IB Bio HL йоу
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Stargardt disease
is a degenerative disease of the eye (retinal cells) leading to blindness. Human embryonic stem cells are obtained from unsuccessful in vitro fertilizations. These cells are differentiated in the lab towards retinal cells and injected into the eye of patients. The new cells replace the degenerate cells in the retina and restore vision
Leukaemia
the cancer of white blood cells (immune cells). Human cord blood is collected after childbirth. The cord blood contains stem cells that differentiate into white blood cells. A patient with leukaemia is irradiated and given chemotherapy to kill all cancerous white blood cells. The killed cells are then replaced by the matching cord blood cells which are able to differentiate into all kinds of white blood cells in the patient
Compartmentalization
the separation of a cell's interior into distinct compartments
Homeostasis
Living things maintain a stable internal environment
Nutrition
Living things exchange materials and gases with the environment
Excretion
Living things exhibit the removal of waste products
Lysosomes
membrane-bound organelles, found in eukaryotic cells, that contain digestive enzymes responsible for breaking down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign invaders, acting as the cell's "garbage disposal system".
where can dna be in a eukaryotic cell
Chloroplast, mitochondria, nucleus
where can dna be in a prokaryotic cell
Nucleoid, plasmid
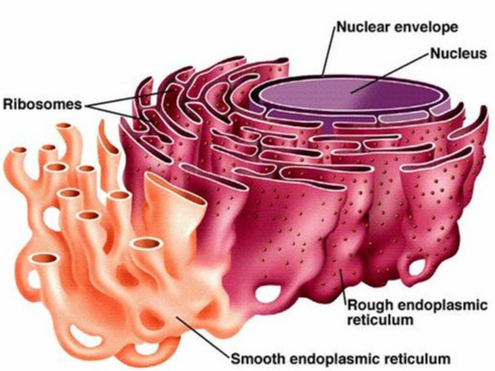
rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Centrioles
Chromosome separation during mitosis
Where (organelle) is DNA in eukaryotes?
enclosed in the nuclear membrane
Binary fission
a form of asexual reproduction where a parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells, primarily observed in prokaryotes like bacteria,
Phospholipids Head
glycerol + negatively charged phosphate group
Amphipathic
opposite properties
Polar
uneven distribution of electrons, creating partial positive (+) and negative (-) charges.
Non-polar
even distribution of electrons, no significant charge separation.
Fluid
tails will always be facing tails, and the heads will always face outside, but the position of individual phospholipids in a layer may change
Cholesterol in membrane
keeps the fluidity of the membrane constant at a variety of temperatures. When it is cold, it increases fluidity and when hot, it makes the membrane more rigid(solid)
Semi-permeable
only certain molecules (small, polar) can freely cross the membrane
Selective
with the use of transport proteins, it can select what comes in and out and what does not
Active transport
low conc - high conc
Passive transport
high conc - low conc
supercoil
Cytokinesis
he process where a cell's cytoplasm divides, resulting in two daughter cells, completing the final stage of cell division after nuclear division (mitosis or meiosis
Photolysis
Terminal differentiation
G0, a cell permanently exits the cell, no longer divides
G1
cell grows , performance of its daily functions.
Grow in size
Specific enzymes are produced
DNA base units are accumulated (накапливаются)
S
Chromosome number is doubled, DNA synthesis, (replication), gets ready for mitosis
G2
last preparations for mitosis: the cell duplicates its organelles and prepares enzymes and proteins needed for mitosis
Cyclins
a group of stress-sensitive proteins in controlling cell death and survival in DNA damage response / regulate the cell cycle
what will influence the progression of the cell cycle.
An increase or decrease in the concentration of cyclins
Anabolism
synthesis of larger molecules.
Catabolism
breakdown of larger molecules.
Endosymbiosis
prokaryotes evolved first, with eukaryotes likely arising from prokaryotic ancestors
Dimer
a compound made from the bonding of two monomers
Lipids
Can store more energy / not soluble in water