module 2: actual
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
two bones under the pectoral girdle
scapula
clavicle
how many bones in cranium
22
braincase 8
facial 14
+each 3 auditory ossicles found in eat
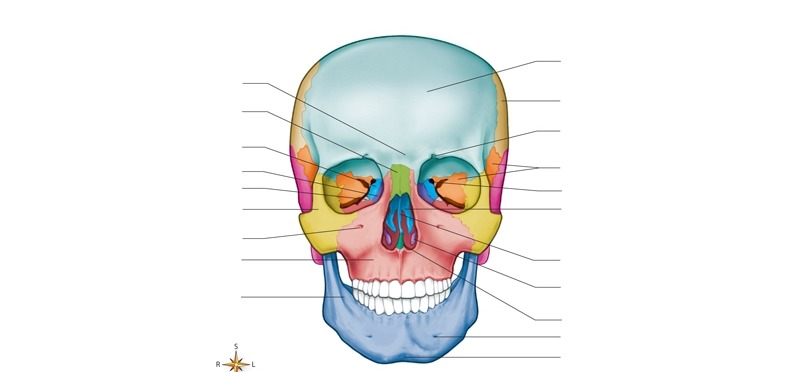
blue - anterior part of cranium, forms forehead, the roof of the orbits
frontal bone
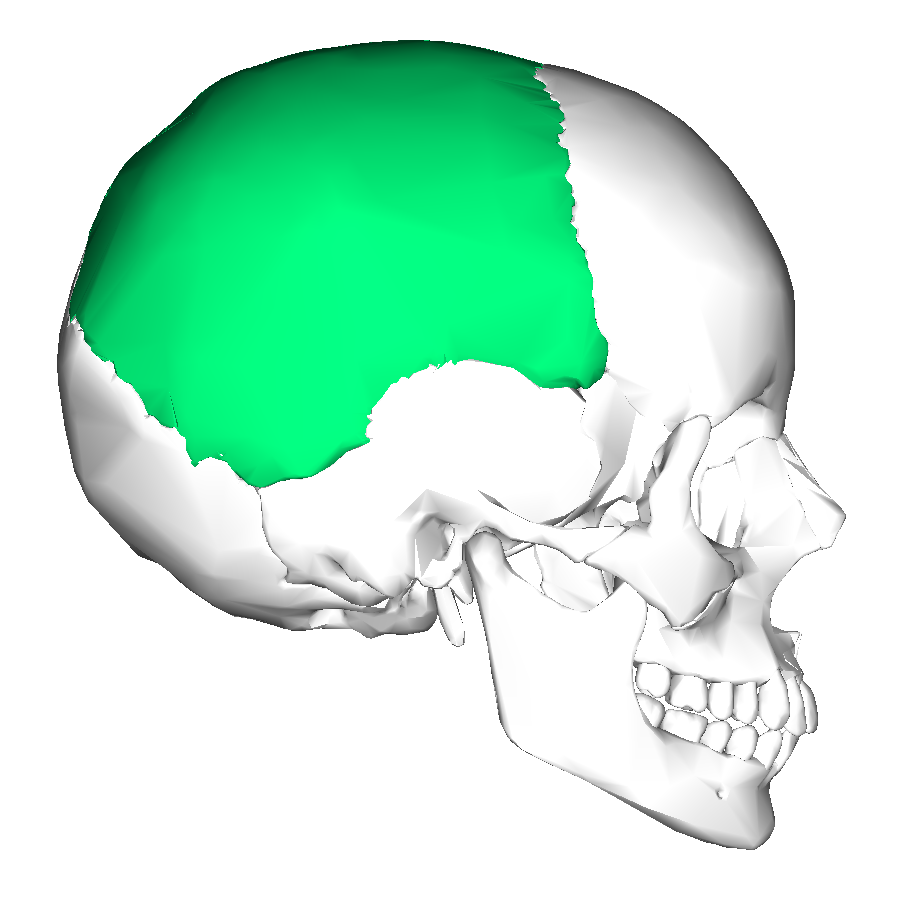
sides and roof of cranium, accommodates blood vessels
parietal bones
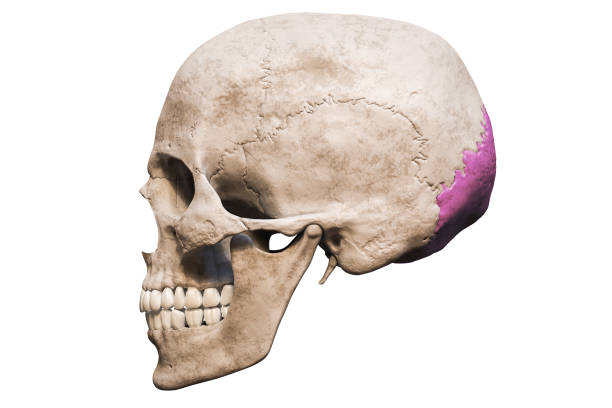
posterior portion and floor of cranium
occipital bone
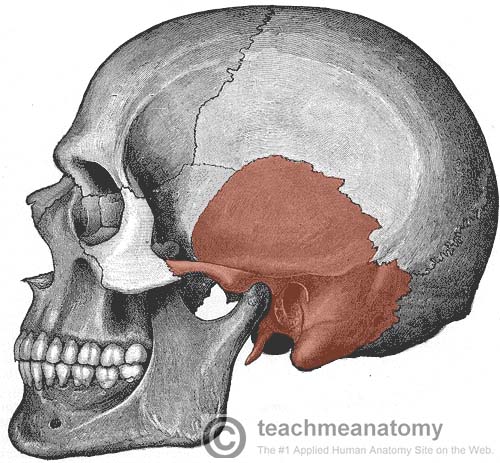
inferior to parietal bones, found on each side of the cranium
temporal bones
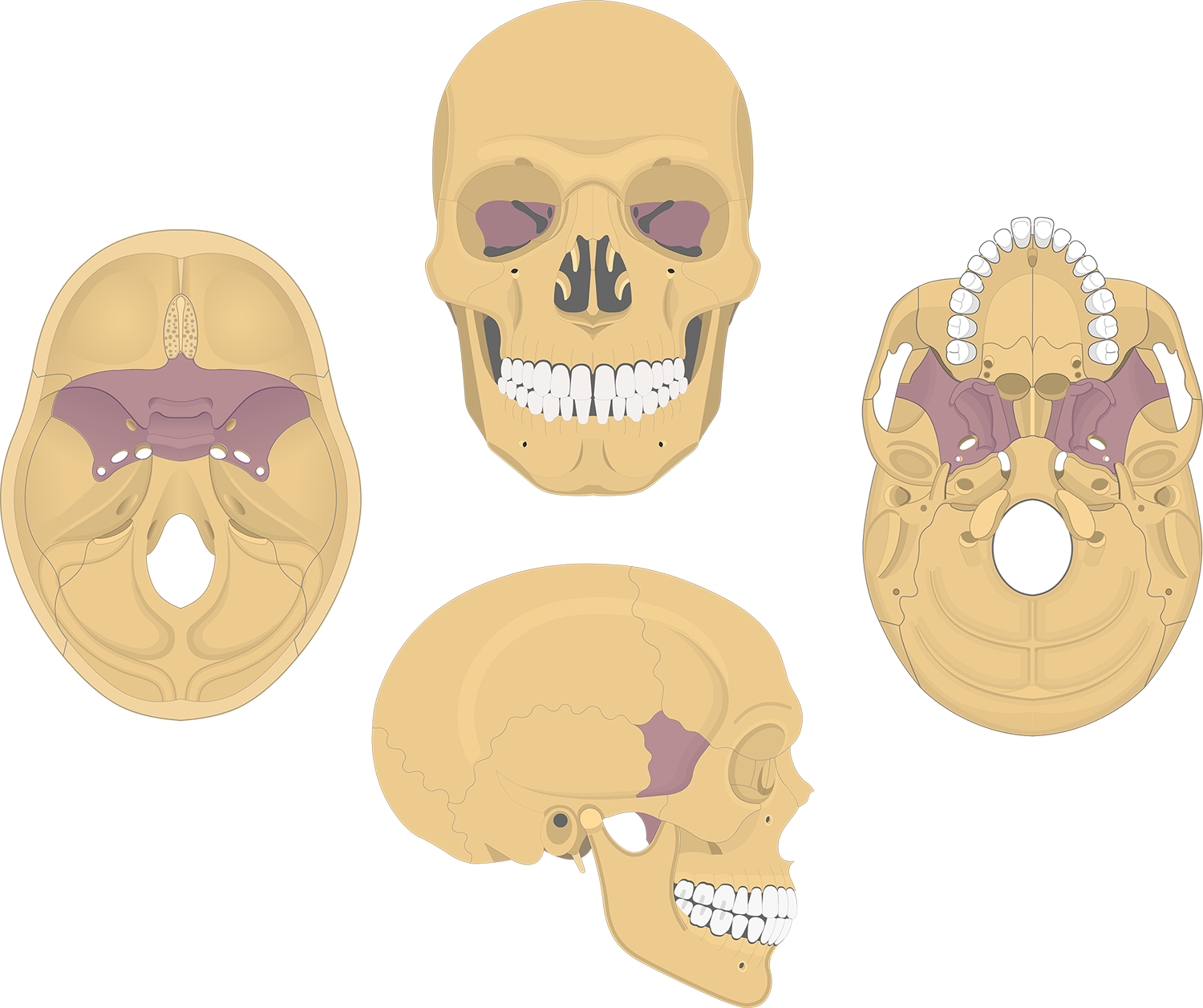
middle part of the cranial base, called keystone as it holds the other cranial bones together
sphenoid bone
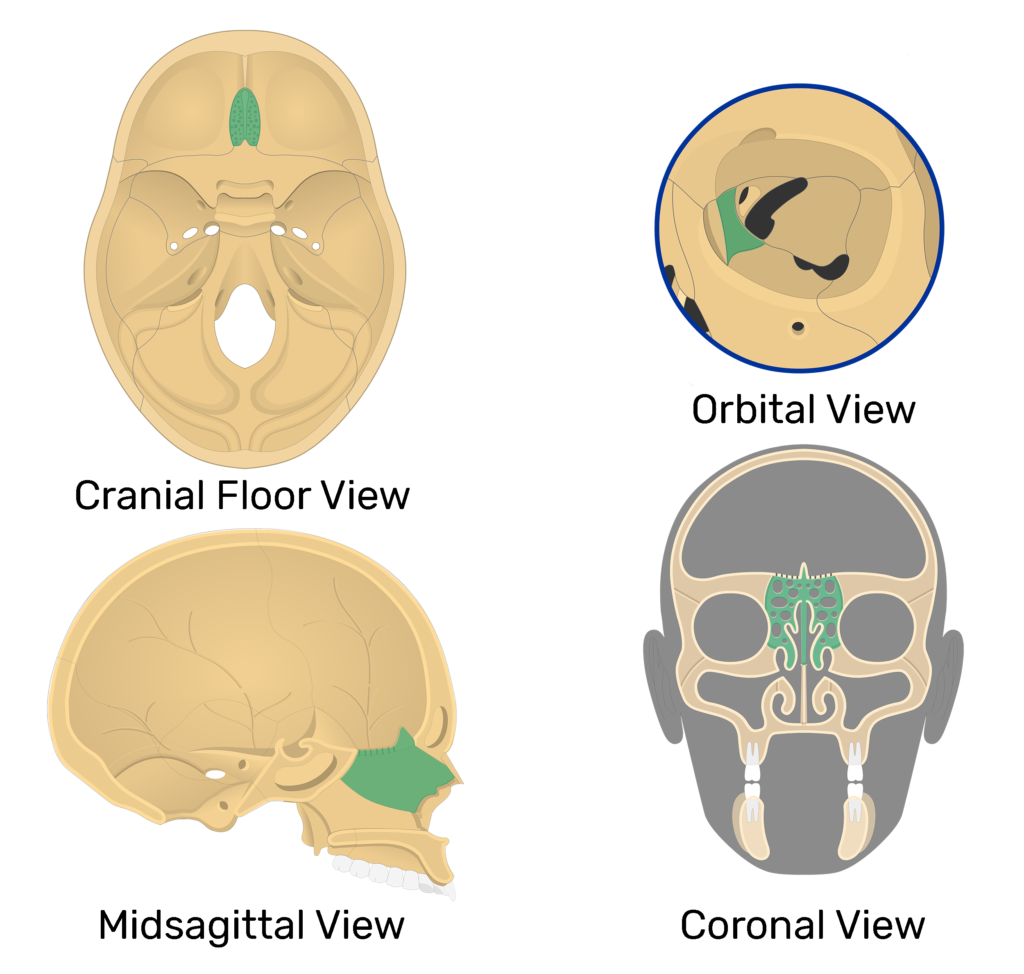
includes medial surface of eye orbit and roof of nasal cavity
ethmoid bone
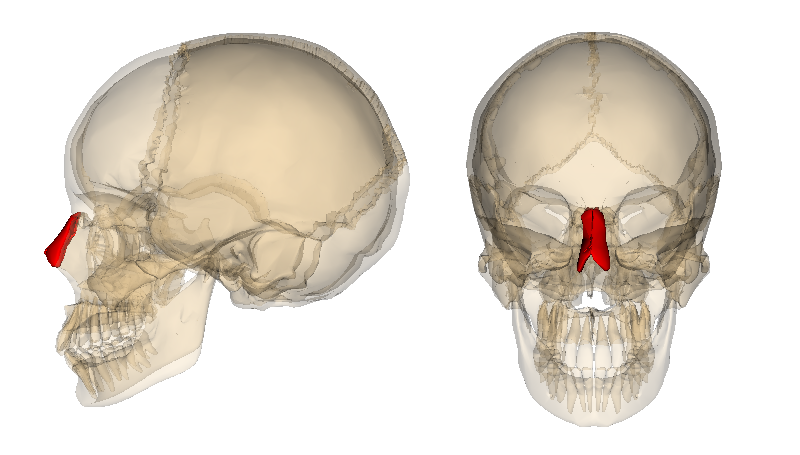
forms the bridge of nose
2 nasal bones
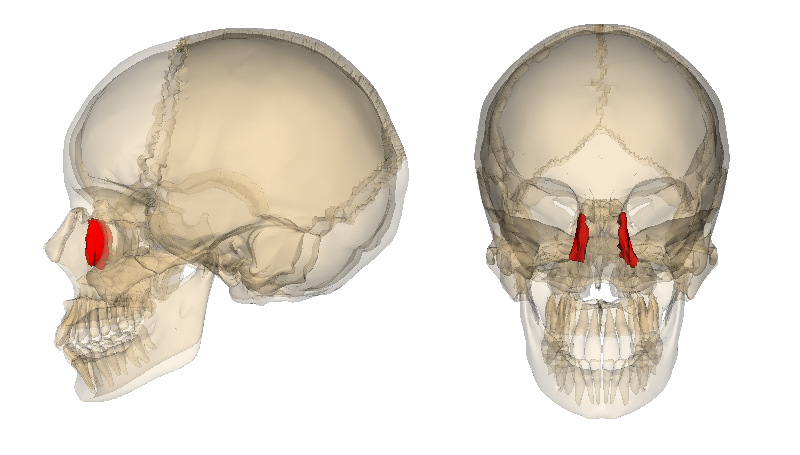
medial surfaces of eye orbits
2 lacrimal bones
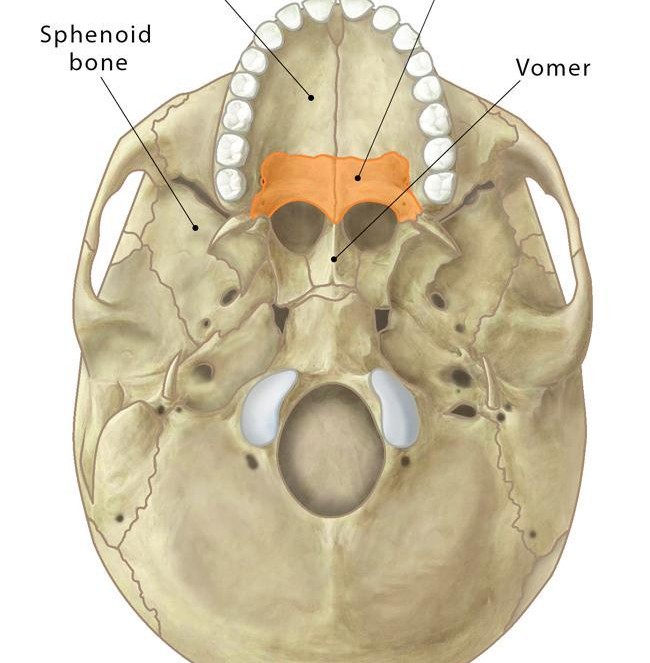
forms the posterior portion of the hard palate
2 palatine bones
attached to lateral walls of nasal cavity
increases the surface area of the nasal cavity and help swirl and filter air before it passes into the lungs
2 inferior nasal conchae
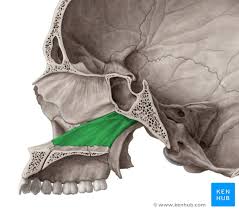
triangular bone that forms the inferior part of the nasal septum
vomer
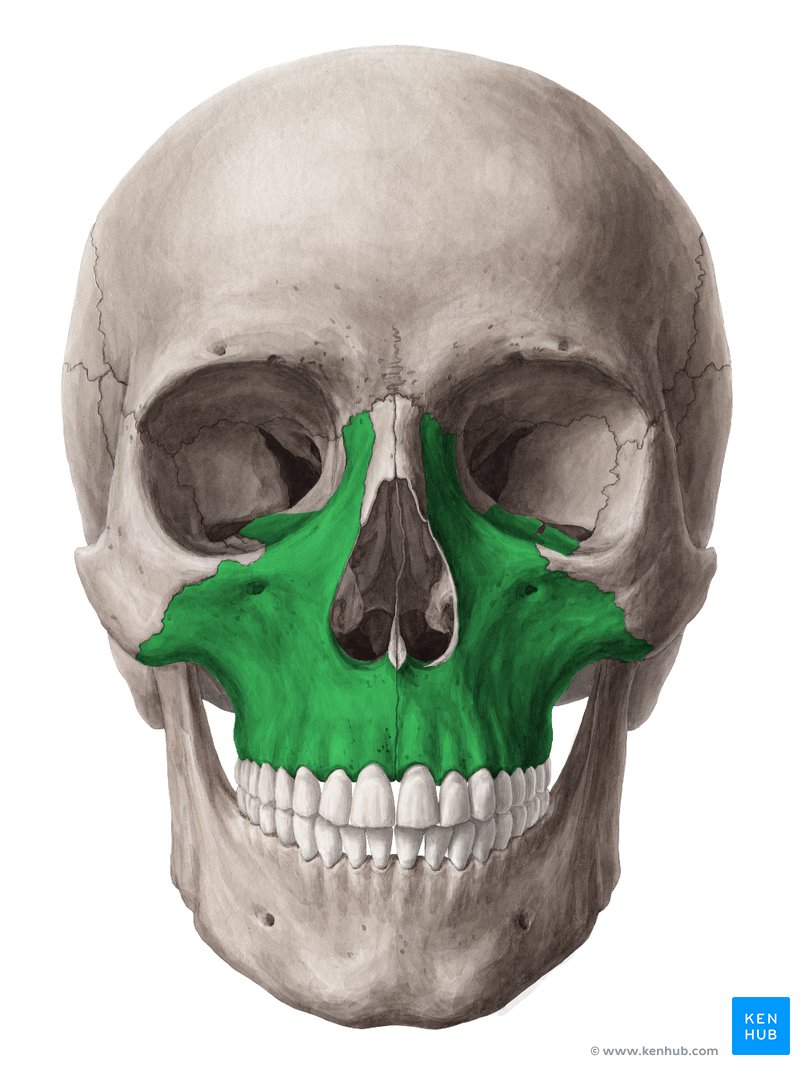
unite to form the upper jawbone
maxillae
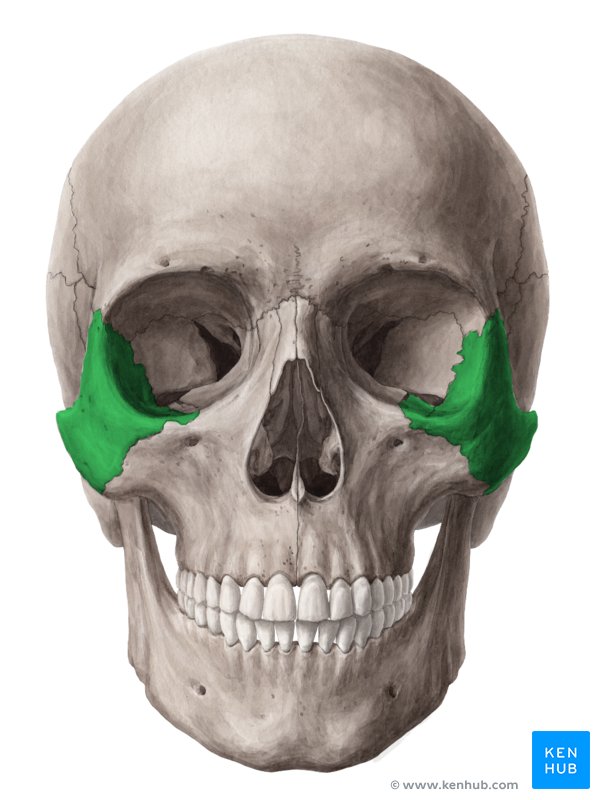
cheek bones
zygomatic bones
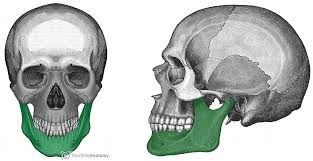
lower jawbone, largest and strongest facial bone, only movable skull bone
mandible
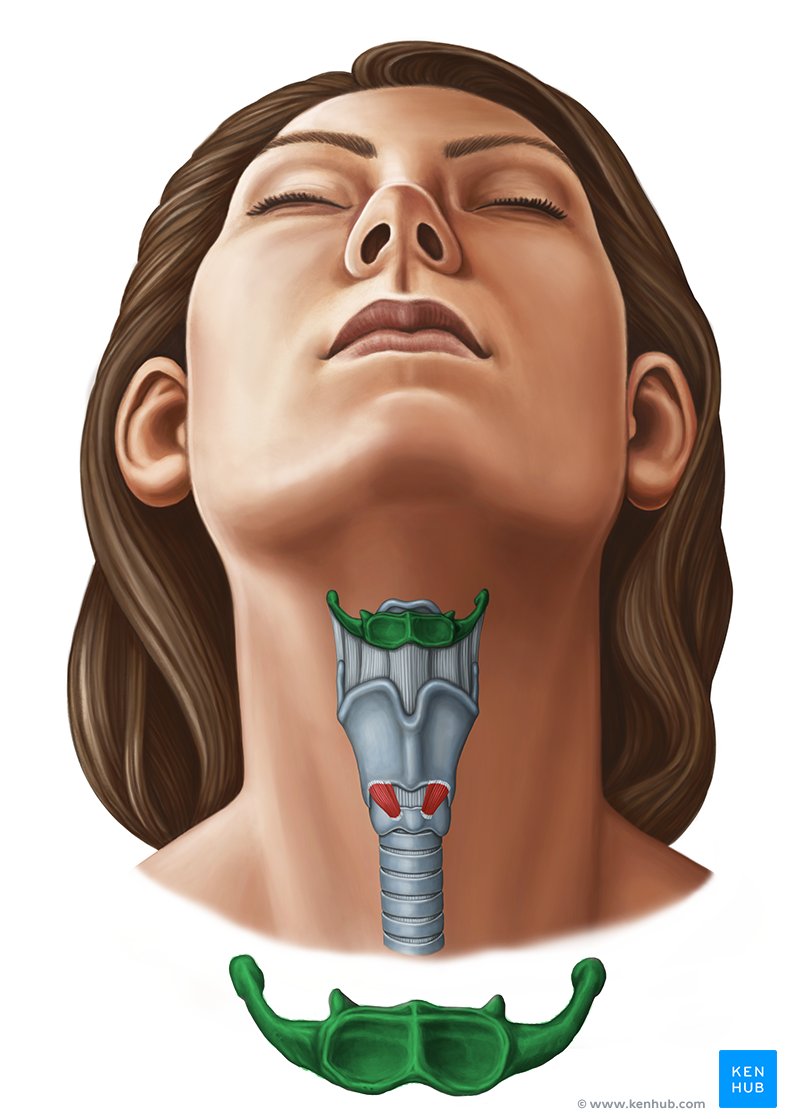
unpaired bone that is not part of the skull and has no direct bony attachment
suspended from the styloid processes of the temporal bones
supports the tongue
hyoid bone
the spine, backbone, or spinal column
vertebral column
what are the 26 vertebrae
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
1 sacrum
1 coccyx
normal curves of the vertebral column
cervical (
thoracic )
lumbar (
pelvic )
parts of vertebra
vertebral body - weight bearing
vertebral arch - two processes
processes of the vertebral arch
2 transverse
1 spinous
2 superior articular
2 inferior articular
first two cervical vertebrae
Atlas (C1) - lacks a body and a spinous process
yes
Axis (C2) - has a unique, tooth-like projection called the dens
no
bone structure that protects vital organs
thoracic cage (sternum + ribs)
sternum
manubrium
body
xiphoid process
ribs
7 true ribs
5 false ribs
8, 9, 10 - vertebrochondral ribs
11, 12 - floating ribs
how many bones in axial skeleton
80
how many bones in appendicular skeleton
126
how many bones in an adult skeleton
206
shoulder blade
scapula
collar bone
clavicle
shape of clavicle
slender, s-shaped clavicle
shape of scapula
large, triangular flat bone
how many bones in the upper limb?
30 bones in three locations: arm, forearms, and hands
upper limb, skeleton of the arm
humerus
the bone from the pinky to the elbow
ulna
the bone from the thumb to the elbow
radius
eight small bones of the wrist joined to one another by ligaments
carpals
five bones forming the intermediate region of the hand
metacarpals
bones of the digits, make up the distal part of the hand
phalanges
where lower limbs attach to the body
pelvic hip girdle
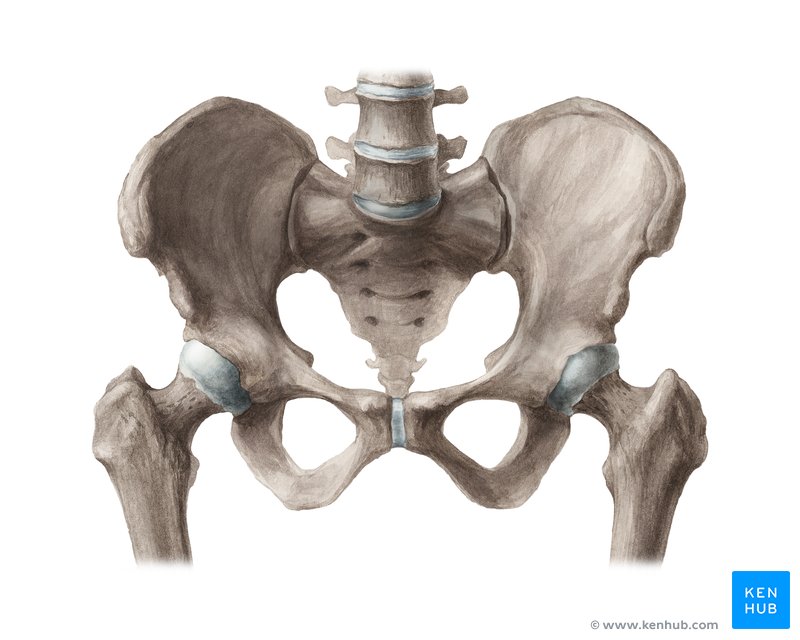
the large bony structure near the base of the spine to which the hind limbs or legs are attached
pelvis
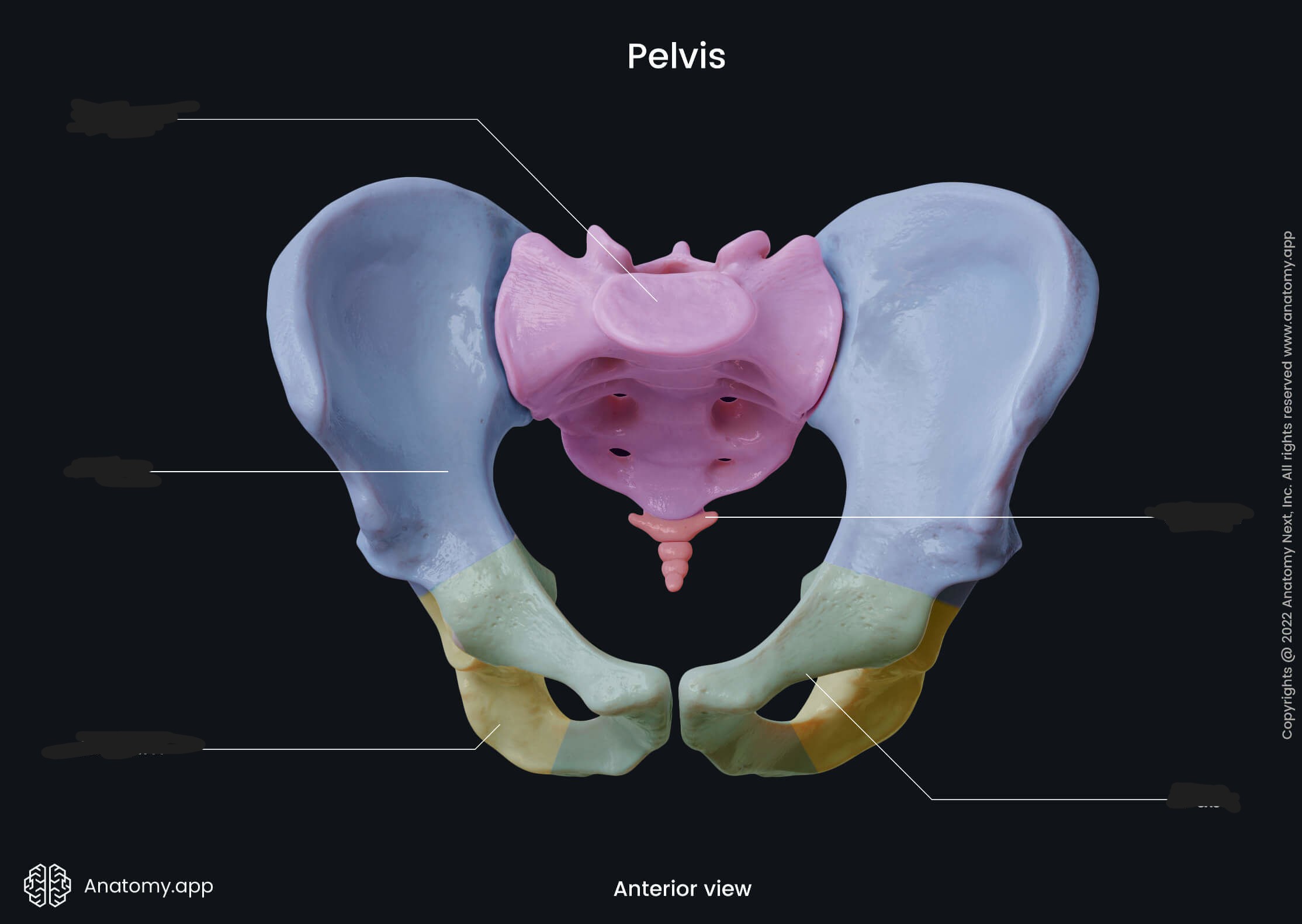
green - the curved bone forming the interior base of each half of the pelvis
ischium
blue - the superior large broad bone forming each half of the pelvis
ilium
yellow - most anterior part of the pelvis and is located where the two pubic bones meet in the front at a joint
pubis
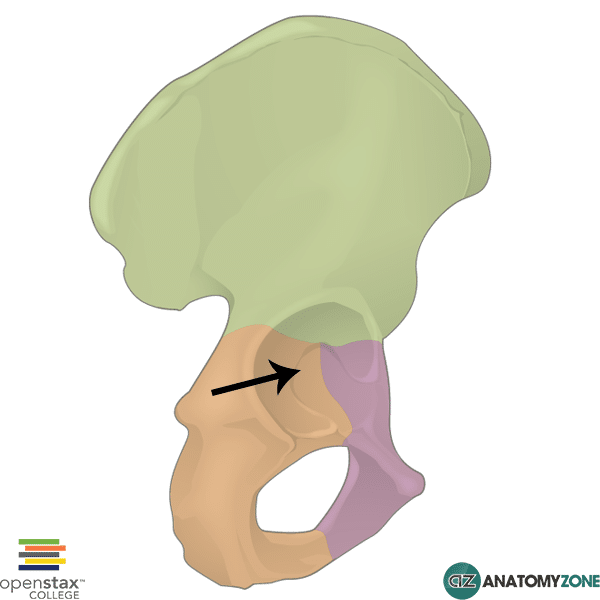
the socket of the hipbone
acetabulum
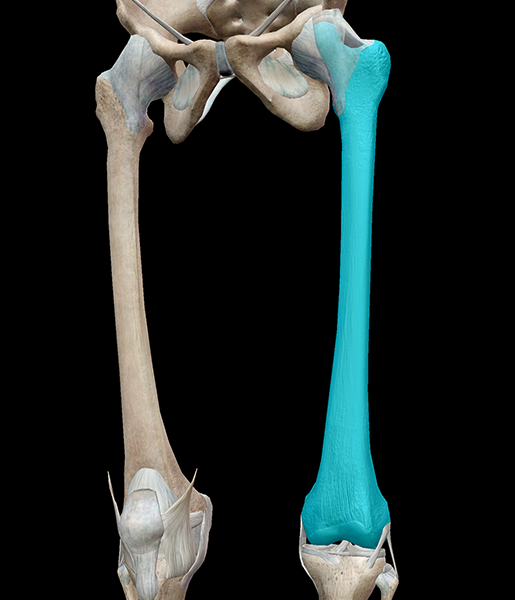
longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the body
femur
knee cap
patella
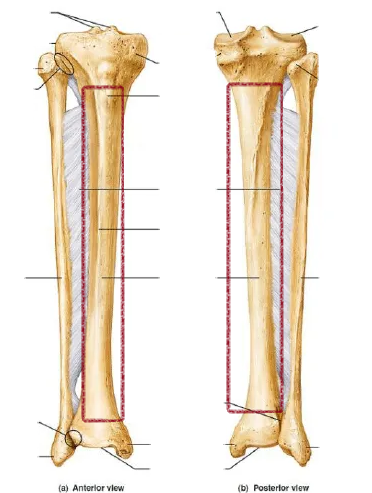
the larger of the two bones in the lower leg that bears weight
tibia
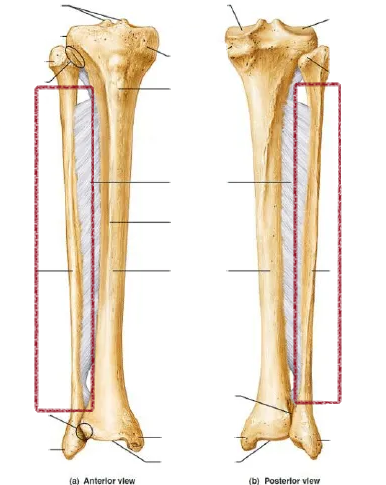
the outer and usually smaller of the two bones between the knee and the ankle
fibula
7 bones of the proximal region of the foot
tarsals
5 bones in the intermediate region of the foot
metatarsals
toes and fingers
phalanges
bending
flexion
straightening
extension
movement away from the midline * →
abduction
movement toward the midline * ←
adduction
rotation of the forearm with palms down
pronation
rotation of the forearm with palms up
supination
movement of a structure about the long axis
rotation
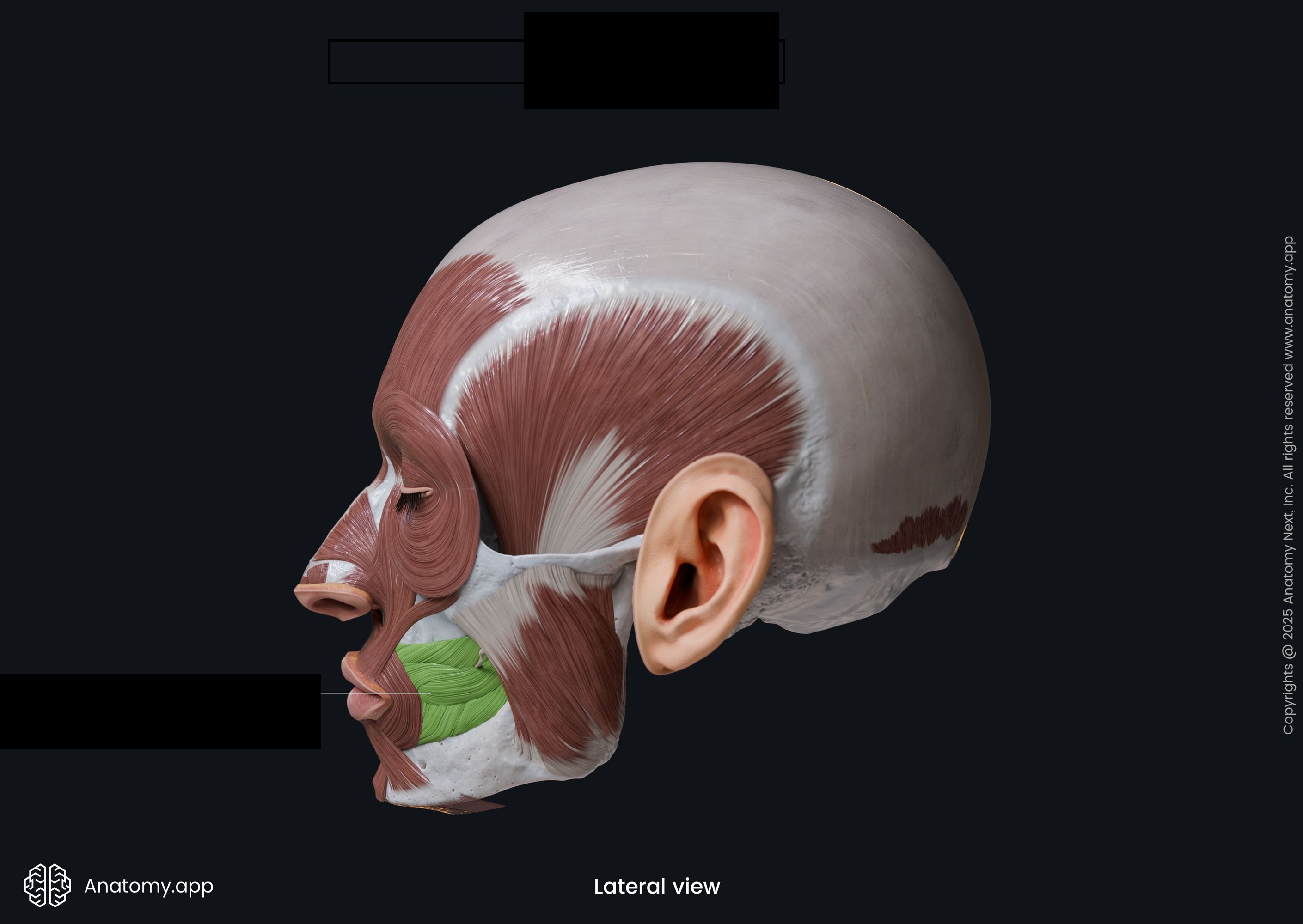
wall of the cheeks
buccinator
lowers corners of mouth/depresses the corner of mouth
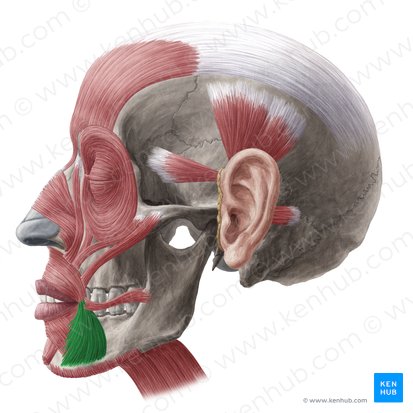
depressor anguli oris
elevates upper lip
levator labii superioris
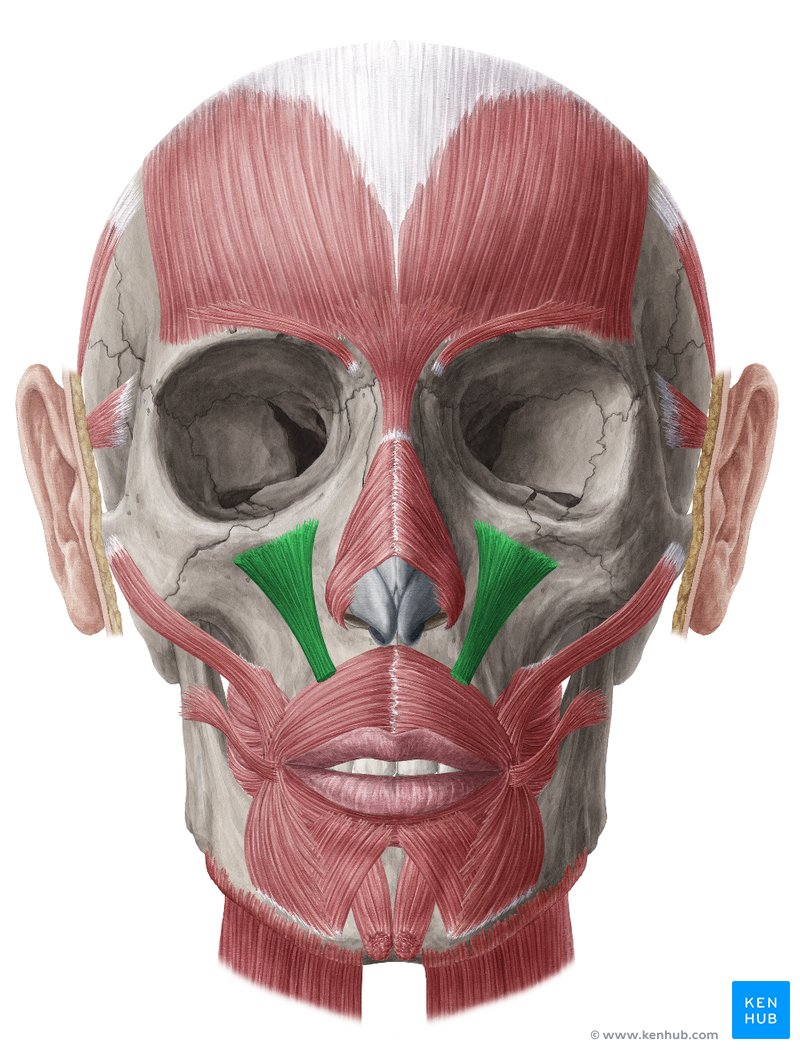
moves scalp, raises eyebrows, and wrinkles your fore head
occipitofrontalis
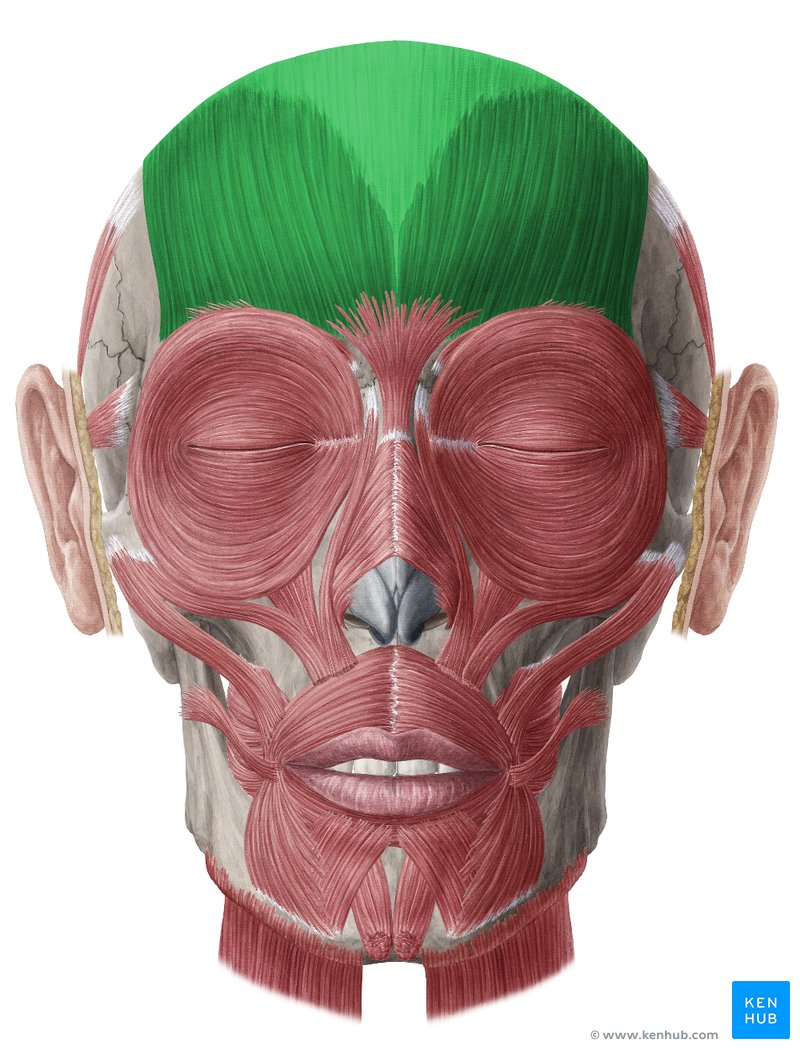
closes the mouth and protrudes the lips
orbicularis oris
elevate the upper lip and corner of the mouth
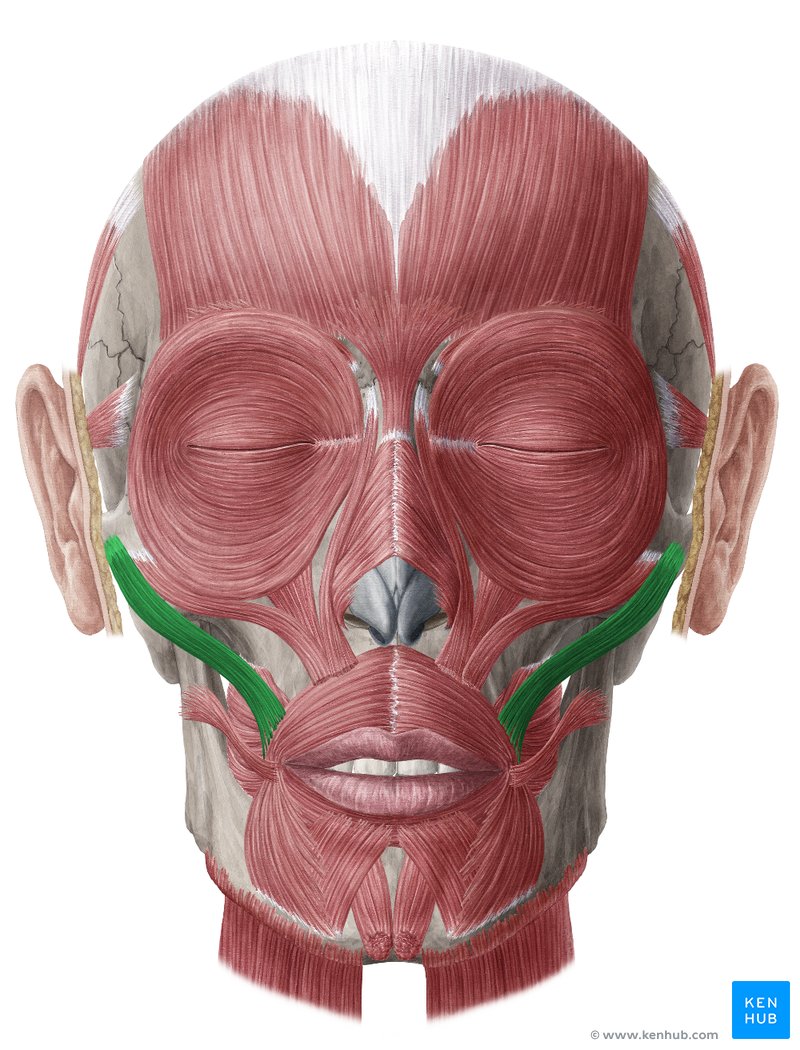
zygomaticus
closes the jaw by elevating and pushing the mandible anteriorly
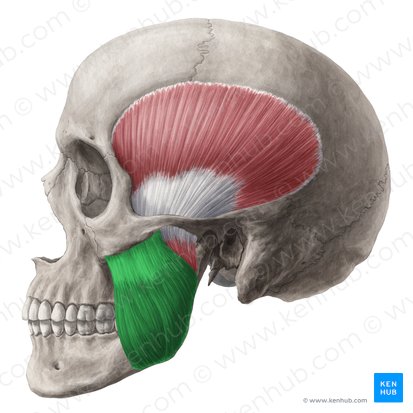
masseter
elevates and draws the mandible posteriorly
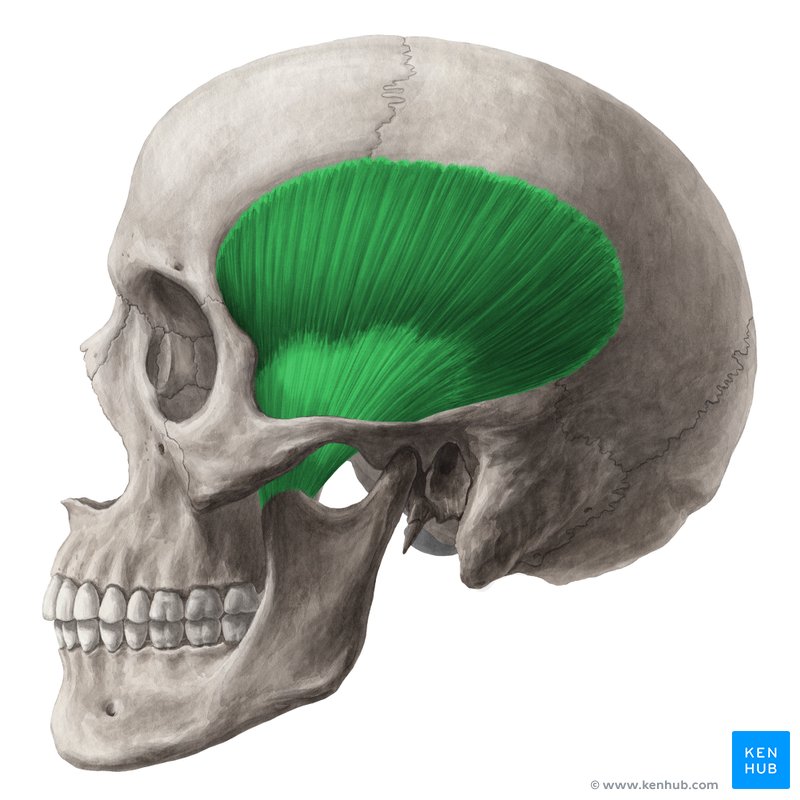
temporalis
jaw movement and chewing
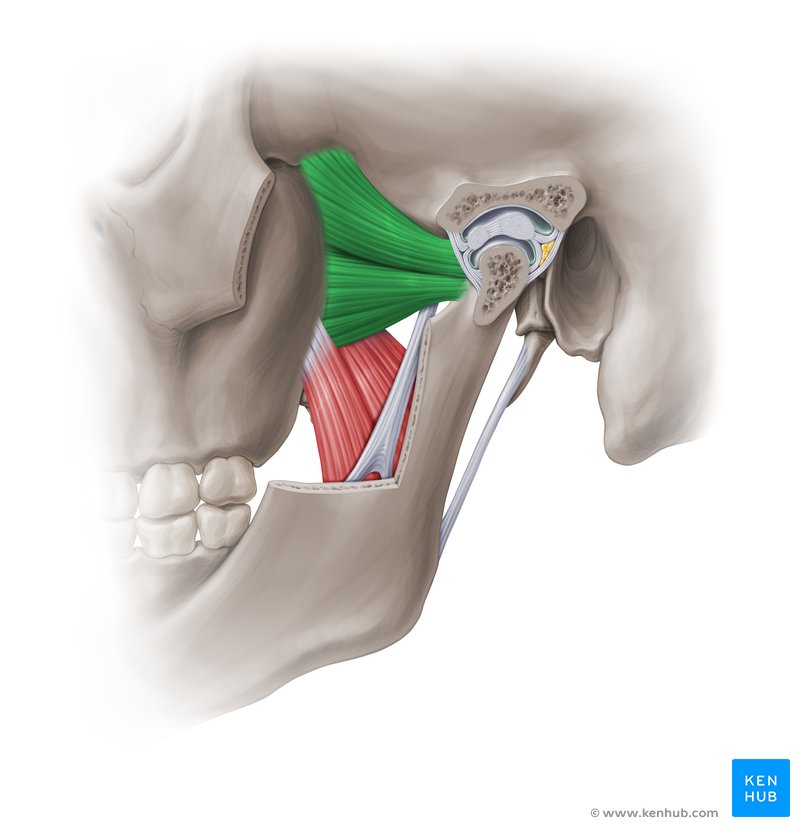
pterygoids
tongue muscle that change the shape of the tongue
intrinsic
tongue muscle that moves the tongue
extrinsic
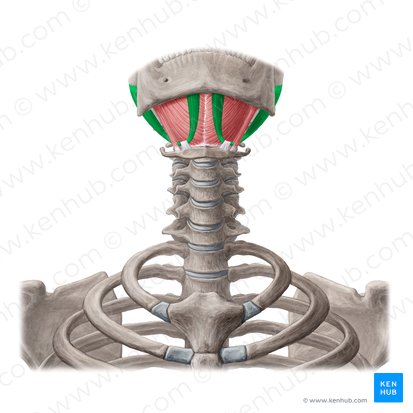
above hyoid; elevates or stabilizes hyoid
suprahyoid
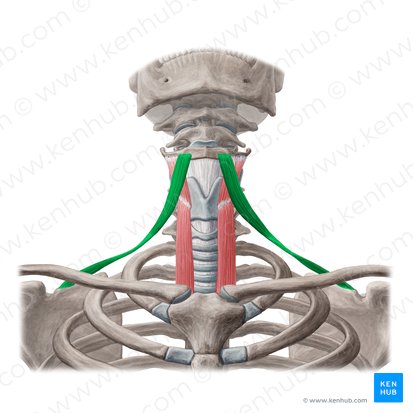
below hyoid; depresses or stabilizes hyoid
infrahyoid
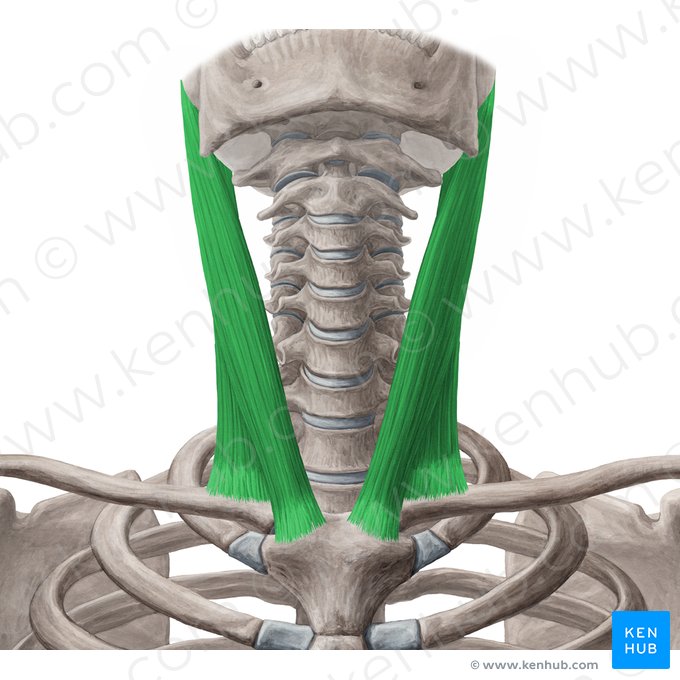
neck muscles that individually rotate the head; together it flex the neck
sternocleidomastoid
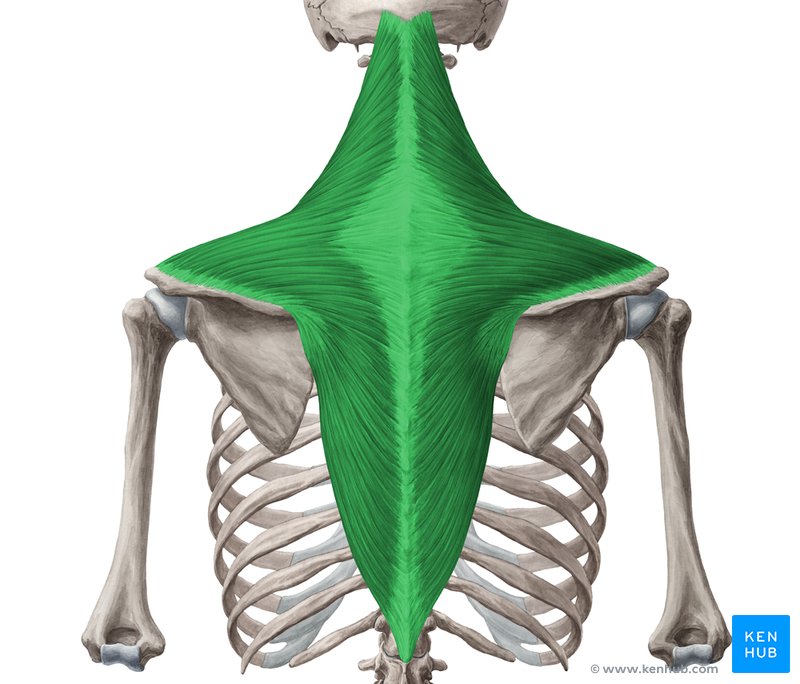
neck muscles that extends and laterally flexes the neck
trapezius
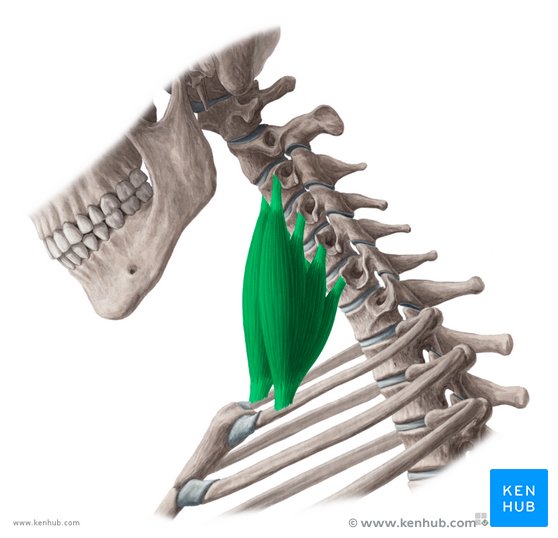
neck muscles that laterally flex and rotate neck
scalene
parts of the trunk muscles
vertebral column
thorax
abdominal wall
pelvic floor
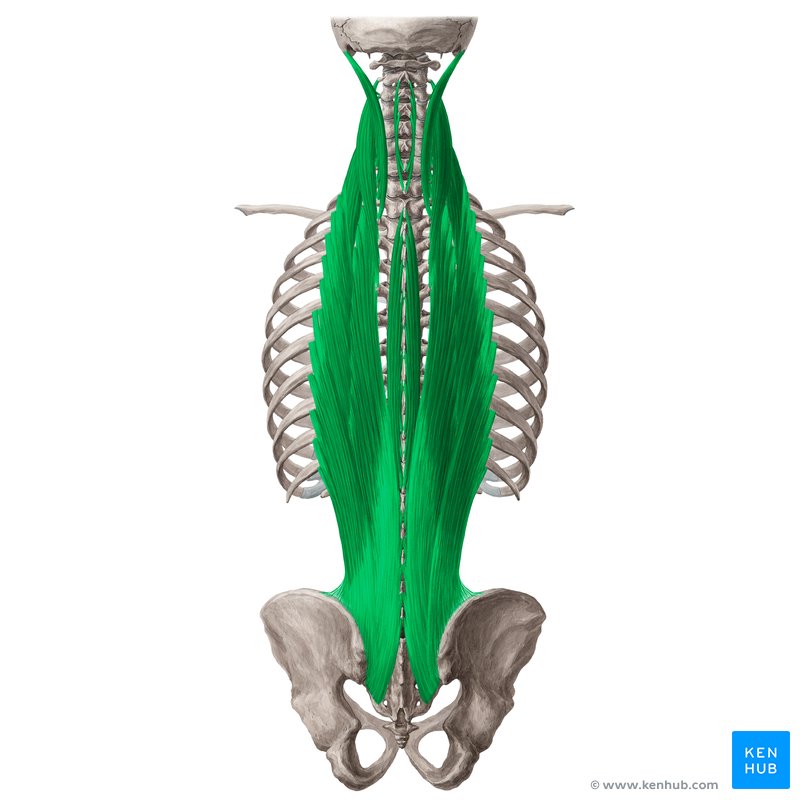
extends vertebral column and maintains posture
erector spinae
three different columns of the erector spinae
iliocostalis
longissimus
spinalis
elevate ribs during quiet resting inhalation
external intercostals
depress ribs during forced exhalation
internal intercostals
dome shaped muscle that moves during quiet breathing, elevate ribs
diaphragm
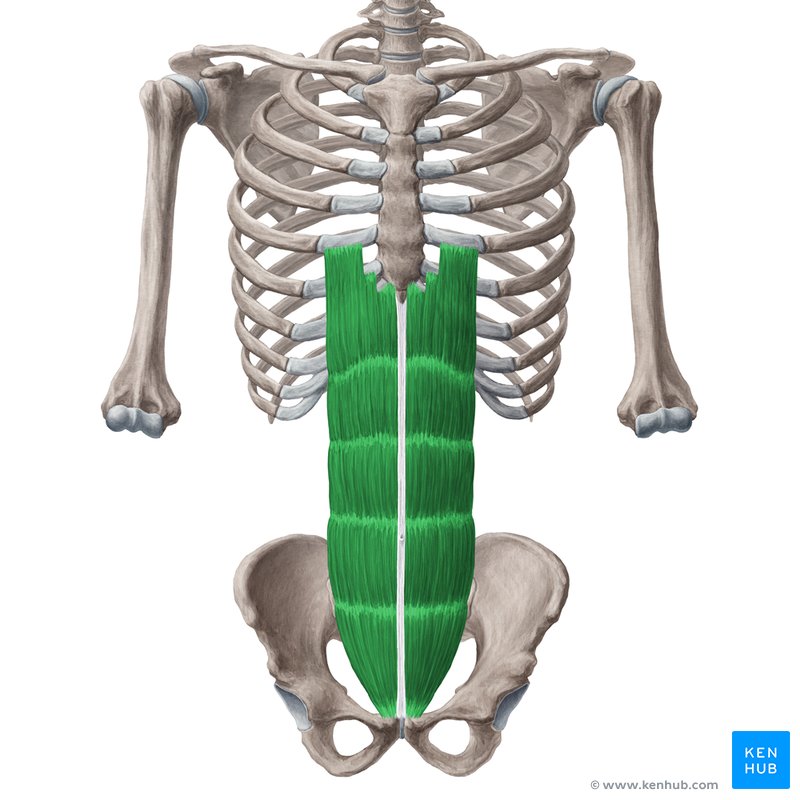
center of abdomen
rectus abdominis
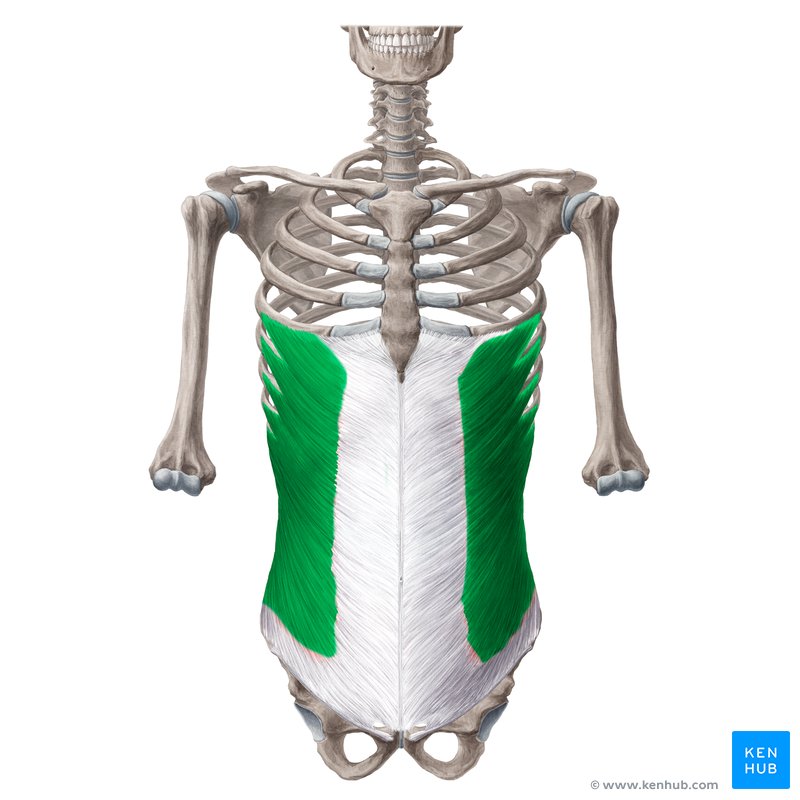
side of abdomen
external and internal abdominal oblique
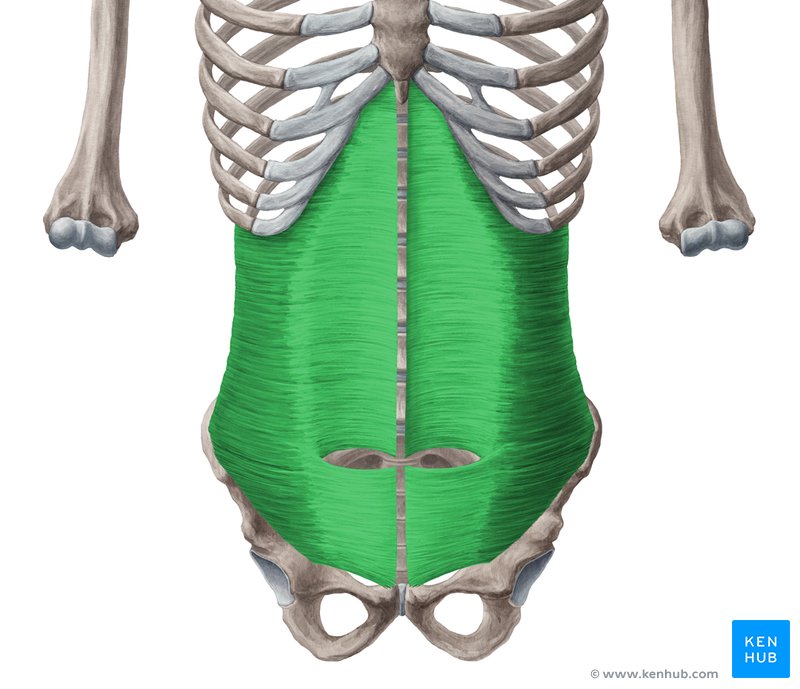
comprises the deepest layer of lateral abdominal wall and compresses abdomen
transversus abdominis
axial skeleton consists of
skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage