chapter 12: psychomotor stimulants: cocaine and the amphetamines
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Erythroxylon coca plant
- Cocaine is an alkaloid found in the leaves
- native to South America and cultivated in northern and central Andes Mountains
- practice of chewing coca leaves began
~5000 years ago
Sigmund Freud
- recommended it for many ailments: treatment of alcoholism, morphine addiction, depression, and digestive disorders
- declared it was non-addictive (PO)
In 1886, Coca-Cola: introduced by...
John Pemberton
- contained caffeine and cocaine (until 1903)
- marketed as an alternative to alcohol during the temperance movement
~900,000 in US meet criteria for cocaine use disorder
Cocaine alkaloid
- extracted from coca leaves (0.6% -1.8% cocaine)
- converted to a hydrochloride (HCl) salt and crystallized
- water-soluble: can be taken orally, intranasally (insufflation), or by IV—not heat stable
smokable cocaine (e.g., “Rock”, freebase form)
How to make crack:
- Mix dissolved cocaine HCl with baking soda, heat the mixture, then dry it
- freebase crystals “crackle” when heated
- Produces profound euphoria
- Far less expensive than cocaine powder
- Antidrug Abuse Act of 1986:
1:100 rule crack : cocaine
- Fair Sentencing Act of 2010
reduced it to 1:18
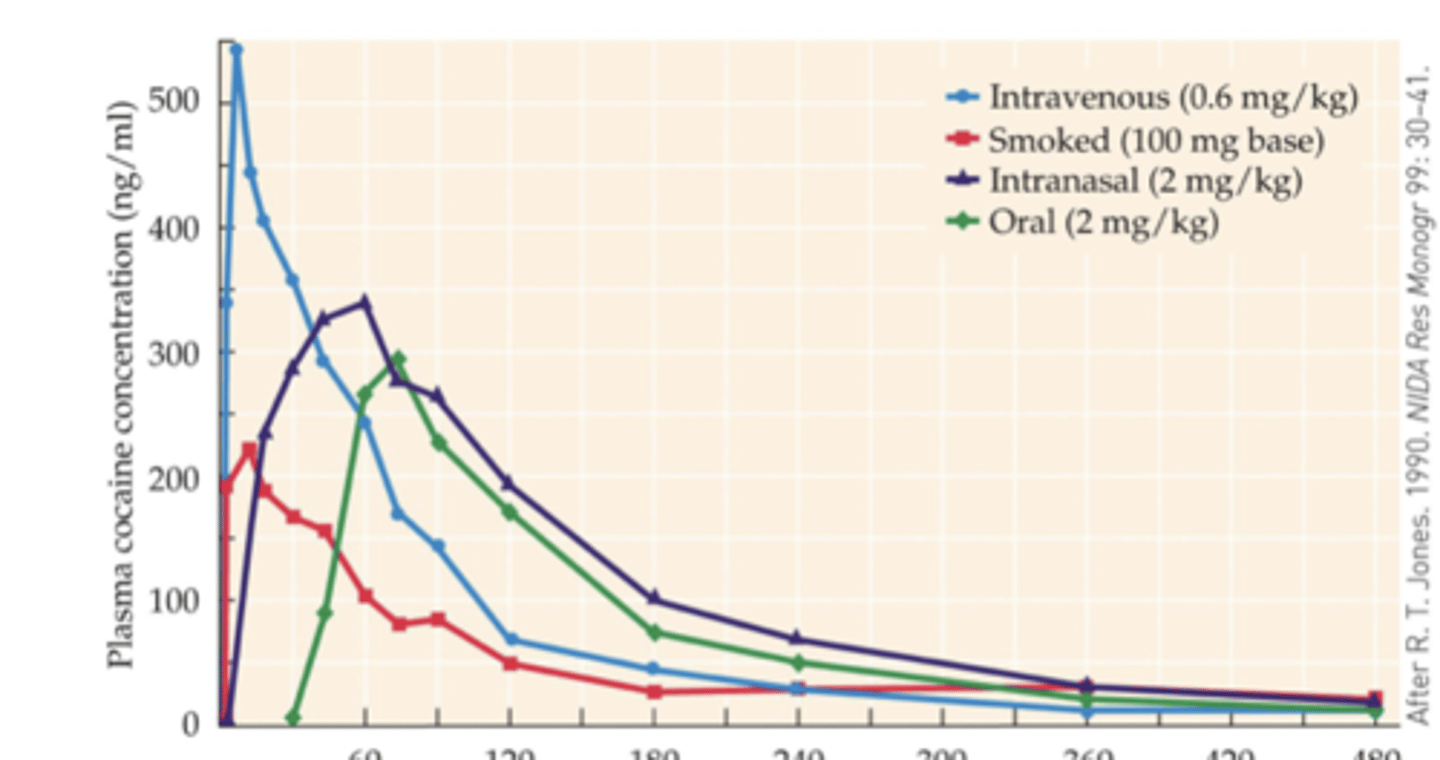
Smoking results in a...
- large surge of cocaine in the brain that is not reflected in peripheral blood concentrations
- Rapid entry into the brain is an important factor in the strong addictive properties of crack cocaine
Lipophilic
- readily passes through blood–brain barrier
- broken down by enzymes in the blood and liver (non-CYP)
- Rapidly eliminated
- half-life ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 hrs
- “high” lasts ~30 minutes
Metabolites
- benzoylecgonine>>>detected in the urine for several days
- When taken together, cocaine and alcohol produce a
unique metabolite: cocaethylene
-has biological activity similar to cocaine and has a longer half-life.
Monoamine reuptake inhibitor
- Blocks reuptake of dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), and serotonin (5-HT)
- Cocaine binds with highest affinity to the 5-HT transporter
- Blocking DA reuptake appears to be most important for cocaine’s
stimulating, reinforcing, and addictive properties (very important)
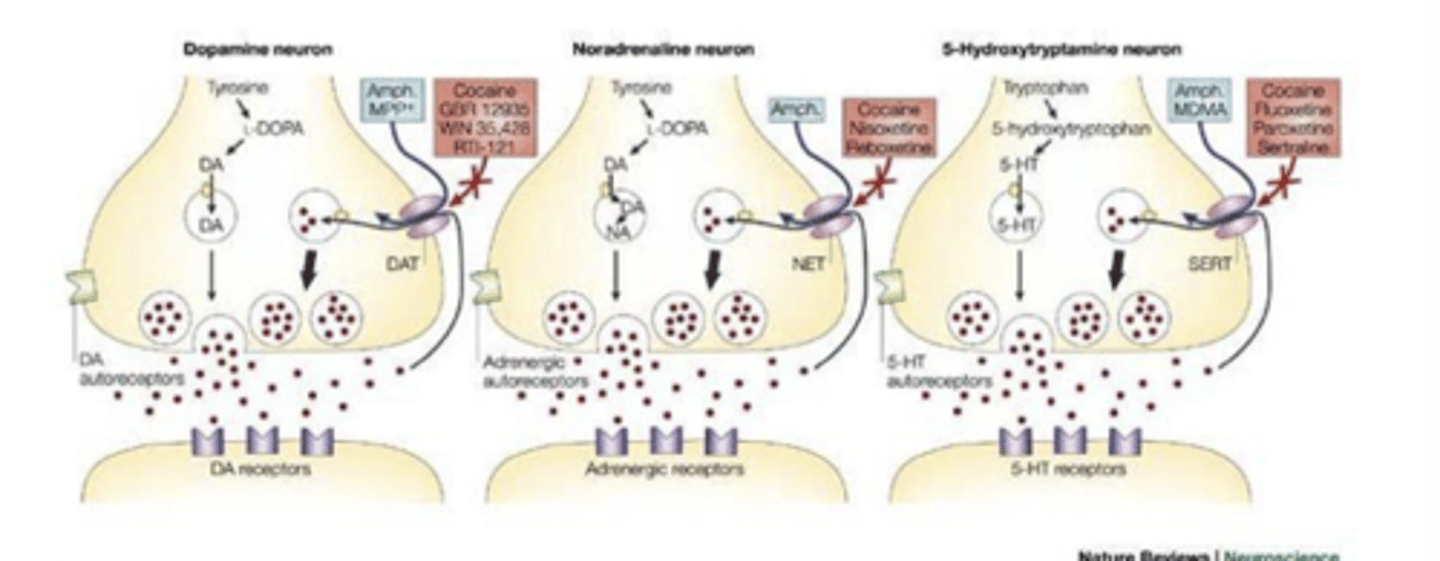
How do we know it is inhibition of DA reuptake that mediates the psychoactive effects?
- SSRIs and SNRIs do not produce psychostimulant effects
- DAT KO Mice display no further cocaine-induced increase
in activity SERT KO and NET KO show cocaine-induced increases in
activity
- destruction of NET nerve fibers has little effect on psychostimulant effects of cocaine
- destruction of DAT nerve fibers does not produce psychostimulant effects of cocaine
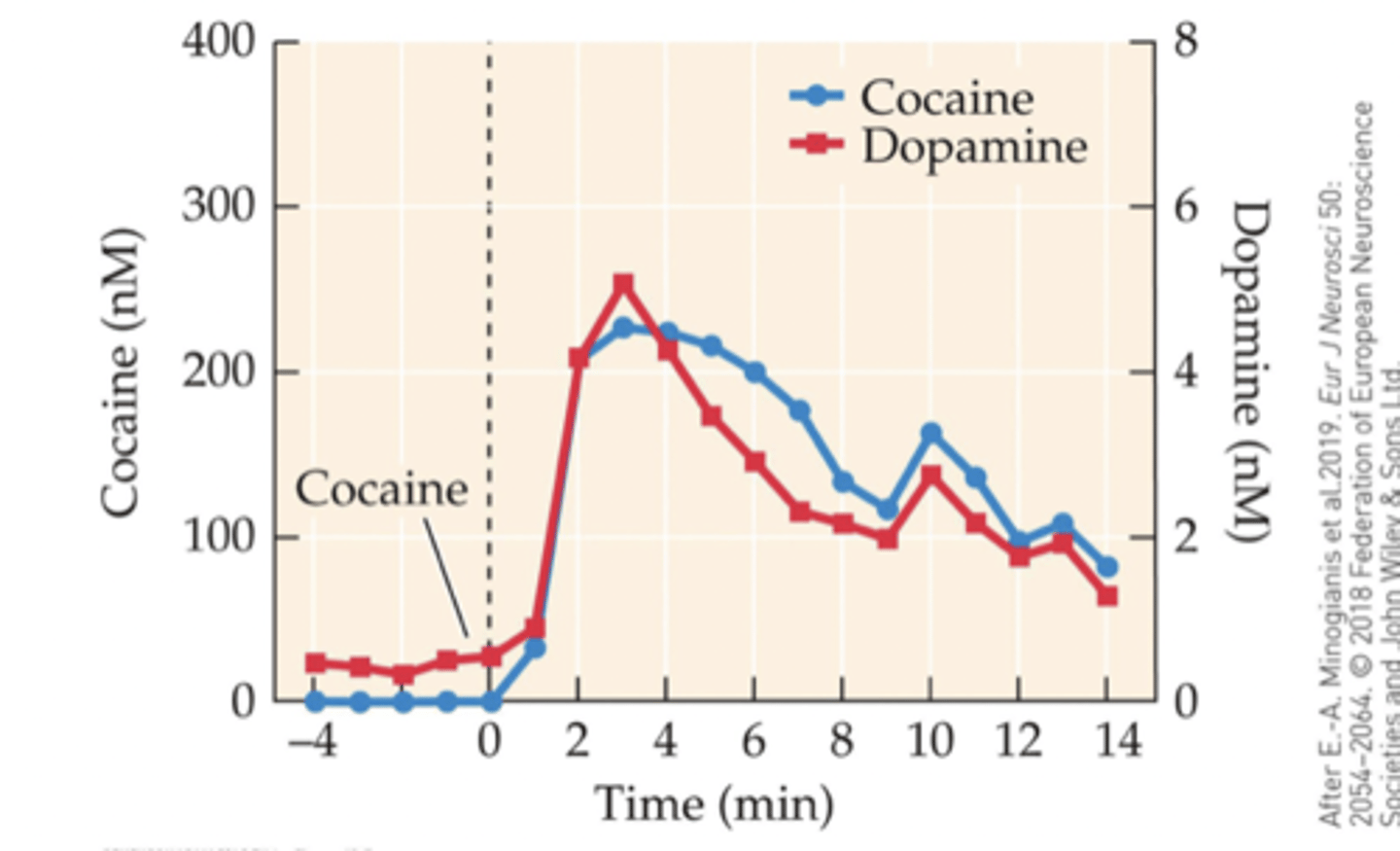
Time course of striatal cocaine and DA concentrations following rapid IV cocaine infusion
What happens at high concentrations of cocaine?
also inhibits voltage-gated Na+ channels
- acts as a local anesthetic
- Prevents transmission of signals along sensory nerves
- Schedule II drug
- Procaine (Novocain) and
lidocaine (Xylocaine) -> based on the structure of cocaine
- Also, a potent vasoconstrictor
Which of the following statements about crack cocaine is FALSE?
Crack cocaine is typically more expensive than powdered cocaine
Many positive characteristics that may contribute to its reinforcing properties become...
negative or aversive with higher dose and duration
Mesolimbic DA pathway
Key role in the reinforcing effects:
- Rats will self-admin cocaine directly into NAcc
- Re-instatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in previously extinguished animals: stimulated by microinjection of DA receptor agonists directly into the NAcc
- mutant mice expressing a cocaine- insensitive DAT (transported DA across the cell membrane but was not blocked by cocaine) show reduced cocaine self-administration
some methodological flaws in self administration studies
- All species readily learn to self-administer IV cocaine
- Unlimited access in primates and rodents>>>>leads
to continuous self-administration
- Will not eat or drink!
- powerful reinforcing properties and high abuse potential
- In self-admin studies, there is often no alternative reinforcer available
- Cocaine is available 24/7
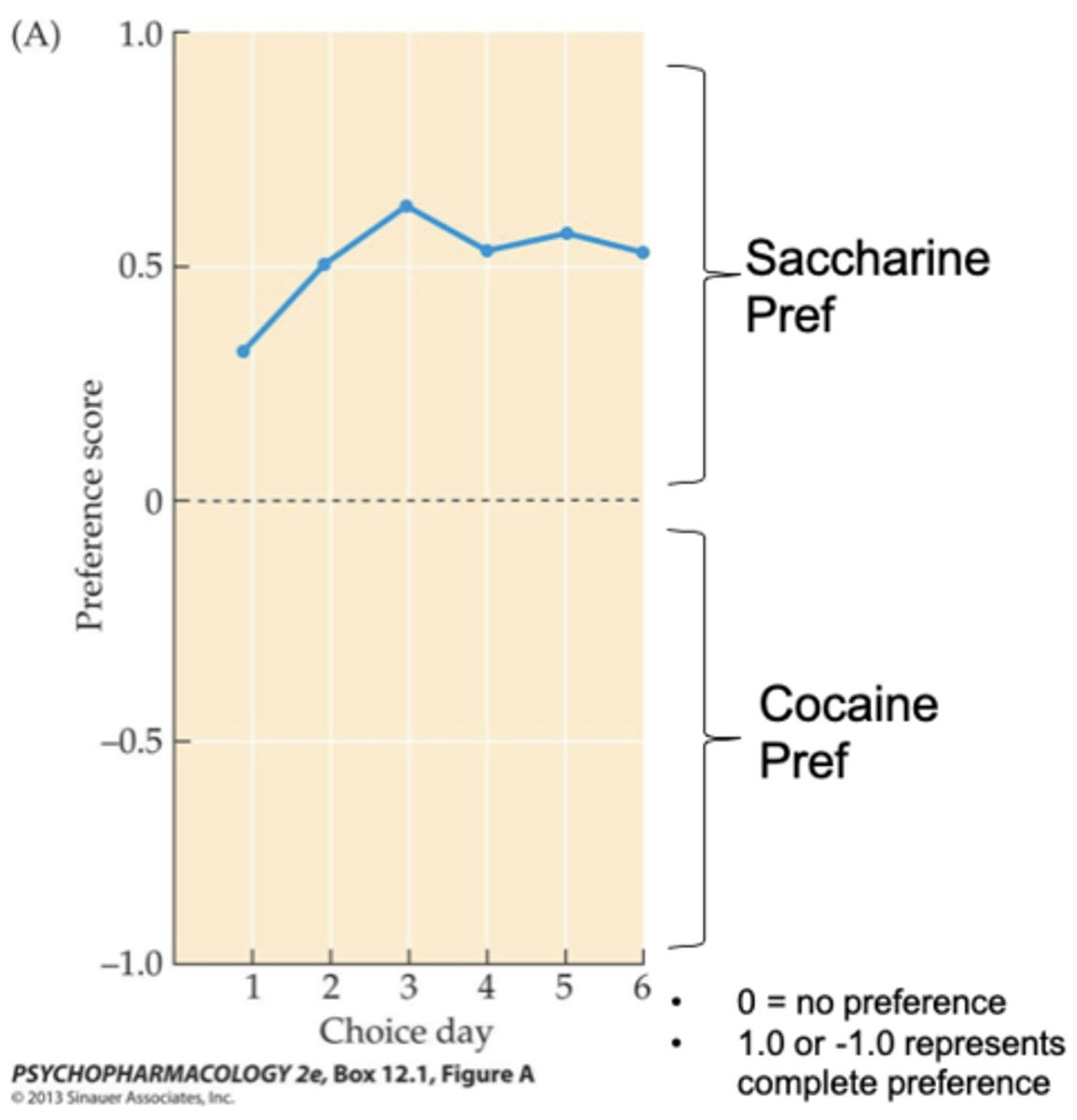
What happens when two reinforcers available?
- Animals were trained to press a lever for either .2% saccharin (very sweet!) or IV cocaine on FR1 schedule, separately
- Both reinforcers were made available at the time of test
- Cocaine has a higher breaking point than saccharine
Cocaine: sympathomimetic
- Activates sympathetic NS
- Increased heart rate, vasoconstriction>>> hypertension, hyperthermia
- Low doses: usually not harmful to the individual
- High doses can be toxic or even fatal
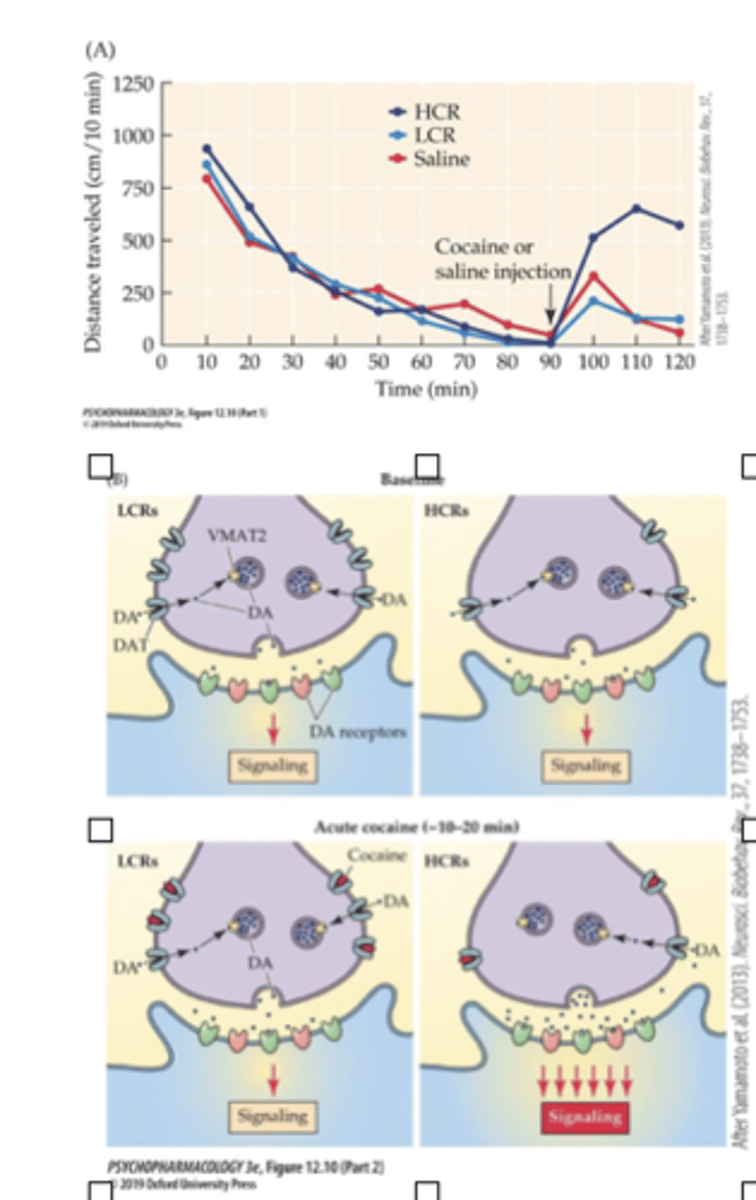
Rats divided into two groups based on response to single dose of cocaine...
1. Low cocaine responder (LCR)
2. high cocaine responder (LCR)
Baseline (Top):
- LCRs have higher basal #’s of striatal DAT than the HCR rats
- did not influence extracellular DA levels, DA signaling, or locomotor behavior under drug-free conditions
Acute cocaine challenge (Bottom):
- lower # of reuptake sites in HCR group resulted in more synaptic DA in HCR group (Bottom)
- There is spare “free” DAT in LCR group
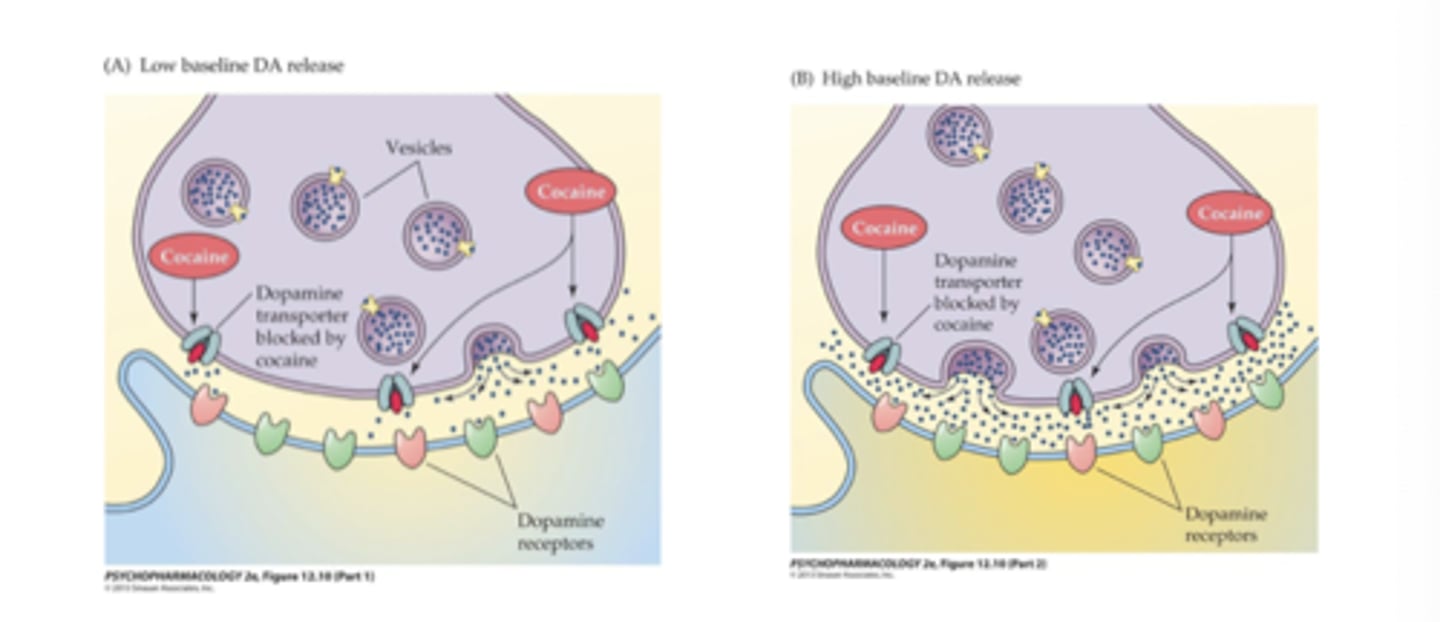
In humans, intensity of the "high" depends on...
amount of DAT occupancy ( to experience a “high”, DAT occupancy needs to be ~50%) but also on:
- Rate at which DAT occupancy occurs>>>ROI-dependent
- Baseline level of DA release in the mesolimbic pathway
-Individual differences—may account for susceptibility to
abuse
Capture ratio of cocaine:
~15% of initial intranasal users become abusers (“cocaine use disorder”)— most do not
- People usually start by snorting; some have a strong anxiety response and don’t try it again
- reinforcers in the early stages: stimulating, euphoric, and confidence-enhancing effects
- In humans, the euphoric effect of cocaine shows tolerance over time
- Contributes to increased drug-taking
Social responses may play a role in abuse— positive attention from friends
Other factors contributing to abuse
- Comorbidity with other psychiatric disorders
- “incubation” of cocaine craving
- Craving increases over time following termination of use>>>relapse
- Abnormal function of PFC in patients with Cocaine dependency—disinhibition, lack of self-monitoring
- “Driving a car without brakes”
- Seen in studies of primates repeatedly exposed to cocaine
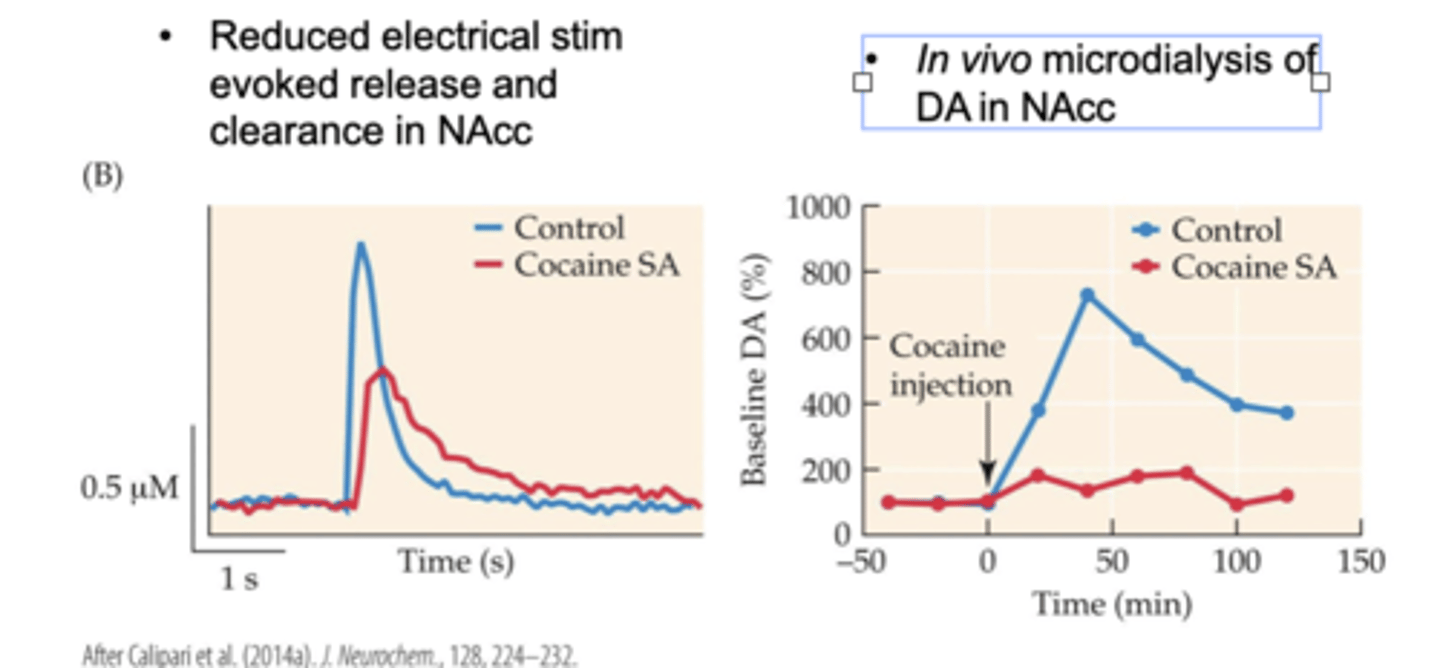
Neurochemistry of Tolerance in NAcc
- adaptations in the NAcc underlying tolerance due to long-
access cocaine self-administration
- Reduced electrical stim evoked release and clearance in NAcc
- In vivo microdialysis of DA in NAcc
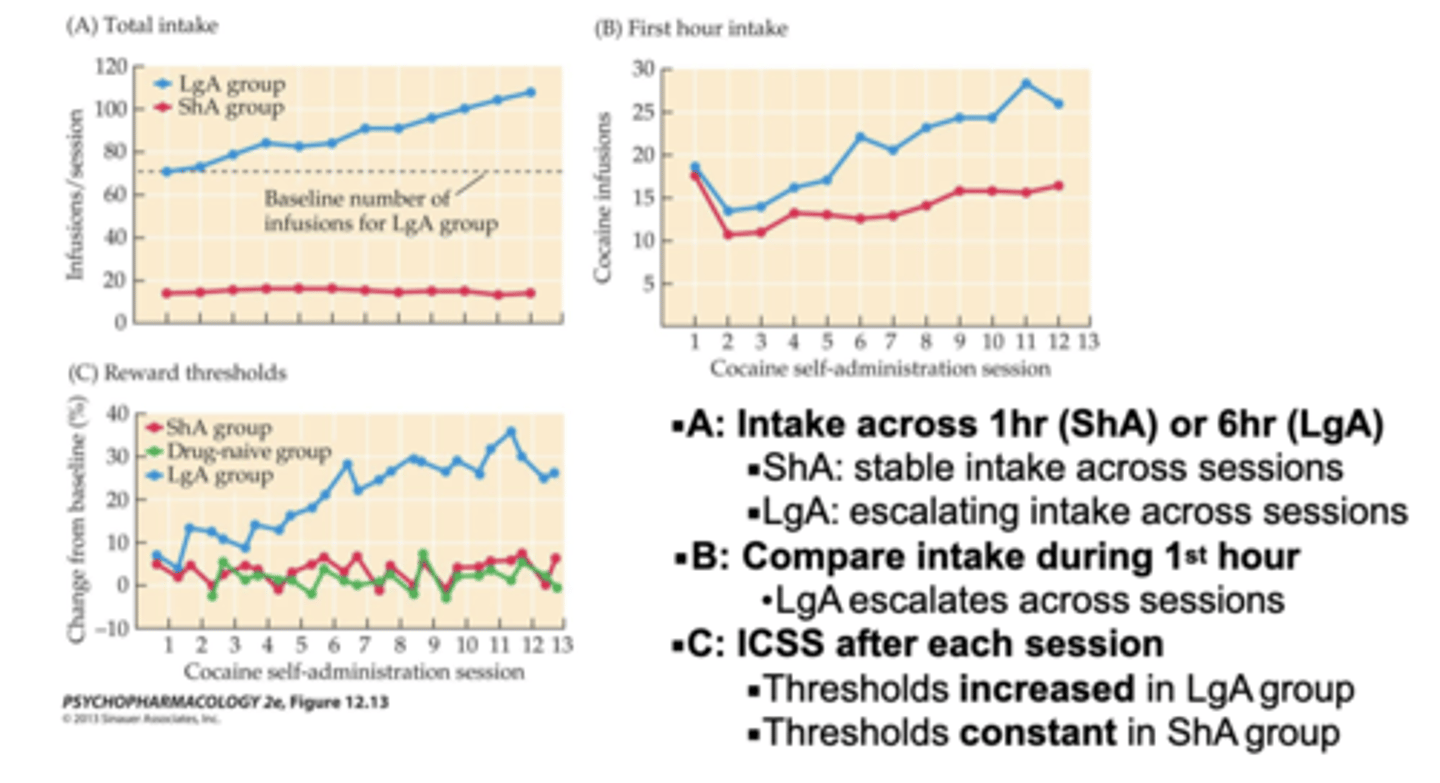
Modelling the transition from recreational to compulsive use
ShA-1 hour access sessions
LgA- 6 hour access sessions
A: Intake across 1hr (ShA) or 6hr (LgA)
ShA: stable intake across sessions
LgA: escalating intake across sessions
B: Compare intake during 1st hour
LgA escalates across sessions
C: ICSS after each session
Thresholds increased in LgA group
Thresholds constant in ShA group
PET imaging of cocaine-dependent
individuals:
- Baseline D2 receptor binding is reduced in the cocaine-dependent subjects (Comparison: Between Subjects)
- MP (Methylphenidate) has a greater effect in the control subjects (Comparison: Within Subjects)
- DA system in dependent individuals is less responsive to DA reuptake blocking>>>contributes to behavioral tolerance
- a "hypodopaminergic" state>>> lower levels of D2 receptors
Raclopride binding
Raclopride binds to D2 receptors and is displaced by released DA
Systemic effects of chronic cocaine use:
- Organ systems: heart, lungs, GI system, kidneys
- perforation of the nasal septum ( from frequent snorting)
- Cocaine use during pregnancy:
- Some studies show attention deficits and behavioral or cognitive abnormalities in the child
- High-dose use >>> panic attacks or temporary paranoid psychosis with delusions and hallucinations
- Elevated body temperature >>>multiple organ
failure is a major cause of OD death
Pharmacological approaches to treat cocaine abuse:
No FDA-approved medications
•Ketamine?
•A Diabetes Drug?
•Gene therapy?
Cocaine self-administration disrupted by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist ketamine: a randomized, crossover trial
- a significant decrease in cocaine use—by 67 percent relative to baseline (>24 hr post infusion)
- A few patients remained abstinent for two weeks
Ozempic (Semaglutide)
- All completed clinical trials used older GLP-1 analogs
- Semaglutide binds more tightly to the GLP-1 receptor and induces greater weight loss than previous drugs.
- almost all new trials use
semaglutide, hoping they will reveal greater capabilities against addiction, help identify which patients are most likely to benefit, and clarify how the drugs work.
- Insurance Issues--$12k/year
- Proabably not a cure-all--might be more like antidepressants, which only work for a fraction of patients.
- "You can help a lot of people even if
only one in five responds."
GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide)
- a satiety hormone—produced in intestine when food enters
- a neuropeptide—produced in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of hindbrain
- GLP-1 neurons in NTS send direct projections to VTA and nucleus accumbens
- GLP-1 receptors in brain regulate intake of highly palatable food
Injection of GLP-1 agonists directly into the VTA...
reduces intake of palatable food
- no effect on consumption of normal chow
GLP-1 signaling in the brain may represent a...
‘brake’ that functions to reduce cocaine craving-induced relapse
Amphetamine
- Synthetic derivative of
phenylethylamine
- parent compound of a family of synthetic psychostimulants that are structurally related to DA
- indirect catecholamine
agonists
natural amphetamines
cathinone, ephedrine, pseudoephedrine
Amphetamine and methamphetamine
- indirect agonists of the catecholaminergic (NET and DAT) systems
Two modes of action:
1. enter DA (NE) nerve terminals via uptake by DAT (NET) and cause vesicles to release DA (NE) into cytoplasm
2. Reversal of DAT (NET)
- Reversal of DA transport is mediated by DAT phosphorylation by calcium/calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII) and protein kinase C (PKC).
- Leads to very high levels of DA (NE) in the synaptic cleft
Amphetamine: PO or IV
"uppers," "bennies," "dexies," "black beauties," "diet pills"
Methamphetamine
more potent on CNS than Amphetamine
- “meth,” “speed,” “crank,” “zip,”
“go”
- taken orally, snorted, injected
IV, or smoked
- Methamphetamine hydrochloride (HCL) in a crystalline form >>>smoking (“ice” or “crystal”)
Methamphetamine:
- usually synthesized from pseudoephedrine
- inexpensive to make and is highly addictive
- Some users (“speed freaks”) go on binges of repeated IV injections to experience recurrent highs
- During a “run”, the drug is typically ingested every 2 hours for as long as 3 to 6 days, with little sleep or eating
- Barbiturates or other depressants are sometimes used to “take the edge off” during a run or to aid sleep afterward
speedball
IV amphetamine or methamphetamine + heroin
Amphetamine and methamphetamine are metabolized by the...
liver at a slow rate
long half-lives
Amphetamine: ~6 hours
Methamphetamine: ~12 hours
Therapeutic uses:
Nasal and bronchial decongestants (Benzedrine, OTC: late 30’s)
- Taken off OTC market in 1959
- Favored by artists and mathematicians: powered a great deal of innovation in mid 20th century
- Narcolepsy (Modafinil)
A- ppetite suppression and weight loss—Desoxyn
- Induces CART
- Psychostimulants (methylphenidate) in low doses produce a calming effect in more than half of children with ADHD
Stimulant Meds for ADHD
- Dexedrine (D-amphetamine)
- Adderall (amphetamine salts)
- Vyanse (lisdexamfetamine)
- Ritalin (Methylphenidate)—DAT and NET blocker
These are amphetamines, leading to backlash. So, can we have drugs that specifically act on norepinephrine system.
Non-stimulant Meds (No direct effect on DA)
- Strattera (atomoxetine): NET inhibitor
- DA is also an effective substrate for NET
- NET, not DAT, is the major source of DA uptake and clearance in the PFC.
- atomoxetine acts like methylphenidate in the PFC by increasing extracellular levels of both NE and DA
- Intuniv (guanfacine): a2 agonist (post-synaptic)
Hypothesis for ADHD
DA and NE activity in the PFC is deficient in patients with ADHD
trends for ADHD
- Over the 20-year period, the estimated prevalence of diagnosed ADHD in US children and adolescents increased from 6.1% in 1997-1998 to 10.2% in 2015-2016 (P for
trend <.001).
- All subgroups by age, sex, race/ethnicity, family income, and geographic regions showed a significant increase in the prevalence from 1997-1998 to 2015-2016.
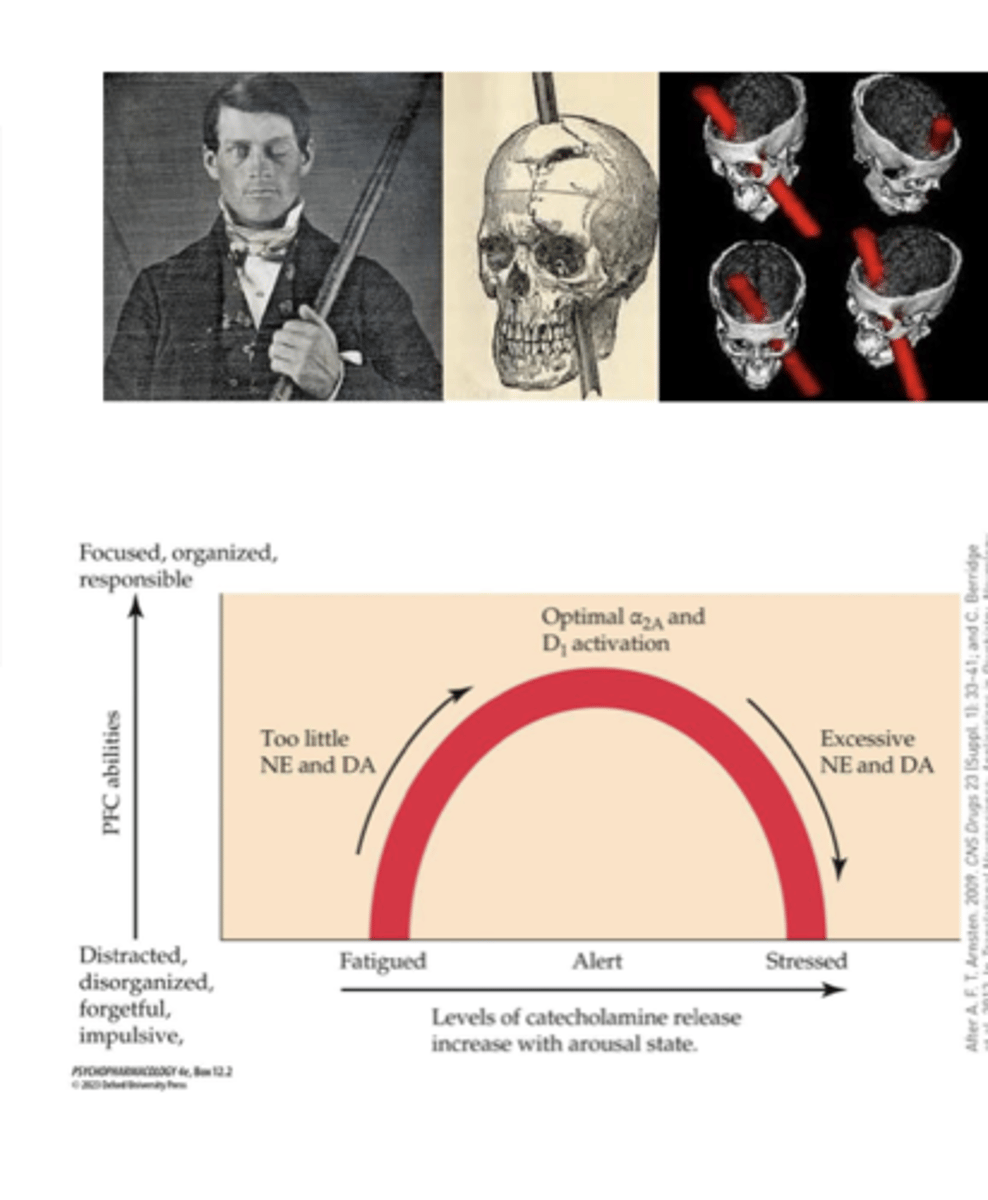
PFC functioning is an...
inverted U-shaped function mediated by the activity of catecholaminergic systems
- ADHD meds enhance catecholaminergic activity in the PFC to restore balance
- ADHD is fatigued state
too much catecholamine can have negative effects
Amphetamine-induced psychosis
Provided initial impetus and support for the DA hypothesis of Schizophrenia
- Chronic, high-dose abuse
>>>psychotic reactions
- visual, olfactory, and/or auditory hallucinations
- development of a paranoid state with delusions of persecution though some insight remains
- Formication
- Extreme anxiety and fear
None of these symptoms are all that relevant to schizophrenia
Neurotoxicity
- Methamphetamine use causes damage to DA axons and terminals
- Remember Ricuarte?
- doses used are often much higher than those used in human users
- also damages serotonergic fibers in several brain areas (neocortex, hippocampus, and striatum)
Many potential mechanisms for neurotoxicity
oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, neuroinflammation (microglial activation), and mitochondrial dysfunction
Brain imaging in amphetamines
reduction in striatal DAT binding with
chronic methamphetamine and methcathinone use
- Damage is similar in a Parkinson’s disease patient,
- DA innervation of the striatum is known to be severely compromised
- However, loss of cell bodies in SN is not seen-–a neurochemical response, not physical damage?
Heavy methamphetamine use ->
- cardiovascular problems including elevated heart and blood pressure, atherosclerosis, heart attack, increased risk of stroke, and increased mortality rate
- anecdotal evidence of premature aging
Meth Mouth
- broken, discolored and rotting teeth
- salivary glands dry out>>>allows the mouth's acids to eat away at the tooth enamel, causing cavities
- Teeth are further damaged when users obsessively grind their teeth, binge on sugary food and drinks, and neglect to brush or floss for long periods of time
Synthetic cathinones (“Bath Salts”, ”Zombie drugs”, Flakka )
- contain one or more human-made chemicals related to cathinone
- chemically similar to amphetamines, cocaine, and MDMA
- marketed as cheap substitutes for these drugs
- PO, snorted, smoked, or IV
- Animals will self-administer
Symptoms:
- excited delirium: extreme agitation and violent behavior
- paranoia
- increased sociability
- increased sex drive
- hallucinations
- panic attacks
For many years, cocaine and amphetamine were ____ thought to be addictive substances
not
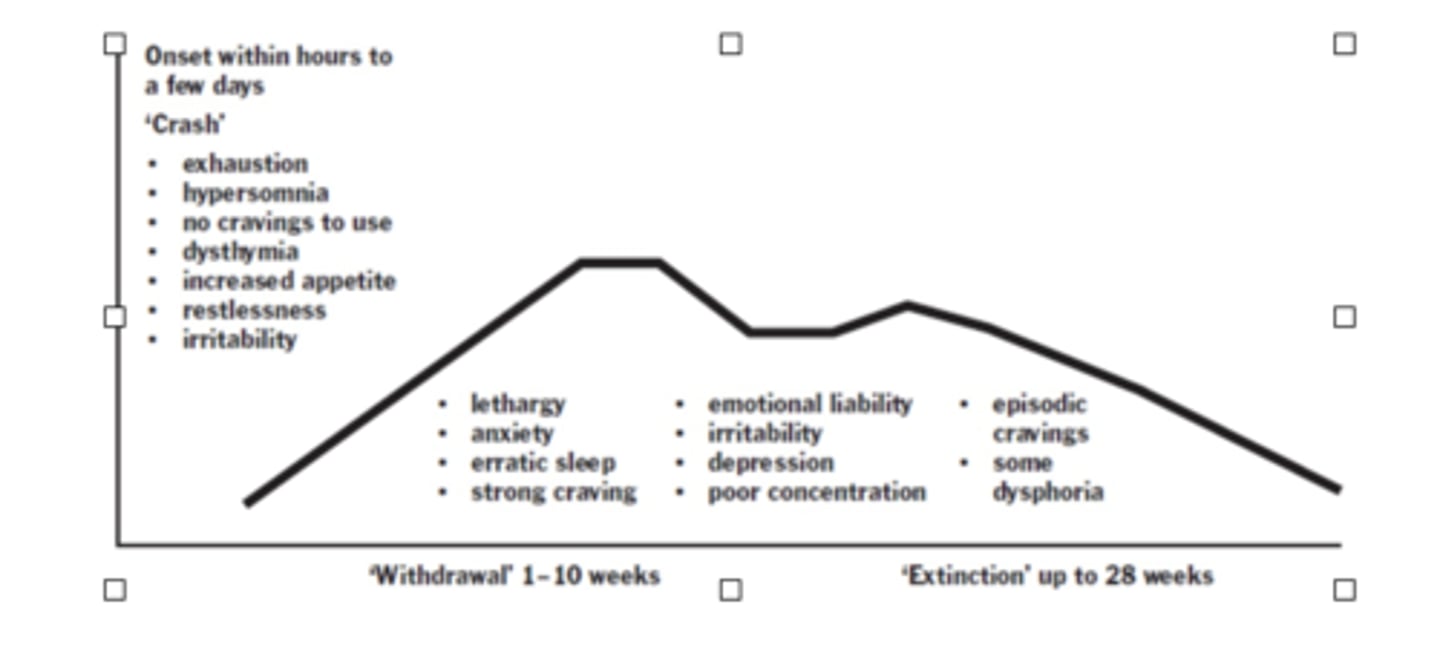
Psychostimulant withdrawal often has...
no visible physical symptoms
Withdrawal from cocaine occurs rapidly after...
last dose
- Due to the relatively short half-life of cocaine
Gawin and Kleber's Phasal Model of Cocaine Withdrawal (1986)