02 Experimental Chemistry
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Collection of gases
Depends on two factors
Solubility of the gas in water
Density of the gas as compared to air
Displacement of water: gas is insoluble/slightly soluble in water
Downward delivery: gas is denser than air
Upward delivery: gas is less dense than air
Collecting a dry sample of gas
Concentrated sulfuric acid
used to dry acidic gases
cannot be used to dry alkaline gases as it reacts with them
Quicklime (calcium oxide)
used to dry alkaline gases
cannot be used to dry acidic gases as it reacts with them
Fused calcium chloride
can be used to dry most gases
cannot be used to dry ammonia
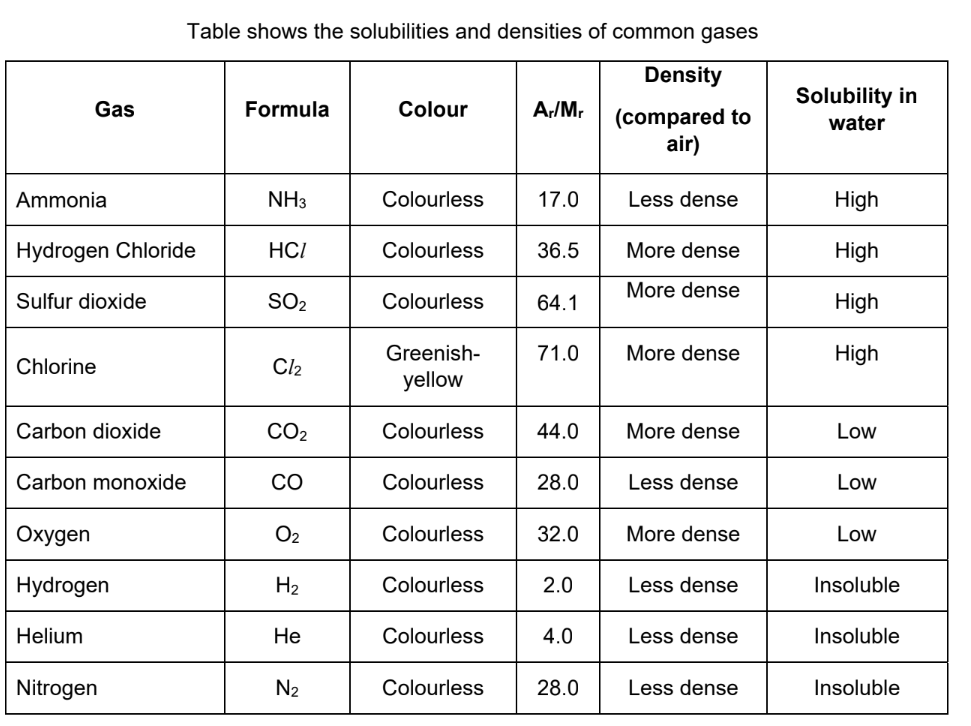
Properties of common gases
memorise colour, solubility in water and formula
see notes for bigger table
Definitions of chemistry terms
Atom
smallest particle of an element that has the chemical properties of the element
Molecule
two or more atoms covalently bonded together
Element
pure substances that cannot be split into two or more simpler substances by physical or chemical means
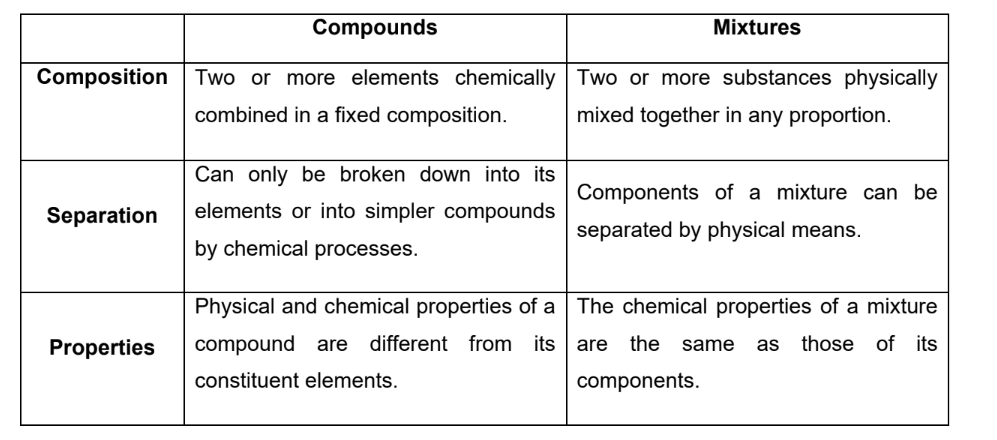
Compound
substance which contains two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed composition
Mixture
two or more substances physically mixed in any proportion
Differences between compunds and mixtures
What are the different methods of separation?
filtration
separating funnel
crystallization
evaporation
sublimation
simple distillation
fractional distillation
paper chromatography
Filtration
used to separate a mixture of an insoluble solid and a liquid/solution
residue: solid that remains on filter paper
filtrate: liquid that passes through the filter paper
Use of a separating funnel
used to separate immiscible liquids
mixture is poured into the funnel and the layers are allowed to separate out
The lower, more dense layer is run off by opening the tap and is collected first
Crystallisation
used to recover a soluble solid from a liquid
solution is first heated to make it saturated
saturated solution is cooled to form crystals
filter mixture to obtain crystals as residue
crystals are washed with a small amount of cold, distilled water
drying of the crystals between filter paper
employed for substances whose solubility differs appreciably with temperature (solubility must decrease significantly with decreasing temperature)
used for substances that will decompose on heating
Evaporation to dryness
used to recover souble solid from a liquid
recover solutes whose solubility do not change much with temperature
not used for substances that may decompose on heating
not used for crystals which lose their water of crystallisation and collapses into powders on heating
Sublimation
process by which a substance in the solid state changes to the gaseous state without passing through the immediate liquid state
separate a solid mixture from a sublimable component from a non-sublimable component by heating the mixture