Distance Magnification and Telescopes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Telescopes are used as ________ vision devices for short ______ tasks such as street signs, bus numbers, recognizing persons face, or ______ distance vision such as television, movies etc.
distance vision
spotting
extended
T or F: telescopes may be used for extended near and intermediate vision
TRUE
ie. computer work, reading, other activities
Examples of functional goals
street signs
bus numbers
whiteboard at school
television
T or F: telescopes should be used for active mobility purposes
FALSE
** since objects look closer than their actual distance - objects may move faster when observed through telescopes (dangerous)
Should patients walk around or step off curbs or walk across the street while looking through telescopes?
NO
List some monocular telescope types
hand help spotting
on clip
finger ring
mounted
( example pics on slides)
List some examples of binocular telescopes
full diameter
bioptic mount
reading position
The convex lens which is closest to the object of regard is known as the _______ lens.
What is this also known as?
objective lens (F1)
Entrance pupil
The convex/ concave lens which is held closest to the eye is known as the ________ lens
what else is this known as?
eyepiece lens (F2)
ocular lens
Two types of telescopes diagram
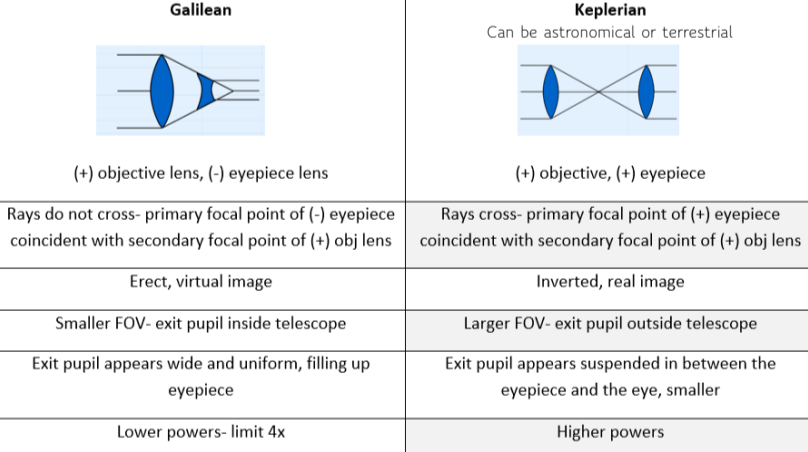
How to create an afocal Galilean telescope? (ie. parallel in, parallel out)
Primary focal point of concave (-) lens (F2) is coincident with the secondary focal point of the convex (+) lens (F1)
** typically used in weaker powers, smaller and lighter weight
How to create an afocal Keplerian telescope? (ie. parallel in, parallel out)
Primary focal point of our second convex lens (+) is coincident with the secondary focal point of our first convex lens
** typically used in stronger powers and are multi-element
in GENERAL, the image (secondary focal point) created by the _____ lens (F1) is coincident with the primary focal point of the ________ (F2)
Objective, Eyepiece
So how do we make the inverted image from Keplerian telescope into a erect image?
using erecting prism
How does erecting prism work?
erecting prism inserted into optical path
results in erect image leaving eyepiece (F2) of the telescope
T or F: the telescopes we almost always Rx are going to be focal telescopes focused for “distance/ not infinity” or “intemrediate/ near tasks)
TRUE
The magnification from these telescopes is _____ and _________ ______ magnification - which results in what?
Angular, relative distance = equivalent power
So for distance, devices and telescopes use what term for magnification?
Hint: X or Diopters?
X
Magnification of telescope formulas
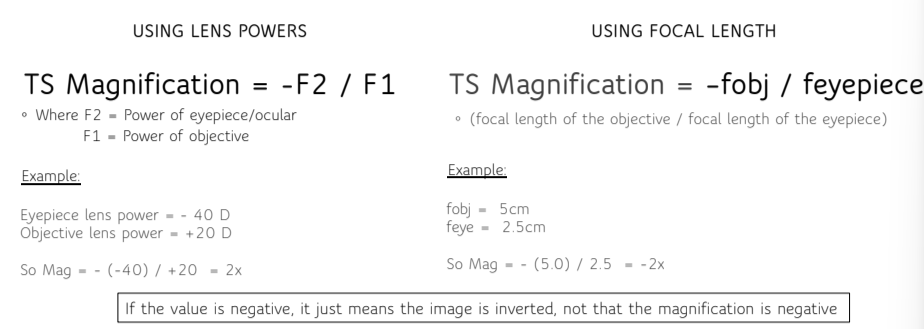
Tube length formula
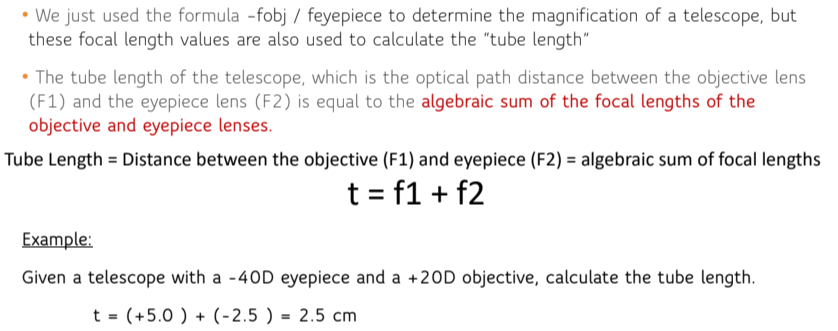
What can tube length help to adjust?
We can ________ the tube length to ________ the overall power of the telescope and focus closer
focus for different distances
increase tube length, decreases overall power
Tube length example

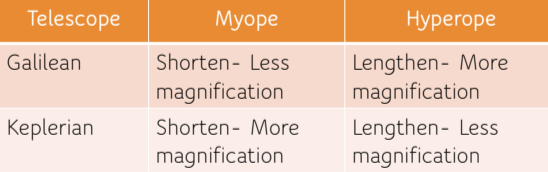
Correcting myopes
myope = shorter tube length
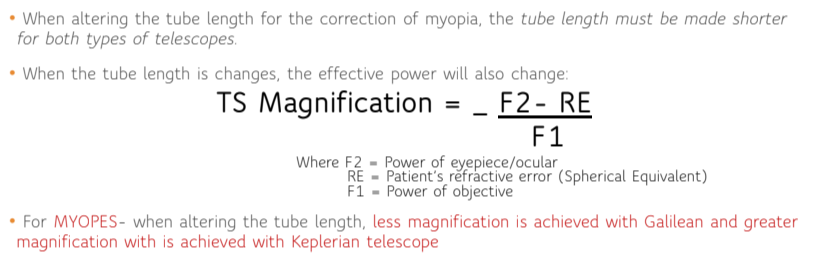
For myopes, when altering tube length = ______ mag achieved with galilean and ________ mag with keplerian
less = galilean, greater = keplarian
How do you correct for hyperopes?
Hyperopes obtains ______ mag w/ galilean and achieve ____ mag w/ keplarian
opposite - tube length must be longer
Galilean = more, keplarian= less
Correcting table diagram
(for both keplerian and galilean)
How are telescopes labelled?
Magnification x objective diameter
What does each part of this mean: 5× 20 11*
5X, 20mm, 11 degree FOV

What is an exit pupil
small image of the OBJECTIVE lens and is seen as the view of the objective lens through the ocular lens
** located quite close to eyepiece
Where is exit pupil located in Galilean?
INSIDE telescope
virtual image
short distance in front of the eye
telescope should be held as CLOSE to user’s eye as possible
Where is exit pupil located in Keplerian telescope?
OUTSIDE telescope
real image
located in space between the viewer’s eye and eyepiece
wider FOV than Galilean
purpose of rubber eye on eyepiece

How to calculate TS Mag: using diameter of exit pupil + objective

Do telescopes reduce or increase the brightness of extended sources of light?
REDUCE - due to reflection off of optical surfaces
4% loss of light - can use antireflective coating
larger pupil = image brightness appears just as bright as observed by naked eye
Smaller pupil = becomes aperture stop (or limiting factor) on the amount of light that reaches the retina
Example with exit pupil of telescope and retinal illuminance
first step = divide each by one another
second step = figure out largest mm so that would be the brighest

pt 2

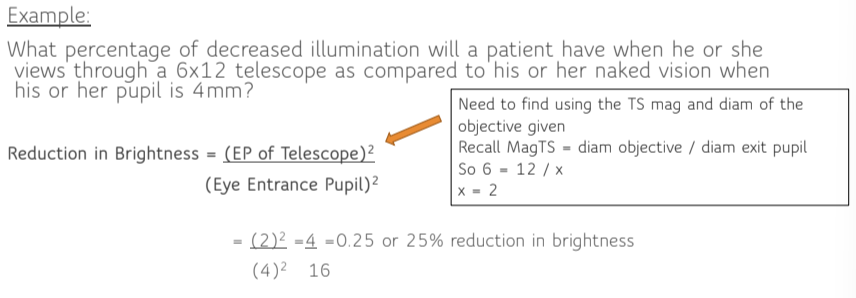
When the exit pupil of telescope is ______ than the eye’s pupil, there will be a ________ in brightness as compared to unaided eye
smaller, reduction
Reduction in brightness formula

Reduction in brightness example
T or F: there is no accommodation needed for pt using afocal telescope for distance vision?
TRUE
What happens when you use a telescope to view an object < 20 ft (ie. less than optical infinity)
accommodation must be employed in order to view the object clearly

______ of a near object is amplified by the optics of the telescope and the patient must use a significantly greater amount of accommodation
divergence
Known as: Vergence amplification
Amplification of vergence formula
M = mag, L = object vergence, t = tube length (m)

Vergence amplification example

Vergence amp (exact formula) example

What are the three ways to adapt telescopes for near vision tasks
decrease ocular power - not practical
add reading cap
increase tube length
So based on the previous example…


Formula for applying reading cap to TS
+2.5D comes from 40 cm object distance

What is the most realistic option to alter for accommodation?
INCREASE tube length
Add objective power to object vergence
add both new distances (f1 and f2)

pt 2

How do you predict TS magnification for telescope
denominator of BCVA / Denominator of GOAL acuity

Predicting magnification problems continued

TS problem
