Lecture 2.6 - Photosynthesis
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts related to photosynthesis and biological systems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Photosynthesis
The process by which chloroplasts in plants capture sunlight energy and convert it into chemical energy in the form of sugars.
Autotrophs
Self-feeder, produce organic molecules from CO2 and other inorganic molecules
Heterotrophs
Other feeding, cannot make their own food and live on compounds produced by other organisms
Chloroplast
Organelles in eukaryotic plant cells that carry out photosynthesis, containing their own DNA and ribosomes.
RuBisCO
An enzyme that catalyzes the fixation of carbon dioxide in the Calvin Cycle, and is considered one of the most important enzymes on Earth.
Calvin Cycle
The second stage of photosynthesis where ATP and NADPH are used to fix CO2 and synthesize simple sugars.
Photorespiration
A process in which RuBisCO adds O2 to the Calvin Cycle instead of CO2, leading to a waste of carbon and energy.
C3 plants
Plants that use RuBisCO for carbon fixation into a 3-carbon sugar, commonly affected by photorespiration under low CO2 conditions.
C4 plants
Plants that fix CO2 into a 4-carbon sugar in a separate layer of cells, allowing efficient photosynthesis in hot and arid environments.
CAM plants
Plants that fix CO2 at night and close stomata during the day to conserve water, incorporating CO2 as organic acids.
Sunlight provides…
The energy needed to feed almost the entire living world
Two main nutrition modes
Autotrophs and heterotrophs
Photoautotrohps
Use sunlight as energy source
Which of the following statements is a correct distinction
between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
1. Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning
with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic.
2. Only heterotrophs require chemical compounds from the environment.
3. Only heterotrophs have mitochondria.
4. Cellular respiration is unique to heterotrophs
Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic
Endosymbiotic theory
Chloroplasts were photosynthetic prokaryotes that lived inside ancestral eukaryotic plant cell
How many membranes does chloroplasts have?
Two, own DNA and ribosomes, divided by binary fission
What is inside the chloroplast?
Stacks of thylakoid sacs, which contain chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
The pigment that absorbs sunlight energy and makes photosynthesis possible
Name
The chemistry of photosynthesis
How is O2 formed
From H2O
Stages of photosynthesis
Light reactions, calvin cycle
Light reactions
Use light to synthesise ATP and harvest electron in NADPH
Calvin cycle
Uses ATP + NADPH to fix CO2 and synthesise simple sugars
Properties of light
Has both wave-like and particle-like properties
A particle of light is called a photon and each photon has a fixed amount of energy
Photosystem
Composed of several pigment molecules surrounding a reaction-center complex
The reaction-center complex is composed of
Special chlorophyll molecules and primary electron acceptor
Special chlorophyll molecules
Transfer energy as e- rather than photon
Primary electron acceptor
Captures that electron (redox reaction)
Name
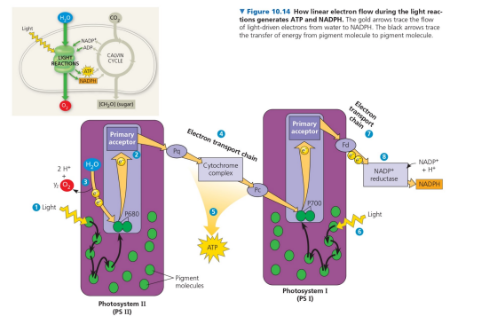
Photosystems 1 and 2
Properties of photosystems 2
Has chlorophyll a that is best at absorbing at 680nm in the reaction center (“P680”)
Harvests electrons from water (H2O → ½O2 + 2H+ + 2e-) to replenish P680
Passes excited e- to an electron transfer chain (ETC), which also powers an ATP synthase via chemiosmosis
Properties of photosystems 1
Has chlorophyll a that is best at absorbing at 700nm in the reaction center (“P700”)
Accepts electrons from ETC to replenish P700
Passes excited e- to another ETC, which reduces NADP+
Plants need more ________ than ________
ATP, NADPH
Photosystems 1 can produce…
ATP instead of NADPH
When light strikes chlorophyll molecules of photosystems 2, they lose electrons, which are ultimately replaced by…
Electrons released by splitting water
Calvin Cycle uses…
3x CO2 as carbon source
6x NADPH as a source of high-energy electrons
9x ATP as energy source to power the anabolic (endergonic) reaction
To make a 3-carbon sugar…
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate which is then used as starting material for organic molecules
What does RuBisCO stand for
Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase
RuBisCO
Catalyses carbon fixation, and thus arguably the most important enzyme on Earth
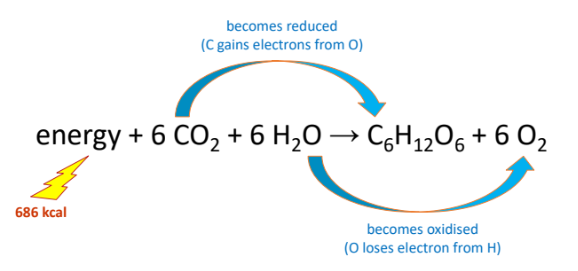
Photosynthesis is a redox reaction. H2O is _________ during the light reactions and CO2 is ________ during the Calvin cycle
Oxidized, reduced
Is RuBisCO perfectly ditinguish between CO2 and O2
RuBISCO does not perfectly distinguish between CO2 and O2
Early atmosphere CO2 and O2 percentage
20-30% CO2 and no O2
CO2 and O2 percentage today
0.04% CO2 and 21% O2
Photorespiration
Adding O2 to the Calvin Cycle instead of CO2, which wastes the cycle and instead of a 3-carbon sugar releases 2 molecules of CO2
What does plant cells need to conduct photosynthesis?
CO2 in and O2 out
Where goes gas exchange occur in plants?
Pores on leaf surface
Stomata
Small openings on the leaf surface that regulate gas exchange by allowing CO2 to enter and O2 to exit.
Main avenue of transpiration in plants
Stomata
What happens to plants on hot days?
Plants close their stomata to reduce water loss but that also means CO2 can no longer get in (or O2 out)
What does most plants rely on?
RuBisCO to fix CO2 into a 3-carbon sugar (called C3 plants)
What happens when internal CO2 levels drop?
RuBisCO starts using O2 instead and wastage by photorespiration increases
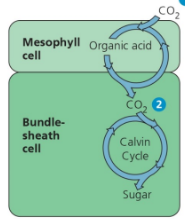
C4 plants
Have additional layer of cells where CO2 is first fixed on a 4-carbon sugar which is then spoon fed to RuBisCO in bundle sheath cells
C4 name
Spatial Separation
CAM plants name
Temporal separation
CAM plants
Others sock up on CO2 during the night, and then close their stomata during the day, slowing releasing the stored CO2 to feed RuBisCO
CAM plants CO2
Incorporated in variety of acids
Name
C4