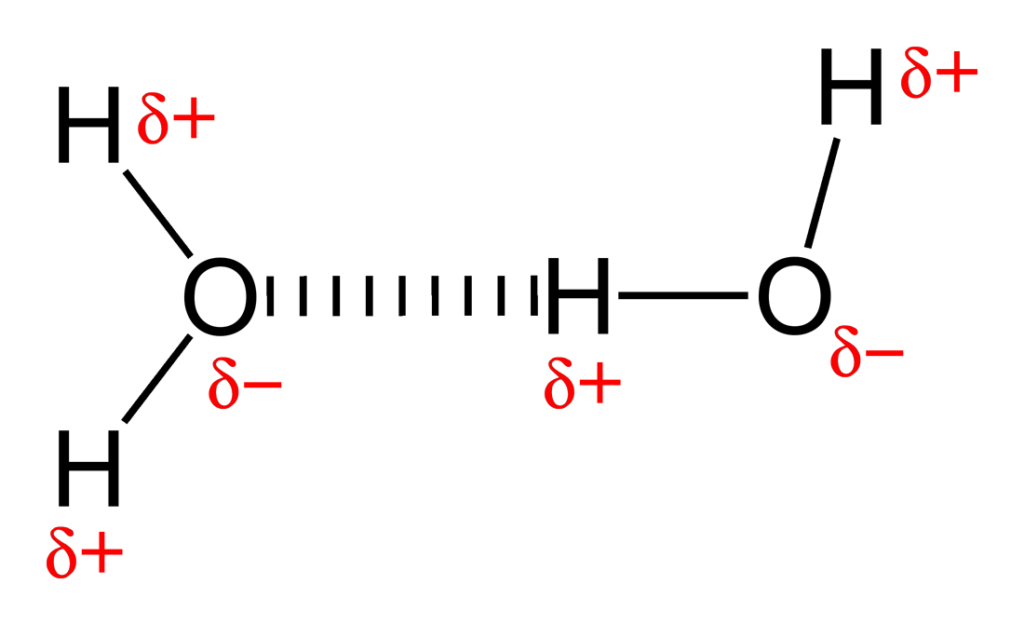
Hydrogen bond
A bond that occurs due to polar molecules specifically ones containing hydrogen. Certain partially positive or negatively charged areas will be attracted to other molecule’s partially negative or positively charged areas respectively.
Van der waals force
Any intermolecular force of attraction not involving covalent bonds or ionic ones. Basically hydrogen bonds or london dispersion forces
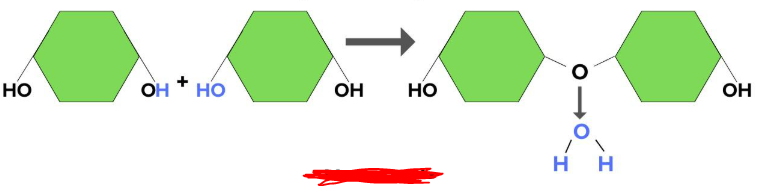
Dehydration Synthesis
The process by which monomers combine together in order to build polymers. In this process a hydroxyl group and hydrogen atom is lost (one hydroxyl from one monomer and a hydrogen from the other) thus creating an H2O molecule (hence the name _________ ________). The leftover missing bonds that were removed from the monomers to create the H2O molecule are then replaced by a bond between the monomers binding them together creating a polymer.
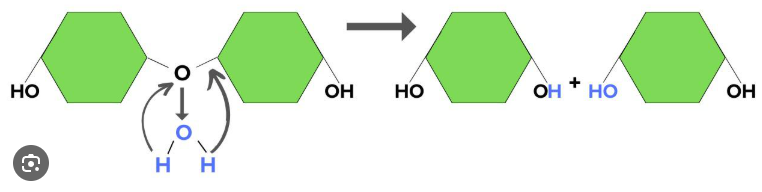
Hydrolysis
The opposite of dehydration synthesis. The process by which polymers are broken down into monomers (fundamental building blocks) in this process an H2O molecule is absorbed and the bond between sub-polymers is broken and replaced by a hydroxyl group on one sub-polymer and by an H atom on the other one.
Polymer
A molecule made up of multiple consecutively bound monomers. The way in which these are bound can be in different ways thus forming different macromolecules.
Monomer
A molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules in order to form a polymer.
Monosaccharide
The fundamental units of carbohydrates. Serve as primary energy and often referred to as “simple sugars”. One of the most popular examples of one is glucose. These are essentially sugar monomers.
Polysaccharide
Long chains of carbohydrate molecules composed of monosaccharides. Essentially long chains of monosaccharides. _____________ and monosaccharides are the same as polymers and monomers. (I.e. the former is a conjunction of the latter and the latter is the building block for the former). This term is essentially an esoteric specific word for sugar polymers.
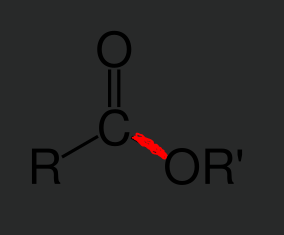
Ester bond
A covalent bond formed between a hydroxyl group from a carboxylic acid and a hydrogen atom from an alcohol. This bond is characterized by a carbonyl group and an oxygen atom single bonded to a carbon. During the creation of this bond the carboxylic acid always loses donates the OH group and the alcohol the H atom.
This bond follows the form
R-C=O_O-R’
Esterification
The process of creating an ester bond. During this process dehydration synthesis occurs to make the bond. These bonds occur between carboxylic acids and alcohols. Note that during _____ the carboxylic acid always provides a hydroxyl group and the alcohol always provides the H atom.
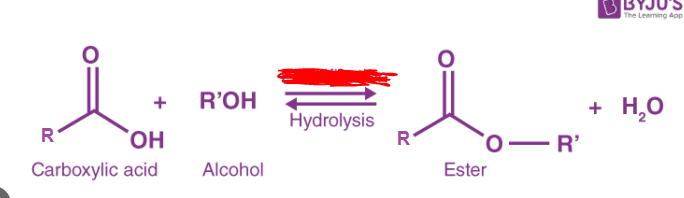
Ester
Any molecule with a carbonyl group and an oxygen that forms a single bond with the same carbon responsible for the carbonyl group (i.e. the carbon also double bonded to another Oxygen). These organic compounds react with water to produce alcohol through hydrolysis and can, in the backwards reaction, undergo esterification/dehydration synthesis.
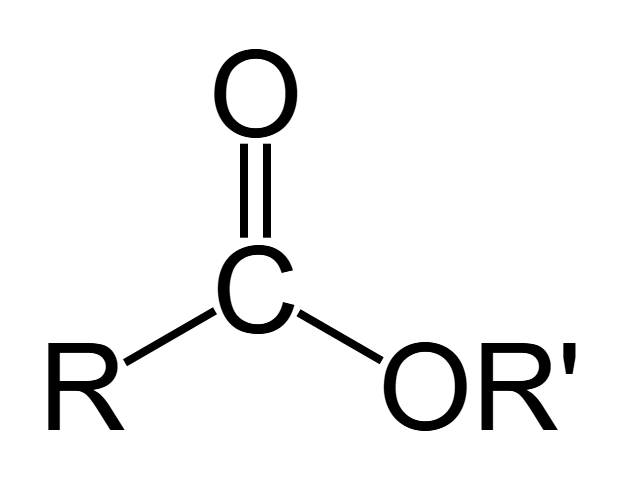
Purines
Nitrogenous bases with 2 rings. This group of nitrogenous bases includes Adenine and Guanine which are both found in DNA.
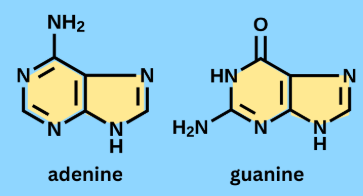
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases with 1 ring. This group of nitrogenous bases includes Thymine which is found in DNA, Uracil which is found in RNA and Cytosine which is found in both.
Amino Acids
The building blocks of protein. Generally follow the form (H-^H-_N)-R-_C^-H-(C^=O_-O-H)
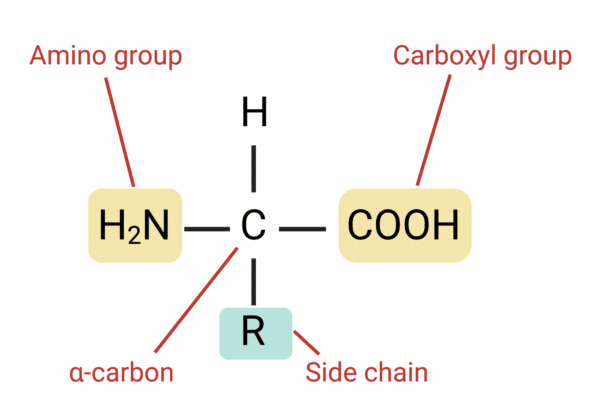
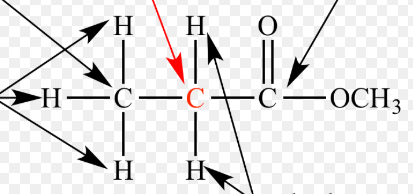
Alpha Carbon
The carbon that is next to a functional group in an organic compound.
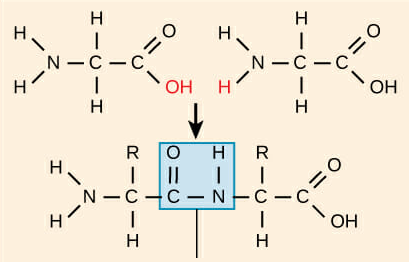
Polypeptide
A chain of more than one amino acid.
Monopeptide
A chain of one amino acid, the building block of a protein.
Peptide bond
The bond created between amino acids that form polypeptides. These bonds are created through dehydration synthesis between the amino acids. In this type of bond a covalent bond is created between a nitrogen and carbon atom.
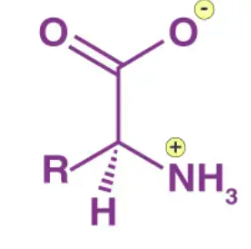
Zwitterions
Molecules with parts that are charged i.e. parts that have excess electrons or a lack of but regardless still overall neutrally charged due to the charged parts being opposite and cancelling out. One example of __________ are amino acids at physiological PH as they donate H+ cations on one side but attract H+ cations using lone pair electrons on another.
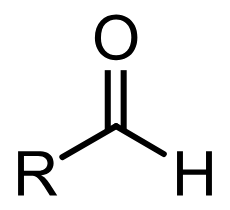
Aldehyde group
A group of functional molecules following the form R-C^=O-H where R is a hydrocarbon or a hydrogen atom or a chain of saturated carbon molecules bonded to hydroxyl groups and hydrogen. Basically ketones but with a hydrogen atom attached instead of another molecule. These are found in carbohydrates that are not ketones i.e. ones that have their double bond carbon atom at the end of their chains.
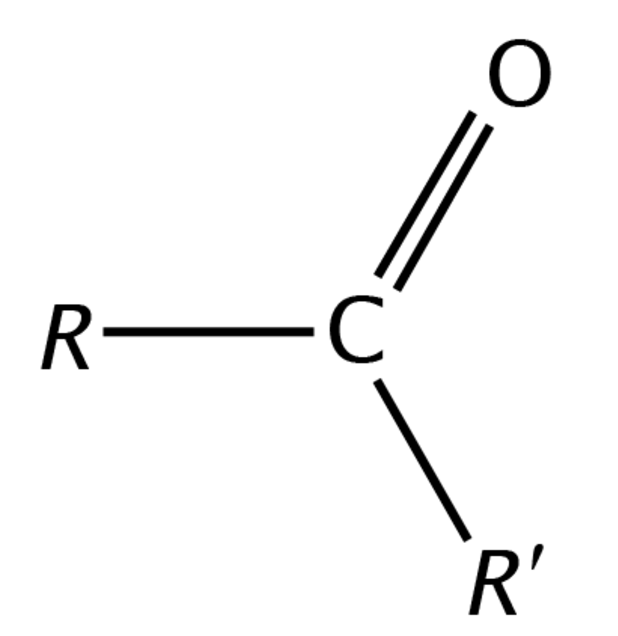
Ketone group
A group of functional molecules following the form R-C^=O-R’ where R and R’ are hydrocarbons or chains of saturated carbon molecules bonded to hydroxyl groups and hydrogen. This is a sub-group of the larger group carbonyls.
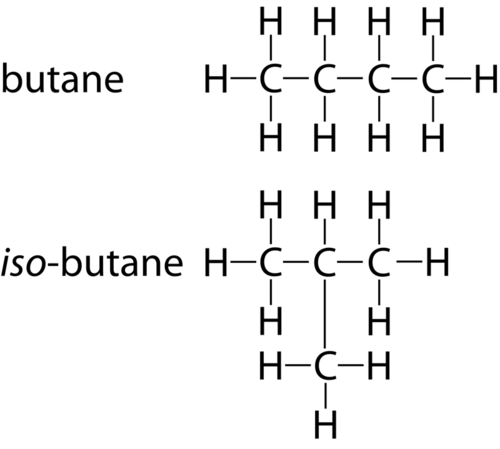
Isomer
A name for a distinct configuration of an element. Molecules can have the same formula but some molecules arrange themselves and bond in distinct ways and orders and thus can give the molecule specific properties depending on the arrangement. A specific configuration/arrangement of a molecule is called an ________. For example an _____ of glucose is fructose. Picture shows an example of a _____.
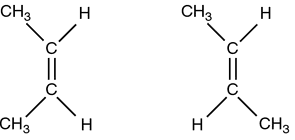
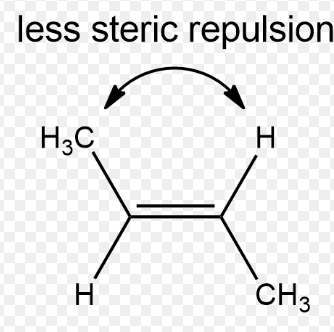
Stereoisomers
An isomer of an element that only differs in the way in which atoms arrange themselves around one or more atoms. An ______ of an element will have atoms bonded in the same order but when viewed in 3d the seperation between certain atoms and the direction in which they point may differ among ________. Trans and Cis molecules are examples of ________. Picture shows an example of a _________.
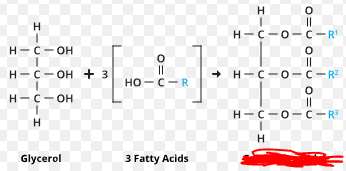
Glycerol
A molecule involved in the formation of most fats and triacylglycerol. Also an alcohol. Has 3 carbons and 3 hydroxyl groups. Forms an ester bond through dehydration synthesis in order to create triacylglycerol.
Cis configuration
Configuration of an isomer in which a sub-molecule on one side will have the same position if the whole molecule is mirrored.
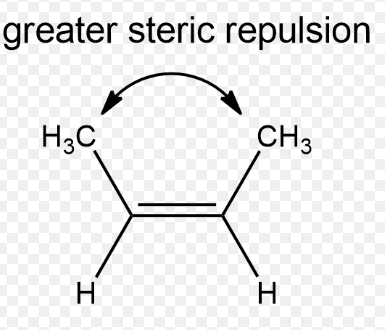
Trans configuration
Configuration of an isomer in which a sub-molecule on one side will have the same position if the whole molecule is mirrored and flipped upside down.
Triacylglycerol
The building block of most lipids and fats. (Some lipids do not contain three carboxylic acids hence not all lipids). These are made up of a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids.
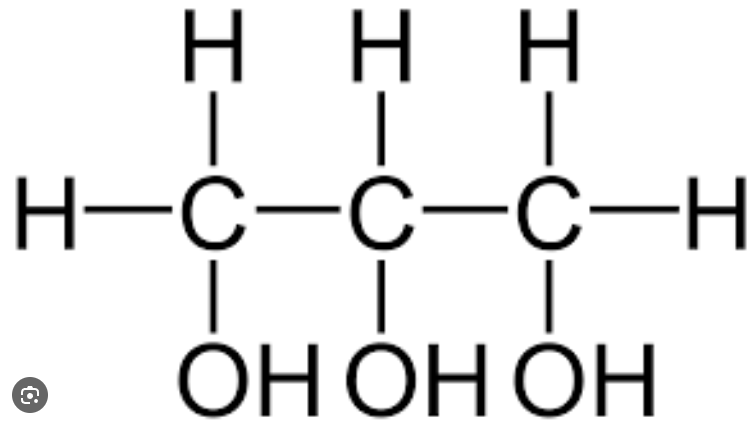
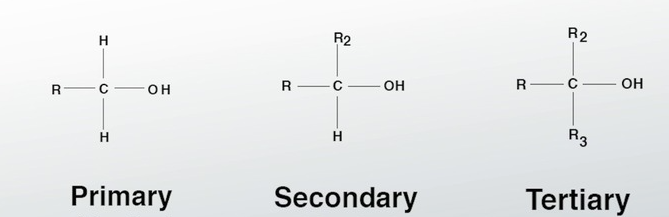
Alcohol
Any molecule with a hydroxyl group that is connected to a saturated carbon atom.
Primary ____ have only one extra molecule attached, 2 hydrogen ones and a hydroxyl group
Secondary ____ have two extra molecules attached, 1 hydrogen and one hydroxyl
Tertiary ____ have 3 extra molecules attached, 0 hydrogen and one hydrxyl.
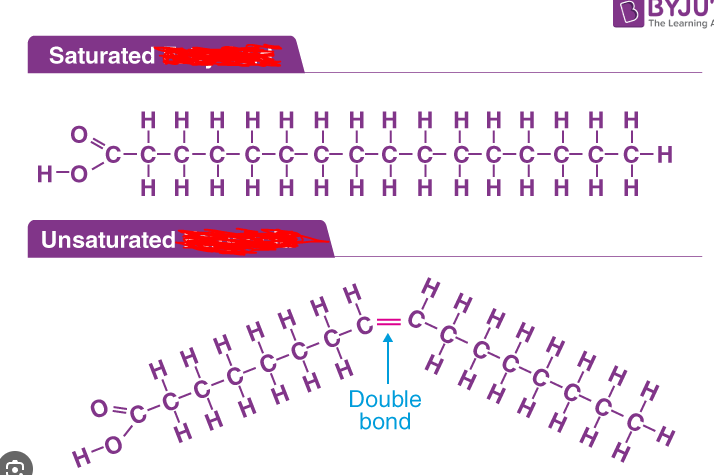
Saturated Molecule
A molecule within which all available bonding sites are occupied. In a _____ molecule the molecule has made a bond with as many molecules as it possibly can. Note that this implies a molecule like CH4 is saturated but one such as RR’CO is not (because it has a double bond with the oxygen rather a new molecule and hence a bonding site is available).
Fatty acid
Molecules with a carboxylic end and a hydrocarbon tail/chain. These undergo esterification with other molecules, specifically alcohols, in order to create fats.
Fats
Any ester of fatty acids and alcohols or a mixture of such compounds. Basically any molecule that must undergo dehydration synthesis at least once with a molecule that has a carboxylic group and a hydrocarbon chain (fatty acid), and another molecule which has a hydroxyl group connected to a saturated carbon atom (alcohol), in order to form. Usually these come in the form of 3 of these molecules bonded through esterification.