Understanding Rocks and Minerals in the Lithosphere
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Lithosphere
The outer part of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
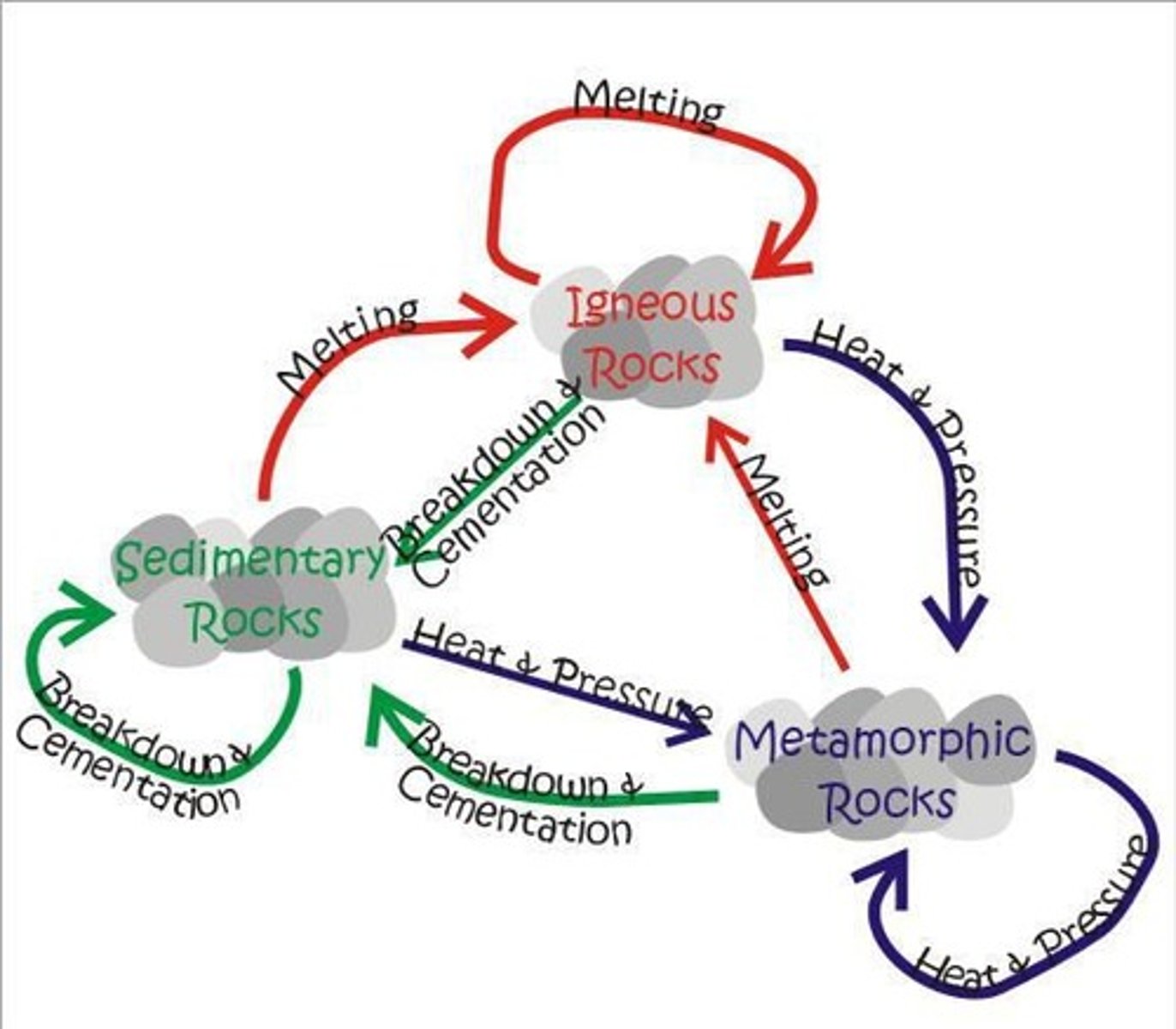
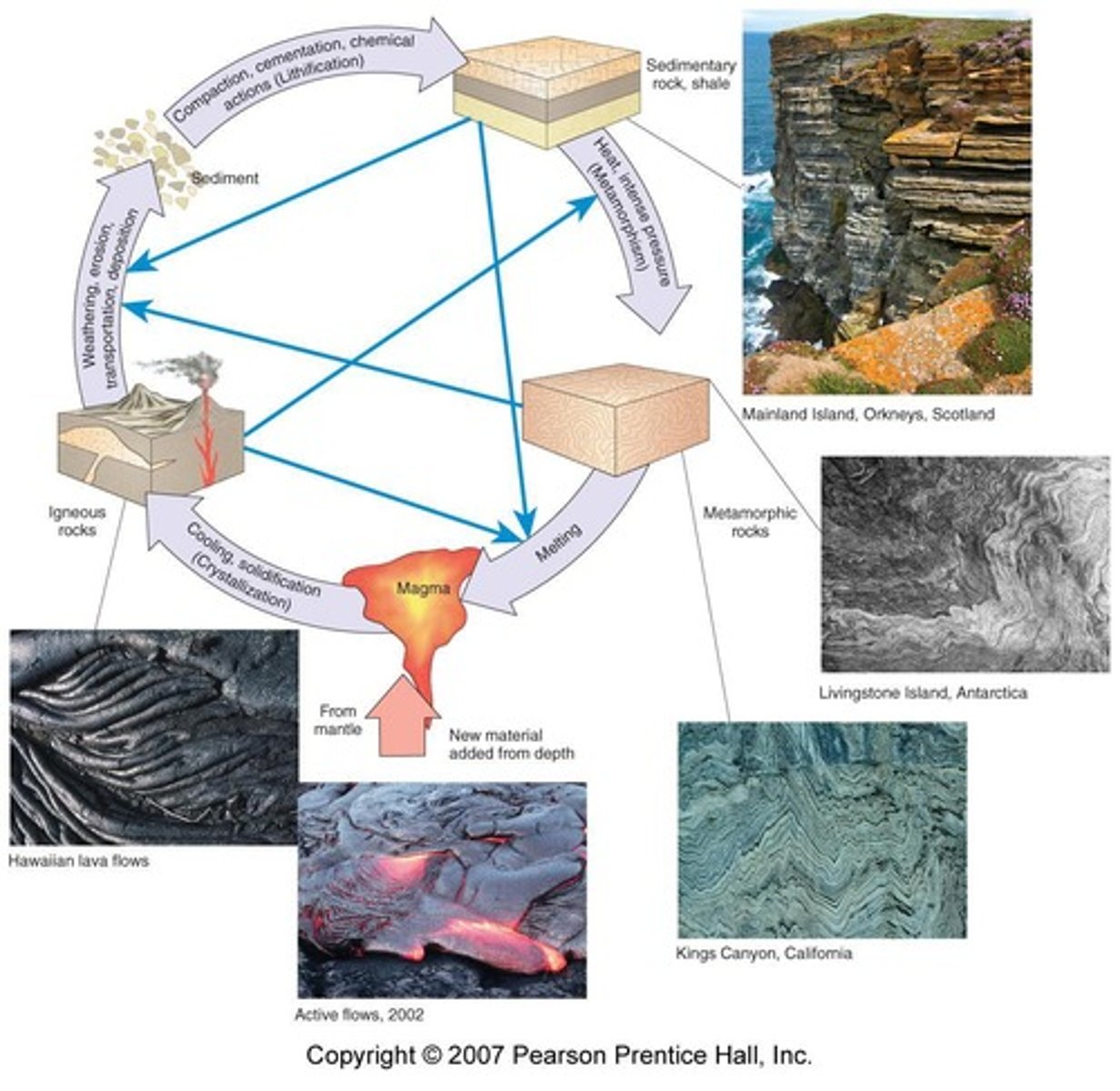
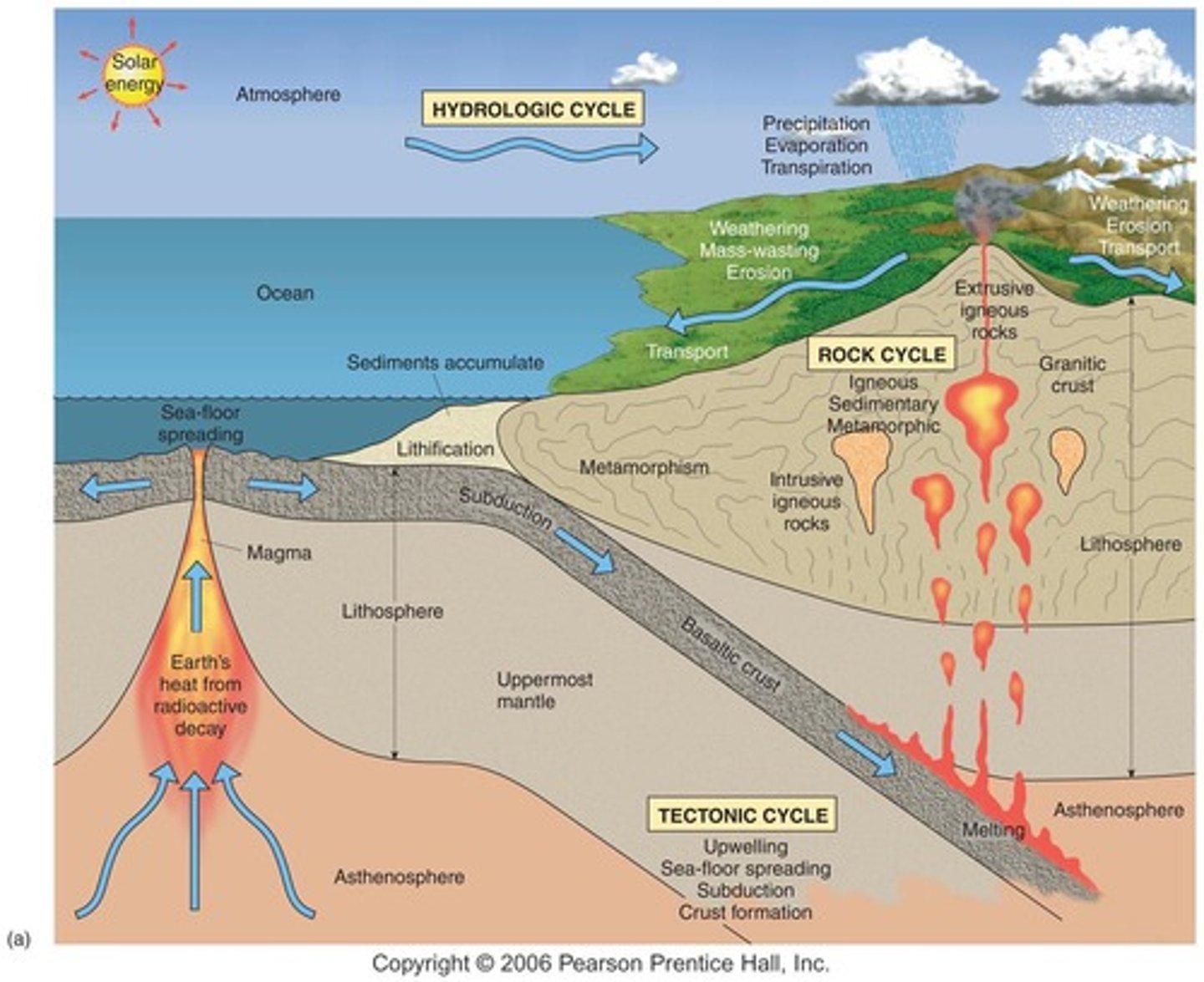
Geological Cycle
The cycle that describes the transformation of rocks through processes such as erosion, sedimentation, and metamorphism.
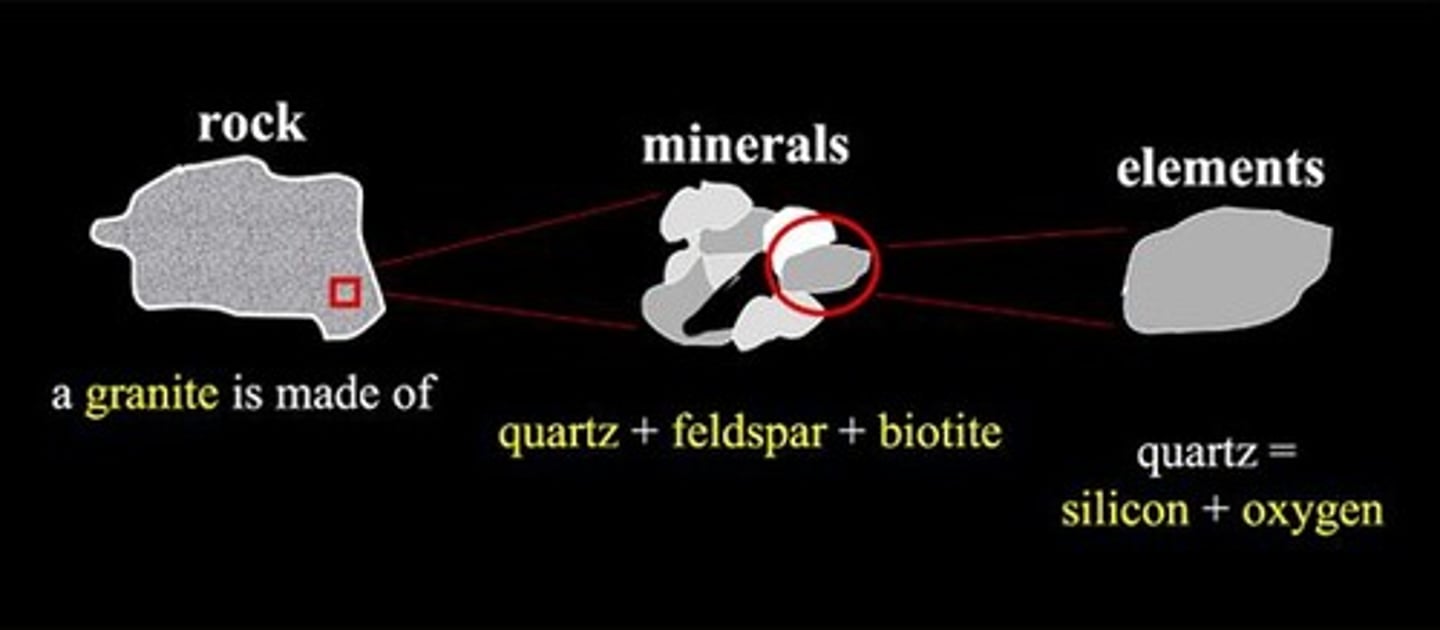
Mineral
Solid, naturally occurring, inorganic, crystalline substance.
Igneous Rocks
Rocks formed from the cooling and solidification of magma.
Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed by the accumulation and compaction of mineral and organic particles.
Metamorphic Rocks
Rocks that have been transformed by heat, pressure, or chemically active fluids.
Geologic Time Scale
A system of chronological dating that relates geological strata to time. The earth is 4.54 Billion years old, and the universe is 13.80 billion years old.
Quartz
A mineral composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), the most common single mineral in Earth's crust.

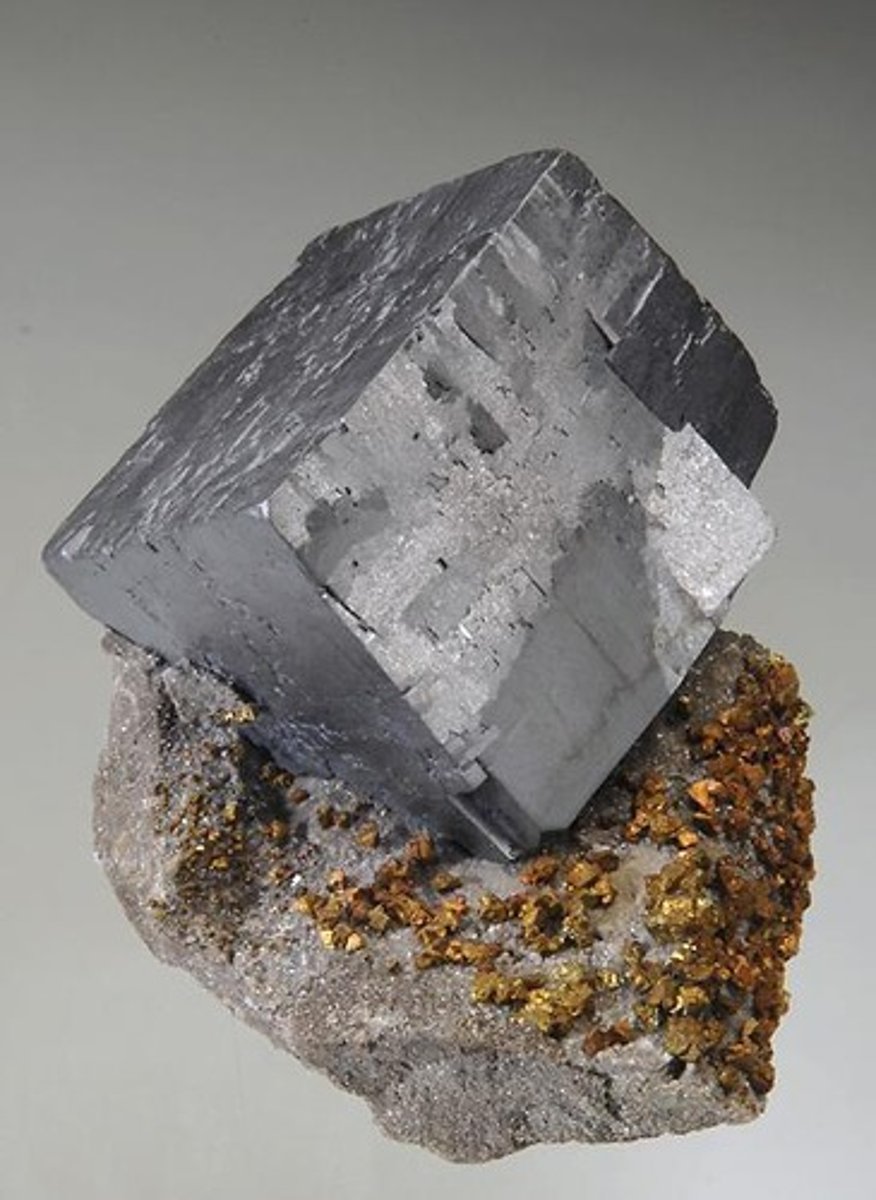
Galena
A mineral composed of lead sulfide (PbS), often found in ore deposits.

Felsic
Igneous rocks that are rich in silica and light in color.
Mafic
Igneous rocks that are rich in magnesium and iron, darker in color.
Extrusive Rocks
Igneous rocks that form from lava that cools quickly on the Earth's surface.
Intrusive Rocks
Igneous rocks that form from magma that cools slowly beneath the Earth's surface.
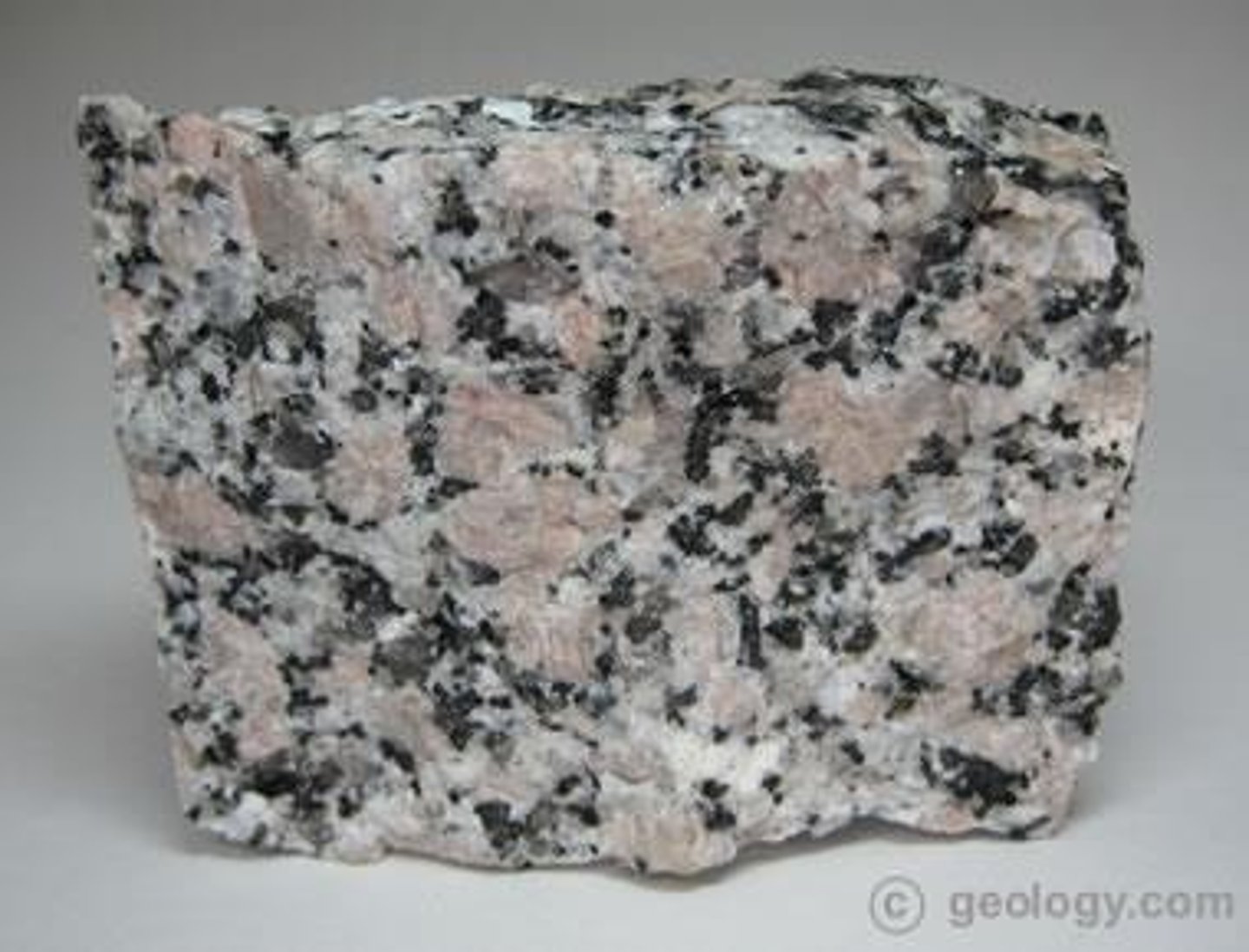
Granite
A felsic, intrusive igneous rock with a coarse texture.

Basalt
A mafic, extrusive igneous rock with a fine texture.
Rhyolite
An extrusive igneous rock that is fine-grained and typically light in color.
Crystallization of Magma
The process by which magma cools and solidifies to form igneous rocks.
Cooling Rate
The speed at which magma cools, affecting crystal size in igneous rocks.
Fine-grained Texture
An igneous rock texture characterized by small crystals due to rapid cooling.
Coarse-grained Texture
An igneous rock texture characterized by large crystals due to slow cooling.
Porphyritic Texture
An igneous rock texture characterized by large crystals embedded in a finer-grained matrix.
Glassy Texture
An igneous rock texture that lacks crystal structure, formed by very rapid cooling.
Oceanic Plates
Tectonic plates that are primarily composed of basalt and are denser than continental plates.
Continental Plates
Tectonic plates that are primarily composed of granite and are less dense than oceanic plates.
Tephra
Volcanic material ejected during an eruption, including cinders and ash.
Igneous Rocks
Rocks formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed from the accumulation and compaction of mineral and organic particles.
Weathering
Chemical and/or physical mechanisms that change existing rock into smaller particles.
Transportation
The movement of sediment by ice, air, or water to another area.
Deposition
The process where sediment material comes to rest.
Lithification
The process of turning sediment into rock through compaction and cementation.
Compaction
The process where the weight of overlying sediment decreases pore space.
Cementation
The process where chemical precipitation in pore spaces 'glues' the rock together.
Strata
Layers of sedimentary rock that relate to the depositional environment.
Bedding Planes
Horizontal separations between strata.
Joints
Vertical separations within beds of rock.
Clastic Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed from fragments of older rocks, transported by water, wind, and ice.
Bioclastic Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks made up of shell fragments.
Chemical Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed by the precipitation of dissolved ions in sea or lake water.
Organic Sedimentary Rock
Rocks composed of plant remains, such as coal.
Conglomerate
A type of clastic sedimentary rock consisting of angular or rounded gravel in a sand matrix.
Sandstone
A clastic sedimentary rock formed from sand deposited by oceans, rivers, or wind.
Shale
A clastic sedimentary rock that forms from mud deposited on the floor of shallow oceans.
Limestone
A chemical sedimentary rock primarily composed of calcite (CaCO3).
Dolostone
A chemical sedimentary rock primarily composed of dolomite (MgCaCO3).
Coal
A type of organic sedimentary rock composed of plant remains.
Depositional Environments
Different settings where sediment is deposited, affecting the characteristics of sedimentary rocks.
Mt. Everest
The summit at 29,029 ft above sea level, made of limestone containing ocean fossils.
Rocks
Made-up of minerals
Classes of Rocks
Broken Into 3 Classes: Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic
Metamorphic Rocks
Existing rocks 'Changed' by heat and pressure
Metamorphic agents
Heat, Pressure, Fluids
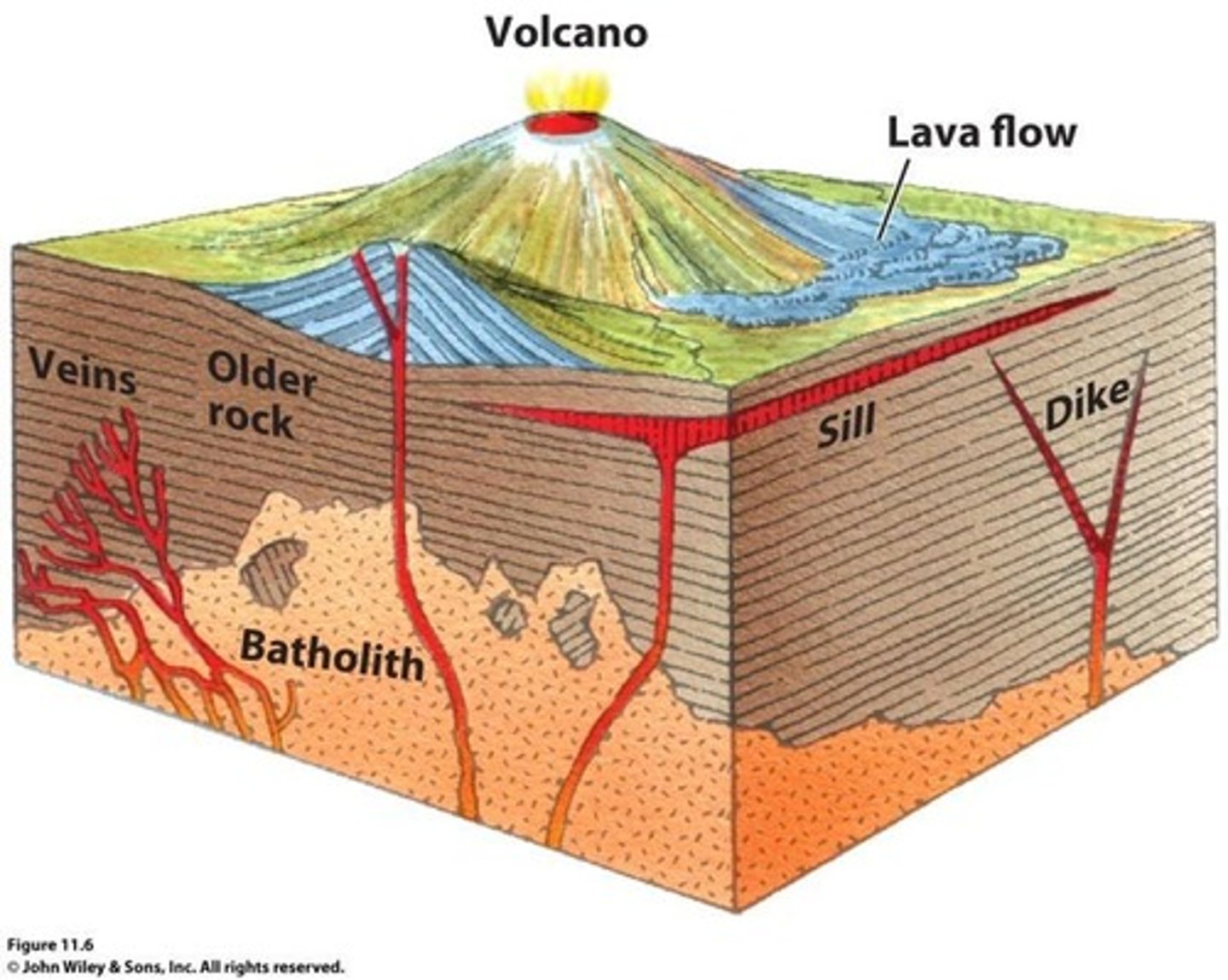
Contact (Heat) metamorphism
Intruding magma forming a batholith and a dike
Regional (Pressure) metamorphism
Changes rock over very large areas (regions) due to burial and tectonic activity
Confining Pressure
Results in horizontal foliation
Differential Stress
Results in wavy foliation
Foliated Metamorphic Rocks
Rocks like Gneiss and Slate formed by heat and pressure
Non-Foliated Metamorphic Rocks
Rocks like Marble and Quartzite formed by heat and pressure
Sedimentary Rocks
Formed when fragments of material and other rocks get compressed and cemented together without heat
Igneous Rocks
Form large portions of oceans and continents
Earth's Age
4.5 billion years old
Oldest dated material on Earth
4.4 billion year old zircon crystal from Australia
Oldest rock
~ 4.0 billion years old from NW Territories, Canada
Oldest rock in WI
~ 2.8 billion year old gneiss (metamorphic)
Importance of Rocks and Minerals
Used to reconstruct much of Earth's history and provide clues to past environments
Water Resources
Limestone Groundwater Aquifers supply ~25% of Global water supply
Granite Groundwater Aquifer
Formed from cracks in rock - joints/faults
Rocks and minerals
Supply valuable raw materials including fossil fuels
Coal Formation
Deposition of organic matter in swamps during the Late Mississippian (325 million years ago)
Tourism/Recreation
Rocks and sedimentary outcrops contribute to economic activities